-Create Deployment
-Rolling update
- ReplicaSet
-Rollback
-Horizontal expansion
@Create Deployment
First, create a deployment, the number of pod copies is 3, use the image nginx:1.19, and create a service
test-deploy-svc.yaml is as follows
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: web
name: web
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: web
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: web
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:1.19
name: nginx
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: web
name: web
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: web
type: NodePort
Create deployment
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f test-deploy-svc.yaml deployment.apps/web created service/web created [root@k8s-master ~]#
View the NodePort of svc, which is 31147
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get svc -o wide NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 19d <none> web NodePort 10.99.203.162 <none> 80:31147/TCP 49s app=web [root@k8s-master ~]#
Query the pod associated with svc
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get endpoints NAME ENDPOINTS AGE kubernetes 192.168.231.121:6443 19d web 10.244.169.161:80,10.244.36.84:80,10.244.36.88:80 2m28s [root@k8s-master ~]#
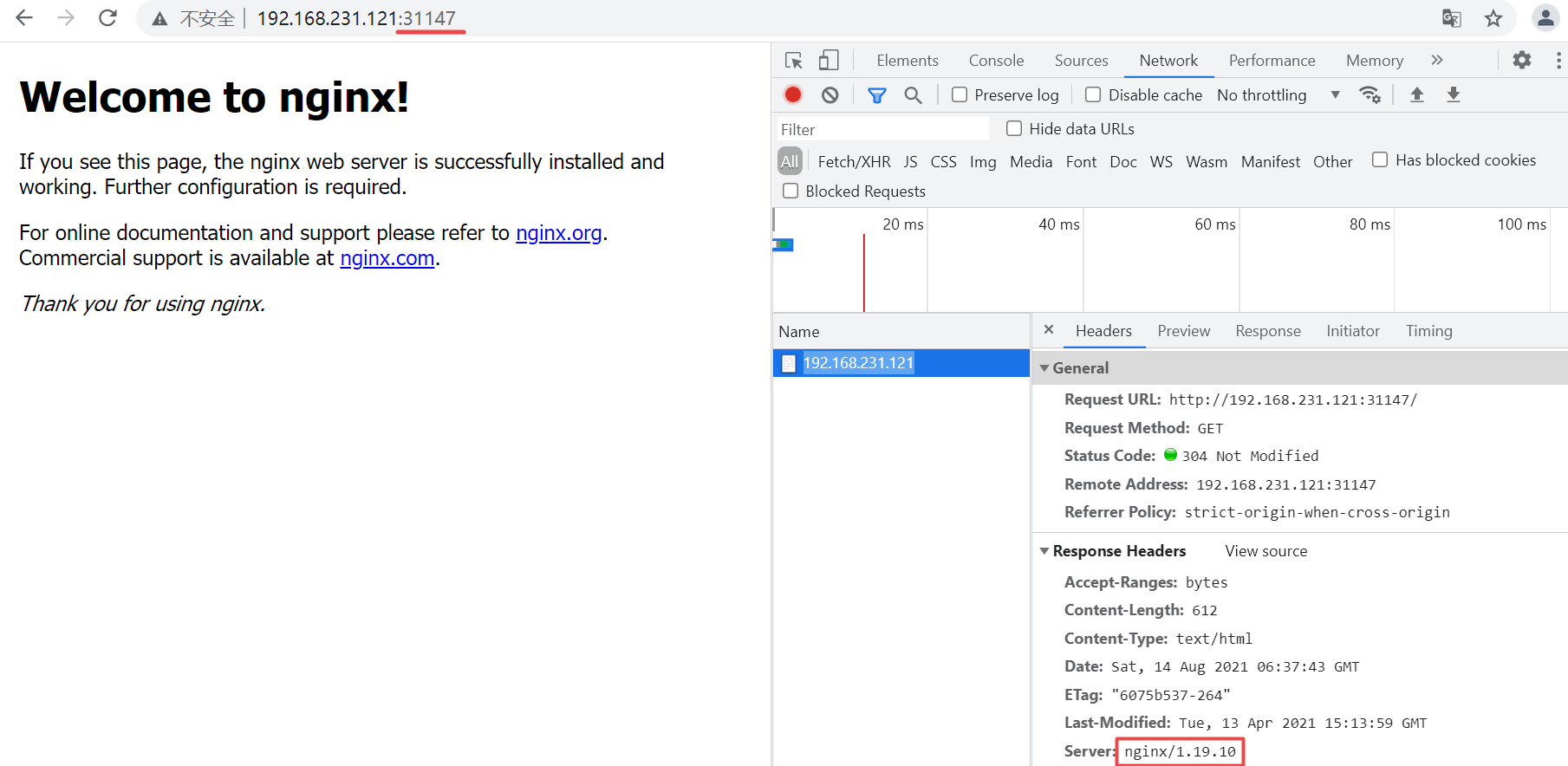
The browser opens the home page, http: / / < address of any node in the cluster >: 31147
At the same time, open the console and check the nginx version. Here is 1.19 ten
@Rolling update
Method 1: kubectl set image deployment web nginx=nginx:1.20
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl set image deployment web nginx=nginx:1.20 deployment.apps/web image updated [root@k8s-master ~]#
Refresh the browser page and update the browser version to nginx / 1.20 one
During this process, the pod will be updated by scrolling (detailed in the next method); check the endpoints, and the pod address associated with svc has changed
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get endpoints NAME ENDPOINTS AGE kubernetes 192.168.231.121:6443 19d web 10.244.169.160:80,10.244.36.81:80,10.244.36.82:80 13m [root@k8s-master ~]#
Method 2: modify the yaml file, apply again, and change the version to 1.21
[root@k8s-master ~]# grep image test-deploy-svc.yaml
- image: nginx:1.19
[root@k8s-master ~]# vim test-deploy-svc.yaml
[root@k8s-master ~]# grep image test-deploy-svc.yaml
- image: nginx:1.21
[root@k8s-master ~]#First record the NAME and IP of the current version 1.20 pod
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES web-7f5844f89c-6sdxt 1/1 Running 0 5m28s 10.244.169.160 k8s-node2 <none> <none> web-7f5844f89c-cxqjf 1/1 Running 0 5m29s 10.244.36.82 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-7f5844f89c-m6655 1/1 Running 0 5m26s 10.244.36.81 k8s-node1 <none> <none> [root@k8s-master ~]#
Execute kubectl apply - F test deploy SVC Yaml update
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f test-deploy-svc.yaml deployment.apps/web configured service/web unchanged [root@k8s-master ~]#
Constantly use the command kubectl get pod -o wide to view the creation of a pod
-->Creating a new pod with status ContainerCreating
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES web-7f5844f89c-6sdxt 1/1 Running 0 6m7s 10.244.169.160 k8s-node2 <none> <none> web-7f5844f89c-cxqjf 1/1 Running 0 6m8s 10.244.36.82 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-7f5844f89c-m6655 1/1 Running 0 6m5s 10.244.36.81 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-d779974b6-j72dv 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 4s <none> k8s-node1 <none> <none> [root@k8s-master ~]#
-->The status of the first new pod changes to Running, an old pod enters Terminating, and a second new pod is created at the same time
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES web-7f5844f89c-6sdxt 1/1 Running 0 6m22s 10.244.169.160 k8s-node2 <none> <none> web-7f5844f89c-cxqjf 1/1 Running 0 6m23s 10.244.36.82 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-7f5844f89c-m6655 1/1 Terminating 0 6m20s 10.244.36.81 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-d779974b6-j72dv 1/1 Running 0 19s 10.244.36.90 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-d779974b6-j9fkf 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s <none> k8s-node2 <none> <none> [root@k8s-master ~]#
......
-->Three new pods are created, and the old three pods are in the Terminating state
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES web-7f5844f89c-6sdxt 0/1 Terminating 0 6m25s 10.244.169.160 k8s-node2 <none> <none> web-7f5844f89c-cxqjf 1/1 Terminating 0 6m26s 10.244.36.82 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-7f5844f89c-m6655 0/1 Terminating 0 6m23s 10.244.36.81 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-d779974b6-9nmb6 1/1 Running 0 2s 10.244.36.91 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-d779974b6-j72dv 1/1 Running 0 22s 10.244.36.90 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-d779974b6-j9fkf 1/1 Running 0 3s 10.244.169.164 k8s-node2 <none> <none> [root@k8s-master ~]#
......
-->All three pod s are "updated" to the new version
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES web-d779974b6-9nmb6 1/1 Running 0 11s 10.244.36.91 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-d779974b6-j72dv 1/1 Running 0 31s 10.244.36.90 k8s-node1 <none> <none> web-d779974b6-j9fkf 1/1 Running 0 12s 10.244.169.164 k8s-node2 <none> <none> [root@k8s-master ~]#
In the above steps, you can see that the new IP is assigned to the pod. You can also see that the pod address bound to the service has been updated by viewing the endpoints
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get ep NAME ENDPOINTS AGE kubernetes 192.168.231.121:6443 19d web 10.244.169.164:80,10.244.36.90:80,10.244.36.91:80 30m [root@k8s-master ~]#
Refresh the browser page to see that the nginx version is updated to {nginx / 1.21 one
@ReplicaSet
Common commands:
kubectl get replicaset
kubectl describe deployment <deployment name>
kubectl describe <replicaset name>
The executor of rolling upgrade is the controller replicaset(rs), which manages the number of copies of the pod and records the released version
Use the command kubectl get replicaset to view rs. the last line of web-d779974b6 with the expected number of copies of 3 is the latest deployment. Corresponding to the latest pod mentioned above, you can find that {pod NAME = deployment NAME + rs NAME + random string
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get replicaset NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE web-7f5844f89c 0 0 0 30m web-bc7cc9f65 0 0 0 40m web-d779974b6 3 3 3 24m [root@k8s-master ~]#
Check the deployment details to see the rolling upgrade process. Pay attention to the last Events section below
(however, if it is executed after a period of time, it will become Events: < none >)
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl describe deployment web
Name: web
Namespace: default
CreationTimestamp: Sat, 14 Aug 2021 14:32:35 +0800
Labels: app=web
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 3
Selector: app=web
Replicas: 3 desired | 3 updated | 3 total | 3 available | 0 unavailable
StrategyType: RollingUpdate
MinReadySeconds: 0
RollingUpdateStrategy: 25% max unavailable, 25% max surge
Pod Template:
Labels: app=web
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx:1.21
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Environment: <none>
Mounts: <none>
Volumes: <none>
Conditions:
Type Status Reason
---- ------ ------
Available True MinimumReplicasAvailable
Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable
OldReplicaSets: <none>
NewReplicaSet: web-d779974b6 (3/3 replicas created)
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 59m deployment-controller Scaled up replica set web-d779974b6 to 1
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 58m deployment-controller Scaled down replica set web-7f5844f89c to 2
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 58m deployment-controller Scaled up replica set web-d779974b6 to 2
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 58m (x3 over 58m) deployment-controller (combined from similar events): Scaled down replica set web-7f5844f89c to 0
[root@k8s-master ~]#
You can also see the version of the tag by viewing the rs information
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl describe rs web-d779974b6
Name: web-d779974b6
Namespace: default
Selector: app=web,pod-template-hash=d779974b6
Labels: app=web
pod-template-hash=d779974b6
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/desired-replicas: 3
deployment.kubernetes.io/max-replicas: 4
deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 3
Controlled By: Deployment/web
Replicas: 3 current / 3 desired
Pods Status: 3 Running / 0 Waiting / 0 Succeeded / 0 Failed
Pod Template:
Labels: app=web
pod-template-hash=d779974b6
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx:1.21
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Environment: <none>
Mounts: <none>
Volumes: <none>
Events: <none>
[root@k8s-master ~]#
@Rollback
Common commands:
kubectl rollout history deployment web
kubectl rollout undo deployment web
kubectl rollout undo deployment web --to-revision=<num>
View historical releases
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl rollout history deployment web deployment.apps/web REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE 1 <none> 2 <none> 3 <none> [root@k8s-master ~]#
Note: when you add -- Record change-case during deployment, there will be records
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl set image deployment web nginx=nginx:1.21 --record deployment.apps/web image updated [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl rollout history deployment web deployment.apps/web REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE 1 <none> 4 <none> 5 kubectl set image deployment web nginx=nginx:1.21 --record=true [root@k8s-master ~]#
Rollback to previous version (common)
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl rollout undo deployment web deployment.apps/web rolled back [root@k8s-master ~]#
You can see the changes of rs
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get rs NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE web-7f5844f89c 3 3 3 88m web-bc7cc9f65 0 0 0 98m web-d779974b6 0 0 0 82m [root@k8s-master ~]#
@Horizontal expansion
Method 1: modify the value of replicas in yaml file
Method 2: use the command kubectl scale deployment web -- replicas = < pod num >
For example, reduce the volume to 2 pod s using method 2
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl scale deployment web --replicas=2 deployment.apps/web scaled [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE web-d779974b6-6rctw 1/1 Running 0 5m41s web-d779974b6-dv7fh 1/1 Running 0 5m40s web-d779974b6-j6n9r 0/1 Terminating 0 5m38s [root@k8s-master ~]# [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE web-d779974b6-6rctw 1/1 Running 0 5m50s web-d779974b6-dv7fh 1/1 Running 0 5m49s [root@k8s-master ~]# [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get rs NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE web-7f5844f89c 0 0 0 128m web-bc7cc9f65 0 0 0 138m web-d779974b6 2 2 2 122m [root@k8s-master ~]#
Then use method 1 to expand the capacity to 3 pod s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f test-deploy-svc.yaml deployment.apps/web configured service/web unchanged [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE web-d779974b6-6rctw 1/1 Running 0 7m34s web-d779974b6-dv7fh 1/1 Running 0 7m33s web-d779974b6-n8p6d 1/1 Running 0 5s [root@k8s-master ~]# [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get rs NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE web-7f5844f89c 0 0 0 131m web-bc7cc9f65 0 0 0 141m web-d779974b6 3 3 3 125m [root@k8s-master ~]#