Previously, the k8s cluster with single master and double nodes was built based on kubedm. The problem is that after the master node is hung, the whole cluster will be unavailable. Therefore, simply study the construction method of multiple masters.
1. Scheme introduction
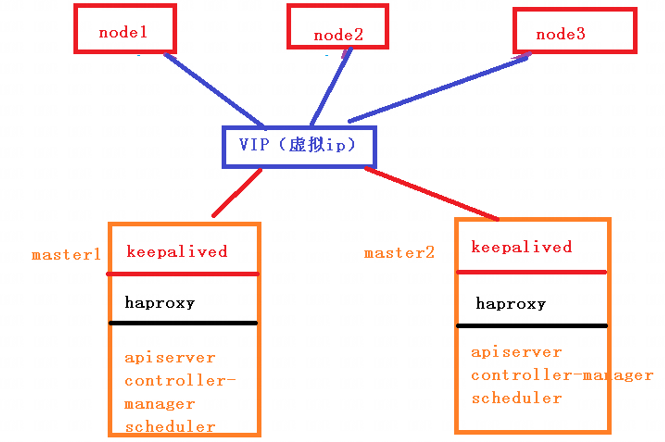
The high availability technologies used are mainly kept and haproxy.
1. keepalived
Keepalived mainly realizes the high availability function through virtual routing redundancy.
Keepalived is a high availability solution of LVS service based on VRRP(Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol), which can be used to solve single point of failure. An LVS service will have two servers running keepalived, one is the MASTER server and the other is the BACKUP server, but the external performance is a virtual IP. The primary server will send a specific message to the BACKUP server. When the BACKUP server cannot receive this message, that is, when the primary server goes down, the BACKUP server will take over the virtual IP, Continue to provide services to ensure high availability.
2. haproxy
Haproxy, similar to nginx, is a load balancing and reverse proxy software. Nginx adopts the master workers process model. Each process is single threaded and multi-core CPU can be fully utilized. Haproxy is multi-threaded, and a single process can achieve high performance, although haproxy also supports multi processes.
2. Build clusters
Basically follow the following procedure.
1. Installation requirements
Deploying Kubernetes cluster machines requires the following conditions:
(1) One or more machines, operating system centos7 x-86_ x64
(2) Hardware configuration: 2GB or more RAM, 2 CPUs or more CPUs, 30GB or more hard disk
(3) If you can access the Internet, you need to pull the image. If the server cannot access the Internet, you need to download the image in advance and import the node
(4) Disable swap partition
2. Prepare the environment
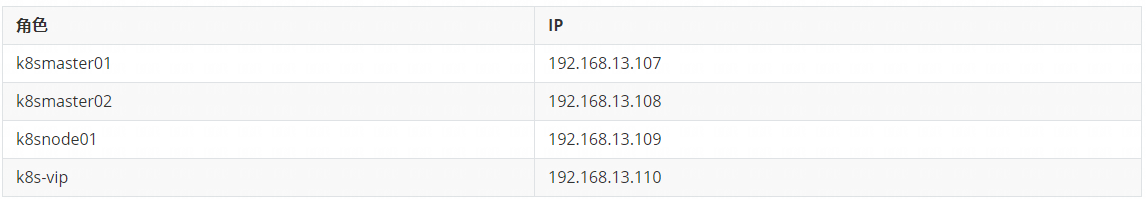
Next, proceed as follows
# Turn off the firewall systemctl stop firewalld systemctl disable firewalld # Close selinux sed -i 's/enforcing/disabled/' /etc/selinux/config # permanent setenforce 0 # temporary # Close swap swapoff -a # temporary sed -ri 's/.*swap.*/#&/' /etc/fstab # permanent # Set the host name according to the plan hostnamectl set-hostname <hostname> # Add hosts in master cat >> /etc/hosts << EOF 192.168.13.110 master.k8s.io k8s-vip 192.168.13.107 master01.k8s.io k8smaster01 192.168.13.108 master02.k8s.io k8smaster02 192.168.13.109 node01.k8s.io k8snode01 EOF # The chain that passes bridged IPv4 traffic to iptables cat > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf << EOF net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 EOF sysctl --system # take effect # time synchronization yum install ntpdate -y ntpdate time.windows.com
3. All master nodes are deployed with keepalived
1. Install relevant packages and keepalived
yum install -y conntrack-tools libseccomp libtool-ltdl yum install -y keepalived
2. Configure the master node
k8smaster01
cat > /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf <<EOF ! Configuration File for keepalived global_defs { router_id k8s } vrrp_script check_haproxy { script "killall -0 haproxy" interval 3 weight -2 fall 10 rise 2 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state MASTER interface ens33 virtual_router_id 51 priority 250 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass ceb1b3ec013d66163d6ab } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.13.110 } track_script { check_haproxy } } EOF
k8smaster02
cat > /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf <<EOF ! Configuration File for keepalived global_defs { router_id k8s } vrrp_script check_haproxy { script "killall -0 haproxy" interval 3 weight -2 fall 10 rise 2 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state BACKUP interface ens33 virtual_router_id 51 priority 200 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass ceb1b3ec013d66163d6ab } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.13.110 } track_script { check_haproxy } } EOF
3. Startup and inspection
# Start keepalived
systemctl start keepalived.service
# Set startup
systemctl enable keepalived.service
# View startup status
systemctl status keepalived.service
Check the network card information of master1 after startup: you can see the information related to vip
ip a s ens33
4. Deploy haproxy
1. Installation
yum install -y haproxy
2. Configuration
The configurations of the two master nodes are the same. In the configuration, the two master node servers of the back-end agent are declared, and the port of haproxy running is 16443. Therefore, port 16443 is the entrance of the cluster
cat > /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg << EOF #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # Global settings #--------------------------------------------------------------------- global # to have these messages end up in /var/log/haproxy.log you will # need to: # 1) configure syslog to accept network log events. This is done # by adding the '-r' option to the SYSLOGD_OPTIONS in # /etc/sysconfig/syslog # 2) configure local2 events to go to the /var/log/haproxy.log # file. A line like the following can be added to # /etc/sysconfig/syslog # # local2.* /var/log/haproxy.log # log 127.0.0.1 local2 chroot /var/lib/haproxy pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid maxconn 4000 user haproxy group haproxy daemon # turn on stats unix socket stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # common defaults that all the 'listen' and 'backend' sections will # use if not designated in their block #--------------------------------------------------------------------- defaults mode http log global option httplog option dontlognull option http-server-close option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8 option redispatch retries 3 timeout http-request 10s timeout queue 1m timeout connect 10s timeout client 1m timeout server 1m timeout http-keep-alive 10s timeout check 10s maxconn 3000 #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # kubernetes apiserver frontend which proxys to the backends #--------------------------------------------------------------------- frontend kubernetes-apiserver mode tcp bind *:16443 option tcplog default_backend kubernetes-apiserver #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # round robin balancing between the various backends #--------------------------------------------------------------------- backend kubernetes-apiserver mode tcp balance roundrobin server master01.k8s.io 192.168.13.107:6443 check server master02.k8s.io 192.168.13.108:6443 check #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # collection haproxy statistics message #--------------------------------------------------------------------- listen stats bind *:1080 stats auth admin:awesomePassword stats refresh 5s stats realm HAProxy\ Statistics stats uri /admin?stats EOF
3. Startup and inspection
Both master s are started
# Set startup
systemctl enable haproxy
# Open haproxy
systemctl start haproxy
# View startup status
systemctl status haproxy
Check port
netstat -lntup|grep haproxy
5. Install docker / kubedm / kubelet on all nodes
By default, the CRI (container runtime) of Kubernetes is Docker, so Docker is installed first.
1. Install docker
wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo yum -y install docker-ce-18.06.1.ce-3.el7 systemctl enable docker && systemctl start docker docker --version
Modify docker image source:
cat > /etc/docker/daemon.json << EOF { "registry-mirrors": ["https://b9pmyelo.mirror.aliyuncs.com"] } EOF
2. Add alicloud YUM software source
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo << EOF [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64 enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 repo_gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOF
3. Install kubedm, kubelet and kubectl
yum install -y kubelet-1.21.3 kubeadm-1.21.3 kubectl-1.21.3 systemctl enable kubelet
6. Deploy k8smaster
1. Create kubedm configuration file
Operate on the master with vip, here is master1
mkdir /usr/local/kubernetes/manifests -p cd /usr/local/kubernetes/manifests/ vi kubeadm-config.yaml apiServer: certSANs: - k8smaster01 - k8smaster02 - master.k8s.io - 192.168.13.110 - 192.168.13.107 - 192.168.13.108 - 127.0.0.1 extraArgs: authorization-mode: Node,RBAC timeoutForControlPlane: 4m0s apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta1 certificatesDir: /etc/kubernetes/pki clusterName: kubernetes controlPlaneEndpoint: "master.k8s.io:16443" controllerManager: {} dns: type: CoreDNS etcd: local: dataDir: /var/lib/etcd imageRepository: registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers kind: ClusterConfiguration kubernetesVersion: v1.21.3 networking: dnsDomain: cluster.local podSubnet: 10.244.0.0/16 serviceSubnet: 10.1.0.0/16 scheduler: {}
2. Execute at k8smaster01 node
kubeadm init --config kubeadm-config.yaml
The prompt after execution is as follows:
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully! To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user: mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run: export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster. Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/ You can now join any number of control-plane nodes by copying certificate authorities and service account keys on each node and then running the following as root: kubeadm join master.k8s.io:16443 --token piealo.bck99wdpdv14rlo6 \ --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:e0579b642a2b62219627f9f19af5227dadb539f9db11992585644d4f126046e5 \ --control-plane Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root: kubeadm join master.k8s.io:16443 --token piealo.bck99wdpdv14rlo6 \ --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:e0579b642a2b62219627f9f19af5227dadb539f9db11992585644d4f126046e5
Follow the prompts to configure environment variables and use the kubectl tool:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Check:
[root@k8smaster01 manifests]# kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8smaster01 NotReady control-plane,master 144m v1.21.3 [root@k8smaster01 manifests]# kubectl get pods -n kube-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE coredns-59d64cd4d4-62bhq 0/1 Pending 0 144m coredns-59d64cd4d4-95dl5 0/1 Pending 0 144m etcd-k8smaster01 1/1 Running 0 144m kube-apiserver-k8smaster01 1/1 Running 0 144m kube-controller-manager-k8smaster01 1/1 Running 0 144m kube-proxy-df8c8 1/1 Running 0 144m kube-scheduler-k8smaster01 1/1 Running 0 145m
3. Install cluster network
mkdir flannel cd flannel wget -c https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
Create and view:
kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
4. k8smaster02 join the node
(1) Copy key and related documents
Copy the key and related files from master1 to master2
ssh root@192.168.13.108 mkdir -p /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd scp /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf root@192.168.13.108:/etc/kubernetes scp /etc/kubernetes/pki/{ca.*,sa.*,front-proxy-ca.*} root@192.168.13.108:/etc/kubernetes/pki scp /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.* root@192.168.13.108:/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd
(2) master2 joins the cluster
When k8smaster02 executes the join command output after init on k8smaster01, the parameter ` -- control plane 'needs to be taken to indicate that the master control node is added to the cluster
kubeadm join master.k8s.io:16443 --token piealo.bck99wdpdv14rlo6 \ --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:e0579b642a2b62219627f9f19af5227dadb539f9db11992585644d4f126046e5 --control-plane
Output after execution:
This node has joined the cluster and a new control plane instance was created: * Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and approval was received. * The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details. * Control plane (master) label and taint were applied to the new node. * The Kubernetes control plane instances scaled up. * A new etcd member was added to the local/stacked etcd cluster. To start administering your cluster from this node, you need to run the following as a regular user: mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Then execute the information output above:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Check status:
[root@k8smaster02 ~]# kubectl get node NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8smaster01 Ready control-plane,master 17h v1.21.3 k8smaster02 NotReady control-plane,master 6m21s v1.21.3 [root@k8smaster02 ~]# kubectl get pods --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE kube-system coredns-59d64cd4d4-62bhq 1/1 Running 0 17h kube-system coredns-59d64cd4d4-95dl5 1/1 Running 0 17h kube-system etcd-k8smaster01 1/1 Running 0 17h kube-system etcd-k8smaster02 1/1 Running 0 6m22s kube-system kube-apiserver-k8smaster01 1/1 Running 0 17h kube-system kube-apiserver-k8smaster02 1/1 Running 0 6m25s kube-system kube-controller-manager-k8smaster01 1/1 Running 1 17h kube-system kube-controller-manager-k8smaster02 1/1 Running 0 6m26s kube-system kube-flannel-ds-p2std 1/1 Running 0 15h kube-system kube-flannel-ds-vc2w2 0/1 Init:ImagePullBackOff 0 6m27s kube-system kube-proxy-df8c8 1/1 Running 0 17h kube-system kube-proxy-nx8dg 1/1 Running 0 6m27s kube-system kube-scheduler-k8smaster01 1/1 Running 1 17h kube-system kube-scheduler-k8smaster02 1/1 Running 0 6m26s
3. k8snode01 join the cluster
(1) Information output before execution on k8snode01 node:
kubeadm join master.k8s.io:16443 --token piealo.bck99wdpdv14rlo6 \ --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:e0579b642a2b62219627f9f19af5227dadb539f9db11992585644d4f126046e5
After execution, the output is as follows:
This node has joined the cluster: * Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received. * The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details. Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.
(2) View in the master node
[root@k8smaster01 manifests]# kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8smaster01 Ready control-plane,master 17h v1.21.3 k8smaster02 NotReady control-plane,master 11m v1.21.3 k8snode01 NotReady <none> 2m26s v1.21.3
(3) Reinstall the network
[root@k8smaster01 flannel]# pwd /root/flannel [root@k8smaster01 flannel]# kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
(4) View the cluster status again
[root@k8smaster01 flannel]# kubectl cluster-info Kubernetes control plane is running at https://master.k8s.io:16443 CoreDNS is running at https://master.k8s.io:16443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'. [root@k8smaster01 flannel]# kubectl get nodes -o wide NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME k8smaster01 Ready control-plane,master 18h v1.21.3 192.168.13.107 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.49.1.el7.x86_64 docker://18.6.1 k8smaster02 Ready control-plane,master 38m v1.21.3 192.168.13.108 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.49.1.el7.x86_64 docker://18.6.1 k8snode01 Ready <none> 28m v1.21.3 192.168.13.109 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-1160.49.1.el7.x86_64 docker://18.6.1
4. Test cluster
[root@k8smaster01 flannel]# kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx deployment.apps/nginx created [root@k8smaster01 flannel]# kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES nginx-6799fc88d8-g7vcg 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 11s <none> k8snode01 <none> <none> [root@k8smaster01 flannel]# kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --type=NodePort service/nginx exposed [root@k8smaster01 flannel]# kubectl get pod,svc NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/nginx-6799fc88d8-g7vcg 1/1 Running 0 98s NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.1.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 18h service/nginx NodePort 10.1.49.27 <none> 80:32367/TCP 60s
Then view the 32367 port of any node from the outside to view nginx. 107, 08, 09 and 110 ip addresses can be accessed.