1. GAN introduction
GAN (generative advantageous networks) is a network proposed by Ian J. Goodfellow and others at the 2014 nips conference. They proposed a new framework for estimating generative models using confrontation processing. The framework can train two models at the same time: one is generative model G (Generator generator Generator), which can be equivalent to a function G(z); The other is discriminant model D (descriptor discriminator), which can also be equivalent to a function D(x).
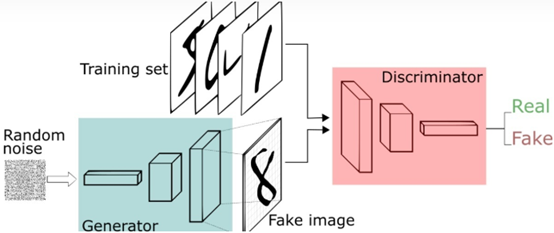
Generator g is used to capture the distribution law of data and generate new false sample data; Discriminator D is used to estimate that a sample comes from real training data rather than generator G. Therefore, the training process of the generator generator is to maximize the error probability of the discriminator descriptor, which is equivalent to that the generator generator should make false samples to deceive the discriminator descriptor as much as possible, so that the discriminator descriptor cannot distinguish whether the false samples are from the real training data or the generator, Therefore, this framework can be considered as a game with the smallest g and the largest d between two players: G players should strive to generate false samples as close as possible to the real samples, D players should accurately judge whether a sample comes from real data or G players, the two players are engaged in confrontation, and the whole network is engaged in confrontation training, So as to finally let g players predict or generate as new sample data as possible. In any function space g and D, there is a unique solution if and only if G restores the distribution of training data, and at this time D is only equal to
1
2
\frac{1}{2}
21.
1.1 theoretical analysis
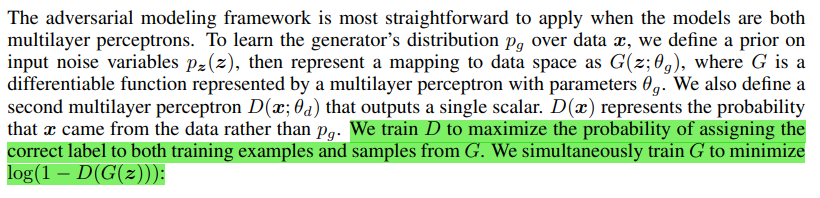
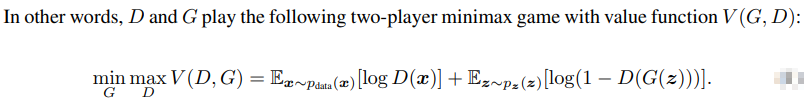
The principle of GAN is to use generator G and discriminator D for confrontation. In essence, the purpose is to make prediction and generation. It is necessary to predict the probability distribution p(x) of the input real sample data X
x
—
—
transport
enter
of
really
real
kind
book
number
according to
x -- input real sample data
Sample input - real data
z
—
—
Noise
sound
number
according to
z - noise data
z - noise data
G
(
z
)
—
—
living
become
implement
G(z) - generator
G(z) - generator
D
(
x
)
—
—
sentence
other
implement
D(x) - discriminator
D(x) - discriminator
x
′
=
G
(
z
)
—
—
living
become
implement
G
root
according to
Noise
sound
z
living
become
of
false
kind
book
x^{'} =G(z) -- false samples generated by generator G according to noise Z
x ′ = G(z) -- false samples generated by generator G according to noise Z
p
d
a
t
a
—
—
really
real
kind
book
number
according to
of
General
rate
branch
cloth
p_{data} - probability distribution of real sample data
pdata -- probability distribution of real sample data
p
z
—
—
Noise
sound
number
according to
of
before
Check
General
rate
branch
cloth
,
from
living
become
implement
G
come
latent
contain
set
righteousness
p_{z} - a priori probability distribution of noise data, which is implicitly defined by generator G
pz -- prior probability distribution of noise data, implicitly defined by generator G
p
g
—
—
living
become
implement
G
Anticipate
Estimate
really
real
kind
book
number
according to
of
General
rate
branch
cloth
p_{g} - generator G estimates the probability distribution of real sample data
pg -- generator G estimates the probability distribution of real sample data
network
Collaterals
Discipline
Practice
of
whole
game
excellent
turn
order
mark
by
:
p
g
=
p
d
a
t
a
The global optimization objective of network training is: p_{g} = p_{data}
The global optimization objective of network training is: pg = pdata
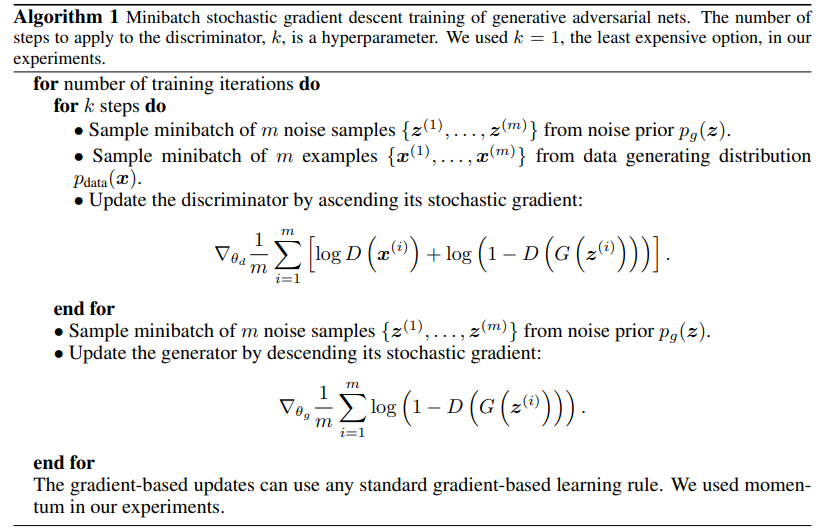
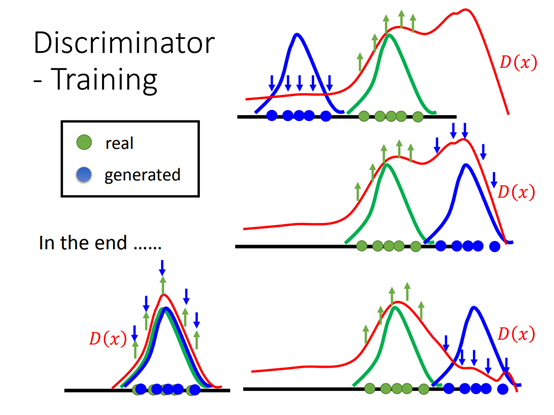
1.2 advantages and disadvantages
The disadvantages of GAN mainly include: the probability distribution of sample data predicted by the generator cannot be obtained
p
g
(
x
)
p_{g}(x)
Explicit expression of pg (x); During training, discriminator D must keep good synchronization and update with generator G.
The advantages of GAN are: there is no need to intervene in the training process, a large number of functions can be applied to this model, which has strong computability and can represent very sharp or even degenerate distribution. For further study of GAN, please refer to:
- Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2014, 27.
- https://speech.ee.ntu.edu.tw/~tlkagk/slide/Tutorial_HYLee_GAN.pdf
- https://tensorflow.google.cn/tutorials/generative/style_transfer?hl=zh_cn
- https://keras.io/examples/generative/
- https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/dcgan_faces_tutorial.html
2. Test environment (Win11 64 bit + GTX 1050ti + CUDA 10.1 + cudnn 7.6.5 + Python 3.6 + tensorflow GPU 2.3.1)
The test environment of this paper is carried out on Win11 64 bit operating system. The graphics card is GTX 1050Ti and CUDA 10.1 and cudnn7.0 are installed 6.5. Finally, Anaconda is used to create the virtual environment of Python 3.6, and pip is used to install the required dependency package tensorflow GPU 2.3.1.
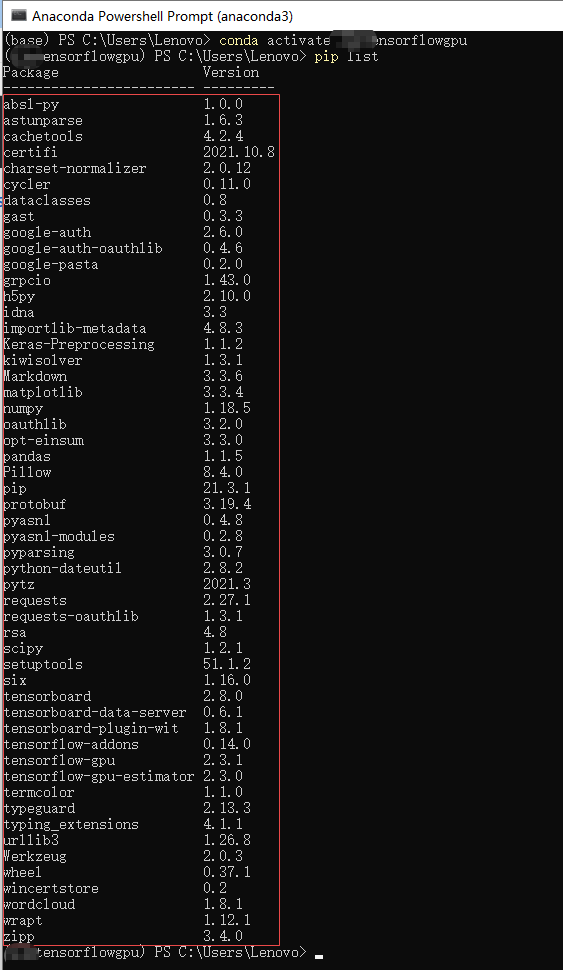
The dependent packages installed by python 3.6 are as follows (pip install package name = = version number):
absl-py==1.0.0 astunparse==1.6.3 cachetools==4.2.4 certifi==2021.10.8 charset-normalizer==2.0.12 cycler==0.11.0 dataclasses==0.8 gast==0.3.3 google-auth==2.6.0 google-auth-oauthlib==0.4.6 google-pasta==0.2.0 grpcio==1.43.0 h5py==2.10.0 idna==3.3 importlib-metadata==4.8.3 Keras-Preprocessing==1.1.2 kiwisolver==1.3.1 Markdown==3.3.6 matplotlib==3.3.4 numpy==1.18.5 oauthlib==3.2.0 opt-einsum==3.3.0 pandas==1.1.5 Pillow==8.4.0 protobuf==3.19.4 pyasn1==0.4.8 pyasn1-modules==0.2.8 pyparsing==3.0.7 python-dateutil==2.8.2 pytz==2021.3 requests==2.27.1 requests-oauthlib==1.3.1 rsa==4.8 scipy==1.2.1 six==1.16.0 tensorboard==2.8.0 tensorboard-data-server==0.6.1 tensorboard-plugin-wit==1.8.1 tensorflow-addons==0.14.0 tensorflow-gpu==2.3.1 tensorflow-gpu-estimator==2.3.0 termcolor==1.1.0 typeguard==2.13.3 typing_extensions==4.1.1 urllib3==1.26.8 Werkzeug==2.0.3 wincertstore==0.2 wordcloud==1.8.1 wrapt==1.12.1 zipp==3.4.0
3. Instance running
The examples used are from eriklindernoren/Keras-GAN , in order to further learn the effects of various GAN, try to run it with sample code. The value of training iteration times in the source code is usually very large (3000 ~ 30000). Due to the poor computer performance, the number of iterations is specially reduced (1000 ~ 2000), so the running results may not be good enough to prove the poor effect of the model.
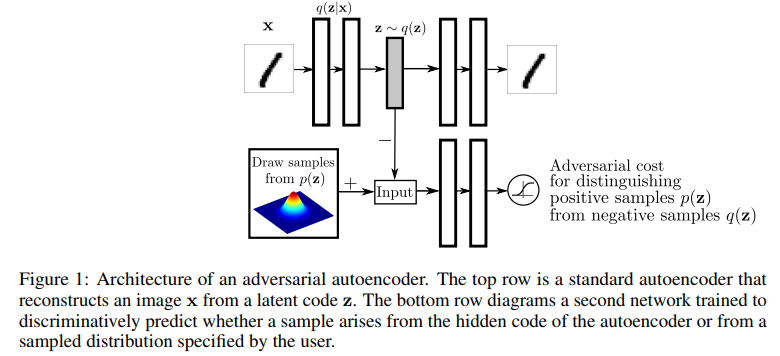
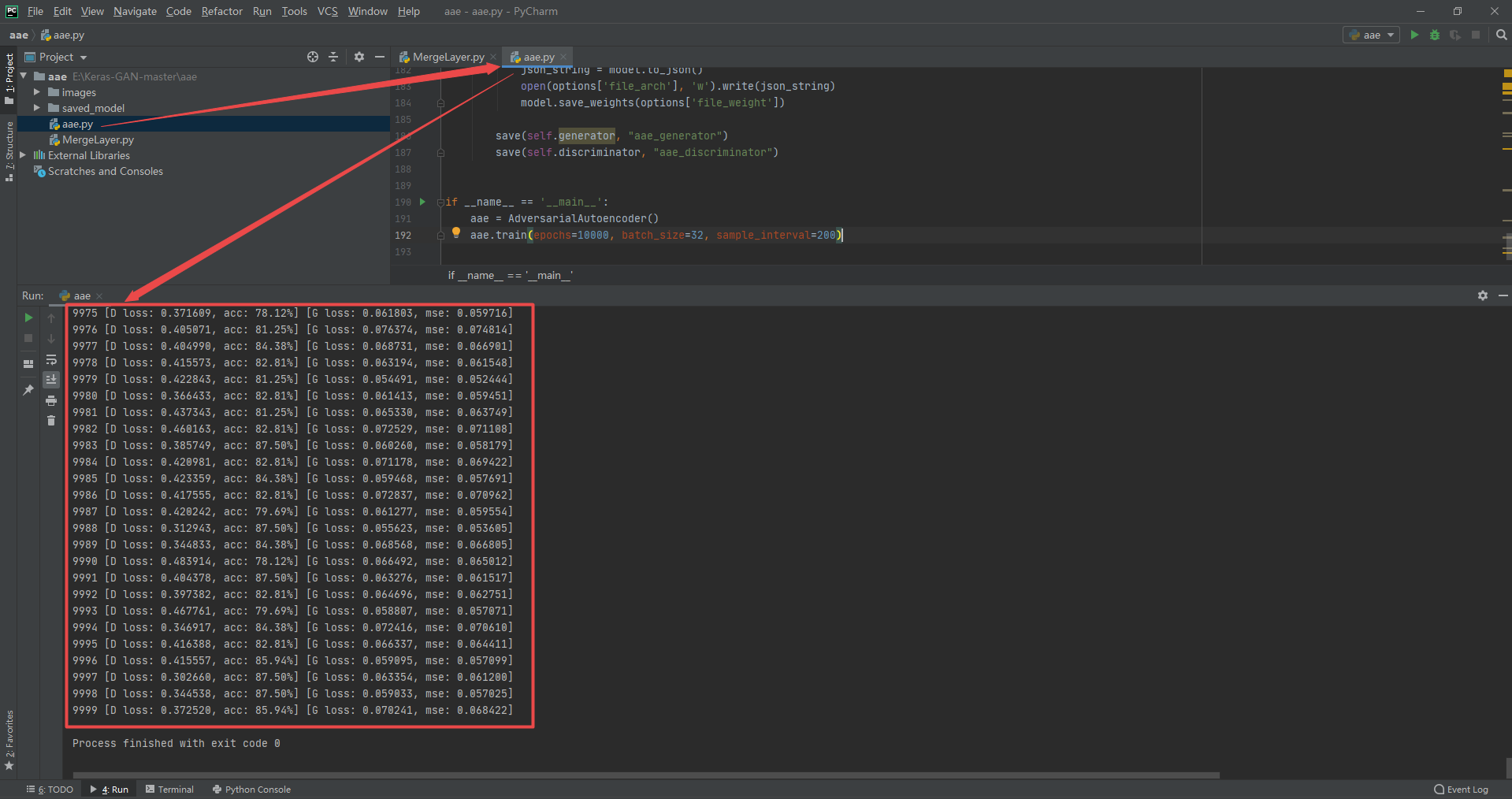
3.1 Adversarial Autoencoder

Code and running results
MergeLayer.py
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Layer
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
class MergeLayer(Layer):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(MergeLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return (input_shape[0][0], input_shape[0][1])
def call(self, x, mask=None):
final_output = x[0] + K.random_normal(K.shape(x[0])) * K.exp(x[1] / 2)
return final_output
aae.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
from MergeLayer import MergeLayer
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, multiply, GaussianNoise
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, Embedding, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import MaxPooling2D, Concatenate
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras import losses
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class AdversarialAutoencoder():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 10
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the encoder / decoder
self.encoder = self.build_encoder()
self.decoder = self.build_decoder()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# The generator takes the image, encodes it and reconstructs it
# from the encoding
encoded_repr = self.encoder(img)
reconstructed_img = self.decoder(encoded_repr)
# For the adversarial_autoencoder model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator determines validity of the encoding
validity = self.discriminator(encoded_repr)
# The adversarial_autoencoder model (stacked generator and discriminator)
self.adversarial_autoencoder = Model(img, [reconstructed_img, validity])
self.adversarial_autoencoder.compile(loss=['mse', 'binary_crossentropy'],
loss_weights=[0.999, 0.001],
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_encoder(self):
# Encoder
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
h = Flatten()(img)
h = Dense(512)(h)
h = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(h)
h = Dense(512)(h)
h = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(h)
mu = Dense(self.latent_dim)(h)
log_var = Dense(self.latent_dim)(h)
latent_repr = MergeLayer()([mu, log_var])
return Model(img, latent_repr)
def build_decoder(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(512, input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh'))
model.add(Reshape(self.img_shape))
model.summary()
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = model(z)
return Model(z, img)
def build_discriminator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(512, input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(256))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(1, activation="sigmoid"))
model.summary()
encoded_repr = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim, ))
validity = model(encoded_repr)
return Model(encoded_repr, validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
latent_fake = self.encoder.predict(imgs)
latent_real = np.random.normal(size=(batch_size, self.latent_dim))
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(latent_real, valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(latent_fake, fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
# Train the generator
g_loss = self.adversarial_autoencoder.train_on_batch(imgs, [imgs, valid])
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f, mse: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss[0], g_loss[1]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 5, 5
z = np.random.normal(size=(r*c, self.latent_dim))
gen_imgs = self.decoder.predict(z)
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
def save_model(self):
def save(model, model_name):
model_path = "saved_model/%s.json" % model_name
weights_path = "saved_model/%s_weights.hdf5" % model_name
options = {"file_arch": model_path,
"file_weight": weights_path}
json_string = model.to_json()
open(options['file_arch'], 'w').write(json_string)
model.save_weights(options['file_weight'])
save(self.generator, "aae_generator")
save(self.discriminator, "aae_discriminator")
if __name__ == '__main__':
aae = AdversarialAutoencoder()
aae.train(epochs=10000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200)

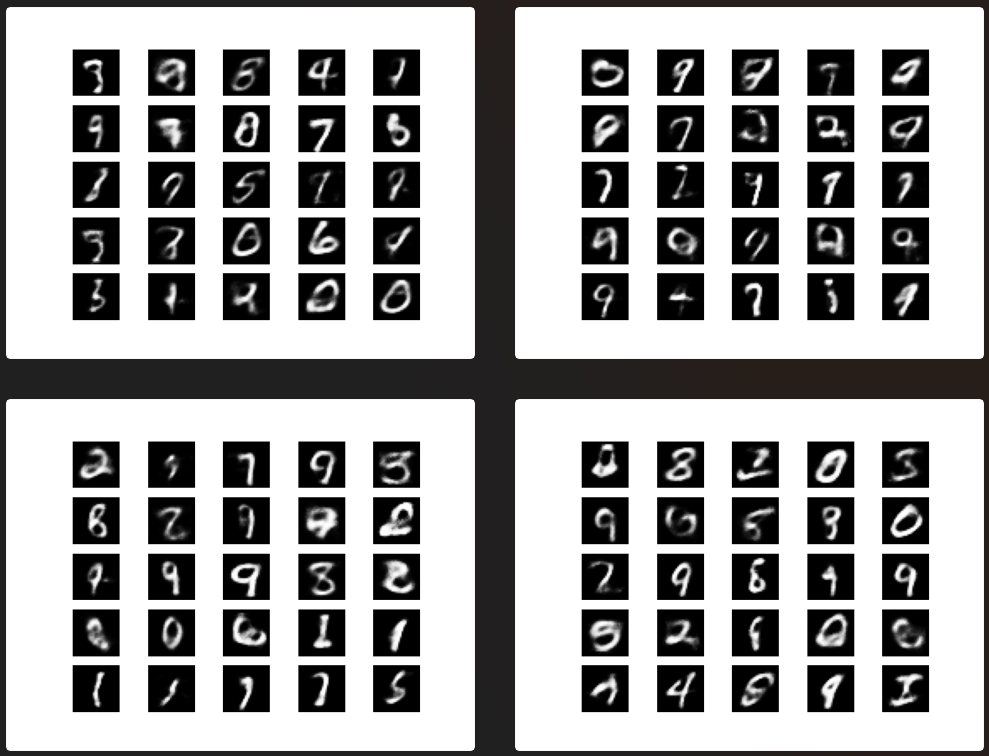
3.2 Auxiliary Classifier Generative Adversarial Network
Code and running results
acgan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, multiply
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, Embedding, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model,Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class ACGAN():
def __init__(self):
# Input shape
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.num_classes = 10
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
losses = ['binary_crossentropy', 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy']
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss=losses,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise and the target label as input
# and generates the corresponding digit of that label
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,))
img = self.generator([noise, label])
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator takes generated image as input and determines validity
# and the label of that image
valid, target_label = self.discriminator(img)
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
# Trains the generator to fool the discriminator
self.combined = Model([noise, label], [valid, target_label])
self.combined.compile(loss=losses,
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
{
model.add(Dense(128 * 7 * 7, activation="relu", input_dim=self.latent_dim)),
model.add(Reshape((7, 7, 128))),
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)),
model.add(UpSampling2D()),
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, padding="same")),
model.add(Activation("relu")),
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)),
model.add(UpSampling2D()),
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, padding="same")),
model.add(Activation("relu")),
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)),
model.add(Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=3, padding='same')),
model.add(Activation("tanh"))
}
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32')
label_embedding = Flatten()(Embedding(self.num_classes, self.latent_dim)(label))
model_input = multiply([noise, label_embedding])
img = model(model_input)
return Model([noise, label], img)
def build_discriminator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(16, kernel_size=3, strides=2, input_shape=self.img_shape, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0,1),(0,1))))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Extract feature representation
features = model(img)
# Determine validity and label of the image
validity = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(features)
label = Dense(self.num_classes, activation="softmax")(features)
return Model(img, [validity, label])
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, y_train), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Configure inputs
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
y_train = y_train.reshape(-1, 1)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
# Sample noise as generator input
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim))
# The labels of the digits that the generator tries to create an
# image representation of
sampled_labels = np.random.randint(0, 10, (batch_size, 1))
# Generate a half batch of new images
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict([noise, sampled_labels])
# Image labels. 0-9
img_labels = y_train[idx]
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, [valid, img_labels])
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, [fake, sampled_labels])
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
# Train the generator
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch([noise, sampled_labels], [valid, sampled_labels])
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%, op_acc: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[3], 100*d_loss[4], g_loss[0]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.save_model()
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 10, 10
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, self.latent_dim))
sampled_labels = np.array([num for _ in range(r) for num in range(c)])
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict([noise, sampled_labels])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt,:,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
def save_model(self):
def save(model, model_name):
model_path = "saved_model/%s.json" % model_name
weights_path = "saved_model/%s_weights.hdf5" % model_name
options = {"file_arch": model_path,
"file_weight": weights_path}
json_string = model.to_json()
open(options['file_arch'], 'w').write(json_string)
model.save_weights(options['file_weight'])
save(self.generator, "generator")
save(self.discriminator, "discriminator")
if __name__ == '__main__':
acgan = ACGAN()
acgan.train(epochs=14000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200)


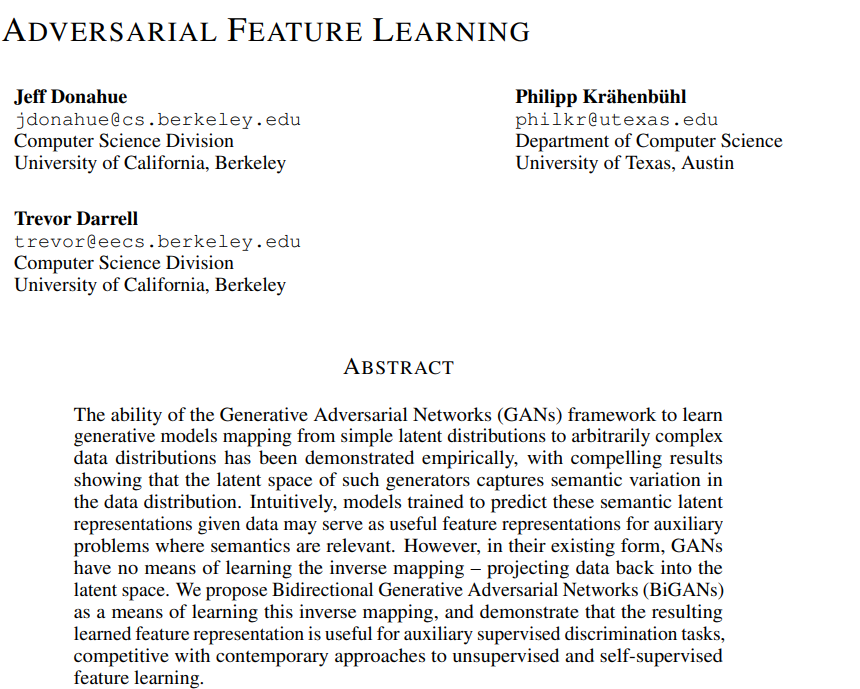
3.3 Bidirectional Generative Adversarial Network
Code and running results
bigan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, multiply, GaussianNoise
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, Embedding, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import MaxPooling2D, concatenate
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras import losses
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class BIGAN():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss=['binary_crossentropy'],
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# Build the encoder
self.encoder = self.build_encoder()
# The part of the bigan that trains the discriminator and encoder
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# Generate image from sampled noise
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim, ))
img_ = self.generator(z)
# Encode image
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
z_ = self.encoder(img)
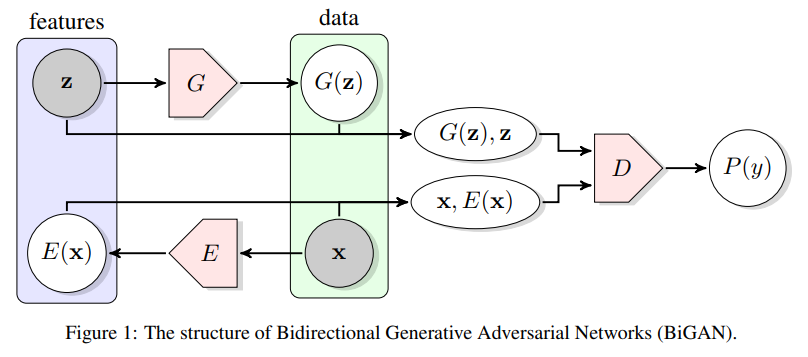
# Latent -> img is fake, and img -> latent is valid
fake = self.discriminator([z, img_])
valid = self.discriminator([z_, img])
# Set up and compile the combined model
# Trains generator to fool the discriminator
self.bigan_generator = Model([z, img], [fake, valid])
self.bigan_generator.compile(loss=['binary_crossentropy', 'binary_crossentropy'],
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_encoder(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Flatten(input_shape=self.img_shape))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(self.latent_dim))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
z = model(img)
return Model(img, z)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(512, input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh'))
model.add(Reshape(self.img_shape))
model.summary()
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
gen_img = model(z)
return Model(z, gen_img)
def build_discriminator(self):
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim, ))
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
d_in = concatenate([z, Flatten()(img)])
model = Dense(1024)(d_in)
model = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(model)
model = Dropout(0.5)(model)
model = Dense(1024)(model)
model = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(model)
model = Dropout(0.5)(model)
model = Dense(1024)(model)
model = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(model)
model = Dropout(0.5)(model)
validity = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(model)
return Model([z, img], validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Sample noise and generate img
z = np.random.normal(size=(batch_size, self.latent_dim))
imgs_ = self.generator.predict(z)
# Select a random batch of images and encode
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
z_ = self.encoder.predict(imgs)
# Train the discriminator (img -> z is valid, z -> img is fake)
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch([z_, imgs], valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch([z, imgs_], fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
# Train the generator (z -> img is valid and img -> z is is invalid)
g_loss = self.bigan_generator.train_on_batch([z, imgs], [valid, fake])
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss[0]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_interval(epoch)
def sample_interval(self, epoch):
r, c = 5, 5
z = np.random.normal(size=(25, self.latent_dim))
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(z)
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
bigan = BIGAN()
bigan.train(epochs=2000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=400)
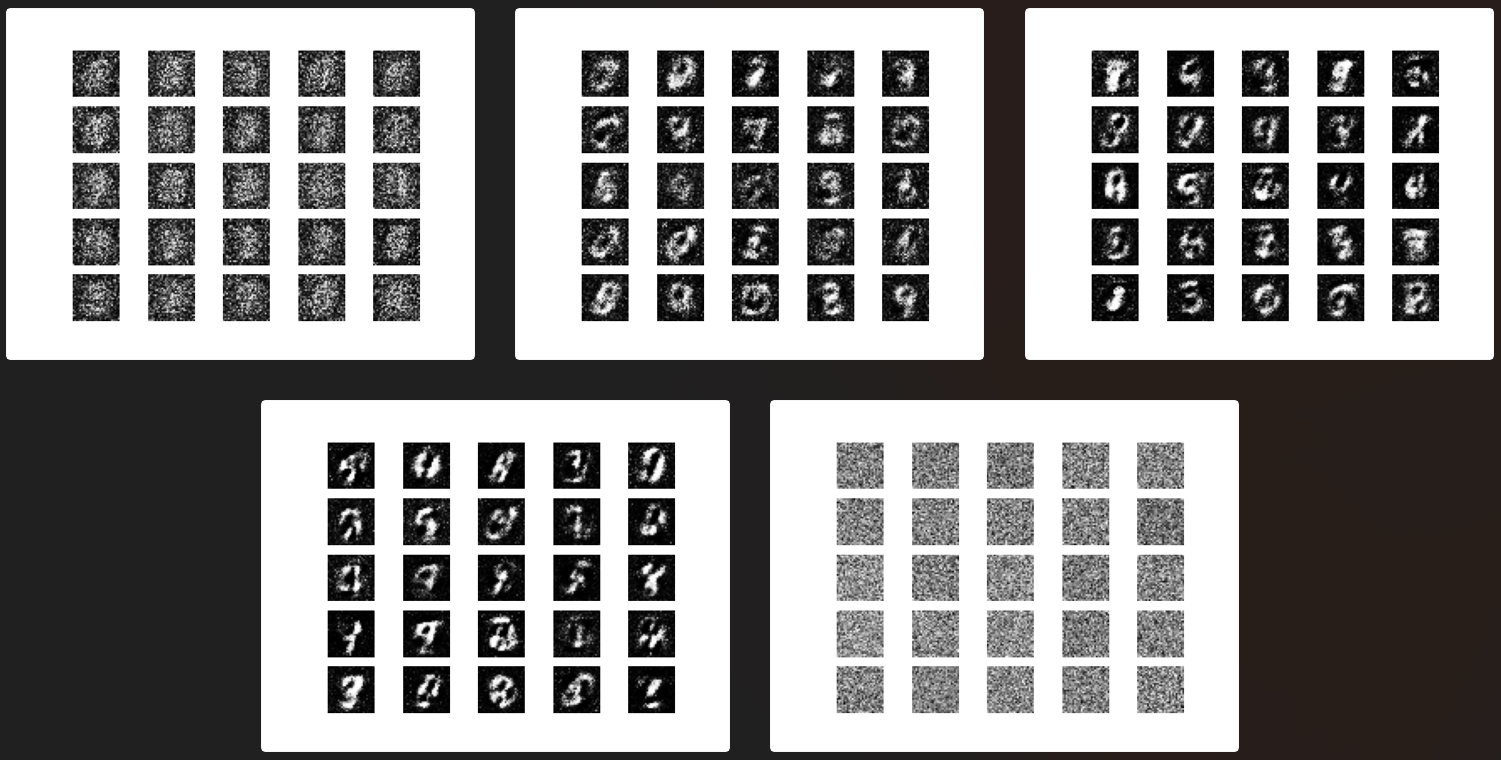
3.4 Boundary-Seeking Generative Adversarial Networks

Code and running results
bgan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import numpy as np
class BGAN():
"""Reference: https://wiseodd.github.io/techblog/2017/03/07/boundary-seeking-gan/"""
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise as input and generated imgs
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = self.generator(z)
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The valid takes generated images as input and determines validity
valid = self.discriminator(img)
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
# Trains the generator to fool the discriminator
self.combined = Model(z, valid)
self.combined.compile(loss=self.boundary_loss, optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(256, input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(1024))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh'))
model.add(Reshape(self.img_shape))
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = model(noise)
return Model(noise, img)
def build_discriminator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Flatten(input_shape=self.img_shape))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(256))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
validity = model(img)
return Model(img, validity)
def boundary_loss(self, y_true, y_pred):
"""
Boundary seeking loss.
Reference: https://wiseodd.github.io/techblog/2017/03/07/boundary-seeking-gan/
"""
return 0.5 * K.mean((K.log(y_pred) - K.log(1 - y_pred))**2)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = X_train / 127.5 - 1.
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim))
# Generate a batch of new images
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(noise, valid)
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 5, 5
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, self.latent_dim))
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
bgan = BGAN()
bgan.train(epochs=3000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200)

3.5 Context-Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks
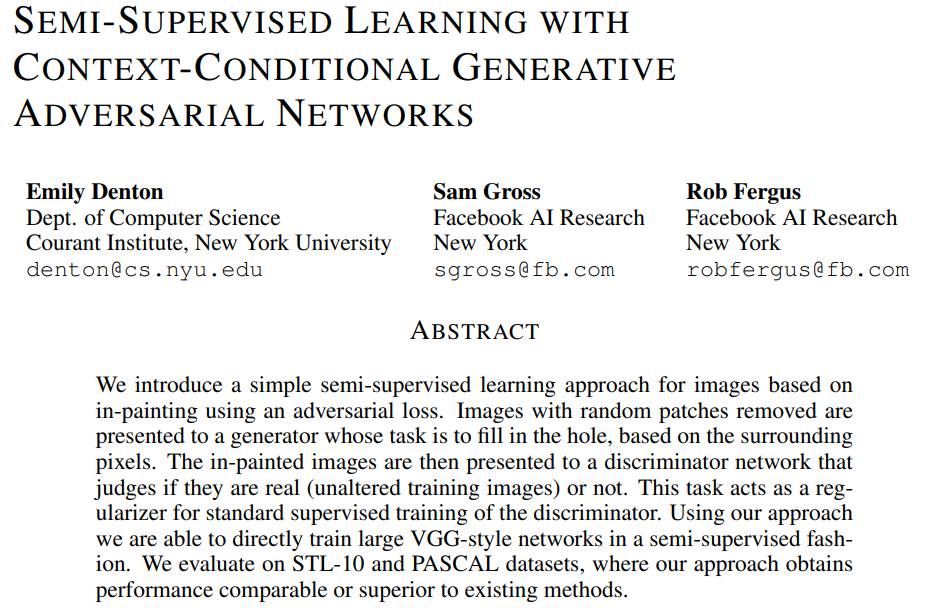
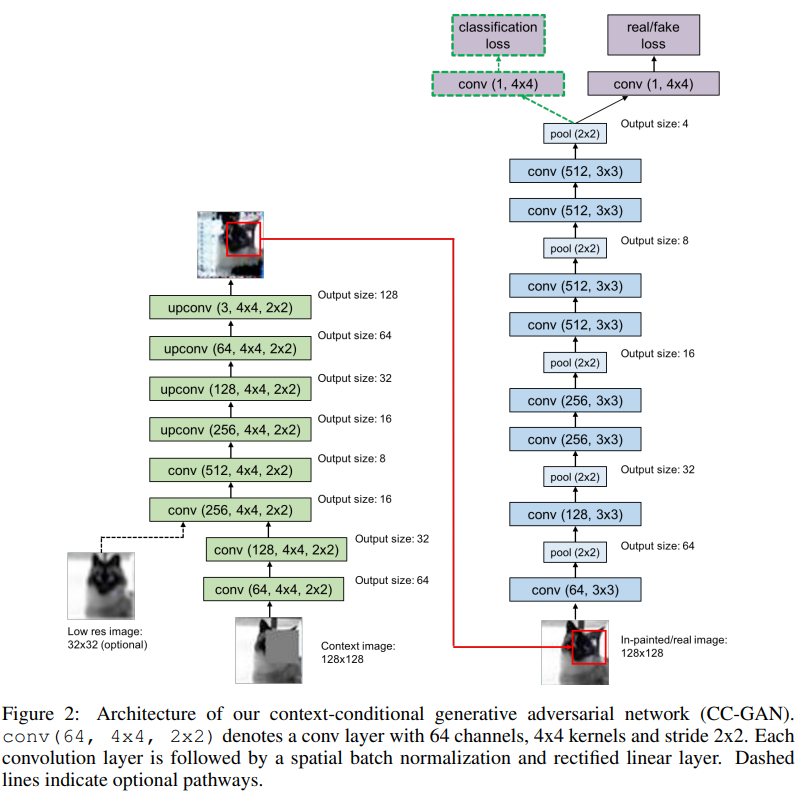
Code and running results
instancenormalization.py
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Layer, InputSpec
from tensorflow.keras import initializers, regularizers, constraints
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
class InstanceNormalization(Layer):
"""Instance normalization layer.
Normalize the activations of the previous layer at each step,
i.e. applies a transformation that maintains the mean activation
close to 0 and the activation standard deviation close to 1.
# Arguments
axis: Integer, the axis that should be normalized
(typically the features axis).
For instance, after a `Conv2D` layer with
`data_format="channels_first"`,
set `axis=1` in `InstanceNormalization`.
Setting `axis=None` will normalize all values in each
instance of the batch.
Axis 0 is the batch dimension. `axis` cannot be set to 0 to avoid errors.
epsilon: Small float added to variance to avoid dividing by zero.
center: If True, add offset of `beta` to normalized tensor.
If False, `beta` is ignored.
scale: If True, multiply by `gamma`.
If False, `gamma` is not used.
When the next layer is linear (also e.g. `nn.relu`),
this can be disabled since the scaling
will be done by the next layer.
beta_initializer: Initializer for the beta weight.
gamma_initializer: Initializer for the gamma weight.
beta_regularizer: Optional regularizer for the beta weight.
gamma_regularizer: Optional regularizer for the gamma weight.
beta_constraint: Optional constraint for the beta weight.
gamma_constraint: Optional constraint for the gamma weight.
# Input shape
Arbitrary. Use the keyword argument `input_shape`
(tuple of integers, does not include the samples axis)
when using this layer as the first layer in a Sequential model.
# Output shape
Same shape as input.
# References
- [Layer Normalization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450)
- [Instance Normalization: The Missing Ingredient for Fast Stylization](
https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.08022)
"""
def __init__(self,
axis=None,
epsilon=1e-3,
center=True,
scale=True,
beta_initializer='zeros',
gamma_initializer='ones',
beta_regularizer=None,
gamma_regularizer=None,
beta_constraint=None,
gamma_constraint=None,
**kwargs):
super(InstanceNormalization, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.supports_masking = True
self.axis = axis
self.epsilon = epsilon
self.center = center
self.scale = scale
self.beta_initializer = initializers.get(beta_initializer)
self.gamma_initializer = initializers.get(gamma_initializer)
self.beta_regularizer = regularizers.get(beta_regularizer)
self.gamma_regularizer = regularizers.get(gamma_regularizer)
self.beta_constraint = constraints.get(beta_constraint)
self.gamma_constraint = constraints.get(gamma_constraint)
def build(self, input_shape):
ndim = len(input_shape)
if self.axis == 0:
raise ValueError('Axis cannot be zero')
if (self.axis is not None) and (ndim == 2):
raise ValueError('Cannot specify axis for rank 1 tensor')
self.input_spec = InputSpec(ndim=ndim)
if self.axis is None:
shape = (1,)
else:
shape = (input_shape[self.axis],)
if self.scale:
self.gamma = self.add_weight(shape=shape,
name='gamma',
initializer=self.gamma_initializer,
regularizer=self.gamma_regularizer,
constraint=self.gamma_constraint)
else:
self.gamma = None
if self.center:
self.beta = self.add_weight(shape=shape,
name='beta',
initializer=self.beta_initializer,
regularizer=self.beta_regularizer,
constraint=self.beta_constraint)
else:
self.beta = None
self.built = True
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
input_shape = K.int_shape(inputs)
reduction_axes = list(range(0, len(input_shape)))
if self.axis is not None:
del reduction_axes[self.axis]
del reduction_axes[0]
mean = K.mean(inputs, reduction_axes, keepdims=True)
stddev = K.std(inputs, reduction_axes, keepdims=True) + self.epsilon
normed = (inputs - mean) / stddev
broadcast_shape = [1] * len(input_shape)
if self.axis is not None:
broadcast_shape[self.axis] = input_shape[self.axis]
if self.scale:
broadcast_gamma = K.reshape(self.gamma, broadcast_shape)
normed = normed * broadcast_gamma
if self.center:
broadcast_beta = K.reshape(self.beta, broadcast_shape)
normed = normed + broadcast_beta
return normed
def get_config(self):
config = {
'axis': self.axis,
'epsilon': self.epsilon,
'center': self.center,
'scale': self.scale,
'beta_initializer': initializers.serialize(self.beta_initializer),
'gamma_initializer': initializers.serialize(self.gamma_initializer),
'beta_regularizer': regularizers.serialize(self.beta_regularizer),
'gamma_regularizer': regularizers.serialize(self.gamma_regularizer),
'beta_constraint': constraints.serialize(self.beta_constraint),
'gamma_constraint': constraints.serialize(self.gamma_constraint)
}
base_config = super(InstanceNormalization, self).get_config()
return dict(list(base_config.items()) + list(config.items()))
ccgan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from instancenormalization import InstanceNormalization # Download instancenormalization Py is imported here without PIP install keras contrib
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, multiply, GaussianNoise
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, Embedding, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Concatenate
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras import losses
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
import scipy
import scipy.misc
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class CCGAN():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 32
self.img_cols = 32
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.mask_height = 10
self.mask_width = 10
self.num_classes = 10
# Number of filters in first layer of generator and discriminator
self.gf = 32
self.df = 32
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss=['mse', 'categorical_crossentropy'],
loss_weights=[0.5, 0.5],
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise as input and generates imgs
masked_img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
gen_img = self.generator(masked_img)
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The valid takes generated images as input and determines validity
valid, _ = self.discriminator(gen_img)
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
# Trains the generator to fool the discriminator
self.combined = Model(masked_img , valid)
self.combined.compile(loss=['mse'],
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
"""U-Net Generator"""
def conv2d(layer_input, filters, f_size=4, bn=True):
"""Layers used during downsampling"""
d = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=2, padding='same')(layer_input)
d = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(d)
if bn:
d = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(d)
return d
def deconv2d(layer_input, skip_input, filters, f_size=4, dropout_rate=0):
"""Layers used during upsampling"""
u = UpSampling2D(size=2)(layer_input)
u = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=1, padding='same', activation='relu')(u)
if dropout_rate:
u = Dropout(dropout_rate)(u)
u = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(u)
u = Concatenate()([u, skip_input])
return u
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Downsampling
d1 = conv2d(img, self.gf, bn=False)
d2 = conv2d(d1, self.gf*2)
d3 = conv2d(d2, self.gf*4)
d4 = conv2d(d3, self.gf*8)
# Upsampling
u1 = deconv2d(d4, d3, self.gf*4)
u2 = deconv2d(u1, d2, self.gf*2)
u3 = deconv2d(u2, d1, self.gf)
u4 = UpSampling2D(size=2)(u3)
output_img = Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=4, strides=1, padding='same', activation='tanh')(u4)
return Model(img, output_img)
def build_discriminator(self):
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=4, strides=2, padding='same', input_shape=self.img_shape))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=4, strides=2, padding='same'))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(InstanceNormalization())
model.add(Conv2D(256, kernel_size=4, strides=2, padding='same'))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(InstanceNormalization())
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
features = model(img)
validity = Conv2D(1, kernel_size=4, strides=1, padding='same')(features)
label = Flatten()(features)
label = Dense(self.num_classes+1, activation="softmax")(label)
return Model(img, [validity, label])
def mask_randomly(self, imgs):
y1 = np.random.randint(0, self.img_rows - self.mask_height, imgs.shape[0])
y2 = y1 + self.mask_height
x1 = np.random.randint(0, self.img_rows - self.mask_width, imgs.shape[0])
x2 = x1 + self.mask_width
masked_imgs = np.empty_like(imgs)
for i, img in enumerate(imgs):
masked_img = img.copy()
_y1, _y2, _x1, _x2 = y1[i], y2[i], x1[i], x2[i],
masked_img[_y1:_y2, _x1:_x2, :] = 0
masked_imgs[i] = masked_img
return masked_imgs
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, y_train), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale MNIST to 32x32
X_train = np.array([scipy.misc.imresize(x, [self.img_rows, self.img_cols]) for x in X_train])
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
y_train = y_train.reshape(-1, 1)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 4, 4, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 4, 4, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Sample half batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
labels = y_train[idx]
masked_imgs = self.mask_randomly(imgs)
# Generate a half batch of new images
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(masked_imgs)
# One-hot encoding of labels
labels = to_categorical(labels, num_classes=self.num_classes+1)
fake_labels = to_categorical(np.full((batch_size, 1), self.num_classes), num_classes=self.num_classes+1)
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, [valid, labels])
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, [fake, fake_labels])
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
# Train the generator
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(masked_imgs, valid)
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, op_acc: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[4], g_loss))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
# Select a random half batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], 6)
imgs = X_train[idx]
self.sample_images(epoch, imgs)
self.save_model()
def sample_images(self, epoch, imgs):
r, c = 3, 6
masked_imgs = self.mask_randomly(imgs)
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(masked_imgs)
imgs = (imgs + 1.0) * 0.5
masked_imgs = (masked_imgs + 1.0) * 0.5
gen_imgs = (gen_imgs + 1.0) * 0.5
gen_imgs = np.where(gen_imgs < 0, 0, gen_imgs)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
for i in range(c):
axs[0,i].imshow(imgs[i, :, :, 0], cmap='gray')
axs[0,i].axis('off')
axs[1,i].imshow(masked_imgs[i, :, :, 0], cmap='gray')
axs[1,i].axis('off')
axs[2,i].imshow(gen_imgs[i, :, :, 0], cmap='gray')
axs[2,i].axis('off')
fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
def save_model(self):
def save(model, model_name):
model_path = "saved_model/%s.json" % model_name
weights_path = "saved_model/%s_weights.hdf5" % model_name
options = {"file_arch": model_path,
"file_weight": weights_path}
json_string = model.to_json()
open(options['file_arch'], 'w').write(json_string)
model.save_weights(options['file_weight'])
save(self.generator, "ccgan_generator")
save(self.discriminator, "ccgan_discriminator")
if __name__ == '__main__':
ccgan = CCGAN()
ccgan.train(epochs=2000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200)
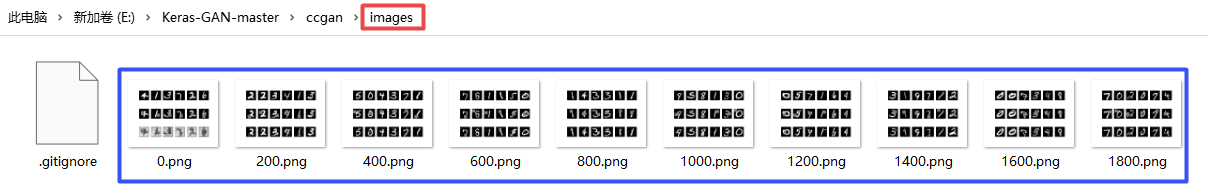

3.6 Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets
Code and running results
cgan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, multiply
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, Embedding, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class CGAN():
def __init__(self):
# Input shape
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.num_classes = 10
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss=['binary_crossentropy'],
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise and the target label as input
# and generates the corresponding digit of that label
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,))
img = self.generator([noise, label])
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator takes generated image as input and determines validity
# and the label of that image
valid = self.discriminator([img, label])
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
# Trains generator to fool discriminator
self.combined = Model([noise, label], valid)
self.combined.compile(loss=['binary_crossentropy'],
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(256, input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(1024))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh'))
model.add(Reshape(self.img_shape))
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32')
label_embedding = Flatten()(Embedding(self.num_classes, self.latent_dim)(label))
model_input = multiply([noise, label_embedding])
img = model(model_input)
return Model([noise, label], img)
def build_discriminator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(512, input_dim=np.prod(self.img_shape)))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.4))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.4))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32')
label_embedding = Flatten()(Embedding(self.num_classes, np.prod(self.img_shape))(label))
flat_img = Flatten()(img)
model_input = multiply([flat_img, label_embedding])
validity = model(model_input)
return Model([img, label], validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, y_train), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Configure input
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
y_train = y_train.reshape(-1, 1)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random half batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs, labels = X_train[idx], y_train[idx]
# Sample noise as generator input
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, 100))
# Generate a half batch of new images
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict([noise, labels])
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch([imgs, labels], valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch([gen_imgs, labels], fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
# Condition on labels
sampled_labels = np.random.randint(0, 10, batch_size).reshape(-1, 1)
# Train the generator
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch([noise, sampled_labels], valid)
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 2, 5
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, 100))
sampled_labels = np.arange(0, 10).reshape(-1, 1)
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict([noise, sampled_labels])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt,:,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].set_title("Digit: %d" % sampled_labels[cnt])
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
cgan = CGAN()
cgan.train(epochs=1000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200)
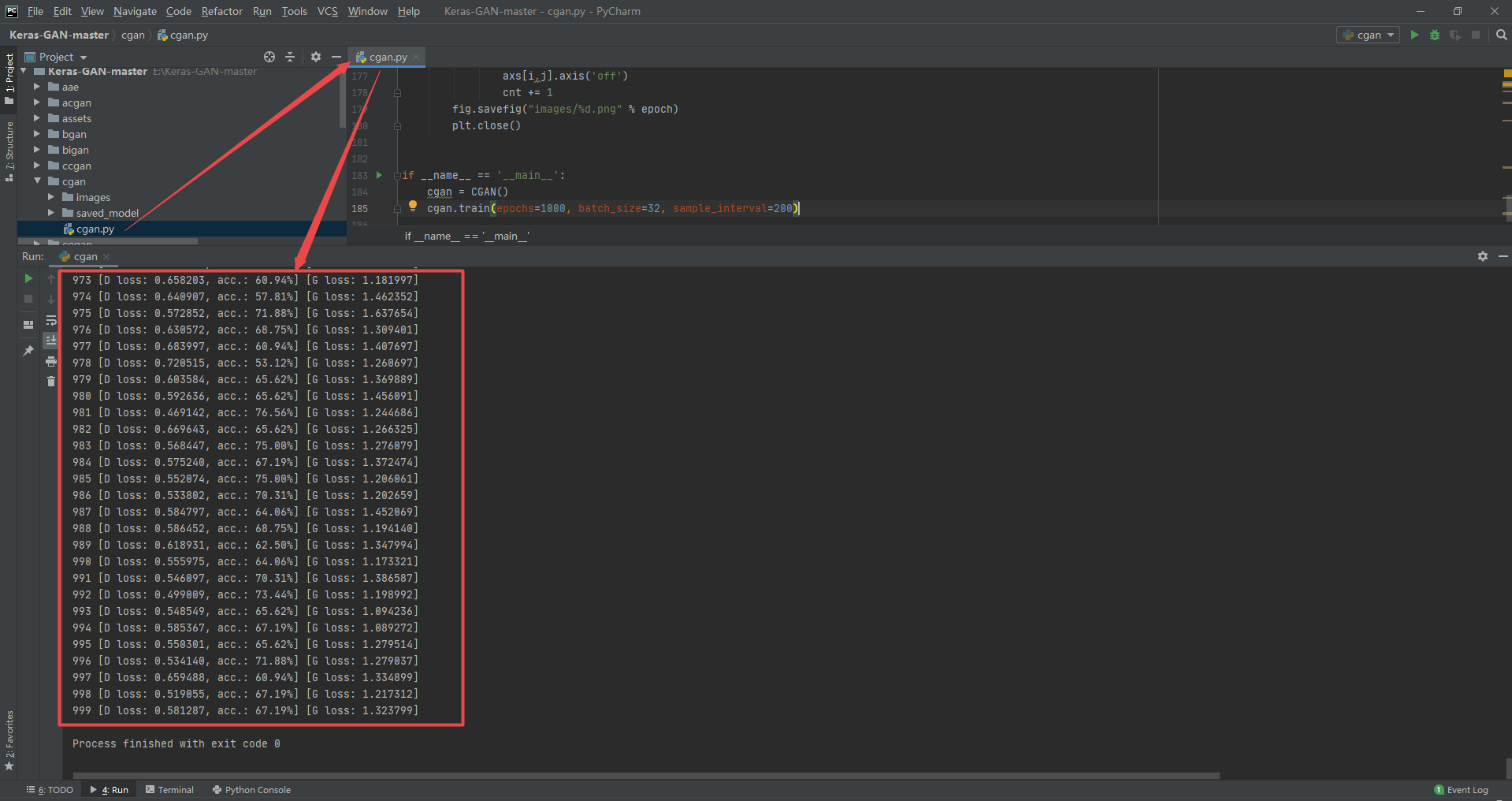

3.7 Coupled generative adversarial networks
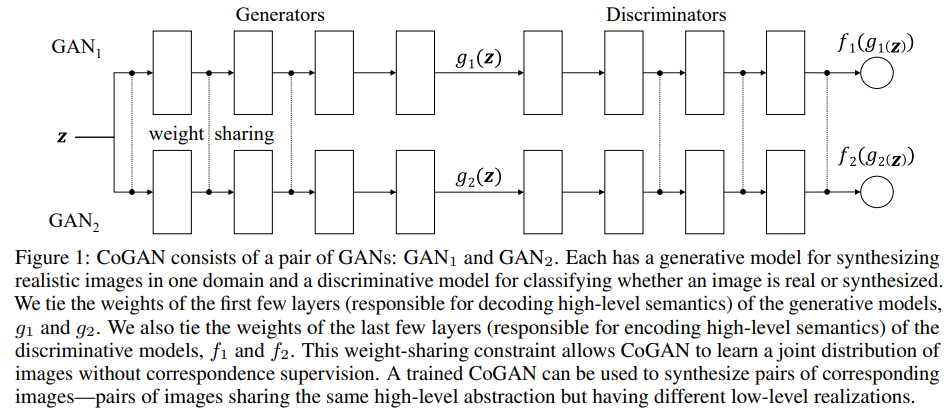
Code and running results
cogan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
import scipy
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import numpy as np
class COGAN():
"""Reference: https://wiseodd.github.io/techblog/2017/02/18/coupled_gan/"""
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.d1, self.d2 = self.build_discriminators()
self.d1.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
self.d2.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.g1, self.g2 = self.build_generators()
# The generator takes noise as input and generated imgs
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img1 = self.g1(z)
img2 = self.g2(z)
# For the combined model we will only train the generators
self.d1.trainable = False
self.d2.trainable = False
# The valid takes generated images as input and determines validity
valid1 = self.d1(img1)
valid2 = self.d2(img2)
# The combined model (stacked generators and discriminators)
# Trains generators to fool discriminators
self.combined = Model(z, [valid1, valid2])
self.combined.compile(loss=['binary_crossentropy', 'binary_crossentropy'],
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generators(self):
# Shared weights between generators
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(256, input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
feature_repr = model(noise)
# Generator 1
g1 = Dense(1024)(feature_repr)
g1 = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(g1)
g1 = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(g1)
g1 = Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh')(g1)
img1 = Reshape(self.img_shape)(g1)
# Generator 2
g2 = Dense(1024)(feature_repr)
g2 = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(g2)
g2 = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(g2)
g2 = Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh')(g2)
img2 = Reshape(self.img_shape)(g2)
model.summary()
return Model(noise, img1), Model(noise, img2)
def build_discriminators(self):
img1 = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
img2 = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Shared discriminator layers
model = Sequential()
model.add(Flatten(input_shape=self.img_shape))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(256))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
img1_embedding = model(img1)
img2_embedding = model(img2)
# Discriminator 1
validity1 = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(img1_embedding)
# Discriminator 2
validity2 = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(img2_embedding)
return Model(img1, validity1), Model(img2, validity2)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Images in domain A and B (rotated)
X1 = X_train[:int(X_train.shape[0]/2)]
X2 = X_train[int(X_train.shape[0]/2):]
X2 = scipy.ndimage.interpolation.rotate(X2, 90, axes=(1, 2))
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ----------------------
# Train Discriminators
# ----------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X1.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs1 = X1[idx]
imgs2 = X2[idx]
# Sample noise as generator input
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, 100))
# Generate a batch of new images
gen_imgs1 = self.g1.predict(noise)
gen_imgs2 = self.g2.predict(noise)
# Train the discriminators
d1_loss_real = self.d1.train_on_batch(imgs1, valid)
d2_loss_real = self.d2.train_on_batch(imgs2, valid)
d1_loss_fake = self.d1.train_on_batch(gen_imgs1, fake)
d2_loss_fake = self.d2.train_on_batch(gen_imgs2, fake)
d1_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d1_loss_real, d1_loss_fake)
d2_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d2_loss_real, d2_loss_fake)
# ------------------
# Train Generators
# ------------------
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(noise, [valid, valid])
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D1 loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [D2 loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" \
% (epoch, d1_loss[0], 100*d1_loss[1], d2_loss[0], 100*d2_loss[1], g_loss[0]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 4, 4
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * int(c/2), 100))
gen_imgs1 = self.g1.predict(noise)
gen_imgs2 = self.g2.predict(noise)
gen_imgs = np.concatenate([gen_imgs1, gen_imgs2])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
gan = COGAN()
gan.train(epochs=1000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200)

3.8 Context Encoders: Feature Learning by Inpainting

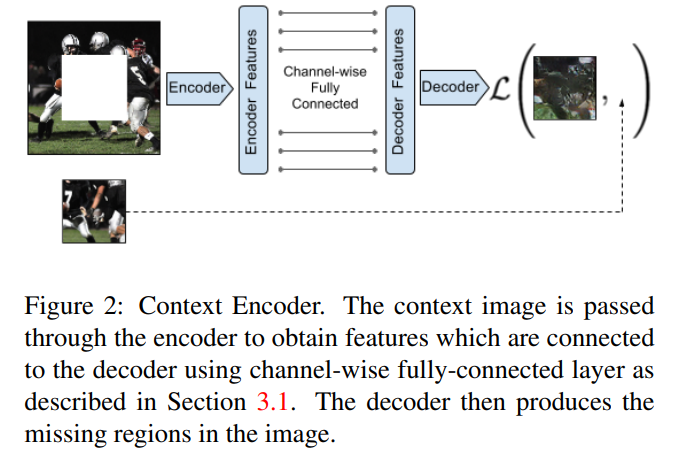
Code and running results
cifar-10-python.tar.gz Download

context_encoder.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
import os
from tensorflow.python.keras.datasets.cifar import load_batch
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import cifar10
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, multiply, GaussianNoise
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, Embedding, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import MaxPooling2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras import losses
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class ContextEncoder():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 32
self.img_cols = 32
self.mask_height = 8
self.mask_width = 8
self.channels = 3
self.num_classes = 2
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.missing_shape = (self.mask_height, self.mask_width, self.channels)
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise as input and generates the missing
# part of the image
masked_img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
gen_missing = self.generator(masked_img)
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator takes generated images as input and determines
# if it is generated or if it is a real image
valid = self.discriminator(gen_missing)
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
# Trains generator to fool discriminator
self.combined = Model(masked_img , [gen_missing, valid])
self.combined.compile(loss=['mse', 'binary_crossentropy'],
loss_weights=[0.999, 0.001],
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
# Encoder
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=3, strides=2, input_shape=self.img_shape, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(512, kernel_size=1, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
# Decoder
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation('tanh'))
model.summary()
masked_img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
gen_missing = model(masked_img)
return Model(masked_img, gen_missing)
def build_discriminator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, input_shape=self.missing_shape, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(256, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.missing_shape)
validity = model(img)
return Model(img, validity)
def mask_randomly(self, imgs):
y1 = np.random.randint(0, self.img_rows - self.mask_height, imgs.shape[0])
y2 = y1 + self.mask_height
x1 = np.random.randint(0, self.img_rows - self.mask_width, imgs.shape[0])
x2 = x1 + self.mask_width
masked_imgs = np.empty_like(imgs)
missing_parts = np.empty((imgs.shape[0], self.mask_height, self.mask_width, self.channels))
for i, img in enumerate(imgs):
masked_img = img.copy()
_y1, _y2, _x1, _x2 = y1[i], y2[i], x1[i], x2[i]
missing_parts[i] = masked_img[_y1:_y2, _x1:_x2, :].copy()
masked_img[_y1:_y2, _x1:_x2, :] = 0
masked_imgs[i] = masked_img
return masked_imgs, missing_parts, (y1, y2, x1, x2)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
num_train_samples = 50000
path = 'cifar-10-batches-py'
x_train = np.empty((num_train_samples, 3, 32, 32), dtype='uint8')
y_train = np.empty((num_train_samples,), dtype='uint8')
for i in range(1, 6):
fpath = os.path.join(path, 'data_batch_' + str(i))
(x_train[(i - 1) * 10000:i * 10000, :, :, :],
y_train[(i - 1) * 10000:i * 10000]) = load_batch(fpath)
fpath = os.path.join(path, 'test_batch')
x_test, y_test = load_batch(fpath)
y_train = np.reshape(y_train, (len(y_train), 1))
y_test = np.reshape(y_test, (len(y_test), 1))
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_last':
x_train = x_train.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
x_test = x_test.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
x_test = x_test.astype(x_train.dtype)
y_test = y_test.astype(y_train.dtype)
# (X_train, y_train), (_, _) = cifar10.load_data()
X_train,Y_train = x_train,y_train
# Extract dogs and cats
X_cats = X_train[(y_train == 3).flatten()]
X_dogs = X_train[(y_train == 5).flatten()]
X_train = np.vstack((X_cats, X_dogs))
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = X_train / 127.5 - 1.
y_train = y_train.reshape(-1, 1)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
masked_imgs, missing_parts, _ = self.mask_randomly(imgs)
# Generate a batch of new images
gen_missing = self.generator.predict(masked_imgs)
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(missing_parts, valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_missing, fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(masked_imgs, [missing_parts, valid])
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f, mse: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss[0], g_loss[1]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], 6)
imgs = X_train[idx]
self.sample_images(epoch, imgs)
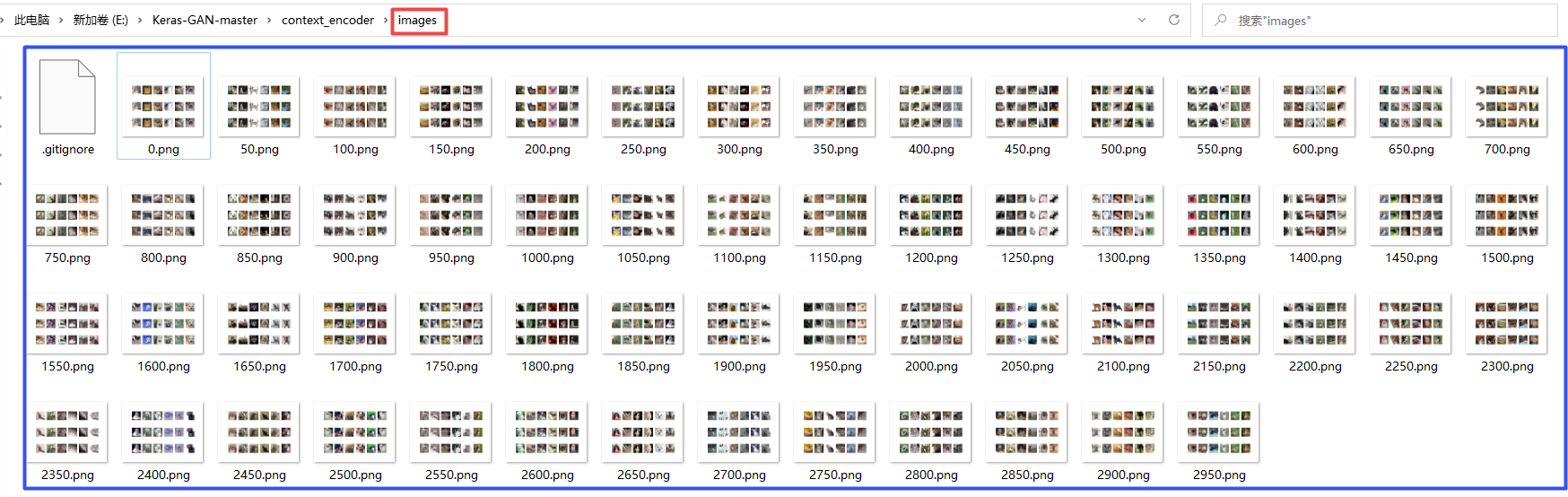
def sample_images(self, epoch, imgs):
r, c = 3, 6
masked_imgs, missing_parts, (y1, y2, x1, x2) = self.mask_randomly(imgs)
gen_missing = self.generator.predict(masked_imgs)
imgs = 0.5 * imgs + 0.5
masked_imgs = 0.5 * masked_imgs + 0.5
gen_missing = 0.5 * gen_missing + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
for i in range(c):
axs[0,i].imshow(imgs[i, :,:])
axs[0,i].axis('off')
axs[1,i].imshow(masked_imgs[i, :,:])
axs[1,i].axis('off')
filled_in = imgs[i].copy()
filled_in[y1[i]:y2[i], x1[i]:x2[i], :] = gen_missing[i]
axs[2,i].imshow(filled_in)
axs[2,i].axis('off')
fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
def save_model(self):
def save(model, model_name):
model_path = "saved_model/%s.json" % model_name
weights_path = "saved_model/%s_weights.hdf5" % model_name
options = {"file_arch": model_path,
"file_weight": weights_path}
json_string = model.to_json()
open(options['file_arch'], 'w').write(json_string)
model.save_weights(options['file_weight'])
save(self.generator, "generator")
save(self.discriminator, "discriminator")
if __name__ == '__main__':
context_encoder = ContextEncoder()
context_encoder.train(epochs=3000, batch_size=64, sample_interval=50)

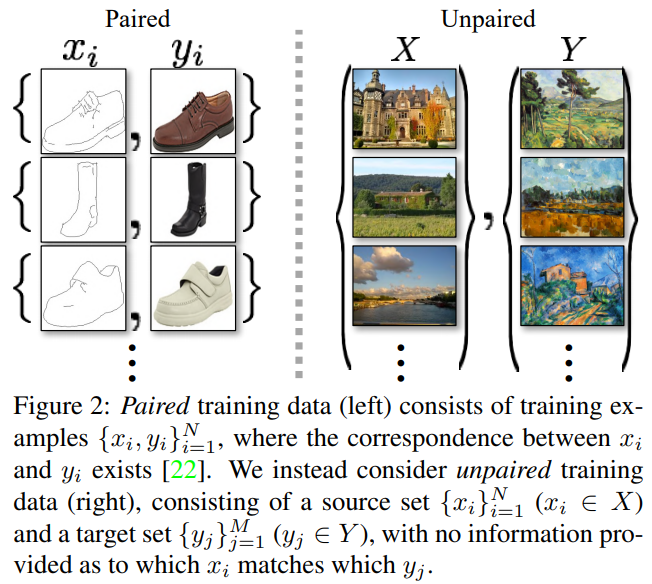
3.9 Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks

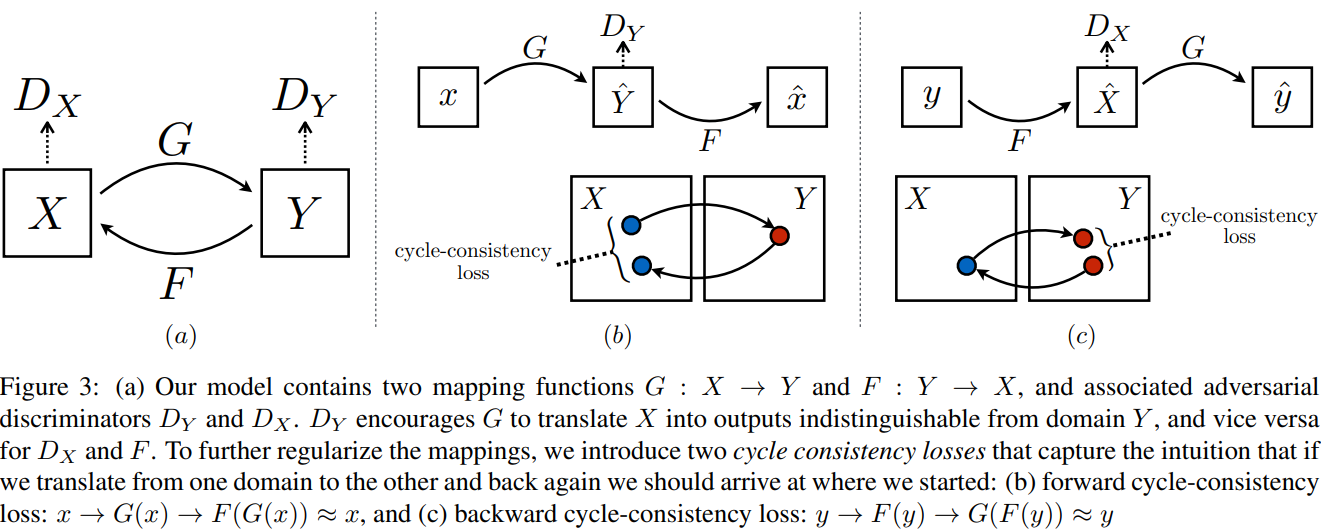
Code and running results
data_loader.py
import scipy
from glob import glob
import numpy as np
class DataLoader():
def __init__(self, dataset_name, img_res=(128, 128)):
self.dataset_name = dataset_name
self.img_res = img_res
def load_data(self, domain, batch_size=1, is_testing=False):
data_type = "train%s" % domain if not is_testing else "test%s" % domain
path = glob('./datasets/%s/%s/*' % (self.dataset_name, data_type))
batch_images = np.random.choice(path, size=batch_size)
imgs = []
for img_path in batch_images:
img = self.imread(img_path)
if not is_testing:
img = scipy.misc.imresize(img, self.img_res)
if np.random.random() > 0.5:
img = np.fliplr(img)
else:
img = scipy.misc.imresize(img, self.img_res)
imgs.append(img)
imgs = np.array(imgs)/127.5 - 1.
return imgs
def load_batch(self, batch_size=1, is_testing=False):
data_type = "train" if not is_testing else "val"
path_A = glob('./datasets/%s/%sA/*' % (self.dataset_name, data_type))
path_B = glob('./datasets/%s/%sB/*' % (self.dataset_name, data_type))
self.n_batches = int(min(len(path_A), len(path_B)) / batch_size)
total_samples = self.n_batches * batch_size
# Sample n_batches * batch_size from each path list so that model sees all
# samples from both domains
path_A = np.random.choice(path_A, total_samples, replace=False)
path_B = np.random.choice(path_B, total_samples, replace=False)
for i in range(self.n_batches-1):
batch_A = path_A[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
batch_B = path_B[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
imgs_A, imgs_B = [], []
for img_A, img_B in zip(batch_A, batch_B):
img_A = self.imread(img_A)
img_B = self.imread(img_B)
img_A = scipy.misc.imresize(img_A, self.img_res)
img_B = scipy.misc.imresize(img_B, self.img_res)
if not is_testing and np.random.random() > 0.5:
img_A = np.fliplr(img_A)
img_B = np.fliplr(img_B)
imgs_A.append(img_A)
imgs_B.append(img_B)
imgs_A = np.array(imgs_A)/127.5 - 1.
imgs_B = np.array(imgs_B)/127.5 - 1.
yield imgs_A, imgs_B
def load_img(self, path):
img = self.imread(path)
img = scipy.misc.imresize(img, self.img_res)
img = img/127.5 - 1.
return img[np.newaxis, :, :, :]
def imread(self, path):
return scipy.misc.imread(path, mode='RGB').astype(np.float)
instancenormalization.py
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Layer, InputSpec
from tensorflow.keras import initializers, regularizers, constraints
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
class InstanceNormalization(Layer):
"""Instance normalization layer.
Normalize the activations of the previous layer at each step,
i.e. applies a transformation that maintains the mean activation
close to 0 and the activation standard deviation close to 1.
# Arguments
axis: Integer, the axis that should be normalized
(typically the features axis).
For instance, after a `Conv2D` layer with
`data_format="channels_first"`,
set `axis=1` in `InstanceNormalization`.
Setting `axis=None` will normalize all values in each
instance of the batch.
Axis 0 is the batch dimension. `axis` cannot be set to 0 to avoid errors.
epsilon: Small float added to variance to avoid dividing by zero.
center: If True, add offset of `beta` to normalized tensor.
If False, `beta` is ignored.
scale: If True, multiply by `gamma`.
If False, `gamma` is not used.
When the next layer is linear (also e.g. `nn.relu`),
this can be disabled since the scaling
will be done by the next layer.
beta_initializer: Initializer for the beta weight.
gamma_initializer: Initializer for the gamma weight.
beta_regularizer: Optional regularizer for the beta weight.
gamma_regularizer: Optional regularizer for the gamma weight.
beta_constraint: Optional constraint for the beta weight.
gamma_constraint: Optional constraint for the gamma weight.
# Input shape
Arbitrary. Use the keyword argument `input_shape`
(tuple of integers, does not include the samples axis)
when using this layer as the first layer in a Sequential model.
# Output shape
Same shape as input.
# References
- [Layer Normalization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450)
- [Instance Normalization: The Missing Ingredient for Fast Stylization](
https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.08022)
"""
def __init__(self,
axis=None,
epsilon=1e-3,
center=True,
scale=True,
beta_initializer='zeros',
gamma_initializer='ones',
beta_regularizer=None,
gamma_regularizer=None,
beta_constraint=None,
gamma_constraint=None,
**kwargs):
super(InstanceNormalization, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.supports_masking = True
self.axis = axis
self.epsilon = epsilon
self.center = center
self.scale = scale
self.beta_initializer = initializers.get(beta_initializer)
self.gamma_initializer = initializers.get(gamma_initializer)
self.beta_regularizer = regularizers.get(beta_regularizer)
self.gamma_regularizer = regularizers.get(gamma_regularizer)
self.beta_constraint = constraints.get(beta_constraint)
self.gamma_constraint = constraints.get(gamma_constraint)
def build(self, input_shape):
ndim = len(input_shape)
if self.axis == 0:
raise ValueError('Axis cannot be zero')
if (self.axis is not None) and (ndim == 2):
raise ValueError('Cannot specify axis for rank 1 tensor')
self.input_spec = InputSpec(ndim=ndim)
if self.axis is None:
shape = (1,)
else:
shape = (input_shape[self.axis],)
if self.scale:
self.gamma = self.add_weight(shape=shape,
name='gamma',
initializer=self.gamma_initializer,
regularizer=self.gamma_regularizer,
constraint=self.gamma_constraint)
else:
self.gamma = None
if self.center:
self.beta = self.add_weight(shape=shape,
name='beta',
initializer=self.beta_initializer,
regularizer=self.beta_regularizer,
constraint=self.beta_constraint)
else:
self.beta = None
self.built = True
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
input_shape = K.int_shape(inputs)
reduction_axes = list(range(0, len(input_shape)))
if self.axis is not None:
del reduction_axes[self.axis]
del reduction_axes[0]
mean = K.mean(inputs, reduction_axes, keepdims=True)
stddev = K.std(inputs, reduction_axes, keepdims=True) + self.epsilon
normed = (inputs - mean) / stddev
broadcast_shape = [1] * len(input_shape)
if self.axis is not None:
broadcast_shape[self.axis] = input_shape[self.axis]
if self.scale:
broadcast_gamma = K.reshape(self.gamma, broadcast_shape)
normed = normed * broadcast_gamma
if self.center:
broadcast_beta = K.reshape(self.beta, broadcast_shape)
normed = normed + broadcast_beta
return normed
def get_config(self):
config = {
'axis': self.axis,
'epsilon': self.epsilon,
'center': self.center,
'scale': self.scale,
'beta_initializer': initializers.serialize(self.beta_initializer),
'gamma_initializer': initializers.serialize(self.gamma_initializer),
'beta_regularizer': regularizers.serialize(self.beta_regularizer),
'gamma_regularizer': regularizers.serialize(self.gamma_regularizer),
'beta_constraint': constraints.serialize(self.beta_constraint),
'gamma_constraint': constraints.serialize(self.gamma_constraint)
}
base_config = super(InstanceNormalization, self).get_config()
return dict(list(base_config.items()) + list(config.items()))
cyclegan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
import scipy
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from instancenormalization import InstanceNormalization
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, Concatenate
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
from data_loader import DataLoader
import numpy as np
import os
class CycleGAN():
def __init__(self):
# Input shape
self.img_rows = 128
self.img_cols = 128
self.channels = 3
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
# Configure data loader
self.dataset_name = 'apple2orange'
self.data_loader = DataLoader(dataset_name=self.dataset_name,
img_res=(self.img_rows, self.img_cols))
# Calculate output shape of D (PatchGAN)
patch = int(self.img_rows / 2**4)
self.disc_patch = (patch, patch, 1)
# Number of filters in the first layer of G and D
self.gf = 32
self.df = 64
# Loss weights
self.lambda_cycle = 10.0 # Cycle-consistency loss
self.lambda_id = 0.1 * self.lambda_cycle # Identity loss
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminators
self.d_A = self.build_discriminator()
self.d_B = self.build_discriminator()
self.d_A.compile(loss='mse',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
self.d_B.compile(loss='mse',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
#-------------------------
# Construct Computational
# Graph of Generators
#-------------------------
# Build the generators
self.g_AB = self.build_generator()
self.g_BA = self.build_generator()
# Input images from both domains
img_A = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
img_B = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Translate images to the other domain
fake_B = self.g_AB(img_A)
fake_A = self.g_BA(img_B)
# Translate images back to original domain
reconstr_A = self.g_BA(fake_B)
reconstr_B = self.g_AB(fake_A)
# Identity mapping of images
img_A_id = self.g_BA(img_A)
img_B_id = self.g_AB(img_B)
# For the combined model we will only train the generators
self.d_A.trainable = False
self.d_B.trainable = False
# Discriminators determines validity of translated images
valid_A = self.d_A(fake_A)
valid_B = self.d_B(fake_B)
# Combined model trains generators to fool discriminators
self.combined = Model(inputs=[img_A, img_B],
outputs=[ valid_A, valid_B,
reconstr_A, reconstr_B,
img_A_id, img_B_id ])
self.combined.compile(loss=['mse', 'mse',
'mae', 'mae',
'mae', 'mae'],
loss_weights=[ 1, 1,
self.lambda_cycle, self.lambda_cycle,
self.lambda_id, self.lambda_id ],
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
"""U-Net Generator"""
def conv2d(layer_input, filters, f_size=4):
"""Layers used during downsampling"""
d = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=2, padding='same')(layer_input)
d = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(d)
d = InstanceNormalization()(d)
return d
def deconv2d(layer_input, skip_input, filters, f_size=4, dropout_rate=0):
"""Layers used during upsampling"""
u = UpSampling2D(size=2)(layer_input)
u = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=1, padding='same', activation='relu')(u)
if dropout_rate:
u = Dropout(dropout_rate)(u)
u = InstanceNormalization()(u)
u = Concatenate()([u, skip_input])
return u
# Image input
d0 = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Downsampling
d1 = conv2d(d0, self.gf)
d2 = conv2d(d1, self.gf*2)
d3 = conv2d(d2, self.gf*4)
d4 = conv2d(d3, self.gf*8)
# Upsampling
u1 = deconv2d(d4, d3, self.gf*4)
u2 = deconv2d(u1, d2, self.gf*2)
u3 = deconv2d(u2, d1, self.gf)
u4 = UpSampling2D(size=2)(u3)
output_img = Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=4, strides=1, padding='same', activation='tanh')(u4)
return Model(d0, output_img)
def build_discriminator(self):
def d_layer(layer_input, filters, f_size=4, normalization=True):
"""Discriminator layer"""
d = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=2, padding='same')(layer_input)
d = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(d)
if normalization:
d = InstanceNormalization()(d)
return d
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
d1 = d_layer(img, self.df, normalization=False)
d2 = d_layer(d1, self.df*2)
d3 = d_layer(d2, self.df*4)
d4 = d_layer(d3, self.df*8)
validity = Conv2D(1, kernel_size=4, strides=1, padding='same')(d4)
return Model(img, validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=1, sample_interval=50):
start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
# Adversarial loss ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size,) + self.disc_patch)
fake = np.zeros((batch_size,) + self.disc_patch)
for epoch in range(epochs):
for batch_i, (imgs_A, imgs_B) in enumerate(self.data_loader.load_batch(batch_size)):
# ----------------------
# Train Discriminators
# ----------------------
# Translate images to opposite domain
fake_B = self.g_AB.predict(imgs_A)
fake_A = self.g_BA.predict(imgs_B)
# Train the discriminators (original images = real / translated = Fake)
dA_loss_real = self.d_A.train_on_batch(imgs_A, valid)
dA_loss_fake = self.d_A.train_on_batch(fake_A, fake)
dA_loss = 0.5 * np.add(dA_loss_real, dA_loss_fake)
dB_loss_real = self.d_B.train_on_batch(imgs_B, valid)
dB_loss_fake = self.d_B.train_on_batch(fake_B, fake)
dB_loss = 0.5 * np.add(dB_loss_real, dB_loss_fake)
# Total disciminator loss
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(dA_loss, dB_loss)
# ------------------
# Train Generators
# ------------------
# Train the generators
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch([imgs_A, imgs_B],
[valid, valid,
imgs_A, imgs_B,
imgs_A, imgs_B])
elapsed_time = datetime.datetime.now() - start_time
# Plot the progress
print ("[Epoch %d/%d] [Batch %d/%d] [D loss: %f, acc: %3d%%] [G loss: %05f, adv: %05f, recon: %05f, id: %05f] time: %s " \
% ( epoch, epochs,
batch_i, self.data_loader.n_batches,
d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1],
g_loss[0],
np.mean(g_loss[1:3]),
np.mean(g_loss[3:5]),
np.mean(g_loss[5:6]),
elapsed_time))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if batch_i % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch, batch_i)
def sample_images(self, epoch, batch_i):
os.makedirs('images/%s' % self.dataset_name, exist_ok=True)
r, c = 2, 3
imgs_A = self.data_loader.load_data(domain="A", batch_size=1, is_testing=True)
imgs_B = self.data_loader.load_data(domain="B", batch_size=1, is_testing=True)
# Demo (for GIF)
#imgs_A = self.data_loader.load_img('datasets/apple2orange/testA/n07740461_1541.jpg')
#imgs_B = self.data_loader.load_img('datasets/apple2orange/testB/n07749192_4241.jpg')
# Translate images to the other domain
fake_B = self.g_AB.predict(imgs_A)
fake_A = self.g_BA.predict(imgs_B)
# Translate back to original domain
reconstr_A = self.g_BA.predict(fake_B)
reconstr_B = self.g_AB.predict(fake_A)
gen_imgs = np.concatenate([imgs_A, fake_B, reconstr_A, imgs_B, fake_A, reconstr_B])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
titles = ['Original', 'Translated', 'Reconstructed']
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt])
axs[i, j].set_title(titles[j])
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/%s/%d_%d.png" % (self.dataset_name, epoch, batch_i))
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
gan = CycleGAN()
gan.train(epochs=10, batch_size=1, sample_interval=200)

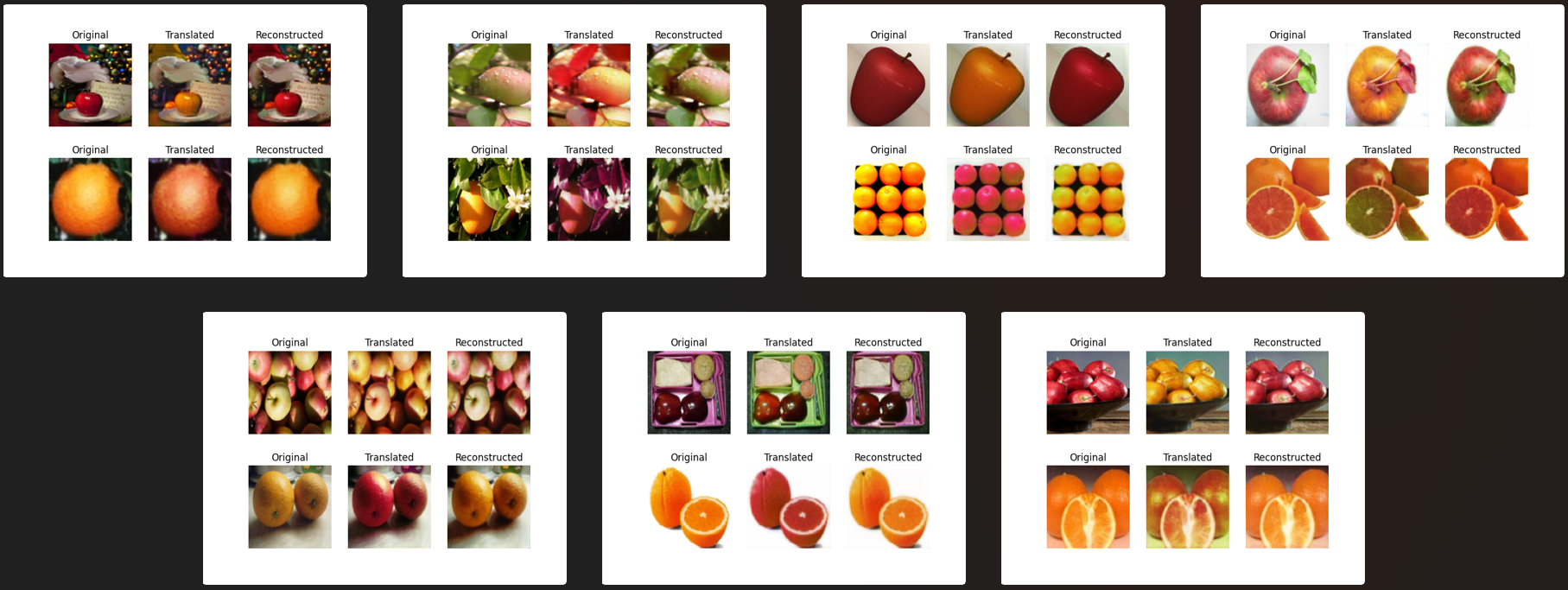
3.10 Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network
Code and running results
dcgan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import numpy as np
class DCGAN():
def __init__(self):
# Input shape
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise as input and generates imgs
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = self.generator(z)
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator takes generated images as input and determines validity
valid = self.discriminator(img)
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
# Trains the generator to fool the discriminator
self.combined = Model(z, valid)
self.combined.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(128 * 7 * 7, activation="relu", input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(Reshape((7, 7, 128)))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation("tanh"))
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = model(noise)
return Model(noise, img)
def build_discriminator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=3, strides=2, input_shape=self.img_shape, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0,1),(0,1))))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(256, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
validity = model(img)
return Model(img, validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, save_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = X_train / 127.5 - 1.
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random half of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
# Sample noise and generate a batch of new images
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim))
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Train the discriminator (real classified as ones and generated as zeros)
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
# Train the generator (wants discriminator to mistake images as real)
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(noise, valid)
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % save_interval == 0:
self.save_imgs(epoch)
def save_imgs(self, epoch):
r, c = 5, 5
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, self.latent_dim))
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
dcgan = DCGAN()
dcgan.train(epochs=4000, batch_size=32, save_interval=50)
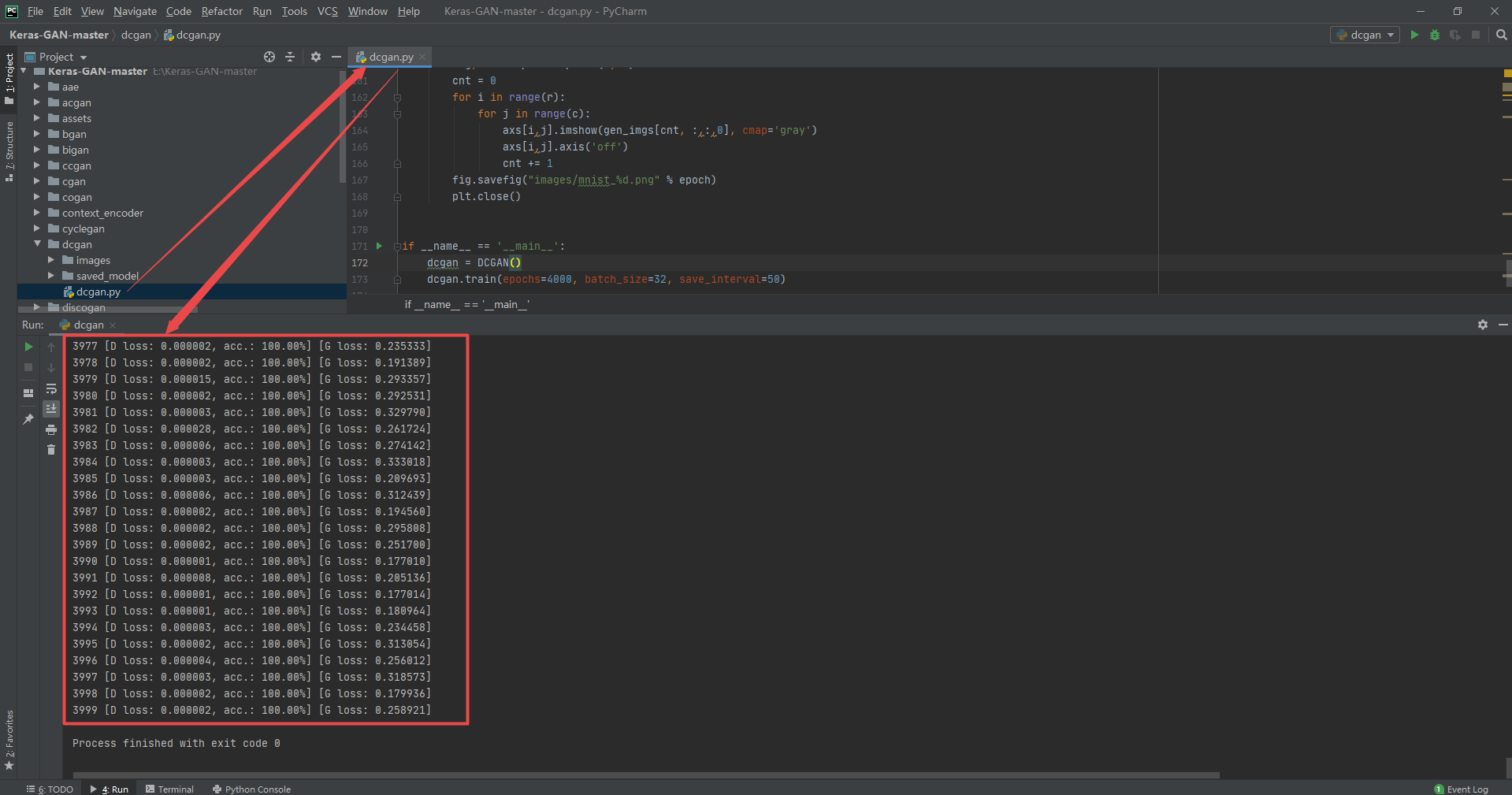
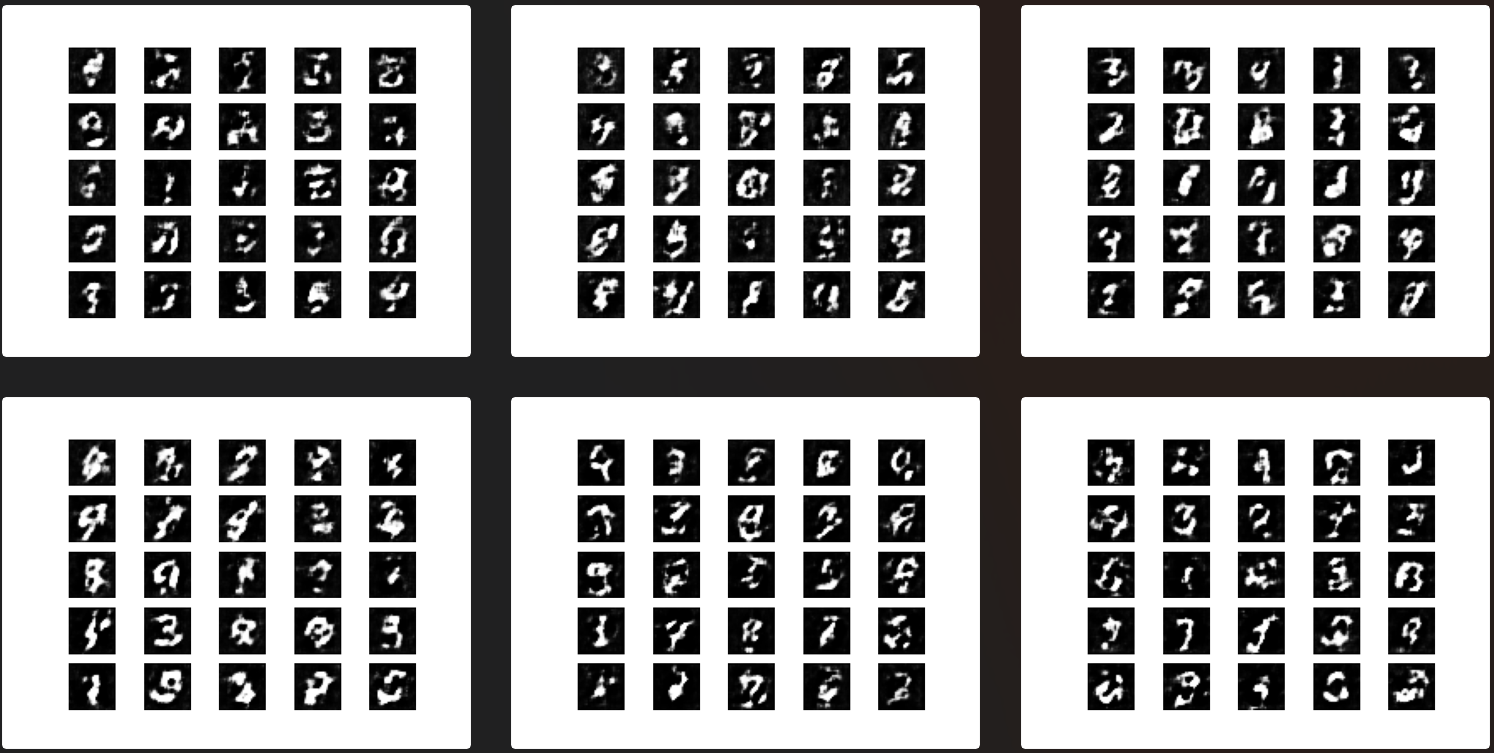
3.11 Discover Cross-Domain Relations with Generative Adversarial Networks
Code and running results
edges2shoes.tar.gz Download

discogan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
import scipy
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from instancenormalization import InstanceNormalization
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, Concatenate
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
from data_loader import DataLoader
import numpy as np
import os
class DiscoGAN():
def __init__(self):
# Input shape
self.img_rows = 128
self.img_cols = 128
self.channels = 3
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
# Configure data loader
self.dataset_name = 'edges2shoes'
self.data_loader = DataLoader(dataset_name=self.dataset_name,
img_res=(self.img_rows, self.img_cols))
# Calculate output shape of D (PatchGAN)
patch = int(self.img_rows / 2**4)
self.disc_patch = (patch, patch, 1)
# Number of filters in the first layer of G and D
self.gf = 64
self.df = 64
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminators
self.d_A = self.build_discriminator()
self.d_B = self.build_discriminator()
self.d_A.compile(loss='mse',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
self.d_B.compile(loss='mse',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
#-------------------------
# Construct Computational
# Graph of Generators
#-------------------------
# Build the generators
self.g_AB = self.build_generator()
self.g_BA = self.build_generator()
# Input images from both domains
img_A = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
img_B = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Translate images to the other domain
fake_B = self.g_AB(img_A)
fake_A = self.g_BA(img_B)
# Translate images back to original domain
reconstr_A = self.g_BA(fake_B)
reconstr_B = self.g_AB(fake_A)
# For the combined model we will only train the generators
self.d_A.trainable = False
self.d_B.trainable = False
# Discriminators determines validity of translated images
valid_A = self.d_A(fake_A)
valid_B = self.d_B(fake_B)
# Objectives
# + Adversarial: Fool domain discriminators
# + Translation: Minimize MAE between e.g. fake B and true B
# + Cycle-consistency: Minimize MAE between reconstructed images and original
self.combined = Model(inputs=[img_A, img_B],
outputs=[ valid_A, valid_B,
fake_B, fake_A,
reconstr_A, reconstr_B ])
self.combined.compile(loss=['mse', 'mse',
'mae', 'mae',
'mae', 'mae'],
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
"""U-Net Generator"""
def conv2d(layer_input, filters, f_size=4, normalize=True):
"""Layers used during downsampling"""
d = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=2, padding='same')(layer_input)
d = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(d)
if normalize:
d = InstanceNormalization()(d)
return d
def deconv2d(layer_input, skip_input, filters, f_size=4, dropout_rate=0):
"""Layers used during upsampling"""
u = UpSampling2D(size=2)(layer_input)
u = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=1, padding='same', activation='relu')(u)
if dropout_rate:
u = Dropout(dropout_rate)(u)
u = InstanceNormalization()(u)
u = Concatenate()([u, skip_input])
return u
# Image input
d0 = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Downsampling
d1 = conv2d(d0, self.gf, normalize=False)
d2 = conv2d(d1, self.gf*2)
d3 = conv2d(d2, self.gf*4)
d4 = conv2d(d3, self.gf*8)
d5 = conv2d(d4, self.gf*8)
d6 = conv2d(d5, self.gf*8)
d7 = conv2d(d6, self.gf*8)
# Upsampling
u1 = deconv2d(d7, d6, self.gf*8)
u2 = deconv2d(u1, d5, self.gf*8)
u3 = deconv2d(u2, d4, self.gf*8)
u4 = deconv2d(u3, d3, self.gf*4)
u5 = deconv2d(u4, d2, self.gf*2)
u6 = deconv2d(u5, d1, self.gf)
u7 = UpSampling2D(size=2)(u6)
output_img = Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=4, strides=1,
padding='same', activation='tanh')(u7)
return Model(d0, output_img)
def build_discriminator(self):
def d_layer(layer_input, filters, f_size=4, normalization=True):
"""Discriminator layer"""
d = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=2, padding='same')(layer_input)
d = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(d)
if normalization:
d = InstanceNormalization()(d)
return d
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
d1 = d_layer(img, self.df, normalization=False)
d2 = d_layer(d1, self.df*2)
d3 = d_layer(d2, self.df*4)
d4 = d_layer(d3, self.df*8)
validity = Conv2D(1, kernel_size=4, strides=1, padding='same')(d4)
return Model(img, validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
# Adversarial loss ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size,) + self.disc_patch)
fake = np.zeros((batch_size,) + self.disc_patch)
for epoch in range(epochs):
for batch_i, (imgs_A, imgs_B) in enumerate(self.data_loader.load_batch(batch_size)):
# ----------------------
# Train Discriminators
# ----------------------
# Translate images to opposite domain
fake_B = self.g_AB.predict(imgs_A)
fake_A = self.g_BA.predict(imgs_B)
# Train the discriminators (original images = real / translated = Fake)
dA_loss_real = self.d_A.train_on_batch(imgs_A, valid)
dA_loss_fake = self.d_A.train_on_batch(fake_A, fake)
dA_loss = 0.5 * np.add(dA_loss_real, dA_loss_fake)
dB_loss_real = self.d_B.train_on_batch(imgs_B, valid)
dB_loss_fake = self.d_B.train_on_batch(fake_B, fake)
dB_loss = 0.5 * np.add(dB_loss_real, dB_loss_fake)
# Total disciminator loss
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(dA_loss, dB_loss)
# ------------------
# Train Generators
# ------------------
# Train the generators
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch([imgs_A, imgs_B], [valid, valid, \
imgs_B, imgs_A, \
imgs_A, imgs_B])
elapsed_time = datetime.datetime.now() - start_time
# Plot the progress
print ("[%d] [%d/%d] time: %s, [d_loss: %f, g_loss: %f]" % (epoch, batch_i,
self.data_loader.n_batches,
elapsed_time,
d_loss[0], g_loss[0]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if batch_i % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch, batch_i)
def sample_images(self, epoch, batch_i):
os.makedirs('images/%s' % self.dataset_name, exist_ok=True)
r, c = 2, 3
imgs_A, imgs_B = self.data_loader.load_data(batch_size=1, is_testing=True)
# Translate images to the other domain
fake_B = self.g_AB.predict(imgs_A)
fake_A = self.g_BA.predict(imgs_B)
# Translate back to original domain
reconstr_A = self.g_BA.predict(fake_B)
reconstr_B = self.g_AB.predict(fake_A)
gen_imgs = np.concatenate([imgs_A, fake_B, reconstr_A, imgs_B, fake_A, reconstr_B])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
titles = ['Original', 'Translated', 'Reconstructed']
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt])
axs[i, j].set_title(titles[j])
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/%s/%d_%d.png" % (self.dataset_name, epoch, batch_i))
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
gan = DiscoGAN()
gan.train(epochs=5, batch_size=1, sample_interval=200)
3.12 DualGAN: Unsupervised Dual Learning for Image-to-Image Translation
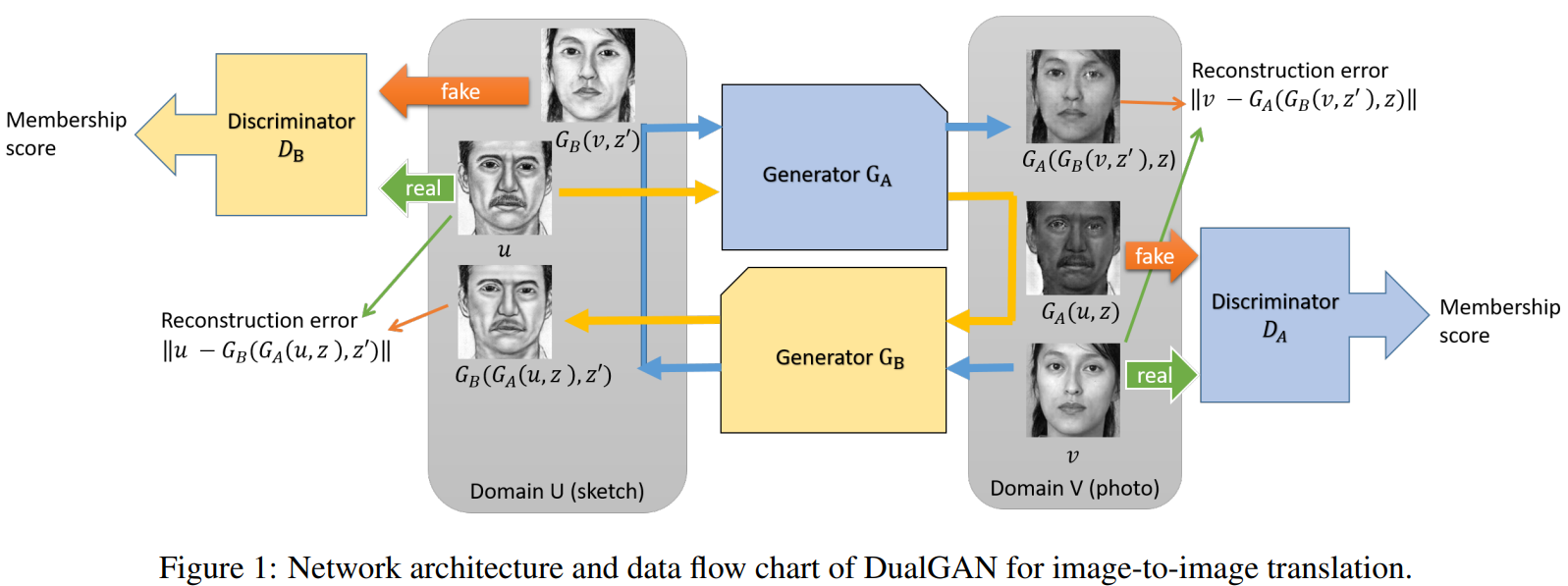
Code and running results
dualgan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
import scipy
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, Concatenate
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import RMSprop, Adam
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import numpy as np
class DUALGAN():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_dim = self.img_rows*self.img_cols
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminators
self.D_A = self.build_discriminator()
self.D_A.compile(loss=self.wasserstein_loss,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
self.D_B = self.build_discriminator()
self.D_B.compile(loss=self.wasserstein_loss,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
#-------------------------
# Construct Computational
# Graph of Generators
#-------------------------
# Build the generators
self.G_AB = self.build_generator()
self.G_BA = self.build_generator()
# For the combined model we will only train the generators
self.D_A.trainable = False
self.D_B.trainable = False
# The generator takes images from their respective domains as inputs
imgs_A = Input(shape=(self.img_dim,))
imgs_B = Input(shape=(self.img_dim,))
# Generators translates the images to the opposite domain
fake_B = self.G_AB(imgs_A)
fake_A = self.G_BA(imgs_B)
# The discriminators determines validity of translated images
valid_A = self.D_A(fake_A)
valid_B = self.D_B(fake_B)
# Generators translate the images back to their original domain
recov_A = self.G_BA(fake_B)
recov_B = self.G_AB(fake_A)
# The combined model (stacked generators and discriminators)
self.combined = Model(inputs=[imgs_A, imgs_B], outputs=[valid_A, valid_B, recov_A, recov_B])
self.combined.compile(loss=[self.wasserstein_loss, self.wasserstein_loss, 'mae', 'mae'],
optimizer=optimizer,
loss_weights=[1, 1, 100, 100])
def build_generator(self):
X = Input(shape=(self.img_dim,))
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(256, input_dim=self.img_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dropout(0.4))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dropout(0.4))
model.add(Dense(1024))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dropout(0.4))
model.add(Dense(self.img_dim, activation='tanh'))
X_translated = model(X)
return Model(X, X_translated)
def build_discriminator(self):
img = Input(shape=(self.img_dim,))
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(512, input_dim=self.img_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(256))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(1))
validity = model(img)
return Model(img, validity)
def sample_generator_input(self, X, batch_size):
# Sample random batch of images from X
idx = np.random.randint(0, X.shape[0], batch_size)
return X[idx]
def wasserstein_loss(self, y_true, y_pred):
return K.mean(y_true * y_pred)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
# Domain A and B (rotated)
X_A = X_train[:int(X_train.shape[0]/2)]
X_B = scipy.ndimage.interpolation.rotate(X_train[int(X_train.shape[0]/2):], 90, axes=(1, 2))
X_A = X_A.reshape(X_A.shape[0], self.img_dim)
X_B = X_B.reshape(X_B.shape[0], self.img_dim)
clip_value = 0.01
n_critic = 4
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = -np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Train the discriminator for n_critic iterations
for _ in range(n_critic):
# ----------------------
# Train Discriminators
# ----------------------
# Sample generator inputs
imgs_A = self.sample_generator_input(X_A, batch_size)
imgs_B = self.sample_generator_input(X_B, batch_size)
# Translate images to their opposite domain
fake_B = self.G_AB.predict(imgs_A)
fake_A = self.G_BA.predict(imgs_B)
# Train the discriminators
D_A_loss_real = self.D_A.train_on_batch(imgs_A, valid)
D_A_loss_fake = self.D_A.train_on_batch(fake_A, fake)
D_B_loss_real = self.D_B.train_on_batch(imgs_B, valid)
D_B_loss_fake = self.D_B.train_on_batch(fake_B, fake)
D_A_loss = 0.5 * np.add(D_A_loss_real, D_A_loss_fake)
D_B_loss = 0.5 * np.add(D_B_loss_real, D_B_loss_fake)
# Clip discriminator weights
for d in [self.D_A, self.D_B]:
for l in d.layers:
weights = l.get_weights()
weights = [np.clip(w, -clip_value, clip_value) for w in weights]
l.set_weights(weights)
# ------------------
# Train Generators
# ------------------
# Train the generators
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch([imgs_A, imgs_B], [valid, valid, imgs_A, imgs_B])
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D1 loss: %f] [D2 loss: %f] [G loss: %f]" \
% (epoch, D_A_loss[0], D_B_loss[0], g_loss[0]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.save_imgs(epoch, X_A, X_B)
def save_imgs(self, epoch, X_A, X_B):
r, c = 4, 4
# Sample generator inputs
imgs_A = self.sample_generator_input(X_A, c)
imgs_B = self.sample_generator_input(X_B, c)
# Images translated to their opposite domain
fake_B = self.G_AB.predict(imgs_A)
fake_A = self.G_BA.predict(imgs_B)
gen_imgs = np.concatenate([imgs_A, fake_B, imgs_B, fake_A])
gen_imgs = gen_imgs.reshape((r, c, self.img_rows, self.img_cols, 1))
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[i, j, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
gan = DUALGAN()
gan.train(epochs=2000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200)
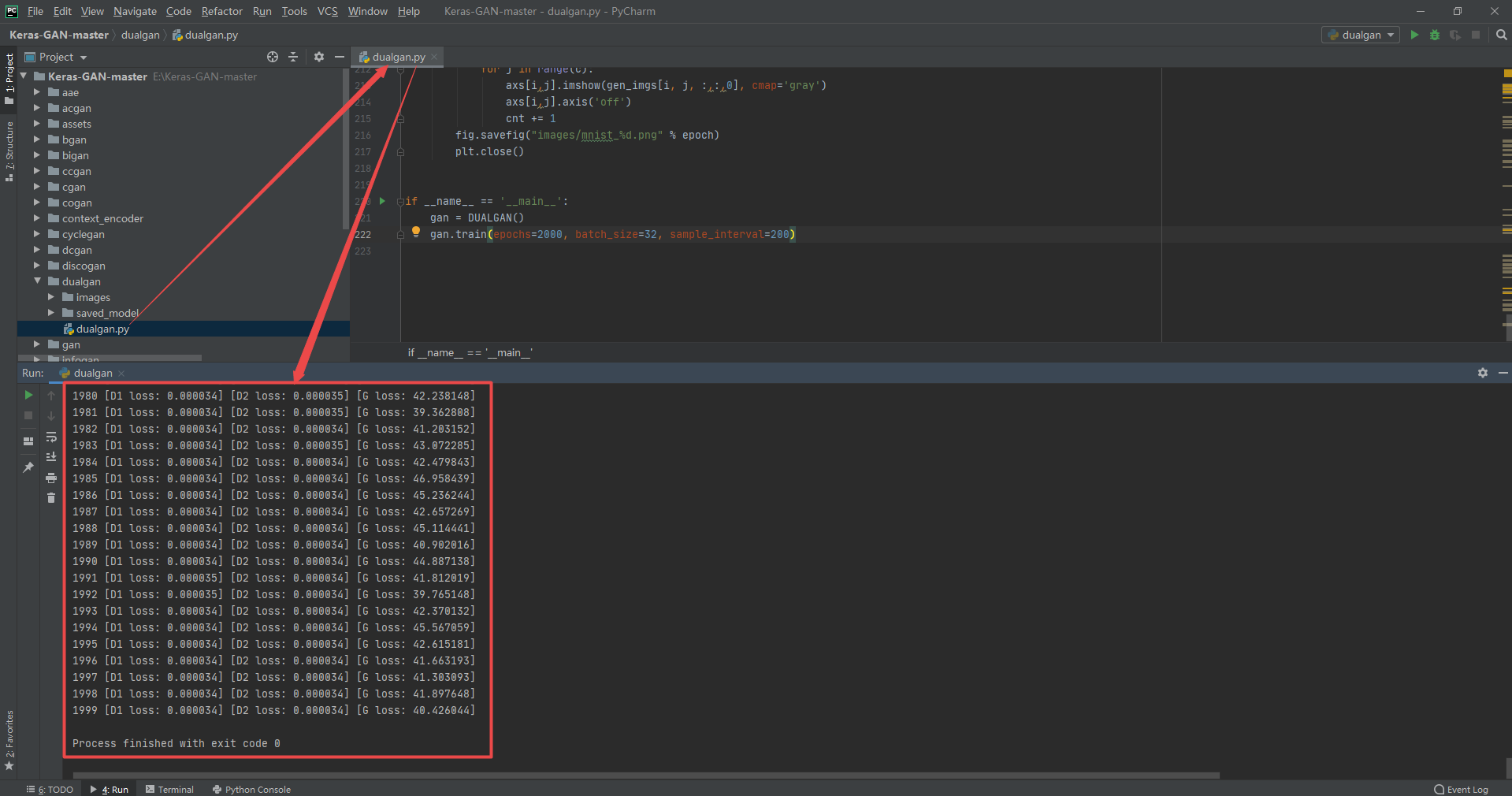
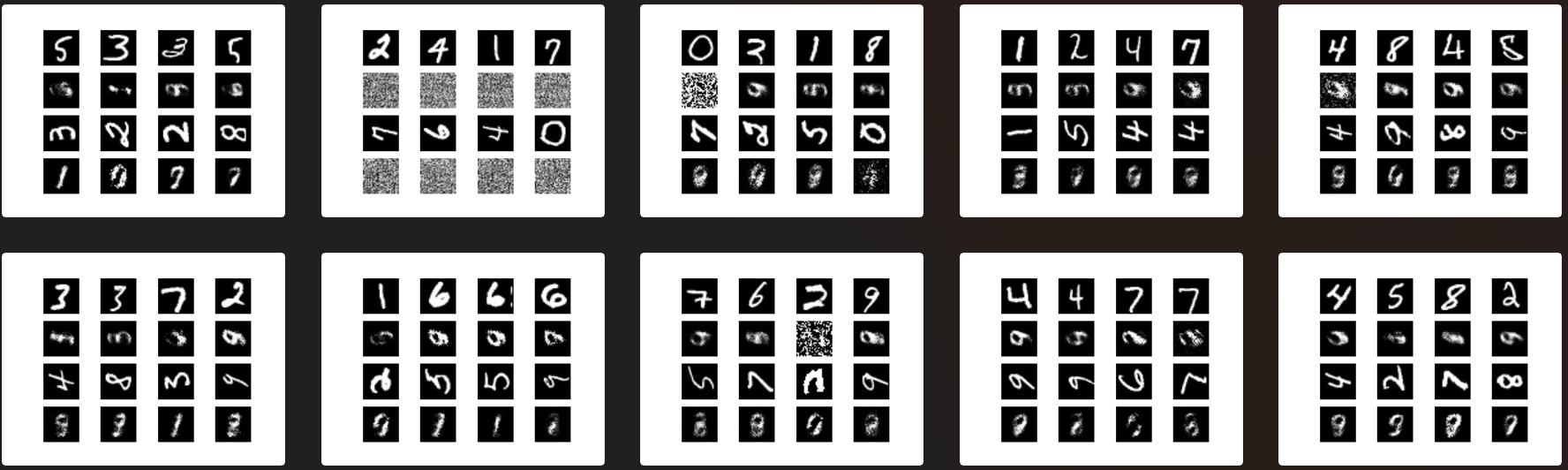
3.13 Generative Adversarial Network

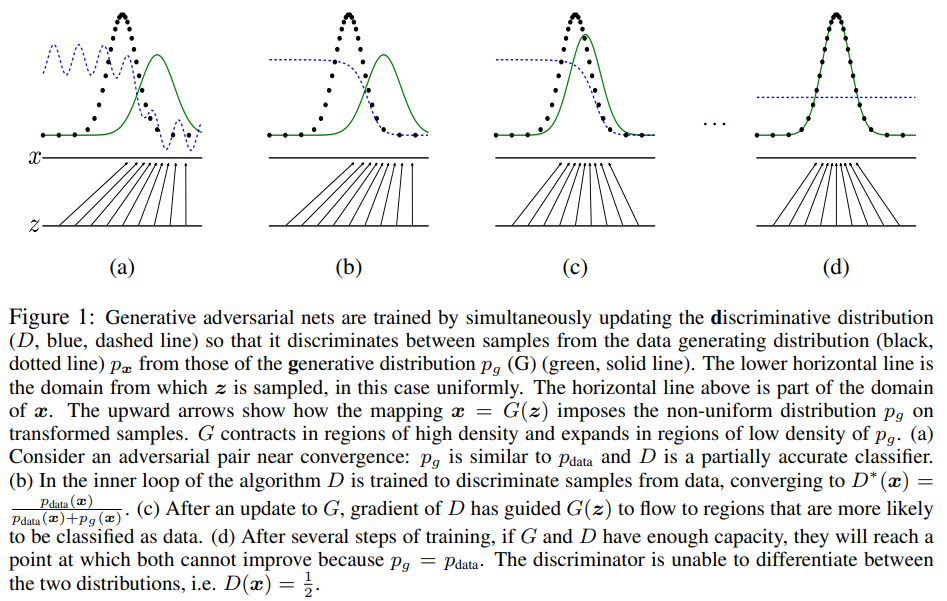
Code and running results
gan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import numpy as np
class GAN():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise as input and generates imgs
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = self.generator(z)
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator takes generated images as input and determines validity
validity = self.discriminator(img)
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
# Trains the generator to fool the discriminator
self.combined = Model(z, validity)
self.combined.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(256, input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(1024))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh'))
model.add(Reshape(self.img_shape))
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = model(noise)
return Model(noise, img)
def build_discriminator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Flatten(input_shape=self.img_shape))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(256))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
validity = model(img)
return Model(img, validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = X_train / 127.5 - 1.
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim))
# Generate a batch of new images
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim))
# Train the generator (to have the discriminator label samples as valid)
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(noise, valid)
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 5, 5
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, self.latent_dim))
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
gan = GAN()
gan.train(epochs=30000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200)
3.14 InfoGAN: Interpretable Representation Learning by Information Maximizing Generative Adversarial Nets
Code and running results
infogan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, multiply, concatenate
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, Embedding, ZeroPadding2D, Lambda
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class INFOGAN():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.num_classes = 10
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 72
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
losses = ['binary_crossentropy', self.mutual_info_loss]
# Build and the discriminator and recognition network
self.discriminator, self.auxilliary = self.build_disk_and_q_net()
self.discriminator.compile(loss=['binary_crossentropy'],
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build and compile the recognition network Q
self.auxilliary.compile(loss=[self.mutual_info_loss],
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise and the target label as input
# and generates the corresponding digit of that label
gen_input = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = self.generator(gen_input)
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator takes generated image as input and determines validity
valid = self.discriminator(img)
# The recognition network produces the label
target_label = self.auxilliary(img)
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
self.combined = Model(gen_input, [valid, target_label])
self.combined.compile(loss=losses,
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(128 * 7 * 7, activation="relu", input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(Reshape((7, 7, 128)))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=3, padding='same'))
model.add(Activation("tanh"))
gen_input = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = model(gen_input)
model.summary()
return Model(gen_input, img)
def build_disk_and_q_net(self):
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Shared layers between discriminator and recognition network
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, input_shape=self.img_shape, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0,1),(0,1))))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(256, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(512, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Flatten())
img_embedding = model(img)
# Discriminator
validity = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(img_embedding)
# Recognition
q_net = Dense(128, activation='relu')(img_embedding)
label = Dense(self.num_classes, activation='softmax')(q_net)
# Return discriminator and recognition network
return Model(img, validity), Model(img, label)
def mutual_info_loss(self, c, c_given_x):
"""The mutual information metric we aim to minimize"""
eps = 1e-8
conditional_entropy = K.mean(- K.sum(K.log(c_given_x + eps) * c, axis=1))
entropy = K.mean(- K.sum(K.log(c + eps) * c, axis=1))
return conditional_entropy + entropy
def sample_generator_input(self, batch_size):
# Generator inputs
sampled_noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, 62))
sampled_labels = np.random.randint(0, self.num_classes, batch_size).reshape(-1, 1)
sampled_labels = to_categorical(sampled_labels, num_classes=self.num_classes)
return sampled_noise, sampled_labels
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, y_train), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
y_train = y_train.reshape(-1, 1)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random half batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
# Sample noise and categorical labels
sampled_noise, sampled_labels = self.sample_generator_input(batch_size)
gen_input = np.concatenate((sampled_noise, sampled_labels), axis=1)
# Generate a half batch of new images
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(gen_input)
# Train on real and generated data
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, fake)
# Avg. loss
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator and Q-network
# ---------------------
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(gen_input, [valid, sampled_labels])
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %.2f, acc.: %.2f%%] [Q loss: %.2f] [G loss: %.2f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss[1], g_loss[2]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 10, 10
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
for i in range(c):
sampled_noise, _ = self.sample_generator_input(c)
label = to_categorical(np.full(fill_value=i, shape=(r,1)), num_classes=self.num_classes)
gen_input = np.concatenate((sampled_noise, label), axis=1)
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(gen_input)
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
for j in range(r):
axs[j,i].imshow(gen_imgs[j,:,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[j,i].axis('off')
fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
def save_model(self):
def save(model, model_name):
model_path = "saved_model/%s.json" % model_name
weights_path = "saved_model/%s_weights.hdf5" % model_name
options = {"file_arch": model_path,
"file_weight": weights_path}
json_string = model.to_json()
open(options['file_arch'], 'w').write(json_string)
model.save_weights(options['file_weight'])
save(self.generator, "generator")
save(self.discriminator, "discriminator")
if __name__ == '__main__':
infogan = INFOGAN()
infogan.train(epochs=1000, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50)
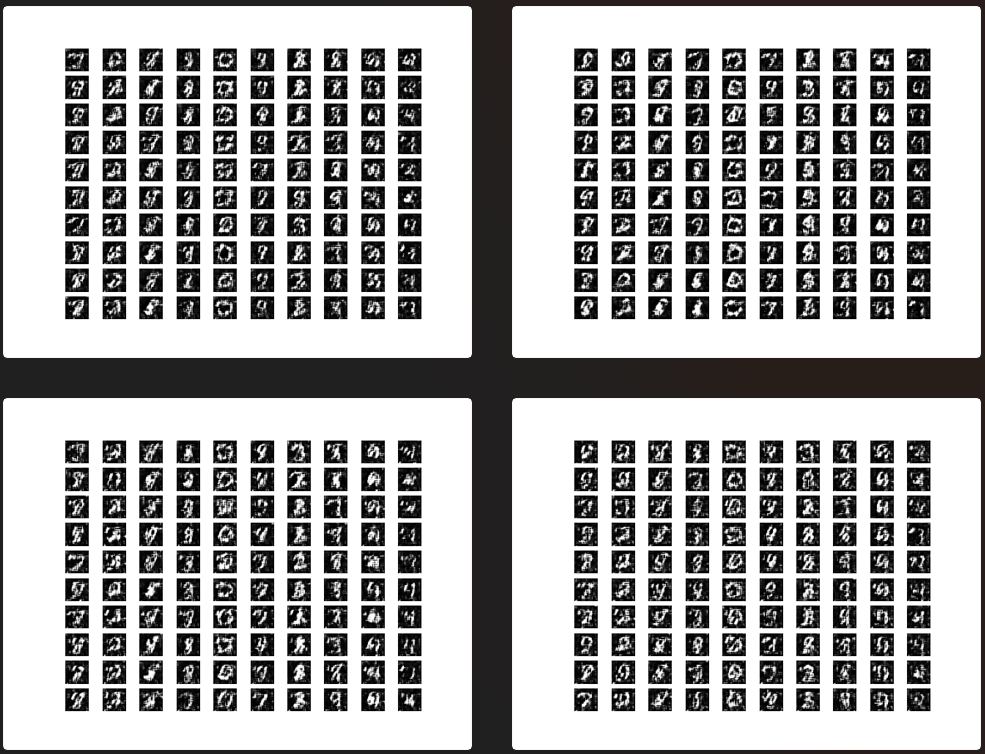
3.15 Least Squares Generative Adversarial Networks

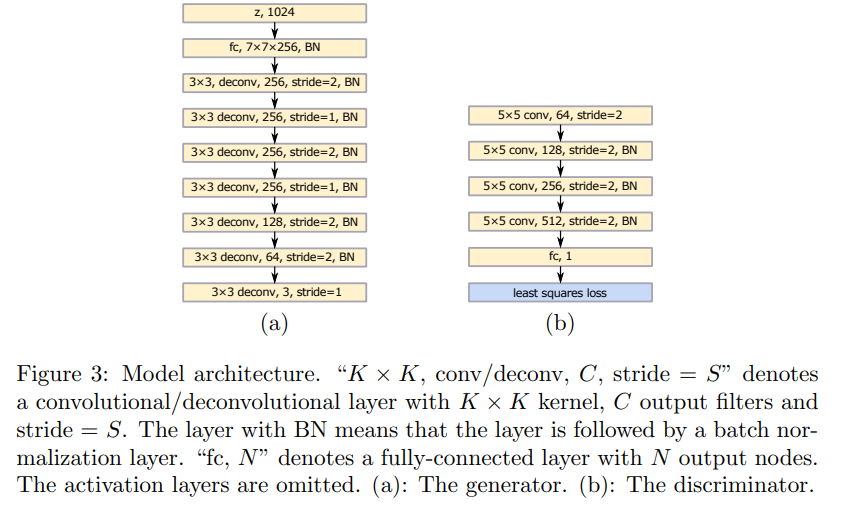
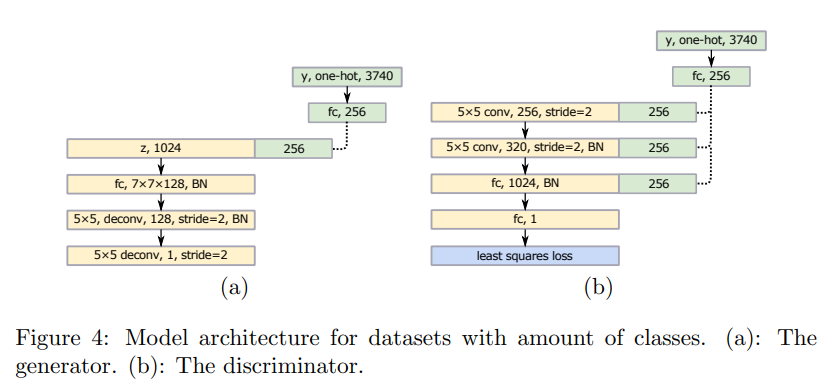
Code and running results
lsgan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import numpy as np
class LSGAN():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss='mse',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise as input and generated imgs
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = self.generator(z)
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The valid takes generated images as input and determines validity
valid = self.discriminator(img)
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
# Trains generator to fool discriminator
self.combined = Model(z, valid)
# (!!!) Optimize w.r.t. MSE loss instead of crossentropy
self.combined.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(256, input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(1024))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh'))
model.add(Reshape(self.img_shape))
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = model(noise)
return Model(noise, img)
def build_discriminator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Flatten(input_shape=self.img_shape))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(256))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
# (!!!) No softmax
model.add(Dense(1))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
validity = model(img)
return Model(img, validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
# Sample noise as generator input
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim))
# Generate a batch of new images
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(noise, valid)
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 5, 5
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, self.latent_dim))
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
gan = LSGAN()
gan.train(epochs=30000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200)
3.16 Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks
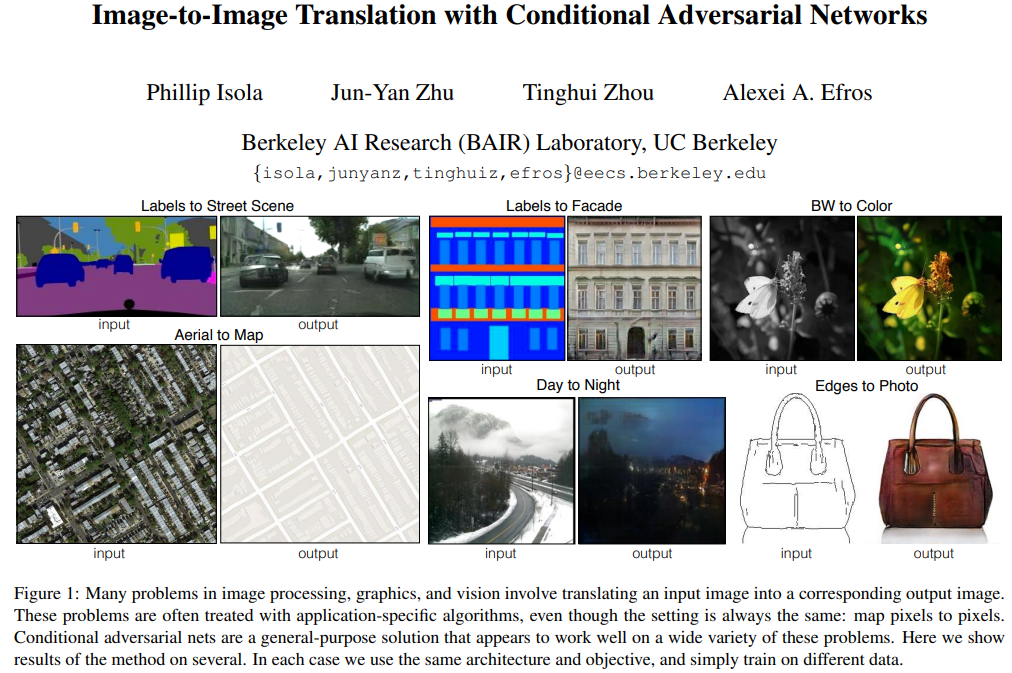
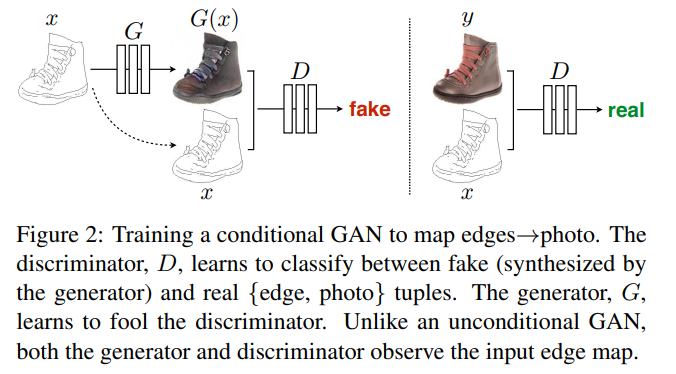
Code and running results

pix2pix.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
import scipy
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from instancenormalization import InstanceNormalization
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, Concatenate
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
from data_loader import DataLoader
import numpy as np
import os
class Pix2Pix():
def __init__(self):
# Input shape
self.img_rows = 256
self.img_cols = 256
self.channels = 3
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
# Configure data loader
self.dataset_name = 'facades'
self.data_loader = DataLoader(dataset_name=self.dataset_name,
img_res=(self.img_rows, self.img_cols))
# Calculate output shape of D (PatchGAN)
patch = int(self.img_rows / 2**4)
self.disc_patch = (patch, patch, 1)
# Number of filters in the first layer of G and D
self.gf = 64
self.df = 64
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss='mse',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
#-------------------------
# Construct Computational
# Graph of Generator
#-------------------------
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# Input images and their conditioning images
img_A = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
img_B = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# By conditioning on B generate a fake version of A
fake_A = self.generator(img_B)
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# Discriminators determines validity of translated images / condition pairs
valid = self.discriminator([fake_A, img_B])
self.combined = Model(inputs=[img_A, img_B], outputs=[valid, fake_A])
self.combined.compile(loss=['mse', 'mae'],
loss_weights=[1, 100],
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
"""U-Net Generator"""
def conv2d(layer_input, filters, f_size=4, bn=True):
"""Layers used during downsampling"""
d = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=2, padding='same')(layer_input)
d = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(d)
if bn:
d = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(d)
return d
def deconv2d(layer_input, skip_input, filters, f_size=4, dropout_rate=0):
"""Layers used during upsampling"""
u = UpSampling2D(size=2)(layer_input)
u = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=1, padding='same', activation='relu')(u)
if dropout_rate:
u = Dropout(dropout_rate)(u)
u = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(u)
u = Concatenate()([u, skip_input])
return u
# Image input
d0 = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Downsampling
d1 = conv2d(d0, self.gf, bn=False)
d2 = conv2d(d1, self.gf*2)
d3 = conv2d(d2, self.gf*4)
d4 = conv2d(d3, self.gf*8)
d5 = conv2d(d4, self.gf*8)
d6 = conv2d(d5, self.gf*8)
d7 = conv2d(d6, self.gf*8)
# Upsampling
u1 = deconv2d(d7, d6, self.gf*8)
u2 = deconv2d(u1, d5, self.gf*8)
u3 = deconv2d(u2, d4, self.gf*8)
u4 = deconv2d(u3, d3, self.gf*4)
u5 = deconv2d(u4, d2, self.gf*2)
u6 = deconv2d(u5, d1, self.gf)
u7 = UpSampling2D(size=2)(u6)
output_img = Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=4, strides=1, padding='same', activation='tanh')(u7)
return Model(d0, output_img)
def build_discriminator(self):
def d_layer(layer_input, filters, f_size=4, bn=True):
"""Discriminator layer"""
d = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=2, padding='same')(layer_input)
d = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(d)
if bn:
d = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(d)
return d
img_A = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
img_B = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Concatenate image and conditioning image by channels to produce input
combined_imgs = Concatenate(axis=-1)([img_A, img_B])
d1 = d_layer(combined_imgs, self.df, bn=False)
d2 = d_layer(d1, self.df*2)
d3 = d_layer(d2, self.df*4)
d4 = d_layer(d3, self.df*8)
validity = Conv2D(1, kernel_size=4, strides=1, padding='same')(d4)
return Model([img_A, img_B], validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=1, sample_interval=50):
start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
# Adversarial loss ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size,) + self.disc_patch)
fake = np.zeros((batch_size,) + self.disc_patch)
for epoch in range(epochs):
for batch_i, (imgs_A, imgs_B) in enumerate(self.data_loader.load_batch(batch_size)):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Condition on B and generate a translated version
fake_A = self.generator.predict(imgs_B)
# Train the discriminators (original images = real / generated = Fake)
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch([imgs_A, imgs_B], valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch([fake_A, imgs_B], fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# -----------------
# Train Generator
# -----------------
# Train the generators
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch([imgs_A, imgs_B], [valid, imgs_A])
elapsed_time = datetime.datetime.now() - start_time
# Plot the progress
print ("[Epoch %d/%d] [Batch %d/%d] [D loss: %f, acc: %3d%%] [G loss: %f] time: %s" % (epoch, epochs,
batch_i, self.data_loader.n_batches,
d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1],
g_loss[0],
elapsed_time))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if batch_i % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch, batch_i)
def sample_images(self, epoch, batch_i):
os.makedirs('images/%s' % self.dataset_name, exist_ok=True)
r, c = 3, 3
imgs_A, imgs_B = self.data_loader.load_data(batch_size=3, is_testing=True)
fake_A = self.generator.predict(imgs_B)
gen_imgs = np.concatenate([imgs_B, fake_A, imgs_A])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
titles = ['Condition', 'Generated', 'Original']
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt])
axs[i, j].set_title(titles[i])
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/%s/%d_%d.png" % (self.dataset_name, epoch, batch_i))
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
gan = Pix2Pix()
gan.train(epochs=200, batch_size=1, sample_interval=200)
3.17 Unsupervised Pixel-Level Domain Adaptation with Generative Adversarial Networks

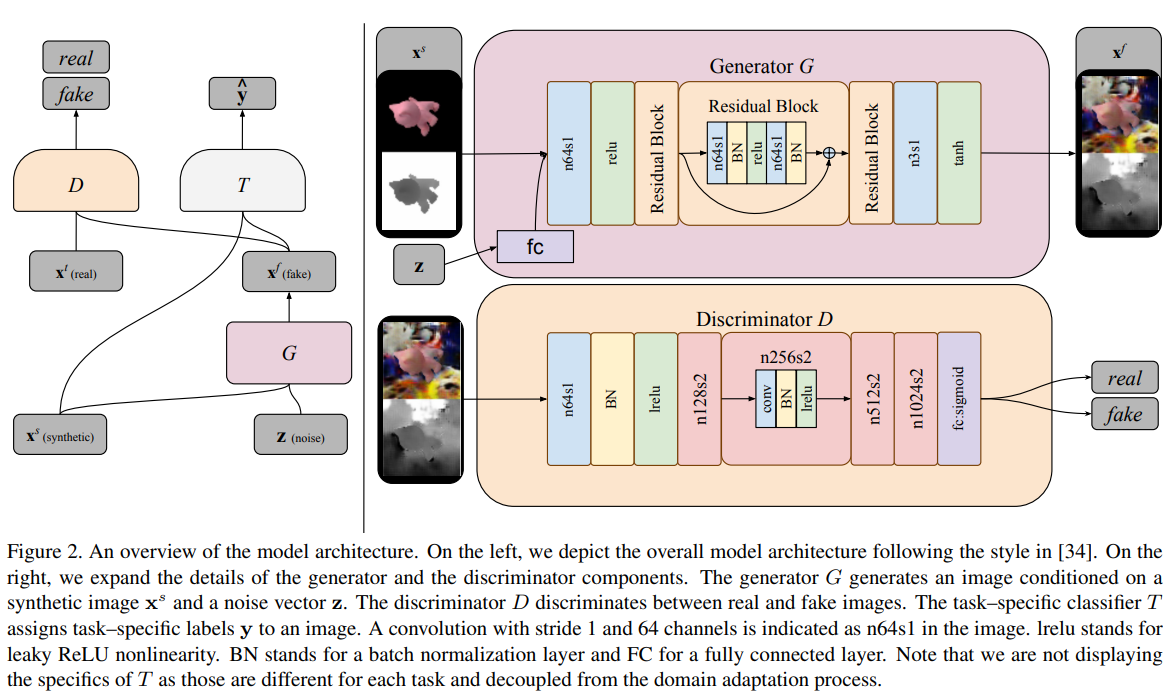
Code and running results
keras_mnistm.pkl.gz Download

instanceNormalization.py
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Layer, InputSpec
from tensorflow.keras import initializers, regularizers, constraints
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
class InstanceNormalization(Layer):
"""Instance normalization layer.
Normalize the activations of the previous layer at each step,
i.e. applies a transformation that maintains the mean activation
close to 0 and the activation standard deviation close to 1.
# Arguments
axis: Integer, the axis that should be normalized
(typically the features axis).
For instance, after a `Conv2D` layer with
`data_format="channels_first"`,
set `axis=1` in `InstanceNormalization`.
Setting `axis=None` will normalize all values in each
instance of the batch.
Axis 0 is the batch dimension. `axis` cannot be set to 0 to avoid errors.
epsilon: Small float added to variance to avoid dividing by zero.
center: If True, add offset of `beta` to normalized tensor.
If False, `beta` is ignored.
scale: If True, multiply by `gamma`.
If False, `gamma` is not used.
When the next layer is linear (also e.g. `nn.relu`),
this can be disabled since the scaling
will be done by the next layer.
beta_initializer: Initializer for the beta weight.
gamma_initializer: Initializer for the gamma weight.
beta_regularizer: Optional regularizer for the beta weight.
gamma_regularizer: Optional regularizer for the gamma weight.
beta_constraint: Optional constraint for the beta weight.
gamma_constraint: Optional constraint for the gamma weight.
# Input shape
Arbitrary. Use the keyword argument `input_shape`
(tuple of integers, does not include the samples axis)
when using this layer as the first layer in a Sequential model.
# Output shape
Same shape as input.
# References
- [Layer Normalization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450)
- [Instance Normalization: The Missing Ingredient for Fast Stylization](
https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.08022)
"""
def __init__(self,
axis=None,
epsilon=1e-3,
center=True,
scale=True,
beta_initializer='zeros',
gamma_initializer='ones',
beta_regularizer=None,
gamma_regularizer=None,
beta_constraint=None,
gamma_constraint=None,
**kwargs):
super(InstanceNormalization, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.supports_masking = True
self.axis = axis
self.epsilon = epsilon
self.center = center
self.scale = scale
self.beta_initializer = initializers.get(beta_initializer)
self.gamma_initializer = initializers.get(gamma_initializer)
self.beta_regularizer = regularizers.get(beta_regularizer)
self.gamma_regularizer = regularizers.get(gamma_regularizer)
self.beta_constraint = constraints.get(beta_constraint)
self.gamma_constraint = constraints.get(gamma_constraint)
def build(self, input_shape):
ndim = len(input_shape)
if self.axis == 0:
raise ValueError('Axis cannot be zero')
if (self.axis is not None) and (ndim == 2):
raise ValueError('Cannot specify axis for rank 1 tensor')
self.input_spec = InputSpec(ndim=ndim)
if self.axis is None:
shape = (1,)
else:
shape = (input_shape[self.axis],)
if self.scale:
self.gamma = self.add_weight(shape=shape,
name='gamma',
initializer=self.gamma_initializer,
regularizer=self.gamma_regularizer,
constraint=self.gamma_constraint)
else:
self.gamma = None
if self.center:
self.beta = self.add_weight(shape=shape,
name='beta',
initializer=self.beta_initializer,
regularizer=self.beta_regularizer,
constraint=self.beta_constraint)
else:
self.beta = None
self.built = True
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
input_shape = K.int_shape(inputs)
reduction_axes = list(range(0, len(input_shape)))
if self.axis is not None:
del reduction_axes[self.axis]
del reduction_axes[0]
mean = K.mean(inputs, reduction_axes, keepdims=True)
stddev = K.std(inputs, reduction_axes, keepdims=True) + self.epsilon
normed = (inputs - mean) / stddev
broadcast_shape = [1] * len(input_shape)
if self.axis is not None:
broadcast_shape[self.axis] = input_shape[self.axis]
if self.scale:
broadcast_gamma = K.reshape(self.gamma, broadcast_shape)
normed = normed * broadcast_gamma
if self.center:
broadcast_beta = K.reshape(self.beta, broadcast_shape)
normed = normed + broadcast_beta
return normed
def get_config(self):
config = {
'axis': self.axis,
'epsilon': self.epsilon,
'center': self.center,
'scale': self.scale,
'beta_initializer': initializers.serialize(self.beta_initializer),
'gamma_initializer': initializers.serialize(self.gamma_initializer),
'beta_regularizer': regularizers.serialize(self.beta_regularizer),
'gamma_regularizer': regularizers.serialize(self.gamma_regularizer),
'beta_constraint': constraints.serialize(self.beta_constraint),
'gamma_constraint': constraints.serialize(self.gamma_constraint)
}
base_config = super(InstanceNormalization, self).get_config()
return dict(list(base_config.items()) + list(config.items()))
data_loader.py
import scipy
from glob import glob
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from scipy.misc import imresize
import pickle
import os
import urllib
import gzip
class DataLoader():
"""Loads images from MNIST (domain A) and MNIST-M (domain B)"""
def __init__(self, img_res=(128, 128)):
self.img_res = img_res
self.mnistm_url = 'https://hub.fastgit.xyz/VanushVaswani/keras_mnistm/releases/download/1.0/keras_mnistm.pkl.gz'
self.setup_mnist(img_res)
self.setup_mnistm(img_res)
def normalize(self, images):
return images.astype(np.float32) / 127.5 - 1.
def setup_mnist(self, img_res):
print ("Setting up MNIST...")
if not os.path.exists('datasets/mnist_x.npy'):
# Load the dataset
(mnist_X, mnist_y), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Normalize and rescale images
mnist_X = self.normalize(mnist_X)
mnist_X = np.array([imresize(x, img_res) for x in mnist_X])
mnist_X = np.expand_dims(mnist_X, axis=-1)
mnist_X = np.repeat(mnist_X, 3, axis=-1)
self.mnist_X, self.mnist_y = mnist_X, mnist_y
# Save formatted images
np.save('datasets/mnist_x.npy', self.mnist_X)
np.save('datasets/mnist_y.npy', self.mnist_y)
else:
self.mnist_X = np.load('datasets/mnist_x.npy')
self.mnist_y = np.load('datasets/mnist_y.npy')
print ("+ Done.")
def setup_mnistm(self, img_res):
print ("Setting up MNIST-M...")
if not os.path.exists('datasets/mnistm_x.npy'):
# Download the MNIST-M pkl file
filepath = 'datasets/keras_mnistm.pkl.gz'
if not os.path.exists(filepath.replace('.gz', '')):
print('+ Downloading ' + self.mnistm_url)
data = urllib.request.urlopen(self.mnistm_url)
with open(filepath, 'wb') as f:
f.write(data.read())
with open(filepath.replace('.gz', ''), 'wb') as out_f, \
gzip.GzipFile(filepath) as zip_f:
out_f.write(zip_f.read())
os.unlink(filepath)
# load MNIST-M images from pkl file
with open('datasets/keras_mnistm.pkl', "rb") as f:
data = pickle.load(f, encoding='bytes')
# Normalize and rescale images
mnistm_X = np.array(data[b'train'])
mnistm_X = self.normalize(mnistm_X)
mnistm_X = np.array([imresize(x, img_res) for x in mnistm_X])
self.mnistm_X, self.mnistm_y = mnistm_X, self.mnist_y.copy()
# Save formatted images
np.save('datasets/mnistm_x.npy', self.mnistm_X)
np.save('datasets/mnistm_y.npy', self.mnistm_y)
else:
self.mnistm_X = np.load('datasets/mnistm_x.npy')
self.mnistm_y = np.load('datasets/mnistm_y.npy')
print ("+ Done.")
def load_data(self, domain, batch_size=1):
X = self.mnist_X if domain == 'A' else self.mnistm_X
y = self.mnist_y if domain == 'A' else self.mnistm_y
idx = np.random.choice(list(range(len(X))), size=batch_size)
return X[idx], y[idx]
pixelda.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
import scipy
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from instancenormalization import InstanceNormalization
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, Concatenate
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D, Add
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
import datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
from data_loader import DataLoader
import numpy as np
import os
class PixelDA():
def __init__(self):
# Input shape
self.img_rows = 32
self.img_cols = 32
self.channels = 3
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.num_classes = 10
# Configure MNIST and MNIST-M data loader
self.data_loader = DataLoader(img_res=(self.img_rows, self.img_cols))
# Loss weights
lambda_adv = 10
lambda_clf = 1
# Calculate output shape of D (PatchGAN)
patch = int(self.img_rows / 2**4)
self.disc_patch = (patch, patch, 1)
# Number of residual blocks in the generator
self.residual_blocks = 6
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Number of filters in first layer of discriminator and classifier
self.df = 64
self.cf = 64
# Build and compile the discriminators
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss='mse',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# Build the task (classification) network
self.clf = self.build_classifier()
# Input images from both domains
img_A = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
img_B = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Translate images from domain A to domain B
fake_B = self.generator(img_A)
# Classify the translated image
class_pred = self.clf(fake_B)
# For the combined model we will only train the generator and classifier
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# Discriminator determines validity of translated images
valid = self.discriminator(fake_B)
self.combined = Model(img_A, [valid, class_pred])
self.combined.compile(loss=['mse', 'categorical_crossentropy'],
loss_weights=[lambda_adv, lambda_clf],
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
def build_generator(self):
"""Resnet Generator"""
def residual_block(layer_input):
"""Residual block described in paper"""
d = Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding='same')(layer_input)
d = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(d)
d = Activation('relu')(d)
d = Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding='same')(d)
d = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(d)
d = Add()([d, layer_input])
return d
# Image input
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
l1 = Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='relu')(img)
# Propogate signal through residual blocks
r = residual_block(l1)
for _ in range(self.residual_blocks - 1):
r = residual_block(r)
output_img = Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='tanh')(r)
return Model(img, output_img)
def build_discriminator(self):
def d_layer(layer_input, filters, f_size=4, normalization=True):
"""Discriminator layer"""
d = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=2, padding='same')(layer_input)
d = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(d)
if normalization:
d = InstanceNormalization()(d)
return d
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
d1 = d_layer(img, self.df, normalization=False)
d2 = d_layer(d1, self.df*2)
d3 = d_layer(d2, self.df*4)
d4 = d_layer(d3, self.df*8)
validity = Conv2D(1, kernel_size=4, strides=1, padding='same')(d4)
return Model(img, validity)
def build_classifier(self):
def clf_layer(layer_input, filters, f_size=4, normalization=True):
"""Classifier layer"""
d = Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=f_size, strides=2, padding='same')(layer_input)
d = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(d)
if normalization:
d = InstanceNormalization()(d)
return d
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
c1 = clf_layer(img, self.cf, normalization=False)
c2 = clf_layer(c1, self.cf*2)
c3 = clf_layer(c2, self.cf*4)
c4 = clf_layer(c3, self.cf*8)
c5 = clf_layer(c4, self.cf*8)
class_pred = Dense(self.num_classes, activation='softmax')(Flatten()(c5))
return Model(img, class_pred)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
half_batch = int(batch_size / 2)
# Classification accuracy on 100 last batches of domain B
test_accs = []
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, *self.disc_patch))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, *self.disc_patch))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
imgs_A, labels_A = self.data_loader.load_data(domain="A", batch_size=batch_size)
imgs_B, labels_B = self.data_loader.load_data(domain="B", batch_size=batch_size)
# Translate images from domain A to domain B
fake_B = self.generator.predict(imgs_A)
# Train the discriminators (original images = real / translated = Fake)
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs_B, valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(fake_B, fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# --------------------------------
# Train Generator and Classifier
# --------------------------------
# One-hot encoding of labels
labels_A = to_categorical(labels_A, num_classes=self.num_classes)
# Train the generator and classifier
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(imgs_A, [valid, labels_A])
#-----------------------
# Evaluation (domain B)
#-----------------------
pred_B = self.clf.predict(imgs_B)
test_acc = np.mean(np.argmax(pred_B, axis=1) == labels_B)
# Add accuracy to list of last 100 accuracy measurements
test_accs.append(test_acc)
if len(test_accs) > 100:
test_accs.pop(0)
# Plot the progress
print ( "%d : [D - loss: %.5f, acc: %3d%%], [G - loss: %.5f], [clf - loss: %.5f, acc: %3d%%, test_acc: %3d%% (%3d%%)]" % \
(epoch, d_loss[0], 100*float(d_loss[1]),
g_loss[1], g_loss[2], 100*float(g_loss[-1]),
100*float(test_acc), 100*float(np.mean(test_accs))))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 2, 5
imgs_A, _ = self.data_loader.load_data(domain="A", batch_size=5)
# Translate images to the other domain
fake_B = self.generator.predict(imgs_A)
gen_imgs = np.concatenate([imgs_A, fake_B])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
#titles = ['Original', 'Translated']
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt])
#axs[i, j].set_title(titles[i])
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % (epoch))
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
gan = PixelDA()
gan.train(epochs=3000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=500)
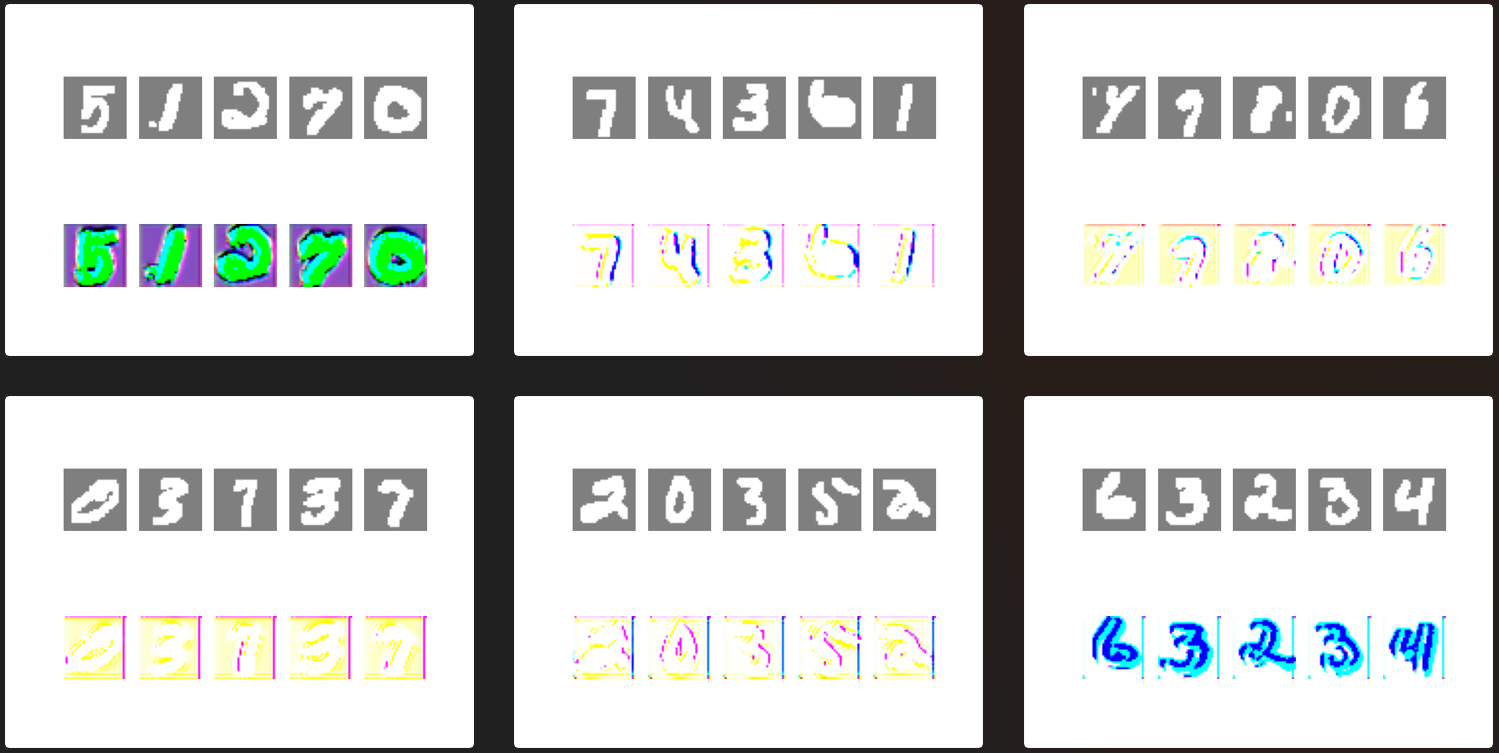
test.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
import scipy
import datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
from data_loader import DataLoader
import numpy as np
import os
# Configure MNIST and MNIST-M data loader
data_loader = DataLoader(img_res=(32, 32))
mnist, _ = data_loader.load_data(domain="A", batch_size=25)
mnistm, _ = data_loader.load_data(domain="B", batch_size=25)
r, c = 5, 5
for img_i, imgs in enumerate([mnist, mnistm]):
#titles = ['Original', 'Translated']
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(imgs[cnt])
#axs[i, j].set_title(titles[i])
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("%d.png" % (img_i))
plt.close()
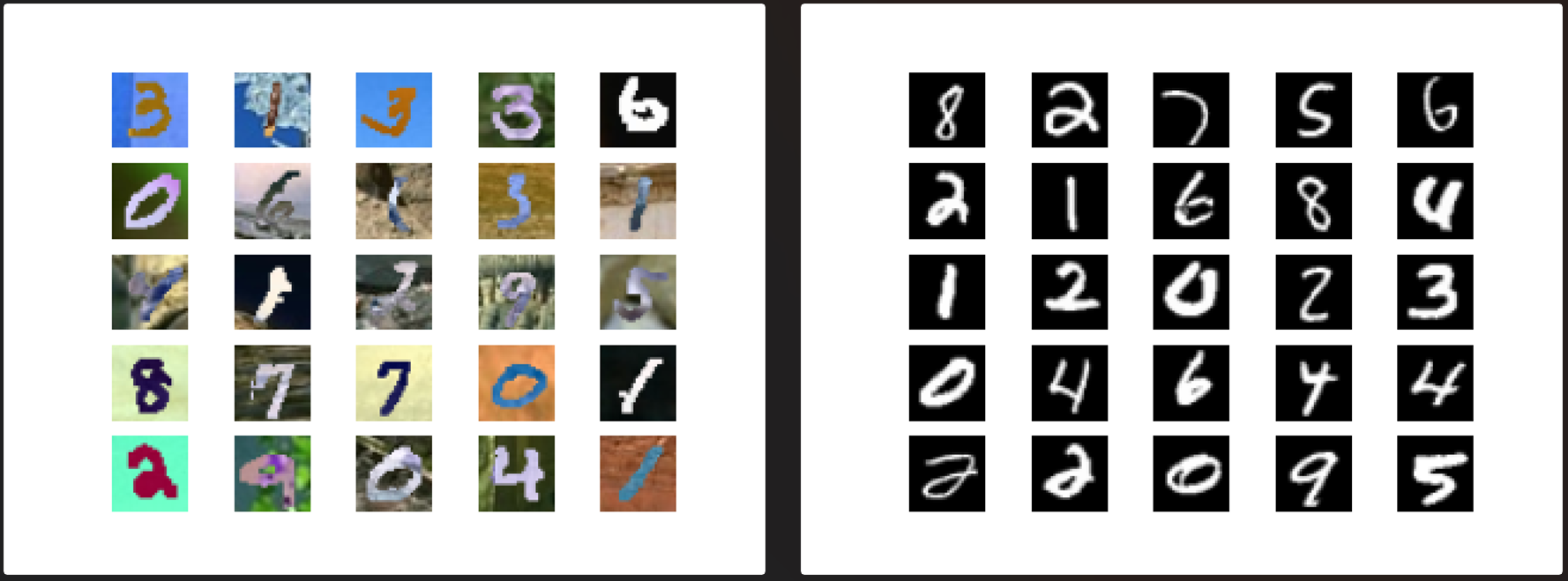
3.18 Wasserstein GAN

Code and running results
wgan.py
from __future__ import print_function, division
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.layers import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import RMSprop
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import numpy as np
class WGAN():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 100
# Following parameter and optimizer set as recommended in paper
self.n_critic = 5
self.clip_value = 0.01
optimizer = RMSprop(lr=0.00005)
# Build and compile the critic
self.critic = self.build_critic()
self.critic.compile(loss=self.wasserstein_loss,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise as input and generated imgs
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = self.generator(z)
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.critic.trainable = False
# The critic takes generated images as input and determines validity
valid = self.critic(img)
# The combined model (stacked generator and critic)
self.combined = Model(z, valid)
self.combined.compile(loss=self.wasserstein_loss,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
def wasserstein_loss(self, y_true, y_pred):
return K.mean(y_true * y_pred)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(128 * 7 * 7, activation="relu", input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(Reshape((7, 7, 128)))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=4, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=4, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=4, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation("tanh"))
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = model(noise)
return Model(noise, img)
def build_critic(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(16, kernel_size=3, strides=2, input_shape=self.img_shape, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0,1),(0,1))))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(1))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
validity = model(img)
return Model(img, validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = -np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
for _ in range(self.n_critic):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
# Sample noise as generator input
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim))
# Generate a batch of new images
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Train the critic
d_loss_real = self.critic.train_on_batch(imgs, valid)
d_loss_fake = self.critic.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_fake, d_loss_real)
# Clip critic weights
for l in self.critic.layers:
weights = l.get_weights()
weights = [np.clip(w, -self.clip_value, self.clip_value) for w in weights]
l.set_weights(weights)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(noise, valid)
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, 1 - d_loss[0], 1 - g_loss[0]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 5, 5
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, self.latent_dim))
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
wgan = WGAN()
wgan.train(epochs=1000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=50)
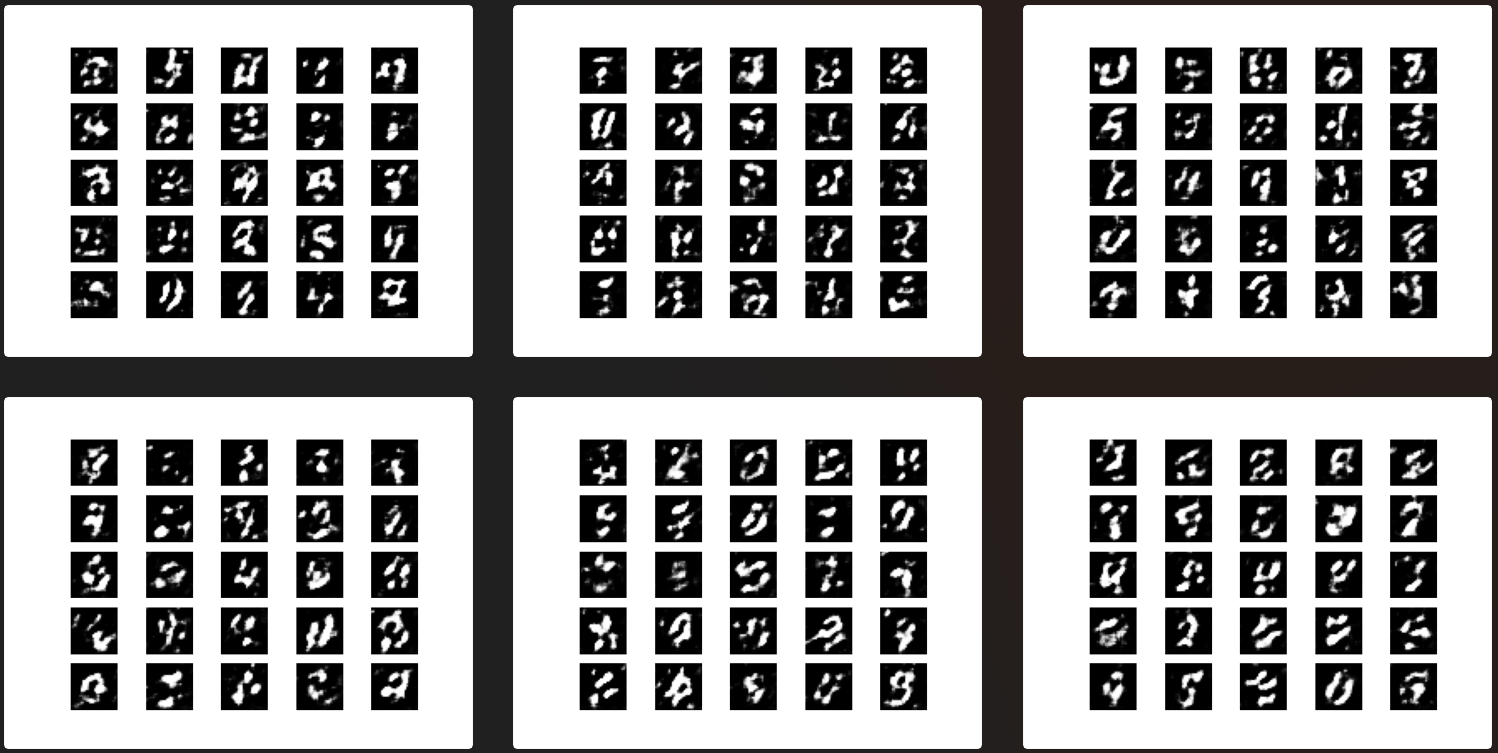
4. Application Summary
In general, the generation confrontation network GAN shows great potential and applications in style migration, animation generation, image super-resolution reconstruction, image restoration, target detection, face synthesis and so on. Scholars have made many improvements and improvements, Keras,TensorFlow and PyTorch There are many GAN sample codes on the official website. Researchers, developers and learning enthusiasts can study, test and study, and feel the charm of deep learning. It has to be said that the model parameters obtained on the basis of a large number of data set training, the ability of deep network to capture deep abstract features is really incredible, and the effect is amazing to a certain extent.