1, HTML+CSS
2, JavaScript
3, JQuery, BootStrap framework
4, XML
5, Web overview and Tomcat server
5.1 preparation before using tomcat
- Install and configure jdk
- Download and unzip Tomcat
- Configure environment variables
Variable name: CATALINA_HOME
Variable value: path just installed
5.2 directory structure of Tomcat
| Directory name | effect |
|---|---|
| bin | Executable program specially used to store Tomcat server |
| conf | Store the configuration file of Tomcat |
| lib | jar package for storing Tomcat |
| logs | Store the log output by Tomcat server during operation |
| temp | Store temporary data generated by Tomcat runtime |
| webapps | Store the deployed Web project |
| work | Tomcat's working time directory |
5.3 starting and shutting down Tomcat server
Start Tomcat server
-
Find the startup. In bin under Tomcat directory DAT, double-click to start.
-
Open the command line, cd to bin, and the catalina run command
Shut down Tomcat server
-
Close the command window
-
Find the shutdown. Under bin Bat execution
-
Put the Tomcat service window on the current page, ctrl+c
Test Tomcat
-
http://locathost:8080
-
http://127.0.0.1:8080
-
http: / / real IP: 8080
5.4 other settings of Tomcat
-
Modify port number
Find the conf directory under the Tomcat directory and find the server XML modify port number

-
Configure host name

-
Deploy web project
hold Web Copy project directory to Tomcat Directory webapps in
-
The difference between the way of hand holding and accessing at http:ip port number / project name
The file: / / protocol is used
Enter http: / / in the browser using the HTTP protocolWhen we enter the access address in the browser address bar and there is no project name, the default access is the root project
When we enter the access address in the browser address bar and there is no resource name, the index file is accessed by default
Principles of website access
1. Enter the domain name and press enter
2. Is there a domain name mapping under the local c:/windows/System32/drivers/Etc/Hosts configuration file
Return the corresponding ip address
Did not go to the dns server to find it and put it back
5.5 Web overview
-
What is java web?
JavaWeb Is dynamic Web Resource development technology, All pass Java General name of programs written in language that can be accessed through browser, be called JavaWeb JavaWeb It is developed based on request and response -
What is a request?
request(Request)It refers to that the client sends data to the server.
-
What is response?
response(Response)It refers to the data returned by the server to the client.
-
The connection between the two?
When there is a request, there is a response!
-
Classification of Web resources
Web resources can be divided into static resources and dynamic resources according to the implementation technology and presentation effect
Static resources: html css js txt MP4 jpg
Dynamic resources: jsp page Servlet program -
Common Web servers
Tomcat jboss GlassFish Resin WebLogic.....
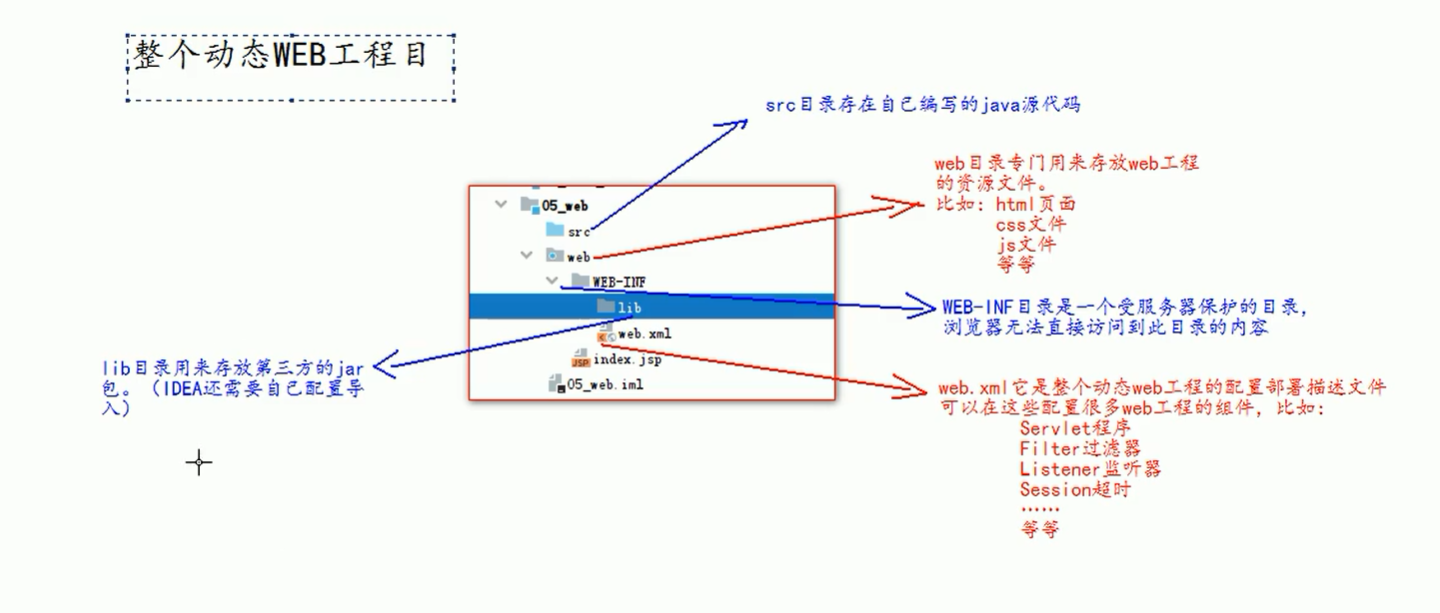
5.6 dynamic Web project directory
6, Servlet program
6.1 introduction to Servlet
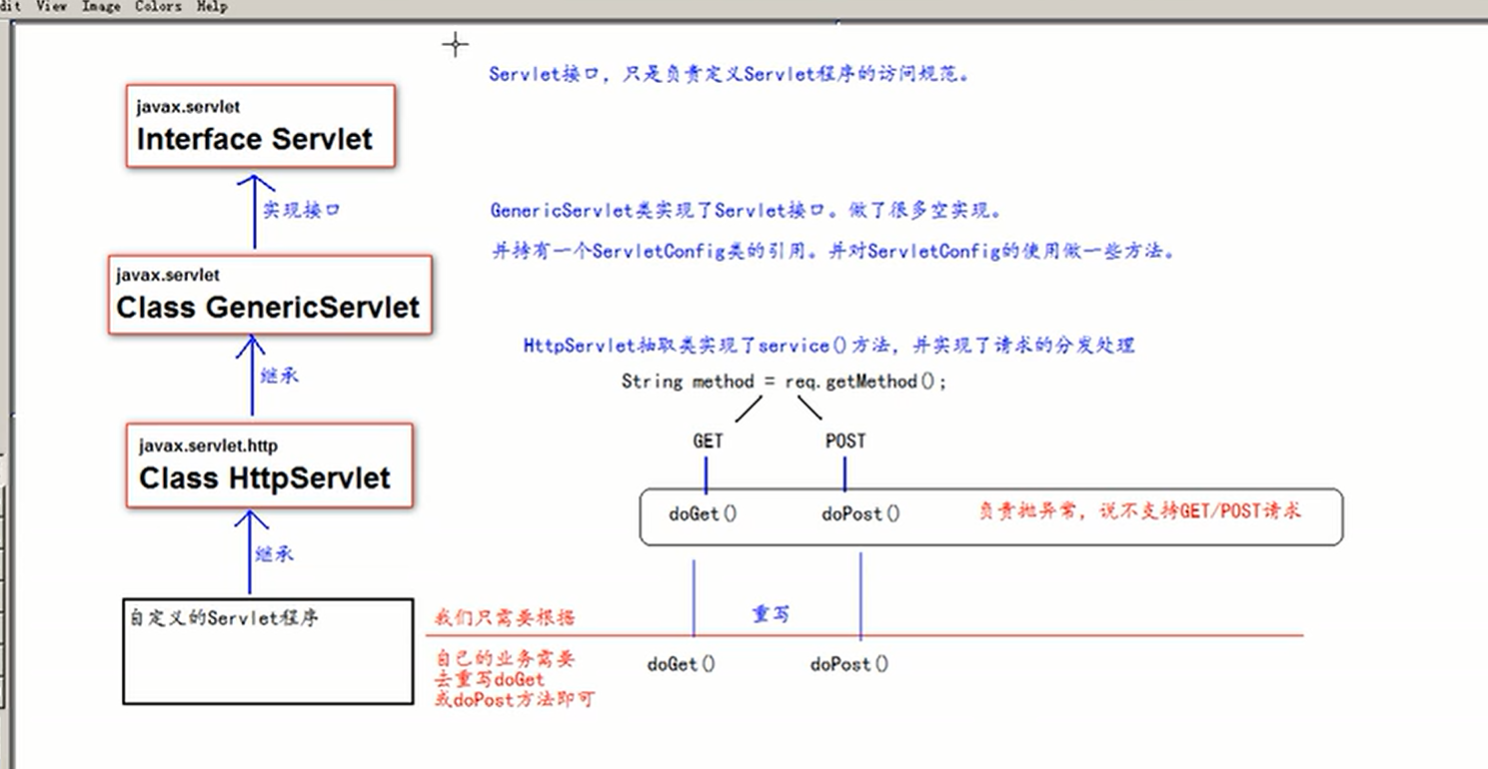
- Servlet is one of the specifications of Java EE, and the specification is the interface.
- Servlet is one of the three components of Java Web. The three components are: servlet program, listener, listener and filter.
- Servlet is a java applet running on the server side. It can receive requests from the client and respond to data.
6.2 implementation of Servlet
-
Method 1: implement Servlet interface
1. Write class implementation Servlet Interface 2. realization Service method, Process requests and respond to data 3. stay Web.xml Medium configuration Servlet Access address of the program
-
Method 2: inherit HttpServlet
1. Write class inheritance httpServlet 2. rewrite doGet doPost Method( Service Method is distributed) note: If rewritten init Method needs to be added to the first line super.init(config); 3. reach web.xml Medium configuration Servlet Access address for
Web.xml execution process 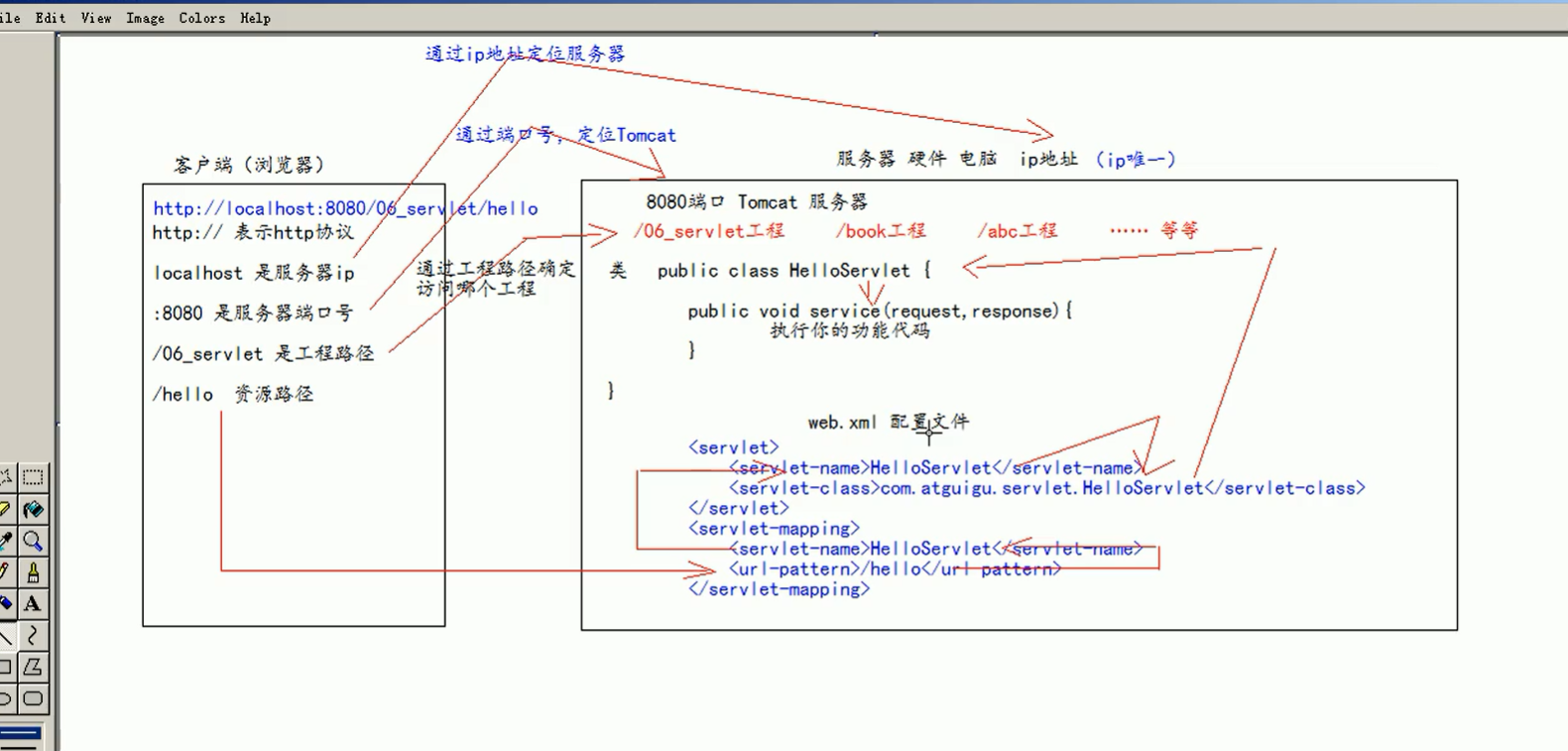
Configure web xml
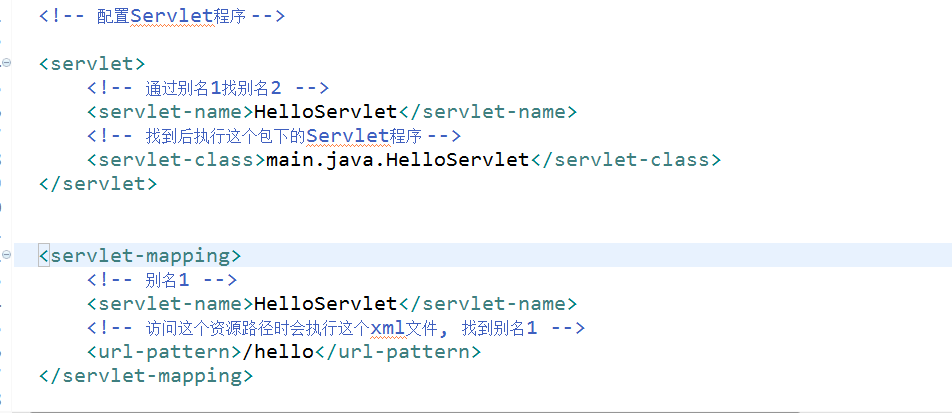
Configuration of Mapping
-
Mapping can specify multiple resource paths (specify more servlet mapping)
-
mapping can specify a generic path (*)
-
mapping can customize the suffix
*.xxx
6.3 Servlet inheritance system
6.4 Servlet life cycle
1. Class loading,Then execute Servlet Construction method
2. web Container execution init()Initialization method initialization Servlet container
First two steps, Is created for the first time Servlet Called when the program
3. implement service method
Called every time
4. implement destroy Destruction method
Called when the project stops
6.5 implementation principle of Servlet
1.The browser sends a message to the server GET request(Request server ServletA) 2.The container logic on the server received the message url,According to this url Judged as Servlet At this time, the container logic will produce two objects: the request object(HttpServletRequest)And response objects(HttpServletResponce) 3.Container logic basis url Find the target Servlet(The goal of this example Servlet by ServletA),And create a thread A 4.The container logic passes the request object and response object just created to the thread A 5.Container logical call Servlet of service()method 6.service()Method depends on the request type(This example is GET request)call doGet()(This example calls doGet())or doPost()method 7.doGet()After execution, the result is returned to the container logic 8.thread A Destroyed or placed in the process pool
be careful:
- In principle, there is only one instance of each Servlet in the container
- Each request corresponds to one thread
- Multiple threads can act on the same Servlet (which is the root cause of unsafe Servlet threads)
- Once each thread completes its task, it is destroyed or placed in the thread pool for recycling
6.6 common classes of Servlet
6.6.1 ServletConfig
ServletConfig In visit Servlet Program by Tomcat establish, yes Servlet Configuration file for
Role of ServletConfig
- Get alias
this.getServletConfig().getServletName(); - Get the initialization parameter init param (need to be configured under servlet)
this.getServletConfig().getInitParameter("root"); - Get ServletContext context object
this.getServletConfig().getServletContext();
6.6.2 ServletContext
-
Introduction to ServletContext
1. ServletContext Is an interface, It means Servlet Context object for 2. One Web There is only one project ServletContext Object instance(Global uniqueness) 3. ServletContext Is a domain(Operating range of accessing data)object similar map object Save operation setAttribute() Fetch operation getAttribute() Delete operation removeAttribute() 4. ServletContext stay web Start on project deployment, Destroy on cessation of work -
The role of ServletContext
- Share data (domain object), request forwarding, get context parameter context param
getServletConfig().getServletContext().getInitParameter("String s") - Get the current project path, format: / Project path
getContextPath()
Get the absolute path on the server hard disk after project deployment
getRealPath("/")
Note: / the address resolved by the server is: http://ip:port/ Project name / map to IDEA code web directory - Access data like map
setAttribute/getAttribute/removeAttribute - Read resource file (read Properties)
- Share data (domain object), request forwarding, get context parameter context param
-
Three ways to get ServletContext
this.getServletContext()
this.getServletConfig().getServletContext()
req.getSession().getServletContext()
6.6.3 HttpServletRequest
Every time there is a request to enter Tomcat The server, Tomcat The server will send the request HTTP The protocol information is parsed and encapsulated Request Object. Then pass it to Service method(doGet/doPost)In, we can pass HttpServletRequest object, Get all requested information.
effect:
Get client information
Get client parameters and request headers
Realize request forwarding and data sharing
common method
getRequestURL() Get the requested resource path(resources url)
getRemoteURL() Gets the absolute path of the request(complete url)
getQueryString() Returns the parameter part of the request line
getRemoteHost() Gets the host name of the client
getRemoteAddr() Get client's ip address
getRemotePort() Get the port number of the client
getHeader(String s) Get request header
getParameter() Get request parameters
getParameterValue() Get request group
getMethod() Get request type
setAttribute(key,value) Set domain data
getAttribute(key) Get domain data
getRequestDispatcher() Get request forwarding object
solve post Chinese garbled code: req.setCharacterEncoding("char")
6.6.4 HttpServletResponse
and httpServletRequest Same class, Every time you ask to come in, Tomcat The server will create one Response Object passed to Servlet Program to use, If we need to set the information returned to the client, Can pass HttpServletResponse Object(Download File, Write data to the client, Write response header, redirect)
effect: Write data to the client
Byte stream getOutputStream() For download
Character stream getWriter() Used to return string
notes: Only one of two streams can be used at the same time
Write response header
resp.setHeader();
redirect
resp.setHeader("Refresh","5; url= xxxx ");
resp.sendRidect("");
Logic for downloading files
1. Get the absolute path of the file this getServletContext(). Getrealpath ("/ img / related instruction. PNG");
2. Get the file name realpath subString(realPath.lastIndexOf("//")+1)
3. Modify the response header resp setHeader(“content-disposition”, “attachment;filename=”+fileName);
4. io stream operation
When downloading Chinese files, it should be noted that the Chinese file name should use urlencoder Encode with the encode method (URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "character encoding")), otherwise the file name will be garbled.
Solve the problem of garbled code
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
6.6.5 request and redirection
-
Request forwarding
What is request forwarding?
Request forwarding means that after receiving the request, the server operates the request. When the business logic is complex, it needs to transfer the result of Servlet1 to another Servlet program for operation, and finally return to the client. This is request forwarding.
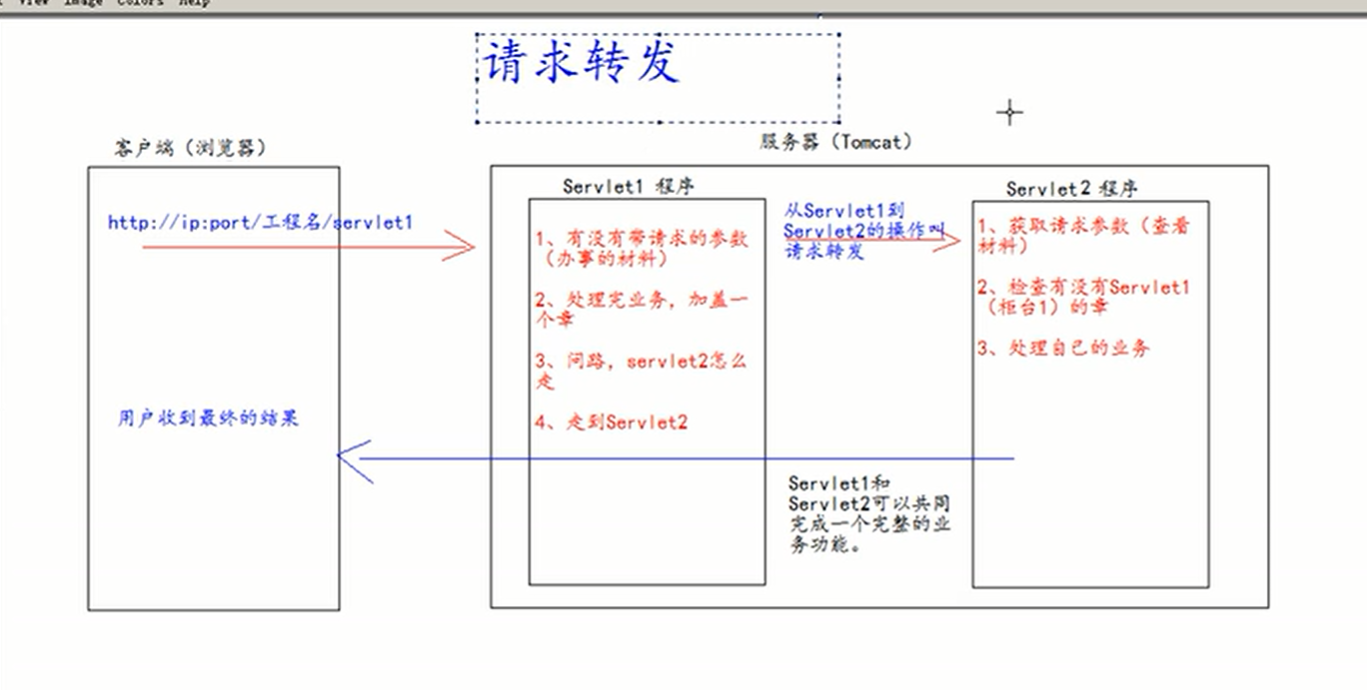
-
redirect
It refers to sending a request to the client and the server, and the server returns some addresses of the client to redirect the client (because the addresses between them may be discarded)
-
The difference between request forwarding and request redirection
-
Same point
The page will jump
-
difference
When requesting forwarding, url No change, Redirect and vice versa. Request forwarding share Request Data for the domain. Request forwarding can be forwarded to WEB-INF Resources under. Request forwarding cannot access resources outside the project. Request forwarding is a request.
6.7 Http protocol
What is HTTP protocol?
Rules to be followed for data sent during communication between client and server, HTTP The data in the protocol is also called message.
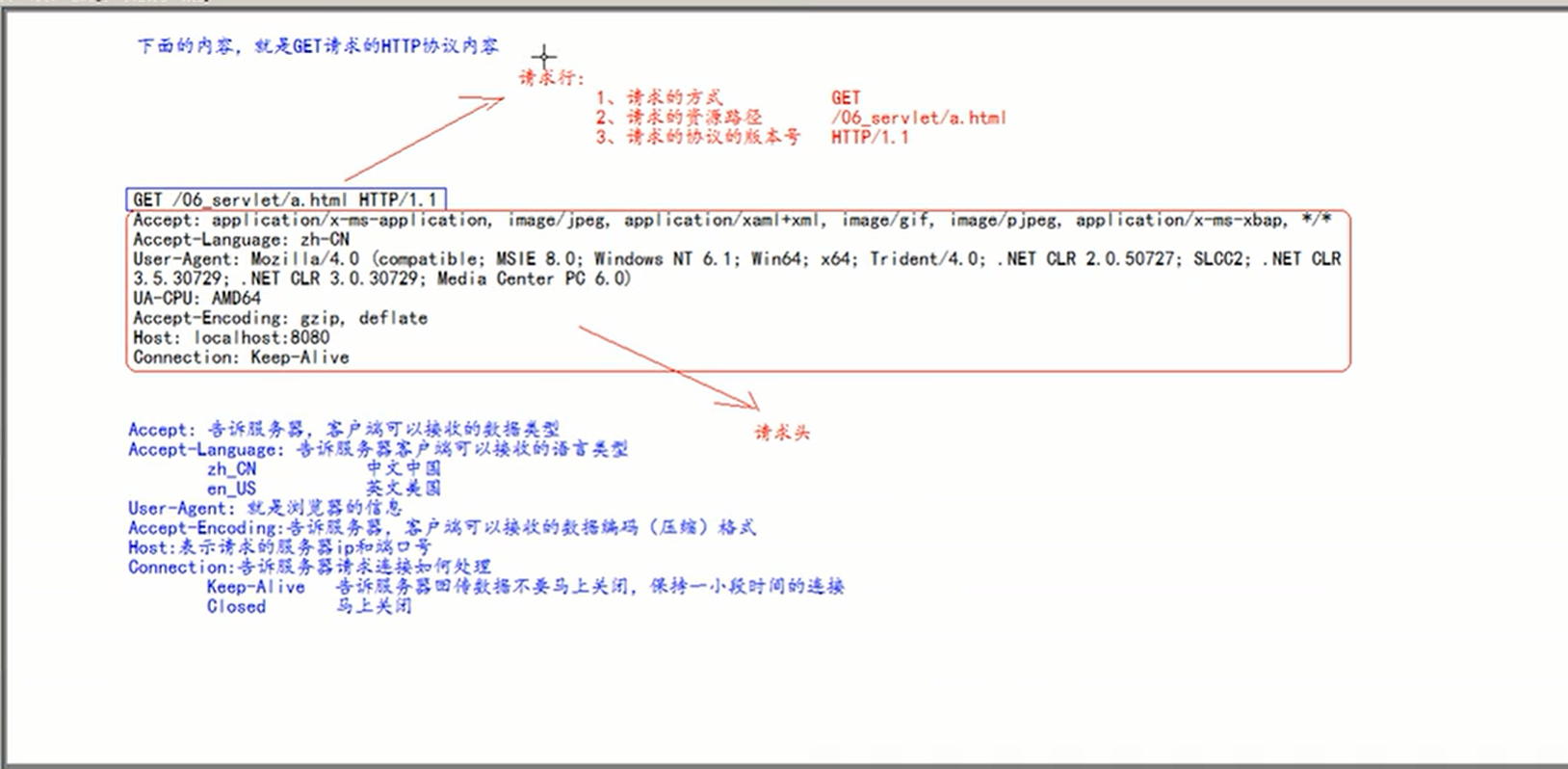
HTTP protocol format of the request
GET
Request line
- Request mode
- Requested resource path[+?+Request parameters]
- Requested protocol version number
Request header
key:value Form different key value pairs, Different meanings
POST
The request line and header are basically the same GET(POST Empty line in request header)
POST Request body == > Data sent to the server
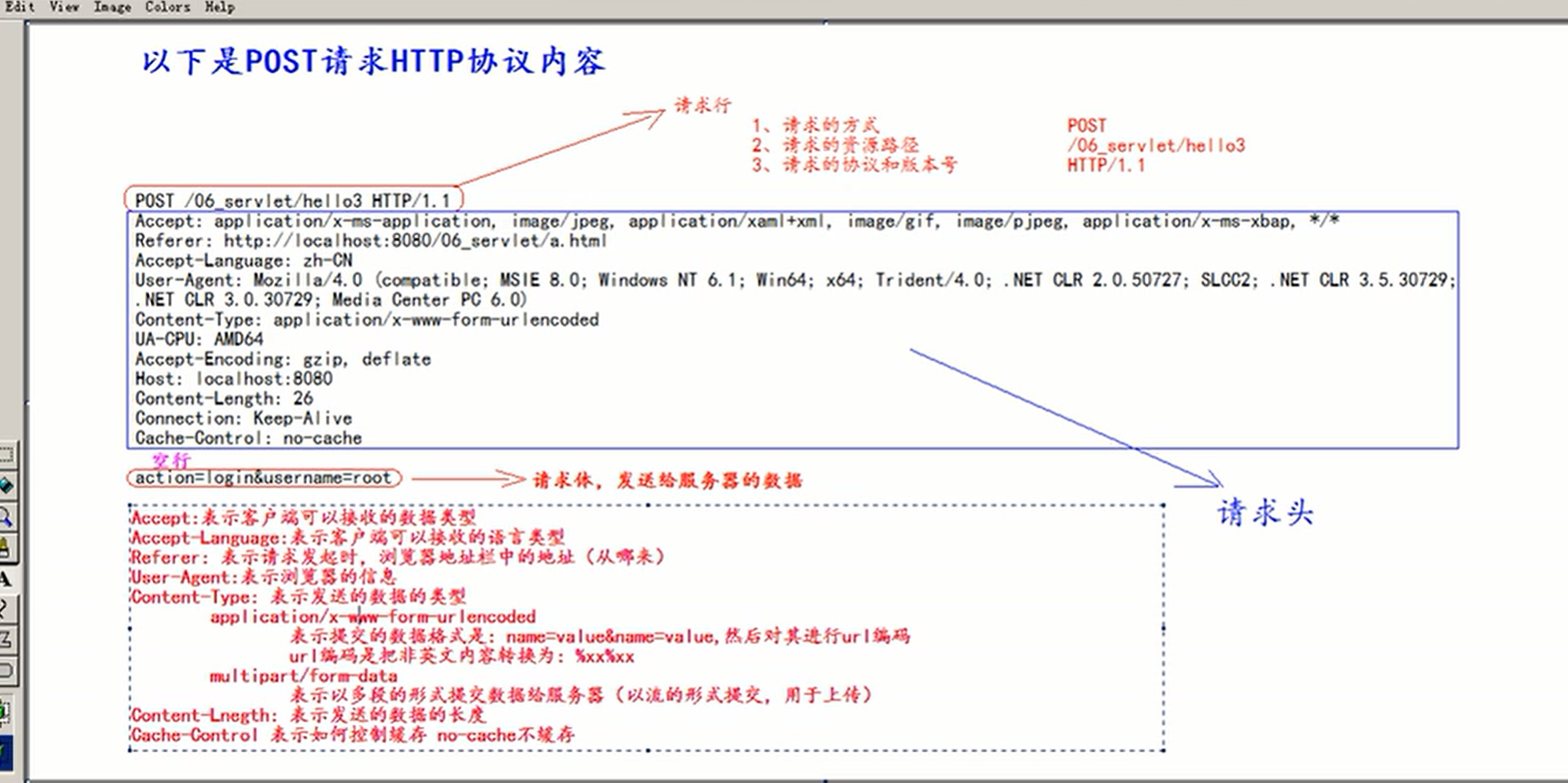
Common request header
Accept: indicates the data type that the client can receive
Accept language: indicates the language type that the client can receive
User agent: represents the information of the client browser
Host: indicates the requested server IP and port number
Responsive HTTP Protocol format
Response line
(1) Protocol and version number of response
(2) Response status
(3) Response state descriptor
Response header
(1) key:value Different response headers, It has different meanings
Empty line
response --> Data returned to the client
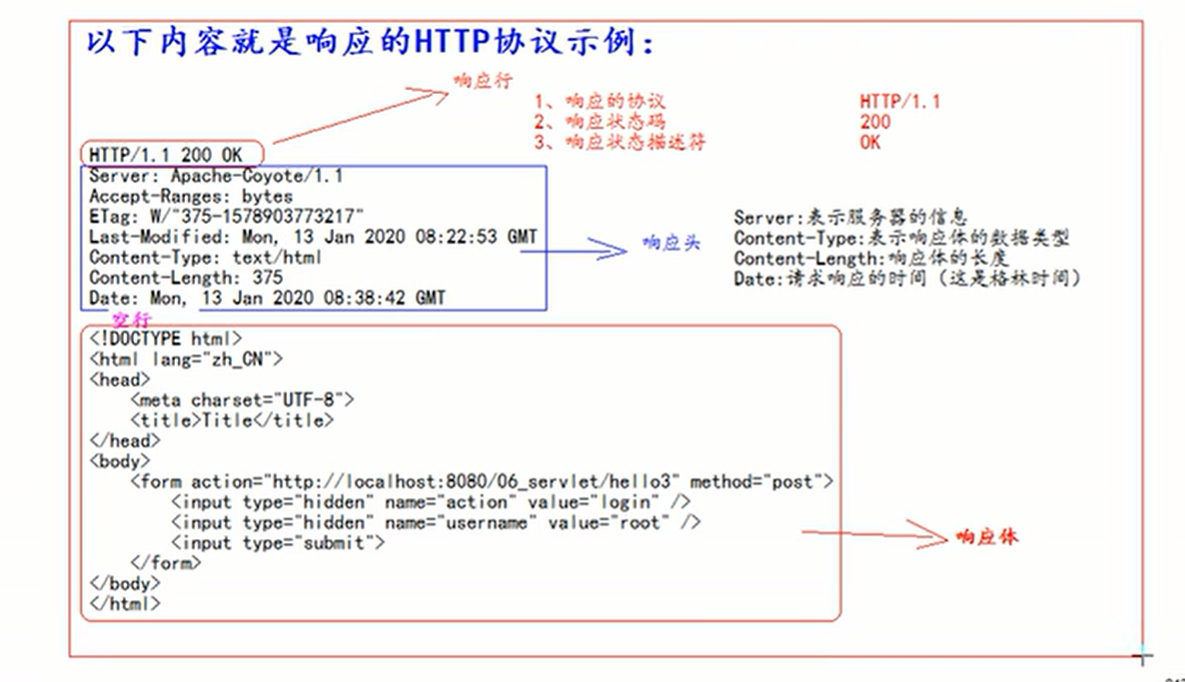
Description of common response codes
200 Request succeeded
302 request redirections
404 The request has been received by the server, But the data does not exist
500 Request server received, But there was an internal error in the server
7, JSP page, EL expression, JSTL tag library
7.1 introduction to JSP
- JSP(Java server pages) Java Service page for - JSP The main function of is to replace Servlet Program return html Page data - because Servlet Program return HTML Page data is a very cumbersome thing, High development and maintenance costs - JSP Is essentially a Servlet program(HttpJspBase Class inherits HttpServlet class) - When we first visited JSP Page time, Tomcat The server will help us jsp The page is translated into a java source file, And compile and generate.class Bytecode program.
7.2 Jsp instruction
1.Page instructions
<%@ page content Type="text/html;charset=utf-8" language="java" %>
JSP of page Instructions can be modified jsp Some important properties in the page, Or behavior
- language express jsp What language file is it after translation
- contentType jsp What is the data type returned, Also in the source code response.setContentType("xxx");This sentence
- pageEncoding jsp Character set of the page
- import Follow java Same as in the source code, Used to guide packages and classes
- autoFlush(Out Output stream dedicated) Set when out When the output stream buffer is full,Whether to refresh buffer automatically
- buffer(Out Output stream dedicated) Set buffer size
- errorPage Set when jsp An error occurred while the page was running, Automatically jump to the wrong page
- isErrorPage Set current jsp Is the page an error message page, Default is false
- session Set access current jsp page,Will it be created HttpSession object,Default is true
- extends set up jsp Who does the translated class inherit by default
note: Except for special cases, it is basically the default
2.include instructions
- JSP Static include label
<%@ include file=""%>
characteristic: 1. Static inclusion will not translate the included jsp page
2. Static inclusion is actually the inclusion of jsp Copy the code of the page to the included location
- JSP Dynamic inclusion label
<jsp:include page=""></jsp:include>
characteristic: 1. Dynamic inclusion will include jsp Page translation java code
2. The underlying code of dynamic inclusion uses the following code to call the included jsp Page execution output
JspRuntimeLibrary.include(request,response,"",out,false)
3. Parameters can be passed
3.Taglib instructions
- introduce jstl Tag library
Custom error page
When an error occurs on a page, use errorPage to jump to the error page
7.3 Jsp common scripts
- Declaration script
<%! Declare java code% >
Function: define attributes and methods for java classes translated from jsp, even static code blocks or internal classes
note: the member variables declared in the declaration script are executed once when the jsp is run for the first time, while the code script is executed every time - Expression script
<% = expression% >
Function: output data on jsp page
Features: 1 All expression scripts will be translated into_ jspService method.
2. All expression scripts will become out Print () is output to the page.
3. Because the content of expression script translation is_ jspService method, so_ All objects in the jspService method can be used directly.
4. Expressions in expression scripts cannot end with semicolons - Code script
<% Java statement% >
Function: we can write our own functions (written java statements) in jsp pages
Features: 1 After the code script is translated_ jspService method
2. Code script due to translation to_ In the jspService method_ All objects in jspService can be used
3. The code script can also complete a complete java statement due to the composition of multiple code script blocks
4. Code script can also be combined with expression script
7.4 JSP comments
html notes <!--Note Content --> Java notes // /* */ JSP notes <%--Note Content --%>
7.5 JSP built-in objects
- jsp Built in objects in, Refers to Tomcat In Translation jsp Page becomes Servlet After source code, Nine objects provided internally.
request Request object
response Response object
PageContext jsp Context object for
session Session object
application ServletContext object
config ServletConfig object
out jsp Output stream object
page Point to current jsp Object of
exception Exception object
- JSP Four domain objects
- PageContext(PageContextImpl class) current jsp Valid within page range
- Request(HttpServletRequest class) Valid within one request
- Session(HttpSession class) Valid within a session scope(Shopping cart, login)
- application(ServletContext class) whole Web Effective within the project
note: 1. Domain objects are similar to map The same object that accesses data, The functions of the four domain objects are the same, The difference is that they have different ranges.
Priority of use: pageContext >> requset >> session >> application
2. Out Output and getWriter Differences in output :
because jsp After translation, The underlying source code is used out To output, Therefore, we should unify to avoid disrupting the order of page output content
7.6 JSP action instructions
jsp:useBean Find or instantiate a JavaBean
jsp:setProperty set up JavaBean Properties of
jsp:getProperty Output a JavaBean Properties of
jsp:forward Forward the request to a new page
Common properties: id(Can pass PageContext call),scope(Define lifecycle)
Use example
jsp:useBean id="" class=""
jsp:setProperty name="id" Property="" value=""
Called here bean of set method
/jsp:userBean
jsp:getProperty name= Property
Called here bean of get method
7.7 JavaBean
JavaBean It's a kind of Java Reusable components written in. javaBean,It refers to those that meet the following standards Java Class: Serializable Class is public There is a public constructor without parameters(Through reflection mechanism) There is Privatization attribute and corresponding get,set method
Users can use JavaBeans to package functions, processing, values, database access and any other objects that can be created with Java code, and other developers can use these objects through internal JSP pages, servlets, other JavaBeans, applet programs or applications. Users can think that JavaBeans provide a function of copying and pasting anytime, anywhere, without caring about any changes.
7.8 EL expression
-
EL expression language is the expression language
- It mainly replaces the expression script in the jsp page to output data in the jsp page
- Output data, perform operations and obtain objects
-
Format of EL expression: ${expression}
Note: when EL expression outputs null value, empty string will be output. -
The order in which EL expressions search for domain data
Search for value from the smallest range of key s
7.8.1 EL calculation
- Relational operation
== eq
> gt
< lt
>= ge
<= le
!= ne
- Logical operation
and or not
&& || !
- arithmetic operation
+ - * / /div %/mod
- empty operation
empty You can judge whether a data is empty, Output Boolean
The following cases are empty
1. Value is null value
2. Empty string
3. Object Class array, Length is 0
4. list aggregate, The number of elements is zero
5. map aggregate, The number of elements is zero
7.8.2 11 implicit objects of EL expression (defined by EL expression itself)
pageContext PageContextLmpl It can get jsp Nine built-in objects in
pageScore Map<String,Object> It can get pageContext Data in domain
requestScope Map<String,Object> It can get Request Data in domain
sessionScope Map<String,Object> It can get Session Data in domain
applicationScope Map<String,Object> It can get ServletContext Data in domain
param Map<String,String> It can get the value of the request parameter
paramValues Map<String,String[]> It can get the value of the request parameter, Used when getting multiple values
header Map<String,String> It can get the information of the request header
headerValues Map<String,String[]> It can get the information of the request header, It can get multiple values
cookie Map<String,cookie> It can get the current request Cookie
initParam Map<String,String> It can be obtained in web.xml Configured in context-param Context parameters
7.9 JSTL tag library
7.9.1 introduction to JSTL tag library
- JSTL Tag library(JSP Standard Tag Library) JSP Standard label Library, It is a continuously improving open source system JSP Tag library, EL Expressions are mainly used to replace jsp Expression script in, The tag library is to replace the code script, This makes the whole jsp The page becomes more brief
- JSTL It is composed of five tag libraries with different functions(Database and xml Basically not used)
Core tag library(c)
format(fmt)
function(fn)
- stay jsp Use in tag library taglib Instruction introduction label Library
<%@ taglib prefix="c" url="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="fmt" url="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="fn" url="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions" %>
- Use steps
1. Guide package import jstl Label Library jar package(Import to WEB-INF Lower lib package, Then copy the package to Tomcat of lib lower)
2. use taglib Instruction introduction label Library(IDEA Automatically generated)
3. Use label
7.9.2 common labels
Use of core library
-
<c:set var="" value=""/>
Function: set tag can save data to the domain
Domain object setAttribute(key,value);attribute: scope(Set domain) var(set up key) value - page express PageContext field - request express Request field - session express Session field - application express ServletContext field -
< C: if test = "judgment condition" var = "assign to new variable" scope = "domain range" / >
-
<c:choose>
< C: when test = "judgment condition" > output 1 < / C: when >
< C: otherwise > similar to default in switch < / C: otherwise >
</c:choose> -
<c:forEach>
-var variable output each time
-Set / array of item output
-begin/end sets the start and end positions
-Step step
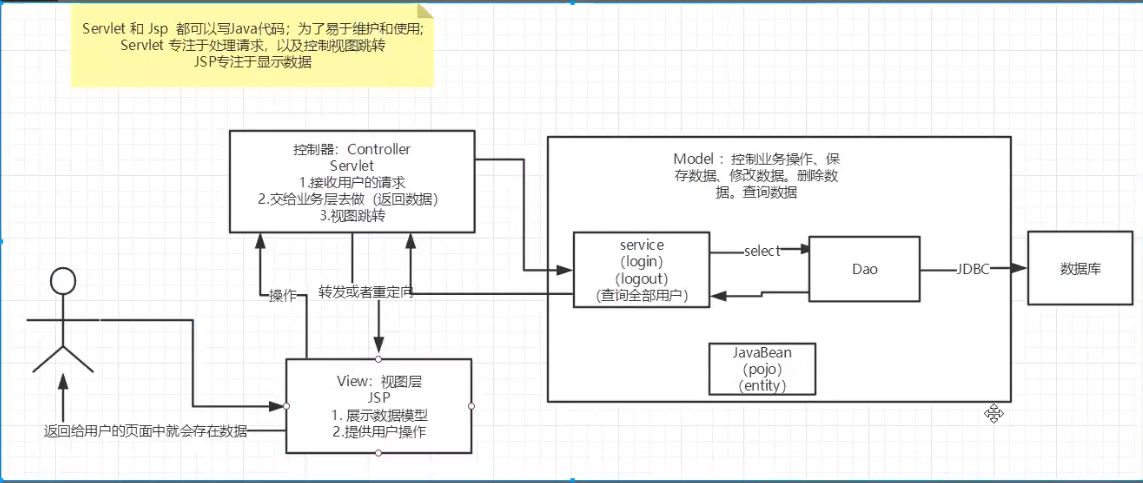
7.10 MVC three-tier architecture
MVC architecture
-
What is MVC? Model view controller
-
Model
- Business processing: business logic (Service)
- Data persistence layer: CURD operation (DAO)
-
View
- Display data
- Provide link to initiate Servlet request (a,form,img)
-
Controller
- Accept the user's request (req: request parameters, Session information)
- Give it to the business layer to process the corresponding code
- Control view jump
8, Listener introduction, Cookie, Session and Session Technology
8.1 session and status session
- It is a session from the user opening the browser to accessing Web resources and finally closing the browser.
- When a user visits a web page for the first time and then visits it again, some settings do not need to be set again. They can access directly. This is called state session.
8.2 two techniques for saving sessions
- Cookie(client)
1.One Cookie Only one information can be saved(Key value pair)
2.One Cookie Size up to 4 kb
3.The server can send 20 messages to the browser cookie
Get client's Cookie
req.getCookie();
Cookie operation
getName() getValue();
delete Cookie
1. Set the validity period to 0 cookie.setMaxAge(0)
2. No validity period is set, Close browser auto clear Cookie
Respond to clients Cookie
resp.addCookie(cookie);
cookie.setMaxAge( ns );
Cookie Two parameters of the constructor(key and value)All String
- Session(The server)
1.The server will give each user(browser)Create a Session object
2.One Session Exclusive browser, As long as the browser doesn't close, Sesson Has always existed
3.After user login, The entire website is accessible, Save user information, Shopping cart information.....
- session of id Will take cookie Send to the client, Value is session of id
obtain Session
getSession() return HttpSession
Session operation
set/get/removeAttribute Domain object
getID obtain SessionID
isNew judge Session Is it newly created
Manual logoff Session
session.invalidate()
send Session invalid(web.xml Medium configuration)
<session-config>
<session-timeout>In seconds</session-timeout>
</sessin-config>
8.3 difference between cookie and Session
1.Cookie Is to write the user's data to the user's browser, Browser save(Multiple can be saved) 2.Session It is to write the user's data to the user's exclusive session in, Server side save(Save important information, Reduce server-side resource waste) 3.Session It was created by the server
9, Filter filter
9.1 introduction to filter
Filter: filter, Used to filter the data of the website, JavaWeb One of the three components - Filter yes JavaEE One of the norms - Intercept request, Filter response
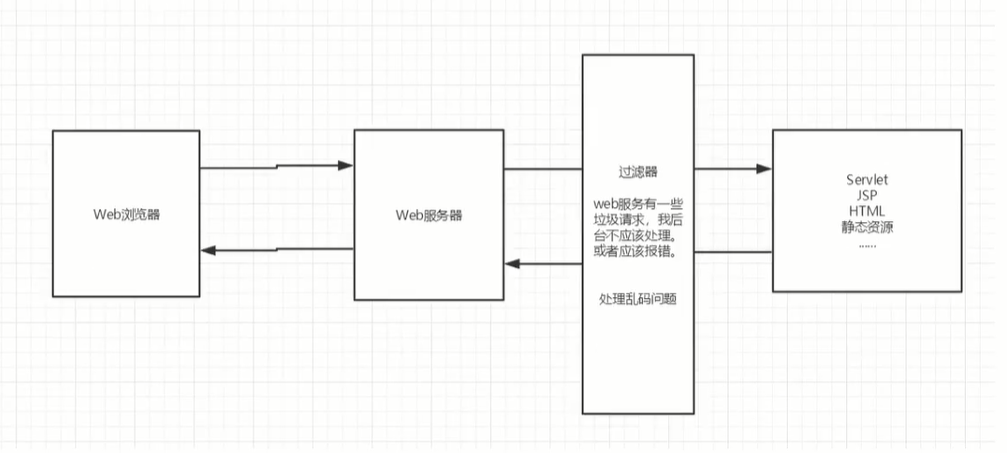
9.2 using Filter
1.realization Filter Interface(javax.servlet) 2.rewrite iniit,destroy,doFilter Method in which the request is intercepted, Filter response)
9.3 filter life cycle
- Execution sequence
1. Constructor method (automatically executed when the Web project starts)
2. Initialize init method (automatically executed when the Web project starts)
3. doFilter filtering method (it will be executed every time a request is intercepted)
4. destroy destruction method (the Filter will be destroyed when the Web project is stopped)
9.4 filter common classes
9.4.1 filterConfig
Filter Filter profile class
Tomcat Every time you create Filter When, One will also be created FilterConfig class, This includes Filter Configuration information for
effect: obtain Filter Configuration content of filter
1. obtain Filter Name of filter-name
2. Get in Filter Initialization parameters in init-param
3. obtain ServletContext object
9.4.2 filterChain filter chain
- Multiple Filter filters form a chain
FilterChain. The role of the dofilter () method
-Execute target resource (no Filter)
-Execute the next filter (with Filter)
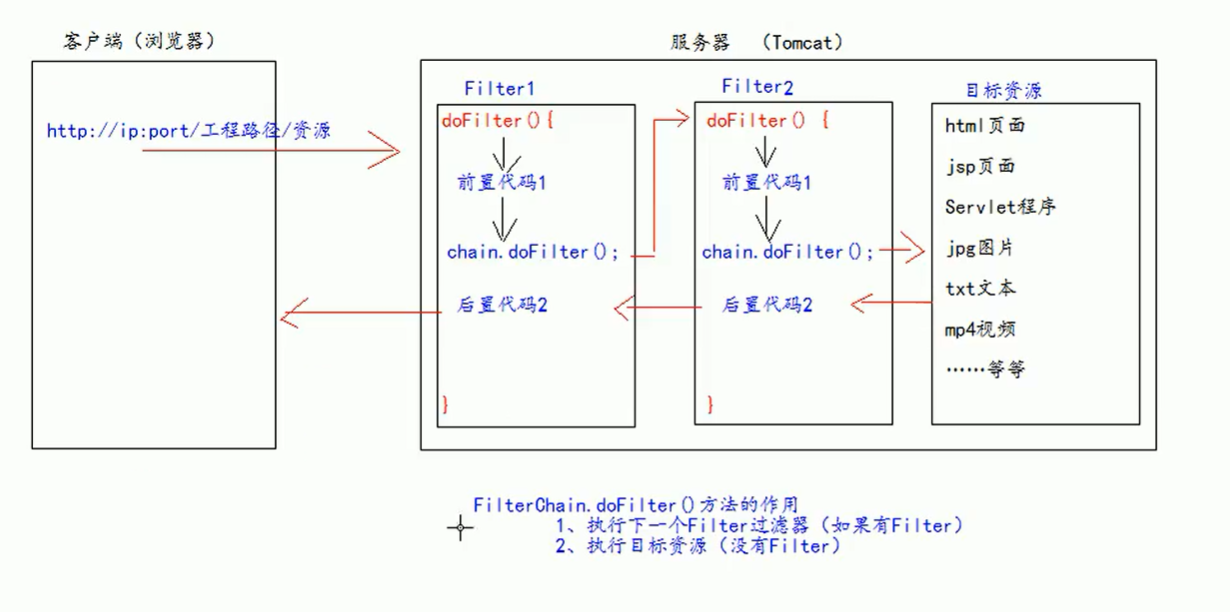
Multiple Filter filters are executed in the order of web Configuration order execution in XML
.
On the web Configuration in XML

- Multiple Filter execution features
- All filter s and target resources are in the same thread by default
- When multiple filter s are executed together, they all use the same Request object
9.4.3 three ways to intercept paths
-- Exact match
url-pattern /target.jsp
-- Directory matching
url-pattern /admin/*
-- Suffix matching
*suffix.xxxxx with xxxx The end can be intercepted
10, Maven project management, GIT & GitHub usage
10.1 Maven automated build tool
10.1.1 Maven's core concepts
10.1.1.1 introduction to maven
10.1.1.2 agreed directory structure and pom file
10.1.1.3 coordinate, dependency and packing type
10.1.1.4 warehouse
10.1.1.5 life cycle, plug-ins and commands
10.1.2 IDEA integrated Maven environment
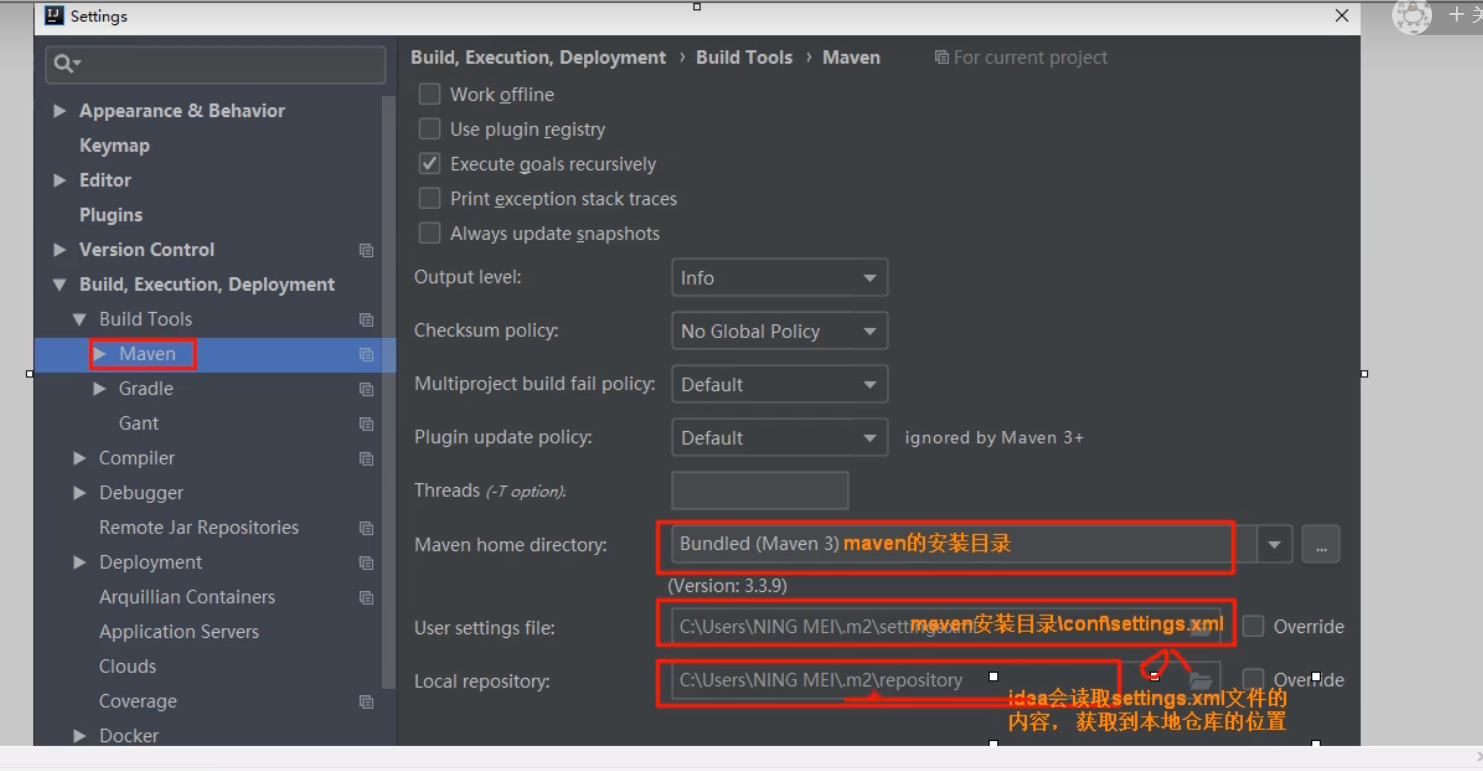
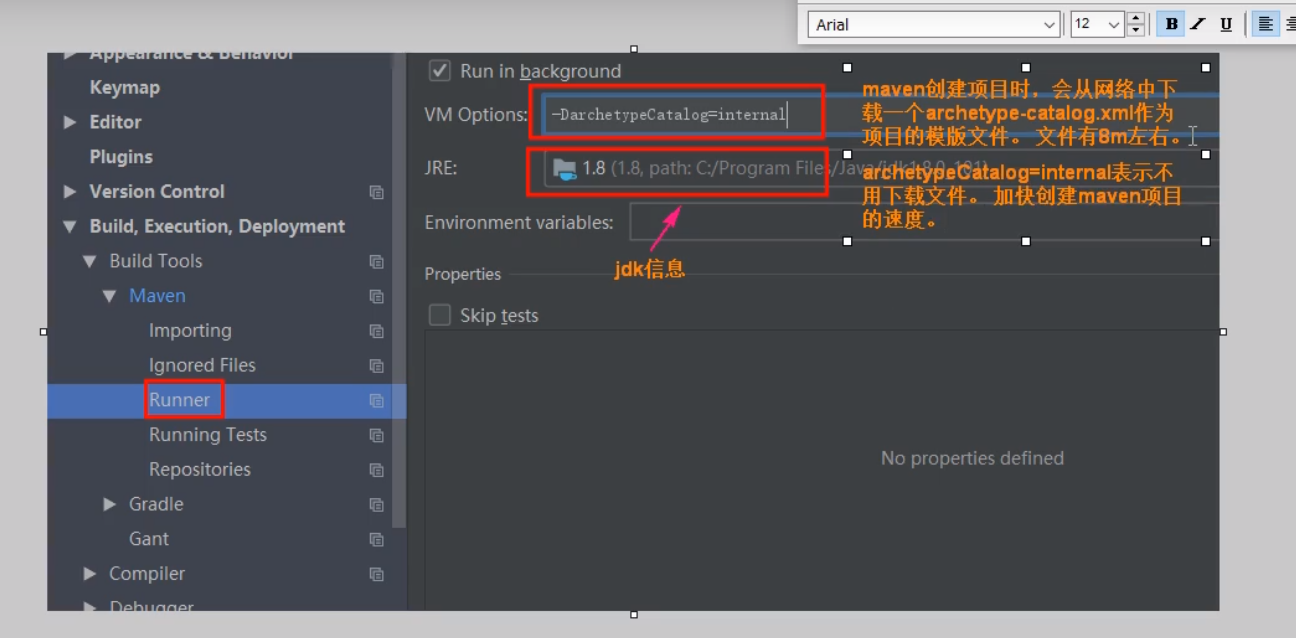
1) Configure local Maven in IDEA
Click file - > settings
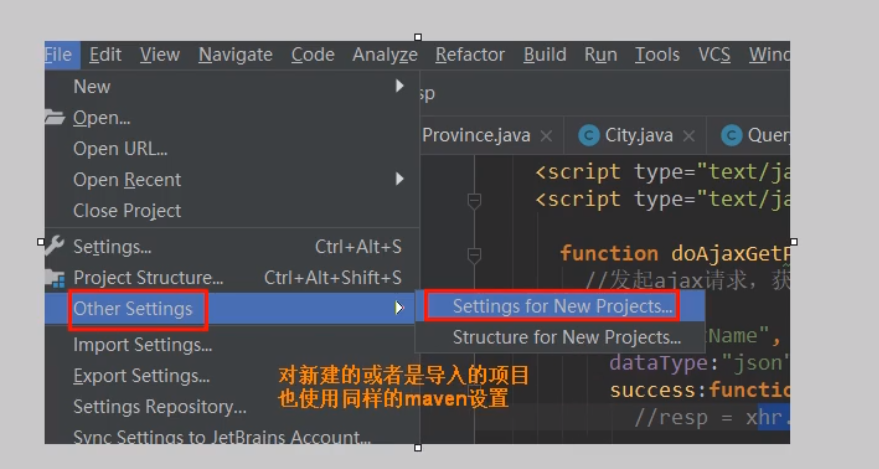
2) Use the old Maven settings for newly imported or newly created projects
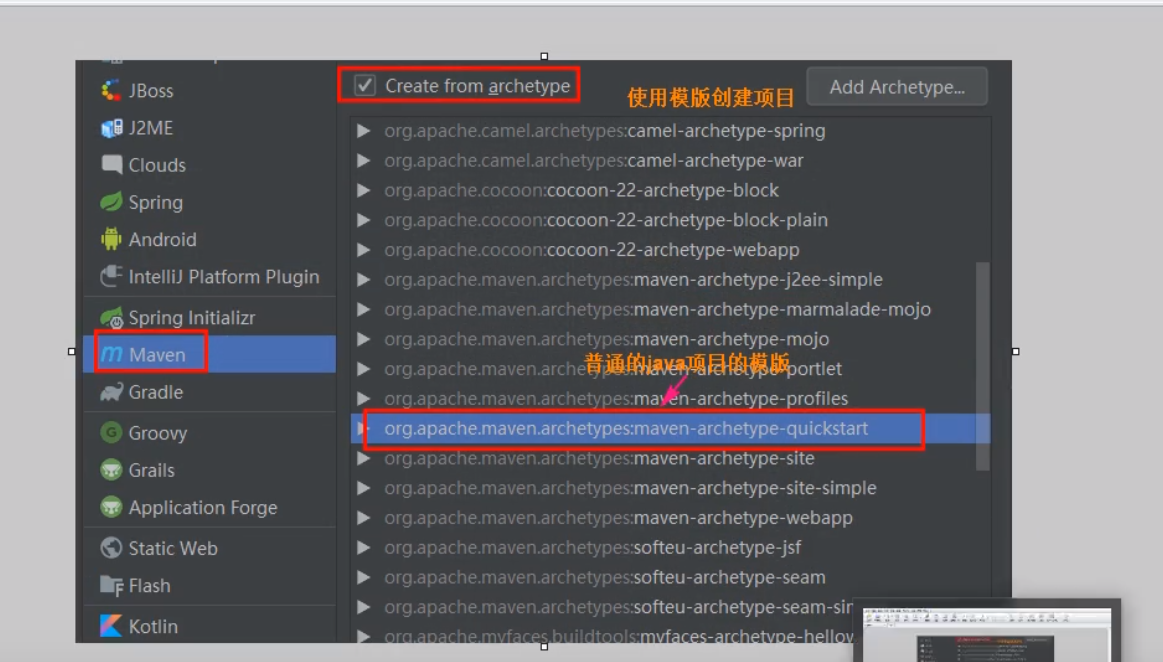
3) Create a Java se project under Maven
4) Maven's work window
5) Configure POM in idea XML file to implement dependency
6) Import Maven project in idea
10.1.3 Maven configuration and dependency management
10.1.3.1 dependency management
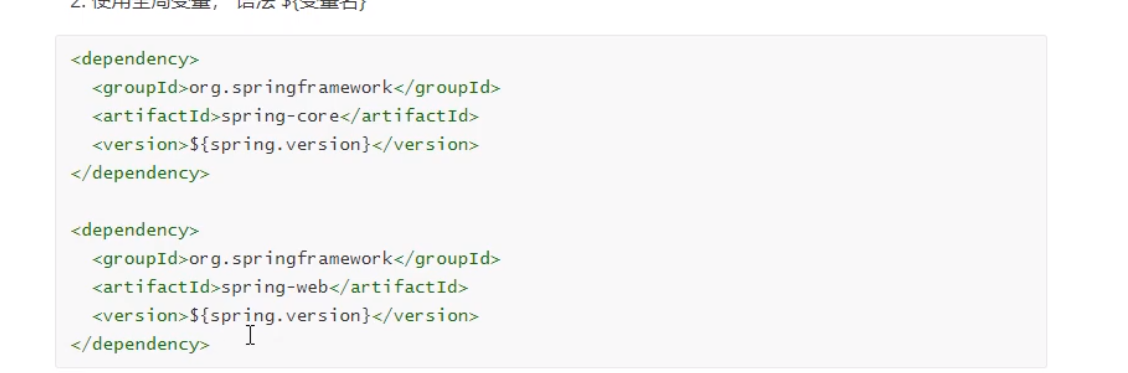
Scope of dependency: use scope Indicates the scope of the dependency
Range representation: This dependency works at that stage of project construction
scope Optional value
compile: default, Participate in all phases of the build project
test: Testing phase
provided: When a provider project is deployed to a server, There is no need to provide this dependency jar, But by the server jar package
10.1.3.2 Maven configuration