Time: Monday, 24 April 2017
Note: Part of the content of this article is from Mucho.com. @ Mu Course Net: http://www.imooc.com
Teaching sample source code: https://github.com/zccodere/s...
Personal learning source code: https://github.com/zccodere/s...
Chapter 1: Course introduction
1-1 Course Introduction
What is Spring Data
Purpose: To provide a familiar and consistent data access framework based on Spring framework. Simplify database access. History: Proposed in 2010 by Rod Johnso, Spring Source Project Website: http://projects.spring.io/spring-data/#quick-start
Overview of Spring Data
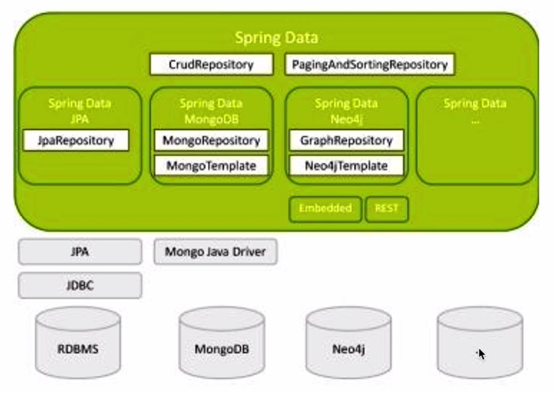
Spring Data contains multiple subprojects
Spring Data JPA Spring Data Mongo DB Spring Data Redis Spring Data Solr
course arrangement
Traditional access to databases Spring Data Quick Start Spring Data JPA Advancement Spring Data JPA Advanced
Chapter 2: Traditional access to databases
2-1 Traditional access to databases
Traditional access to databases
JDBC Spring JdbcTemplate Analysis of Disadvantage
2-2 Preparations
JDBC
Connection Statement ResultSet Test Case
Building Development Environment
Create a maven project Adding database drivers and unit test dependencies Preparing database tables, using mysql database
Create a Java project with POM files as follows:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.zccoder</groupId> <artifactId>myspringdata</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- spring --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>4.3.6.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>4.3.6.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- spring-data-jpa --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-jpa</artifactId> <version>1.11.3.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.Final</version> </dependency> <!-- mysql --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.38</version> </dependency> <!-- junit --> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.10</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
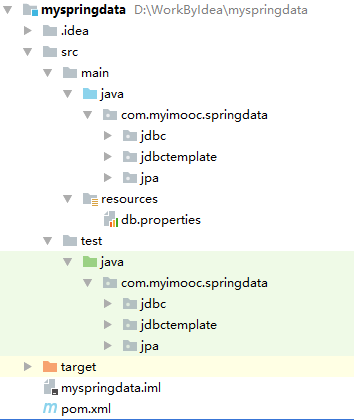
The completed project structure chart:
2-3 JDBCUtil Development
Developing JDBCUtil Tool Class
Get Connection, close Connection, Statement, ResultSet Note: The configuration attributes are placed in the configuration file, and then the data in the configuration file can be loaded by code.
Code example:
package com.myimooc.springdata.jdbc.util; import java.io.InputStream; import java.sql.*; import java.util.Properties; /** * JDBC Tool class: * 1)Get Connection * 2)Releasing resources * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ public class JDBCUtils { /** * Get Connection * @return The JDBC Connection obtained */ public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception{ /** * It is not recommended that you hard-code the configuration into the code. * Best Practices: Configuration Suggestions Written in Configuration Files * */ // String url = "jdbc:mysql:///springdata"; // String username = "root"; // String password = "root"; // String dirverClass = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; InputStream inputStream = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties"); Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.load(inputStream); String url = properties.getProperty("jdbc.url"); String username = properties.getProperty("jdbc.username"); String password = properties.getProperty("jdbc.password"); String driverClass = properties.getProperty("jdbc.driverClass"); Class.forName(driverClass); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password); return connection; } /** * Release DB-related resources * @param resultSet * @param statement * @param connection */ public static void release(ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement,Connection connection){ if(resultSet != null ){ try { resultSet.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(statement != null ){ try { statement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(connection != null ){ try { connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
2-4 Dao Development
Establish object model and DAO layer development.
Code demonstration:
1. Object Model
package com.myimooc.springdata.jdbc.domain; /** * Student Entity class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ public class Student { /** Primary key ID */ private Integer id; /** Full name */ private String name; /** Age */ private int age; @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
2. DAO Interface
package com.myimooc.springdata.jdbc.dao; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbc.domain.Student; import java.util.List; /** * StudentDAO Access Interface * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ public interface StudentDao { /** * Acquire all students * @return All students */ List<Student> listStudent(); /** * Add a student * @param student Students to be added */ void saveStudent(Student student); }
3. DAO Implementation
package com.myimooc.springdata.jdbc.dao.impl; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbc.dao.StudentDao; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbc.domain.Student; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbc.util.JDBCUtils; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * StudentDAO Access Interface Implementation Class: Operated in the most primitive JDBC way * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao { public List<Student> listStudent() { List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(); Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; String sql = "select id,name,age from student"; try { connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); while(resultSet.next()){ Integer id = resultSet.getInt("id"); String name = resultSet.getString("name"); Integer age = resultSet.getInt("age"); Student student = new Student(); student.setId(id); student.setName(name); student.setAge(age); studentList.add(student); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.release(resultSet,preparedStatement,connection); } return studentList; } public void saveStudent(Student student) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; String sql = "insert into student(name,age) values(?,?)"; try { connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1,student.getName()); preparedStatement.setInt(2,student.getAge()); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.release(resultSet,preparedStatement,connection); } } }
4. Unit testing
package com.myimooc.springdata.jdbc.dao; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbc.dao.impl.StudentDaoImpl; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbc.domain.Student; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.List; /** * StudentDao Unit test class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ public class StudentDaoImplTest { @Test public void listStudentTest(){ StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDaoImpl(); List<Student> studentList = studentDao.listStudent(); for(Student student : studentList){ System.out.println(student.toString()); } } @Test public void saveStudentTest(){ StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDaoImpl(); Student student = new Student(); student.setName("test"); student.setAge(30); studentDao.saveStudent(student); } }
2-5 uses JdbcTemplate
Spring JdbcTemplate
Adding maven dependencies DataSource & JdbcTemplate injection Test Case
Code demonstration:
1. Create DB Profile
jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql:///springdata jdbc.username = root jdbc.password = root jdbc.driverClass = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2. Create configuration file classes
package com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * Configuration parameter class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ @PropertySource(value="classpath:db.properties") @Component public class Properties { @Value("${jdbc.driverClass}") private String jdbcDriverClass; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String jdbcUrl; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String jdbcUser; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String jdbcPassword; @Override public String toString() { return "Properties{" + "jdbcDriverClass='" + jdbcDriverClass + '\'' + ", jdbcUrl='" + jdbcUrl + '\'' + ", jdbcUser='" + jdbcUser + '\'' + ", jdbcPassword='" + jdbcPassword + '\'' + '}'; } public String getJdbcDriverClass() { return jdbcDriverClass; } public String getJdbcUrl() { return jdbcUrl; } public String getJdbcUser() { return jdbcUser; } public String getJdbcPassword() { return jdbcPassword; } }
3. Configure DataSource, JdbcTemplate and Spring Annotation Scanning
package com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; /** * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ @Configuration @ComponentScan("com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate") public class SpringConfig { @Autowired private Properties properties; @Bean DriverManagerDataSource getDriverManagerDataSource(){ DriverManagerDataSource driverManagerDataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); driverManagerDataSource.setDriverClassName(properties.getJdbcDriverClass()); driverManagerDataSource.setUrl(properties.getJdbcUrl()); driverManagerDataSource.setUsername(properties.getJdbcUser()); driverManagerDataSource.setPassword(properties.getJdbcPassword()); return driverManagerDataSource; } @Bean JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(){ JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(); jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(getDriverManagerDataSource()); return jdbcTemplate; } }
4. Writing Entity Classes
package com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate.domain; /** * Student Entity class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ public class Student { /** Primary key ID */ private Integer id; /** Full name */ private String name; /** Age */ private int age; @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
5. DAO Interface
package com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate.dao; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate.domain.Student; import java.util.List; /** * StudentDAO Access Interface * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ public interface StudentDao { /** * Acquire all students * @return All students */ List<Student> listStudent(); /** * Add a student * @param student Students to be added */ void saveStudent(Student student); }
6. DAO Implementation
package com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate.dao.impl; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate.dao.StudentDao; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate.domain.Student; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; /** * StudentDAO Access Interface Implementation Class: Operated by JdbcTemplate * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ @Repository public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public List<Student> listStudent() { List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(); String sql = "select id, name, age from student"; List<Map<String,Object>> mapList = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql); for (Map<String,Object> mapTemp : mapList) { Integer id = Integer.parseInt(mapTemp.get("id").toString()); String name = mapTemp.get("name").toString(); Integer age = Integer.parseInt(mapTemp.get("age").toString()); Student student = new Student(); student.setId(id); student.setName(name); student.setAge(age); studentList.add(student); } return studentList; } public void saveStudent(Student student) { String sql = "insert into student(name, age) value(?,?)"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql,student.getName(),student.getAge()); } }
7. Unit test class
package com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate.config.SpringConfig; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate.dao.StudentDao; import com.myimooc.springdata.jdbctemplate.domain.Student; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.util.List; /** * Implementing StudentDao Unit Test Class with JdbcTemplate * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ public class StudentDaoTest { private ApplicationContext ctx = null; private StudentDao studentDao; @Before public void init(){ ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); studentDao = ctx.getBean(StudentDao.class); } @After public void destroy(){ ctx = null; } @Test public void listStudentTest(){ List<Student> studentList = studentDao.listStudent(); for (Student student : studentList){ System.out.println(student.toString()); } } @Test public void saveTest(){ Student student = new Student(); student.setName("test-spring-jdbcTemplate"); student.setAge(25); studentDao.saveStudent(student); } }
2-6 Disadvantage Analysis
Analysis of Disadvantage
There is too much code in DAO DAO implementations have a lot of duplicate code Paging and other functions need to be re-encapsulated
Chapter 3: Quick Start to Spring Data
3-1 Development Environment Construction
Spring Data JPA Quick Start
Construction of Development Environment Spring Data JPA HelloWorld Development
Code demonstration:
1. Create DB Profile
jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql:///springdata jdbc.username = root jdbc.password = root jdbc.driverClass = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2. Create configuration file classes
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ @PropertySource(value="classpath:db.properties") @Component public class PropertiesConfig { @Value("${jdbc.driverClass}") private String jdbcDriverClass; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String jdbcUrl; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String jdbcUser; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String jdbcPassword; @Override public String toString() { return "Properties{" + "jdbcDriverClass='" + jdbcDriverClass + '\'' + ", jdbcUrl='" + jdbcUrl + '\'' + ", jdbcUser='" + jdbcUser + '\'' + ", jdbcPassword='" + jdbcPassword + '\'' + '}'; } public String getJdbcDriverClass() { return jdbcDriverClass; } public String getJdbcUrl() { return jdbcUrl; } public String getJdbcUser() { return jdbcUser; } public String getJdbcPassword() { return jdbcPassword; } }
3. Configure Transaction Manager, EntityManagerFactory and Spring Auto Scan Injection
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.Database; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter; import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; import java.util.Properties; /** * Spring Configuration class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ // Declare as configuration class @Configuration // Enabling transaction management @EnableTransactionManagement // Enable automatic scanning of classes inheriting the JpaRepository interface. // Note that this annotation requires configuration of entity ManagerFactory and transaction Manager // Way 1: Define the fetch Bean methods named entityManagerFactory and transactionManager // Mode 2: Configure the entityManagerFactoryRef attribute of the @EnableJpaRepositories annotation to customize the method name of the Bean. @EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "com.myimooc.springdata.jpa") // Bean with automatic scanning @Component annotation enabled @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.myimooc.springdata.jpa") public class SpringConfig{ @Autowired private PropertiesConfig propertiesConfig; /** * Configuring data sources * @return */ @Bean public DriverManagerDataSource dataSource(){ DriverManagerDataSource driverManagerDataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); driverManagerDataSource.setDriverClassName(propertiesConfig.getJdbcDriverClass()); driverManagerDataSource.setUrl(propertiesConfig.getJdbcUrl()); driverManagerDataSource.setUsername(propertiesConfig.getJdbcUser()); driverManagerDataSource.setPassword(propertiesConfig.getJdbcPassword()); return driverManagerDataSource; } /** * Configuration transaction manager JpaTransaction Manager * @return */ @Bean(name="transactionManager") public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(){ JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager(); transactionManager.setDataSource(this.dataSource()); transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(this.entityManagerFactory().getObject()); return transactionManager; // return new DataSourceTransactionManager(this.dataSource()); // return new JpaTransactionManager(this.entityManagerFactory().getObject()); } /** * Configure JPA's EntityManagerFactory * @return */ @Bean public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(){ LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean(); entityManagerFactory.setDataSource(dataSource()); HibernateJpaVendorAdapter jpaVendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter(); jpaVendorAdapter.setGenerateDdl(true); jpaVendorAdapter.setDatabase(Database.MYSQL); entityManagerFactory.setJpaVendorAdapter(jpaVendorAdapter); entityManagerFactory.setPackagesToScan("com.myimooc.springdata.jpa"); Properties jpaProperties = new Properties(); // jpaProperties.setProperty("hibernate.ejb.naming_strategy","org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy"); jpaProperties.setProperty("hibernate.dialect","org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect"); jpaProperties.setProperty("hibernate.show_sql","true"); jpaProperties.setProperty("hibernate.format_sql","true"); jpaProperties.setProperty("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto","update"); entityManagerFactory.setJpaProperties(jpaProperties); return entityManagerFactory; } }
4. Writing Entity Classes: Employee
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain; import javax.persistence.*; /** * Employee: First develop entity classes, then automatically generate entity tables * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ @Entity @Table(name = "test_employee") public class Employee { @Id @GeneratedValue private Integer id; @Column(length = 20) private String name; private Integer age; @Override public String toString() { return "Employee{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } }
3-2 Start Program Development
Code demonstration:
1. Writing Employee Repository Interface
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain.Employee; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Modifying; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query; import org.springframework.data.repository.Repository; import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import java.util.List; /** * Using Repository Interface * Created by ZC on 2017/4/25. */ // Mode 2: Use the @Repository Definition annotation // @RepositoryDefinition(domainClass = Employee.class,idClass = Integer.class) public interface EmployeeRepository extends Repository<Employee,Integer> {//Mode 1: Inherit Repository Interface /** * Get the employee object by name * @param name * @return */ Employee findByName(String name); }
2. Writing unit test classes: Employee Repository Test
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.config.SpringConfig; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain.Employee; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository.EmployeeRepository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.service.EmployeeService; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * EmployeeRepository Unit test class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ public class EmployeeRepositoryTest { private ApplicationContext ctx = null; private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository = null; @Before public void init(){ ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); employeeRepository = ctx.getBean(EmployeeRepository.class); } @After public void destroy(){ ctx = null; } @Test public void entityManageFactoryTest(){ LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory = (LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean)ctx.getBean(LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean.class); Assert.assertNotNull(entityManagerFactory); } @Test public void findByNameTest(){ System.out.println(employeeRepository); Employee employee = employeeRepository.findByName("cc"); if( null == employee){ System.out.println("Query data is empty"); }else{ System.out.println(employee.toString()); } } }
Repository
Repository: Spring Data Core Class Repository Definition: Configuration with this annotation Repository Query Specification: When querying, method names cannot be scribbled Query Annotation: With this annotation, native SQL queries can be implemented Update/Delete/Transaction: Update and delete operations to support transactions
Repository Hierarchy
CrudRepository: Built-in add, update, delete, query methods PagingAndSortingRespository: Paging and sorting JpaRepository JpaSpecificationExcutor
Chapter 4: Spring Data JPA Advancement
4-1 About Repository Interface
Repository Interface Details
Repository The interface is Spring Data Core interface, no method public interface Repository<T, ID extends Serializable>{} @RepositoryDefinition Use of annotations
Definition of Repository class:
1) Repository is an empty interface, marking the interface. Interfaces that do not contain method declarations
2) If we define the interface Employee Repository extends Repository, it will be managed by Spring.
If our own interface does not have extends Repository, the runtime will report an error without this Bean.
4-2 Repository Subinterface Details
Repository Subinterface Details
CrudRepository: Inheriting Repository, implements CRUD-related methods PagingAndSorting Repository: Inheriting CrudRepository, implements paging sorting related methods JpaRepository: Inheriting PagingAndSorting Repositor, Implementing JPA Specification-related Approaches
4-3 Query Method Definition Rules and Use
Query Method Definition Rules and Use in Repository
Understanding the definition rules of query method names in Spring Data Using Spring Data to Name Complex Query Method Names
Query Method Definition Rules
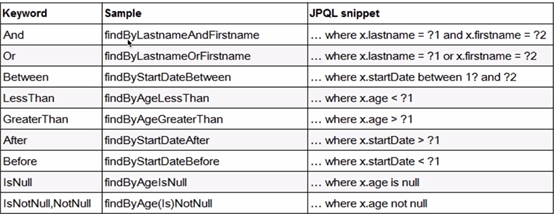
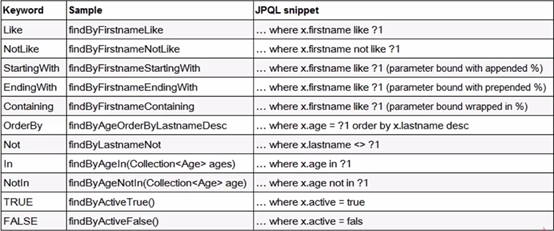
Code demonstration:
1. Write the following code in the Employee Repository interface
// Query using JPA specification // where name like ?% and age < ? List<Employee> findByNameStartingWithAndAgeLessThan(String name,Integer age); // where name like %? and age < ? List<Employee> findByNameEndingWithAndAgeLessThan(String name,Integer age); // where name in (?,?...) or age < ? List<Employee> findByNameInOrAgeLessThan(List<String> name,Integer age); // where name in (?,?...) and age < ? List<Employee> findByNameInAndAgeLessThan(List<String> name,Integer age);
2. Testing in Employee Repository Test Unit Test Class
@Test public void findByNameStartingWithAndAgeLessThanTest(){ System.out.println(employeeRepository); List<Employee> employees = employeeRepository.findByNameStartingWithAndAgeLessThan("test",22); if( null != employees){ for (Employee employee : employees) { System.out.println(employee.toString()); } }else{ System.out.println("Query data is empty"); } } @Test public void findByNameEndingWithAndAgeLessThanTest(){ System.out.println(employeeRepository); List<Employee> employees = employeeRepository.findByNameEndingWithAndAgeLessThan("6",23); if( null != employees && employees.size() > 0){ for (Employee employee : employees) { System.out.println(employee.toString()); } }else{ System.out.println("Query data is empty"); } } @Test public void findByNameInOrAgeLessThanTest(){ List<String> names = new ArrayList<String>(); names.add("test1"); names.add("test2"); names.add("test3"); List<Employee> employees = employeeRepository.findByNameInOrAgeLessThan(names,22); if( null != employees && employees.size() > 0){ for (Employee employee : employees) { System.out.println(employee.toString()); } }else{ System.out.println("Query data is empty"); } } @Test public void findByNameInAndAgeLessThanTest(){ List<String> names = new ArrayList<String>(); names.add("test1"); names.add("test2"); names.add("test3"); List<Employee> employees = employeeRepository.findByNameInAndAgeLessThan(names,22); if( null != employees && employees.size() > 0){ for (Employee employee : employees) { System.out.println(employee.toString()); } }else{ System.out.println("Query data is empty"); } }
There are drawbacks in using method naming rules:
1) The method name is longer: the agreement is greater than the configuration 2) For some complex queries, it is very difficult to implement.
Use the @Query annotation to solve this problem.
4-4 Query annotation use
Query annotation use
In the Respository method, there is no need to follow the query method command rules Just define @Query above the methods in Respository Named parameters and the use of index parameters Local query
Code demonstration:
1. Write the following code in the Employee Repository interface
// Query with @Query annotation /** * Custom Query SQL * */ @Query("select o from Employee o where id=(select max(id) from Employee t1)") Employee getEmployeeByMaxId(); /** * Using placeholders for parameter binding * */ @Query("select o from Employee o where o.name=?1 and o.age=?2") List<Employee> listEmployeeByNameAndAge(String name, Integer age); /** * Binding parameters with named parameters * */ @Query("select o from Employee o where o.name=:name and o.age=:age") List<Employee> listEmployeeByNameAndAge2(@Param("name") String name, @Param("age")Integer age); /** * Custom query SQL, like, placeholder for parameter binding * */ @Query("select o from Employee o where o.name like %?1%") List<Employee> listEmployeeByLikeName(String name); /** * Custom query SQL, like, named parameters for parameter binding * */ @Query("select o from Employee o where o.name like %:name%") List<Employee> listEmployeeByLikeName2(@Param("name") String name); /** * Using native SQL query * @return */ @Query(nativeQuery = true,value = "select count(1) from employee") long getCount();
2. Testing in Employee Repository Test Unit Test Class
// Query with @Query annotation @Test public void getEmployeeByMaxIdTest(){ Employee employee = employeeRepository.getEmployeeByMaxId(); if( null != employee ){ System.out.println(employee.toString()); }else{ System.out.println("Query data is empty"); } } @Test public void listEmployeeByNameAndAgeTest(){ List<Employee> employees = employeeRepository.listEmployeeByNameAndAge("zhangsan",20); if( null != employees && employees.size() > 0){ for (Employee employee : employees) { System.out.println(employee.toString()); } }else{ System.out.println("Query data is empty"); } } @Test public void listEmployeeByNameAndAge2Test(){ List<Employee> employees = employeeRepository.listEmployeeByNameAndAge2("zhangsan",20); if( null != employees && employees.size() > 0){ for (Employee employee : employees) { System.out.println(employee.toString()); } }else{ System.out.println("Query data is empty"); } } @Test public void listEmployeeByLikeNameTest(){ List<Employee> employees = employeeRepository.listEmployeeByLikeName("test1"); if( null != employees && employees.size() > 0){ for (Employee employee : employees) { System.out.println(employee.toString()); } }else{ System.out.println("Query data is empty"); } } @Test public void listEmployeeByLikeName2Test(){ List<Employee> employees = employeeRepository.listEmployeeByLikeName2("test"); if( null != employees && employees.size() > 0){ for (Employee employee : employees) { System.out.println(employee.toString()); } }else{ System.out.println("Query data is empty"); } } @Test public void getCountTest(){ long count = employeeRepository.getCount(); System.out.println(count); }
4-5 Update Operations Integrate Transaction Usage
Update and Delete Operations Integrate the Use of Transactions
@ Modifying annotation use @ Modifying performs update operations with the @Query annotation @ Use of Transaction in Spring Data
The use of transactions in Spring data:
1) Transactions are generally at Service level 2) Comprehensive use of @Query,@Modifying,@Transaction
Code demonstration:
1. Transaction configuration based on javaconfig in SpringConfig class
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.Database; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter; import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; import java.util.Properties; /** * Spring Configuration class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ // Declare as configuration class @Configuration // Enabling transaction management @EnableTransactionManagement // Enable automatic scanning of classes inheriting the JpaRepository interface. // Note that this annotation requires configuration of entity ManagerFactory and transaction Manager // Way 1: Define the fetch Bean methods named entityManagerFactory and transactionManager // Mode 2: Configure the entityManagerFactoryRef attribute of the @EnableJpaRepositories annotation to customize the method name of the Bean. @EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "com.myimooc.springdata.jpa") // Bean with automatic scanning @Component annotation enabled @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.myimooc.springdata.jpa") public class SpringConfig{ @Autowired private PropertiesConfig propertiesConfig; /** * Configuring data sources * @return */ @Bean public DriverManagerDataSource dataSource(){ DriverManagerDataSource driverManagerDataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); driverManagerDataSource.setDriverClassName(propertiesConfig.getJdbcDriverClass()); driverManagerDataSource.setUrl(propertiesConfig.getJdbcUrl()); driverManagerDataSource.setUsername(propertiesConfig.getJdbcUser()); driverManagerDataSource.setPassword(propertiesConfig.getJdbcPassword()); return driverManagerDataSource; } /** * Configuration transaction manager JpaTransaction Manager * @return */ @Bean(name="transactionManager") public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(){ JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager(); transactionManager.setDataSource(this.dataSource()); transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(this.entityManagerFactory().getObject()); return transactionManager; // return new DataSourceTransactionManager(this.dataSource()); // return new JpaTransactionManager(this.entityManagerFactory().getObject()); } /** * Configure JPA's EntityManagerFactory * @return */ @Bean public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(){ LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean(); entityManagerFactory.setDataSource(dataSource()); HibernateJpaVendorAdapter jpaVendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter(); jpaVendorAdapter.setGenerateDdl(true); jpaVendorAdapter.setDatabase(Database.MYSQL); entityManagerFactory.setJpaVendorAdapter(jpaVendorAdapter); entityManagerFactory.setPackagesToScan("com.myimooc.springdata.jpa"); Properties jpaProperties = new Properties(); // jpaProperties.setProperty("hibernate.ejb.naming_strategy","org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy"); jpaProperties.setProperty("hibernate.dialect","org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect"); jpaProperties.setProperty("hibernate.show_sql","true"); jpaProperties.setProperty("hibernate.format_sql","true"); jpaProperties.setProperty("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto","update"); entityManagerFactory.setJpaProperties(jpaProperties); return entityManagerFactory; } }
2. Write the following code in the Employee Repository interface
// Update data @Transactional @Modifying @Query("update Employee o set o.age = :age where o.id = :id") void updateAgeById(@Param("id")Integer id,@Param("age")Integer age);
3. Define Service Layer. In actual development, we need to define interfaces. In order to demonstrate conveniently, we use classes directly.
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.service; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain.Employee; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository.EmployeeCrudRepository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository.EmployeeRepository; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import java.util.List; /** * Created by ZC on 2017/4/25. */ @Service public class EmployeeService { @Autowired private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository; @Autowired private EmployeeCrudRepository employeeCrudRepository; @Transactional public void updateAgeById(Integer id, Integer age){ this.employeeRepository.updateAgeById(id,age); }; @Transactional public void save(List<Employee> employees){ this.employeeCrudRepository.save(employees); } }
4. Writing EmployeeService Unit Test Class
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.service; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.config.SpringConfig; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository.EmployeeRepository; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean; import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager; /** * EmployeeService Unit test class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/25. */ public class EmployeeServiceTest { private ApplicationContext ctx = null; private EmployeeService employeeService = null; @Before public void init(){ ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); employeeService = ctx.getBean(EmployeeService.class); } @After public void destroy(){ ctx = null; } @Test public void transactionManagerTest(){ PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager = (PlatformTransactionManager)ctx.getBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class); Assert.assertNotNull(transactionManager); } // update operation @Test public void updateAgeByIdTest(){ employeeService.updateAgeById(1,55); } }
Chapter 5: Spring Data JPA Advanced
5-1 CrudRepository Interface Use Details
CrudRepository Interface Use Details
save(entity): Save an entity save(entities): Save multiple entities findOne(id): Find an object exists(id): Determine whether an object exists based on ID findAll(): Find all entity objects delete(id): Delete entity objects based on ID delete(entity): Delete entity objects based on entity objects delete(entities): Delete multiple entity objects deleteAll(): Delete all entity objects
Code demonstration:
1. Writing Employee CrudRepository Interface
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain.Employee; import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository; /** * Using CrudRepository Interface * Created by ZC on 2017/4/26. */ public interface EmployeeCrudRepository extends CrudRepository<Employee,Integer>{ }
2. Writing the Employee CrudRepository Test Unit Test Class
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.config.SpringConfig; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain.Employee; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * EmployeeRepository Unit test class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/24. */ public class EmployeeCrudRepositoryTest { private ApplicationContext ctx = null; private EmployeeCrudRepository employeeCrudRepository = null; @Before public void init(){ ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); employeeCrudRepository = ctx.getBean(EmployeeCrudRepository.class); } @After public void destroy(){ ctx = null; } @Test public void saveTest(){ List<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<Employee>(); Employee employee = null; for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ employee = new Employee(); employee.setName("test"+i); employee.setAge(100 - i); employees.add(employee); } employeeCrudRepository.save(employees); } }
5-2 PagingAndSorting Respository Interface Use Details
PagingAndSorting Respository Interface Use Details
This interface includes paging and sorting functions Queries with sorting: findAll(Sort sort) Paging queries with sorting: findAll(Pageable pageable)
Code demonstration:
1. Write Employee PagingAndSorting Repository Interface
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain.Employee; import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository; /** * Paging and sorting using PagingAndSorting Repository * Created by ZC on 2017/4/26. */ public interface EmployeePagingAndSortingRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository<Employee,Integer> { }
2. Write the Employee PagingAndSorting Repository Test Unit Test Class
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.config.SpringConfig; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain.Employee; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository.EmployeePagingAndSortingRepository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.service.EmployeeService; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.data.domain.Page; import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest; import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable; import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort; import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * PagingAndSortingRepository Unit test class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/26. */ public class EmployeePagingAndSortingRepositoryTest { private ApplicationContext ctx = null; private EmployeePagingAndSortingRepository employeePagingAndSortingRepository = null; @Before public void init(){ ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); employeePagingAndSortingRepository = ctx.getBean(EmployeePagingAndSortingRepository.class); } @After public void destroy(){ ctx = null; } /** * Paging Function Testing */ @Test public void pageTest(){ // page: index starts at 0, not from 1 Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(0,9); Page<Employee> employeePage = employeePagingAndSortingRepository.findAll(pageable); System.out.println("Total number of pages queried:"+employeePage.getTotalPages()); System.out.println("Total number of records queried:"+employeePage.getTotalElements()); System.out.println("The current page of the query:"+(employeePage.getNumber() + 1)); System.out.println("A collection of the current pages of the query:"+employeePage.getContent()); System.out.println("Number of records on the current page of the query:"+employeePage.getNumberOfElements()); } /** * Paging and Sorting Function Testing */ @Test public void pageAndSort(){ Sort.Order order = new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.ASC,"id"); Sort sort = new Sort(order); // page: index starts at 0, not from 1 Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(0,5,sort); Page<Employee> employeePage = employeePagingAndSortingRepository.findAll(pageable); System.out.println("Total number of pages queried:"+employeePage.getTotalPages()); System.out.println("Total number of records queried:"+employeePage.getTotalElements()); System.out.println("The current page of the query:"+(employeePage.getNumber() + 1)); System.out.println("A collection of the current pages of the query:"+employeePage.getContent()); System.out.println("Number of records on the current page of the query:"+employeePage.getNumberOfElements()); } }
5-3 JpaRepository Interface Use Details
JpaRepository Interface Use Details
finaAll: Query all records findAll(Sort sort): Query all records and sort them save(entities): Save multiple entity objects fiush: deleteInBatch(entities): Delete those entities in a batch
Code demonstration:
1. Writing Employee Jpa Repository Interface
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain.Employee; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository; /** * Using the JpaRepository interface * Created by ZC on 2017/4/26. */ public interface EmployeeJpaRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee,Integer> { }
2. Writing Employee Jpa Repository Test Unit Test Class
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.config.SpringConfig; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain.Employee; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository.EmployeeJpaRepository; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.data.domain.Page; import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest; import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable; import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository; /** * EmployeeJpaRepository Unit test class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/26. */ public class EmployeeJpaRepositoryTest { private ApplicationContext ctx = null; private EmployeeJpaRepository employeeJpaRepository = null; @Before public void init(){ ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); employeeJpaRepository = ctx.getBean(EmployeeJpaRepository.class); } @After public void destroy(){ ctx = null; } @Test public void findTest(){ Employee employee = employeeJpaRepository.findOne(99); System.out.println("employee"+employee.toString()); System.out.println("employee(10)"+employeeJpaRepository.exists(10)); System.out.println("employee(102)"+employeeJpaRepository.exists(102)); } }
5-4 Jpa Specification Executor Interface Use Details
Jpa Specification Executor Interface Use Details
Specification encapsulates JPA Criteria query conditions
Code demonstration:
1. Writing Employee Jpa Specification Executor Interface
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain.Employee; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor; /** * Using the JpaSpecification Executor interface * Created by ZC on 2017/4/26. */ public interface EmployeeJpaSpecificationExecutor extends JpaRepository<Employee,Integer> , JpaSpecificationExecutor<Employee>{ }
2. Write the Employee Jpa Specification ExecutorTest unit test class
package com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.repository; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.config.SpringConfig; import com.myimooc.springdata.jpa.domain.Employee; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.data.domain.Page; import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest; import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable; import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort; import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.Specification; import javax.persistence.criteria.*; /** * EmployeeJpaSpecificationExecutor Unit test class * Created by ZC on 2017/4/26. */ public class EmployeeJpaSpecificationExecutorTest { private ApplicationContext ctx = null; private EmployeeJpaSpecificationExecutor employeeJpaSpecificationExecutor = null; @Before public void init(){ ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); employeeJpaSpecificationExecutor = ctx.getBean(EmployeeJpaSpecificationExecutor.class); } @After public void destroy(){ ctx = null; } /** * 1,paging * 2,sort * 3,Query condition: age > 50 */ @Test public void queryTest(){ Sort.Order order = new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.DESC,"id"); Sort sort = new Sort(order); // page: index starts at 0, not from 1 Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(0,5,sort); /** * root : That's the type we want to query (Employee) * query : Adding query conditions * cb : Building Predicate */ Specification<Employee> specification = new Specification<Employee>() { // query criteria public Predicate toPredicate(Root<Employee> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) { // root (employee (age)) Path path = root.get("age"); return cb.gt(path,50); } }; Page<Employee> employeePage = employeeJpaSpecificationExecutor.findAll(specification,pageable); System.out.println("Total number of pages queried:"+employeePage.getTotalPages()); System.out.println("Total number of records queried:"+employeePage.getTotalElements()); System.out.println("The current page of the query:"+(employeePage.getNumber() + 1)); System.out.println("A collection of the current pages of the query:"+employeePage.getContent()); System.out.println("Number of records on the current page of the query:"+employeePage.getNumberOfElements()); } }
Chapter Six: Summary of Courses
6-4 Course Summary
Course summary
Overview of Spring Data Traditional access to databases Spring Data Quick Start Spring Data JPA Advancement Spring Data JAP Advanced