In a row of dominoes, A[i] and B[i] represent the top half and bottom half of the ith dominoes, respectively. (a domino is composed of two numbers from 1 to 6 that are tiled in the same column - one on each half of the tile.)
We can rotate the i-th domino so that the values of A[i] and B[i] are exchanged.
Returns the minimum number of rotations that can make all values in A or all values in B the same.
If not, return to -1
Example 1:
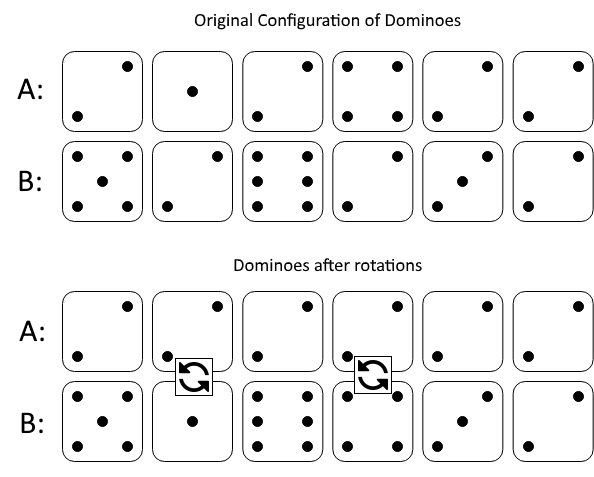
Input: A = [2,1,2,4,2,2], B = [5,2,6,2,3,2] Output: 2 Interpretation: Figure 1 shows the dominoes given by A and B before we rotate. If we rotate the second and fourth dominoes, we can make each value in the above row equal to 2, as shown in Figure 2.
Example 2:
Input: A = [3,5,1,2,3], B = [3,6,3,3,4] Output: -1 Interpretation: In this case, it is not possible to rotate the domino to make a row equal.
Tips:
1 <= A[i], B[i] <= 6
2 <= A.length == B.length <= 20000
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minDominoRotations(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B)
{
int n=A.size();
int m=B.size();
if(m!=n)
{
return -1;
}
vector<int> tmp(7,0);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(A[i]==B[i])
{
tmp[A[i]]++;
}
else
{
tmp[A[i]]++;
tmp[B[i]]++;
}
}
int flag=1;
int val=0;
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++)
{
if(n==tmp[i])
{
val=i;
flag=0;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
int up=0;
int same=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(A[i]==B[i])
{
same++;
}
else
{
if(val==A[i])
{
up++;
}
}
}
return min(up,n-same-up);
}
}
};python
class Solution:
def minDominoRotations(self, A: List[int], B: List[int]) -> int:
n=len(A)
m=len(B)
if m!=n:
return -1
tmp=[0 for i in range(7)]
for i in range(n):
if A[i]==B[i]:
tmp[A[i]]+=1
else:
tmp[A[i]]+=1
tmp[B[i]]+=1
flag=1
val=0
for i in range(1,7):
if n==tmp[i]:
flag=0
val=i
break
if flag:
return -1
else:
up=0
same=0
for i in range(n):
if A[i]==B[i]:
same+=1
else:
if A[i]==val:
up+=1
return min(up,n-same-up)