Linked list
1, Concept of linked list
- A linked list is an ordered list, but the nodes of the linked list are not necessarily continuous in memory.
- The following figure shows the storage structure of linked list in memory
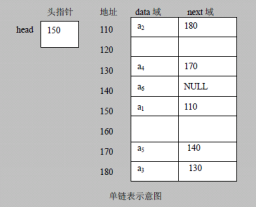
Summary:
a. Linked list is stored in the form of nodes and linked storage
b. Each node contains the data field (stored value) and the next field (pointing to the next node)
c. The nodes of the linked list are not necessarily stored continuously
d. The linked list is divided into the linked list with the leading node and the linked list without the leading node, which is determined according to the actual needs
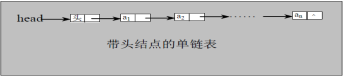
2, Single linked list
-
Schematic diagram of logical structure of single linked list (leading node), which is actually discontinuous
.
-
The creation of a single linked list is not added by number, and the header node is written only once. The idea analysis is as follows
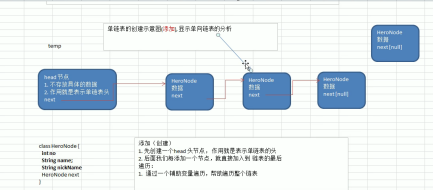
-
The above explains how to create a linked list, which requires a header node (not moving), data and next field. At this time, we create a class to represent the single linked list, and then write the methods of addition, deletion, modification and query to realize a complete linked list. We have manipulated the single linked list
-
Add nodes to the single linked list, regardless of number
//Add nodes to a one-way linked list when the order of numbers is not considered
//1. Find the last node of the current linked list
//2. Point the next of the last node to the new node
public void add(HerNode herNode){
//Because the head node cannot be moved, an auxiliary variable temp is required
HerNode temp = head;
//Traverse the linked list to find the last
while (true){
//Judge whether the current node is the last
if (temp.next==null){
break;
}
//If the last is not found, move temp backward to find the next one
temp=temp.next;
}
//When exiting the while loop, temp points to the end of the linked list
temp.next=herNode;
}
- When considering numbering, insert nodes into the single linked list and analyze the idea
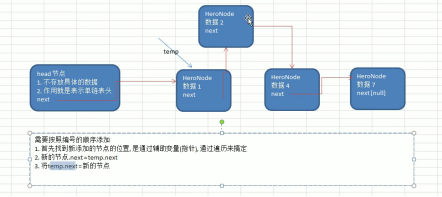
Code implementation:
//When considering numbering sequence
public void addOrder(HerNode herNode){
//Because the head node cannot be moved, we need to use an auxiliary variable to help find the added location
//Because it is a single linked list, the temp we are looking for is the previous node in the add location, otherwise it cannot be inserted
HerNode temp =head;
boolean flag= false;//It is used to mark whether the added number already exists. The default value is false
while (true){
if (temp.next==null){//Note that temp is at the end of the linked list
break;
}
if (temp.next.no>herNode.no){//Find the location and insert it right after temp
break;
}else if (temp.next.no==herNode.no){//Indicates that the number of the heroNode you want to add already exists
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;//Move backward to traverse the current linked list
}
//Judge the value of flag
if (flag){
System.out.printf("Your hero%d Already exists\n",herNode.no);
}else {
//Insert it into the linked list, after temp
herNode.next=temp.next;//The currently inserted node points to the next bit of temp
temp.next=herNode;//temp points to the new node, which is inserted in the middle.
}
}
- Modify the node and code directly
//Modify node
public void update(HerNode newNode){
//Judge whether it is empty
if (head.next==null){
System.out.println("The linked list is empty");
return;
}
//Find the modified node through traversal
HerNode temp=head.next;
boolean flag =false;//Indicates whether the node was found
while (true){
if (temp==null){
break;//Traversal completed
}
if (temp.no== newNode.no){
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
if (flag){
temp.name=newNode.name;
temp.nickName=newNode.nickName;
}else {
System.out.printf("No number found%d Node of",newNode.no);
}
}
- Delete node
a. Idea:
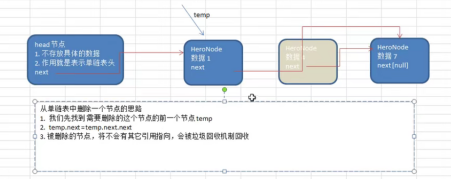
b. Code implementation
//Delete node
//Idea: the head node cannot be moved. We need an auxiliary variable to help us find the previous node of the node to be deleted
// In comparison, it is temp next. Compare no with node no to be deleted
public void delete(int no){
HerNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;//Indicates whether the node to be deleted is found
while (true){
if (temp.next==null){//It has reached the end of the linked list
break;
}
if (temp.next.no==no){//Find the previous node temp of the node to be deleted
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
if (flag){
//delete
temp.next=temp.next.next;
}else {
System.out.println("The node to be deleted does not exist...");
}
}
8. Query the linked list, and query the node data in the linked list according to id or no,
a. Idea: use while traversal until you know the last one. Remember to point to the next after traversal, and then traverse.
b. Code implementation
//Display linked list
public void list(){
//Determine whether the linked list is empty
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("The linked list is empty!");
return;
}
//If it is not empty, there is at least one node, so the traversal starts from the second node,
// The head node cannot be moved, so you need an auxiliary variable to traverse
HerNode temp = head.next;
while (true){
//To the end of the linked list
if (temp==null){
System.out.println("Traverse to the last jump");
break;
}
//Output information of current node
System.out.println(temp);
//Move temp backward to determine the next output
temp=temp.next;
}
}
c. Query nodes according to no
//Query linked list according to code
public void getByNo(int no){
//Determine whether the linked list is empty
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("The linked list is empty!");
return;
}
//If it is not empty, there is at least one node, so the traversal starts from the second node,
// The head node cannot be moved, so you need an auxiliary variable to traverse
HerNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag=false;//Determine whether to find
while (true){
//To the end of the linked list
if (temp==null){
System.out.println("Traverse to the last jump");
break;
}
if (temp.no==no){
flag=true;//existence
break;
}
//Move temp backward to determine the next output
temp=temp.next;
}
if (flag){
System.out.println(temp);
}else {
System.out.println("The number you entered does not exist");
}
}
3, Test code
package linkedlist;
import java.util.Stack;
public class SingleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//test
HerNode hero1 = new HerNode(1, "Song Jiang", "Timely rain");
HerNode hero2 = new HerNode(2, "Lu Junyi", "Jade Kirin");
HerNode hero3 = new HerNode(3, "Wu Yong", "Zhiduoxing");
HerNode hero4 = new HerNode(4, "Lin Chong", "Leopard head");
HerNode hero5 = new HerNode(4, "Lin Chong 2", "Leopard head 2");
//Create a linked list
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList2 = new SingleLinkedList();
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList3 = new SingleLinkedList();
//Join out of order
singleLinkedList.add(hero1);
singleLinkedList.add(hero3);
singleLinkedList2.add(hero2);
singleLinkedList2.add(hero4);
//Merge into a new linked list
HerNode merge = merge(singleLinkedList.getHead(), singleLinkedList2.getHead());
show(merge);
/*System.out.println("Original linked list "");
singleLinkedList.list();
System.out.println("Linked list printed in reverse order ");
reversePrint(singleLinkedList.getHead());
System.out.println("Inverted linked list "");
reversetList(singleLinkedList.getHead());
singleLinkedList.list();*/
/*//Join in order
singleLinkedList.addOrder(hero1);
singleLinkedList.addOrder(hero3);
singleLinkedList.addOrder(hero4);
singleLinkedList.addOrder(hero2);
System.out.println("");
singleLinkedList.list();
singleLinkedList.update(hero5);
System.out.println("");
singleLinkedList.list();
System.out.println("");
singleLinkedList.delete(4);
singleLinkedList.list();
System.out.println("Records queried according to the number ");
singleLinkedList.getByNo(1);
System.out.println("The valid number of single linked lists is: "+ getlength (singlelinkedlist. Gethead());
System.out.println("Find the penultimate node in the single linked list: "+ getNode(singleLinkedList.getHead(),1));*/
}
//Query the linked list through a header node
public static void show(HerNode head) {
HerNode cur = head.next;
if (cur == null) {
System.out.println("The linked list is empty~");
}
while (cur != null) {
System.out.println(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
}
//Define a SIngleLinkedList to manage our heroes
class SingleLinkedList{
//Initialize a header node. The header node does not move and does not store specific data
private HerNode head = new HerNode(0,"","");
//Return header node
public HerNode getHead(){
return head;
}
//Add nodes to a one-way linked list when the order of numbers is not considered
//1. Find the last node of the current linked list
//2. Point the next of the last node to the new node
public void add(HerNode herNode){
//Because the head node cannot be moved, an auxiliary variable temp is required
HerNode temp = head;
//Traverse the linked list to find the last
while (true){
//Judge whether the current node is the last
if (temp.next==null){
break;
}
//If the last is not found, move temp backward to find the next one
temp=temp.next;
}
//When exiting the while loop, temp points to the end of the linked list
temp.next=herNode;
}
//When considering numbering sequence
public void addOrder(HerNode herNode){
//Because the head node cannot be moved, we need to use an auxiliary variable to help find the added location
//Because it is a single linked list, the temp we are looking for is the previous node in the add location, otherwise it cannot be inserted
HerNode temp =head;
boolean flag= false;//It is used to mark whether the added number already exists. The default value is false
while (true){
if (temp.next==null){//Note that temp is at the end of the linked list
break;
}
if (temp.next.no>herNode.no){//Find the location and insert it right after temp
break;
}else if (temp.next.no==herNode.no){//Indicates that the number of the heroNode you want to add already exists
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;//Move backward to traverse the current linked list
}
//Judge the value of flag
if (flag){
System.out.printf("Your hero%d Already exists\n",herNode.no);
}else {
//Insert it into the linked list, after temp
herNode.next=temp.next;//The currently inserted node points to the next bit of temp
temp.next=herNode;//temp points to the new node, which is inserted in the middle.
}
}
//Modify node
public void update(HerNode newNode){
//Judge whether it is empty
if (head.next==null){
System.out.println("The linked list is empty");
return;
}
//Find the modified node through traversal
HerNode temp=head.next;
boolean flag =false;//Indicates whether the node was found
while (true){
if (temp==null){
break;//Traversal completed
}
if (temp.no== newNode.no){
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
if (flag){
temp.name=newNode.name;
temp.nickName=newNode.nickName;
}else {
System.out.printf("No number found%d Node of",newNode.no);
}
}
//Delete node
//Idea: the head node cannot be moved. We need an auxiliary variable to help us find the previous node of the node to be deleted
// In comparison, it is temp next. Compare no with node no to be deleted
public void delete(int no){
HerNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;//Indicates whether the node to be deleted is found
while (true){
if (temp.next==null){//It has reached the end of the linked list
break;
}
if (temp.next.no==no){//Find the previous node temp of the node to be deleted
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
if (flag){
//delete
temp.next=temp.next.next;
}else {
System.out.println("The node to be deleted does not exist...");
}
}
//Display linked list
public void list(){
//Determine whether the linked list is empty
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("The linked list is empty!");
return;
}
//If it is not empty, there is at least one node, so the traversal starts from the second node,
// The head node cannot be moved, so you need an auxiliary variable to traverse
HerNode temp = head.next;
while (true){
//To the end of the linked list
if (temp==null){
System.out.println("Traverse to the last jump");
break;
}
//Output information of current node
System.out.println(temp);
//Move temp backward to determine the next output
temp=temp.next;
}
}
//Query linked list according to code
public void getByNo(int no){
//Determine whether the linked list is empty
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("The linked list is empty!");
return;
}
//If it is not empty, there is at least one node, so the traversal starts from the second node,
// The head node cannot be moved, so you need an auxiliary variable to traverse
HerNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag=false;//Determine whether to find
while (true){
//To the end of the linked list
if (temp==null){
System.out.println("Traverse to the last jump");
break;
}
if (temp.no==no){
flag=true;//existence
break;
}
//Move temp backward to determine the next output
temp=temp.next;
}
if (flag){
System.out.println(temp);
}else {
System.out.println("The number you entered does not exist");
}
}
}
//Define a heroNode, and each node object is a node
class HerNode{
public int no;
public String name;
public String nickName;
public HerNode next;//Point to next node
//constructor
public HerNode(int no,String name,String nickName){
this.no=no;
this.name=name;
this.nickName=nickName;
}
public HerNode(){};
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HerNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", nickName='" + nickName + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
4, Interview questions
1, Find the number of effective nodes in the single linked list (if you take the lead in the linked list, do not add Statistics)
/**
* Find the number of effective nodes in the single linked list (if you take the lead in the linked list, do not add Statistics)
* @param head Head node of linked list
* @return
*/
public static int getLength(HerNode head){
if (head.next==null){
return 0;
}
//Define an auxiliary variable without statistics header node
HerNode temp = head.next;
int count=0;
while (temp!=null){
count++;
temp=temp.next;//ergodic
}
return count;
}
2, Find the penultimate node in the single lin k ed list [Sina interview question]
, the length of getLength inside, that is, the number of valid nodes above.
/**
* Find the penultimate node in the single lin k ed list [Sina interview question]
* @param head Head node
* @param num Value entered
* @return
*/
public static HerNode getNode(HerNode head, int num){
//Judge whether it is empty
if (head.next==null){
return null;//Can't find
}
//Length of the first traversal
int size = getLength(head);
//The position of size num is the penultimate node
if (num<=0 || num>size){
return null;
}
//Define an auxiliary variable to help us traverse
HerNode cur =head.next;
for (int i = 0; i < size-num; i++) {
cur=cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
3, Reversal of single linked list [Tencent interview question, a little difficult]
/**
* Reversal of single linked list [Tencent interview question, a little difficult]
* @param head
*/
public static void reversetList(HerNode head) {
//① If the current linked list is empty or there is only one node, we do not need to reverse and return directly
if (head.next==null || head.next.next==null){
return;
}
// ② Define an auxiliary variable to help us traverse the original linked list
HerNode temp =head.next;
HerNode next = null;//Point to the next node of the current node [temp]
HerNode reverseHead= new HerNode(0,"","");
// ③ Traverse the original linked list. Every time you traverse a node, take it out and put it at the front of the new linked list reverseHead
while (temp!=null){
next=temp.next;//Temporarily save the next node of the current node, which needs to be used later
temp.next=reverseHead.next; //Point the next node of temp to the front end of the new linked list
reverseHead.next=temp; //Connect the extracted nodes to the new linked list
temp=next;//Move temp back
}
//Put head Next points to reversehead Next, reverse
head.next=reverseHead.next;
}
4, Print the single linked list from end to end [Baidu, requires method 1: reverse traversal (which will destroy the original single linked list structure). Method 2: Stack]
/**
* Print the single linked list from end to end [Baidu, requires method 1: reverse traversal. Method 2: Stack]
* Use mode 2 to implement mode 2. stack first in and last out
* @param head
*/
public static void reversePrint(HerNode head){
if (head.next==null){//Empty linked list cannot be printed
return;
}
//Create a stack, press the node into the stack, and then take it out
Stack<HerNode> stack = new Stack<>();
HerNode cur = head.next;
//Push into stack
while (cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
//Move back and press the next one
cur=cur.next;
}
//Print the nodes in the stack and print them out of the stack
while (stack.size()>0){
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
5, Merge two ordered single linked lists, and the merged linked list is still in order
/**
* Merge two ordered single linked lists, and the merged linked list is still in order
*/
public static HerNode merge(HerNode herNode1, HerNode herNode2) {
if (herNode1.next == null) {
return herNode2;
} else if (herNode2.next == null) {
return herNode1;
}
HerNode newNode = new HerNode();
HerNode n1 = newNode;
HerNode l1 = herNode1.next;
HerNode l2 = herNode2.next;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.no < l2.no) {
n1.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
n1 = n1.next;
} else {
n1.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
n1 = n1.next;
}
}
if (l1 == null) {
n1.next = l2;
}
if (l2 == null) {
n1.next = l1;
}
return newNode;
}