1, Disk Foundation
1.1 disk structure
- Physical structure of hard disk
- Disc: the hard disk has multiple discs, each disc has 2 sides
- Magnetic head: one magnetic head on each side
- Data structure of hard disk
- Sector: the disk is divided into multiple sector areas, and each sector stores five 12 bytes of data
- Track: concentric circles with different radii on the same disk
- Cylindrical surface: a cylindrical surface composed of different discs with the same radius
- Hard disk storage capacity = number of heads × Number of tracks (cylinders) × Sectors Per Trark × Bytes per sector
- Cylinder / head / sector can be used to uniquely locate each area on the disk
- Disk interface type
- IDE, SATA, SCSI, SAS, fibre channel
- MBR and disk partition representation
- Master Boot Record (MBR)
- The MBR is located in the first physical sector of the hard disk
- MBR contains the main boot program of the hard disk and the hard disk partition table
- The partition table has four partition record areas, and each partition record area accounts for 16 bytes
- Linux represents hard disk, partition and other devices as files

1.2 disk partition structure
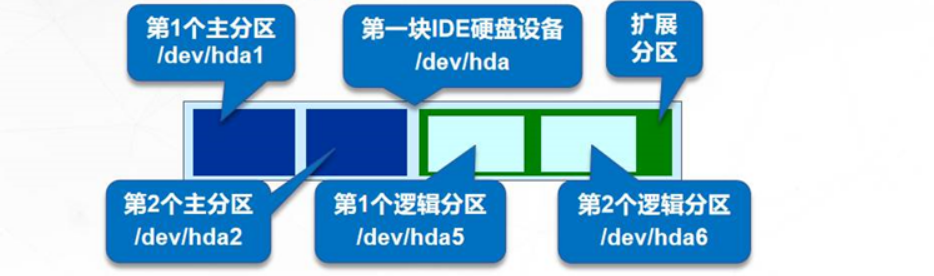
- The number of primary partitions in the hard disk is only 4
- The serial numbers of primary and extended partitions are limited to 1 ~ 4
- The extended partition is subdivided into logical partitions
- The logical partition sequence number will always start with 5
2, File system type
- XFS file system
- Partition for storing file and directory data
- High performance log file system
- File system used by default in Centos 7 system
- SWAP, SWAP file system
- Creating swap partitions for Linux systems
- Other file system types supported by Linux
- FAT16 FAT32 NTFS EXT4 JFS...
3, Steps to add a hard disk under Linux
- Step 1: add a hard disk
- Step 2: partition
- Step 3: format
- Step 4: Mount
Add two hard disks sdb and sdc to the system
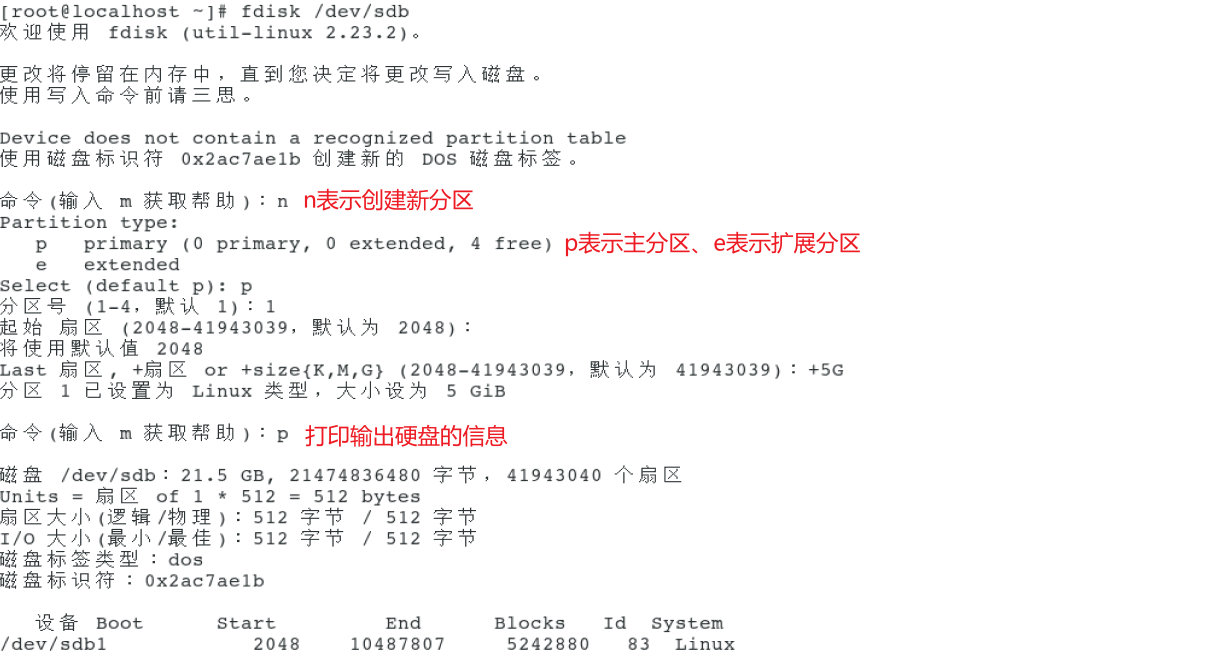
Partition the hard disk with fdisk command

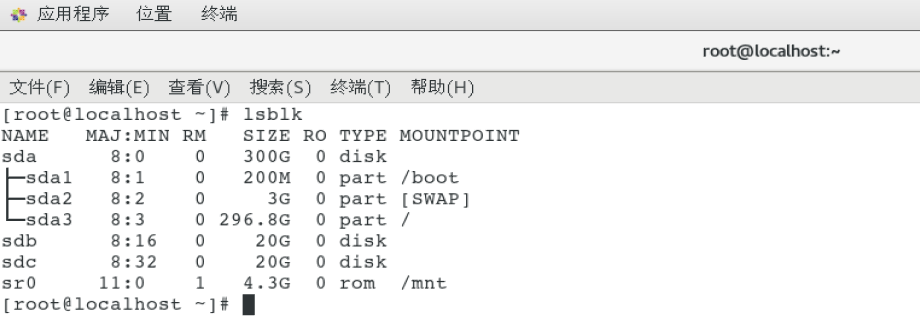
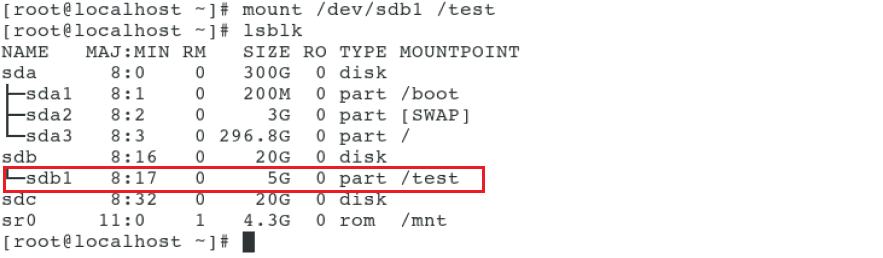
After the partition is completed, check the partition information. Use the lsblk command to view the hard disk information. - f means to view the details
The blkid command checks the formatted file types and UUIDs of all partitions in the system

Use the mkfs command to format the partition

Mount the partition with the mount command (mount is used for temporary mounting, and permanent mounting needs to be written into the configuration file / etc/fstab)
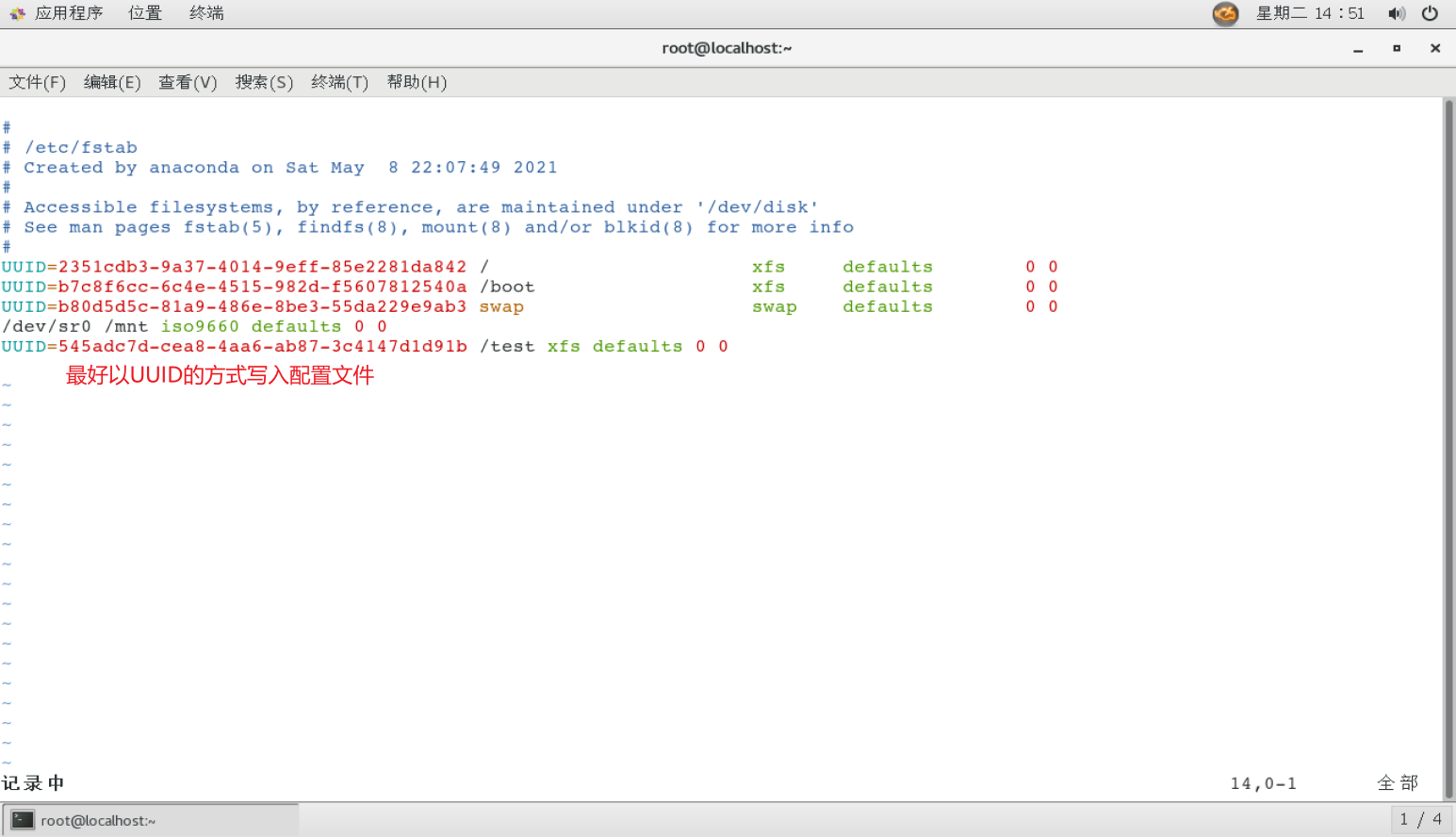
- Use mount -a to take the configuration file into effect immediately
- Use the umount command to unload parameters, which can be used with the partition or mount point umount /dev/sdb1 or umount /test
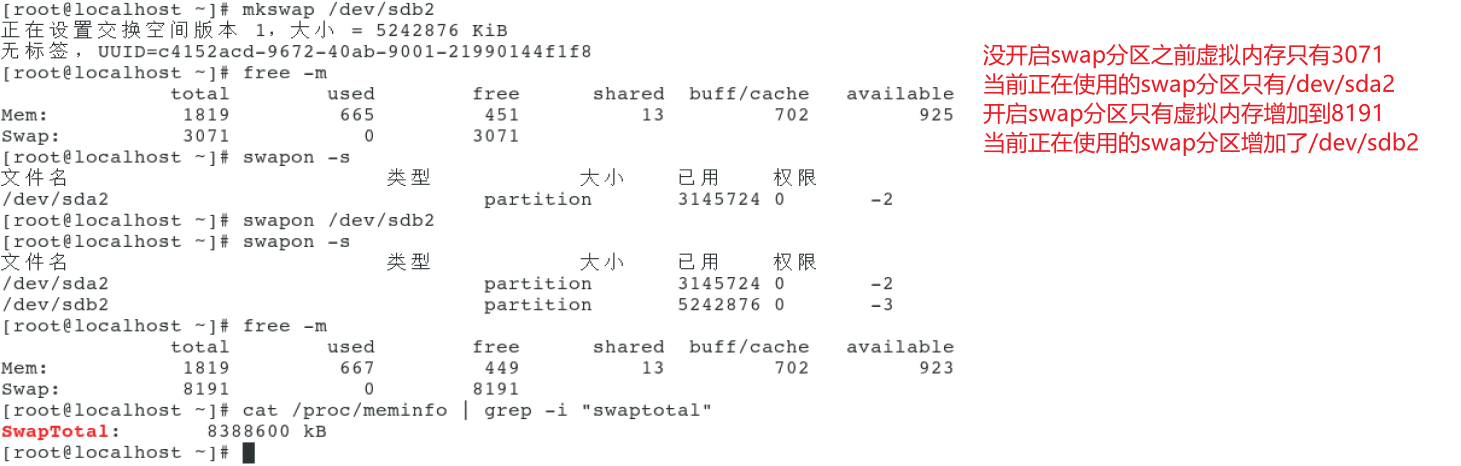
4, Add SWAP partition

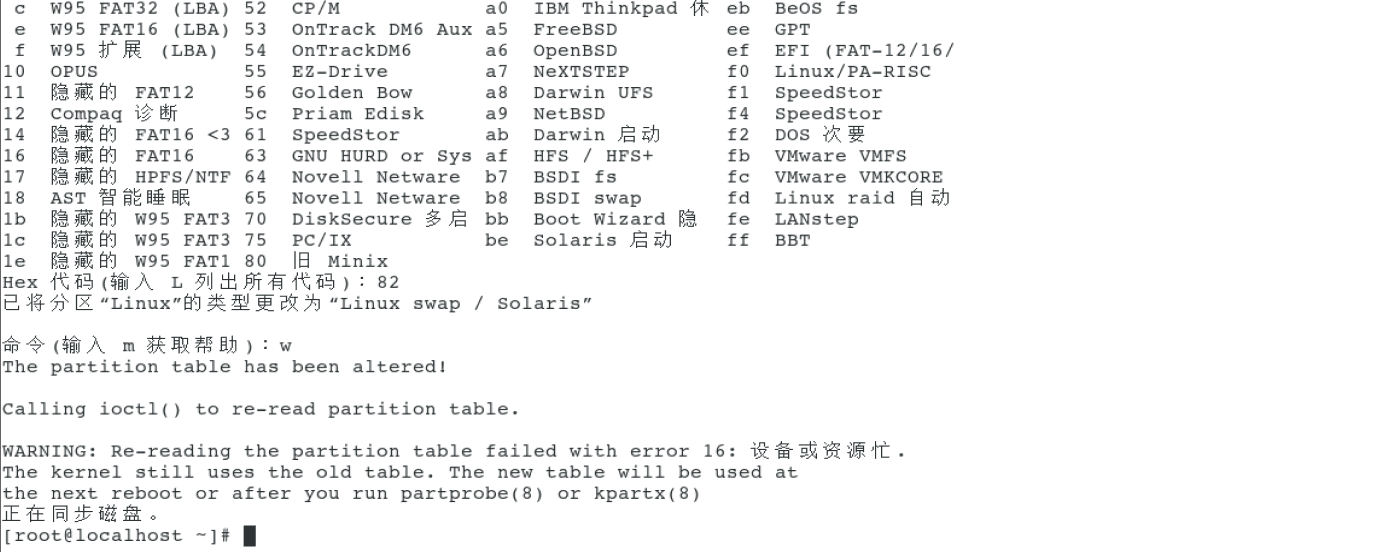
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
The changes remain in memory until you decide to write the changes to disk.
Think twice before using the write command.
command(input m get help): n
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (2-4,Default 2): 2
Start sector (10487808-41943039,The default is 10487808):
The default value 10487808 will be used
Last a sector, +a sector or +size{K,M,G} (10487808-41943039,The default is 41943039): +5G
Partition 2 is set to Linux Type, size set to 5 GiB
command(input m get help): t
Partition number (1,2,Default 2): 2
Hex code(input L List all codes): l
0 empty twenty-four NEC DOS 81 Minix / used Linu bf Solaris
1 FAT12 27 Hidden NTFS Win 82 Linux exchange / So c1 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
2 XENIX root 39 Plan 9 83 Linux c4 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
3 XENIX usr 3c PartitionMagic 84 OS/2 Hidden C: c6 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
4 FAT16 <32M 40 Venix 80286 85 Linux extend c7 Syrinx
5 extend 41 PPC PReP Boot 86 NTFS Volume set da Non file system data
6 FAT16 42 SFS 87 NTFS Volume set db CP/M / CTOS / .
7 HPFS/NTFS/exFAT 4d QNX4.x 88 Linux pure text de Dell tool
8 AIX 4e QNX4.x Part 2 8 e Linux LVM df BootIt
9 AIX Can start 4f QNX4.x Part 3 93 Amoeba e1 DOS visit
a OS/2 Launch manager 50 OnTrack DM 94 Amoeba BBT e3 DOS R/O
b W95 FAT32 51 OnTrack DM6 Aux 9f BSD/OS e4 SpeedStor
c W95 FAT32 (LBA) 52 CP/M a0 IBM Thinkpad Hugh eb BeOS fs
e W95 FAT16 (LBA) 53 OnTrack DM6 Aux a5 FreeBSD ee GPT
f W95 extend (LBA) 54 OnTrackDM6 a6 OpenBSD ef EFI (FAT-12/16/
10 OPUS 55 EZ-Drive a7 NeXTSTEP f0 Linux/PA-RISC
11 Hidden FAT12 56 Golden Bow a8 Darwin UFS f1 SpeedStor
12 Compaq diagnosis 5c Priam Edisk a9 NetBSD f4 SpeedStor
14 Hidden FAT16 <3 61 SpeedStor ab Darwin start-up f2 DOS secondary
16 Hidden FAT16 63 GNU HURD or Sys af HFS / HFS+ fb VMware VMFS
17 Hidden HPFS/NTF 64 Novell Netware b7 BSDI fs fc VMware VMKCORE
18 AST Intelligent sleep sixty-five Novell Netware b8 BSDI swap fd Linux raid automatic
1b Hidden W95 FAT3 70 DiskSecure Duoqi bb Boot Wizard latent fe LANstep
1c Hidden W95 FAT3 75 PC/IX be Solaris start-up ff BBT
1e Hidden W95 FAT1 80 used Minix
Hex code(input L List all codes): 82
Partitioned“ Linux"Change the type of to“ Linux swap / Solaris"
command(input m get help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: Device or resource busy.
The kernel still uses the old table. The new table will be used at
the next reboot or after you run partprobe(8) or kpartx(8)
Synchronizing disks.
[root@localhost ~]#
- Format swap swap partition using mkswap command