1, DHCP overview
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, which can dynamically assign IP address and subnet mask to clients. It uses ports 67 and 68 of udp, 68port for clients and 67port for server s
DHCP role
- Dynamically allocate IP addresses to reduce the workload of administrators and the possibility of incorrect input of IP addresses
- It automatically assigns addresses to a large number of clients, provides centralized management, and avoids IP address conflicts
- Improved IP address utilization
Main information of DHCP assignment
- IP address and subnet mask of network card
- Corresponding network address and broadcast address
- Default gateway address
- DNS server address
DHCP allocation method
- Auto assign: assign an IP address and use it permanently
- Manual assignment: the IP address is automatically assigned by the DHCP server administrator
- Dynamic allocation: give the assigned IP address a lease term, and release the IP address for other customers as soon as the time comes
DHCP lease process
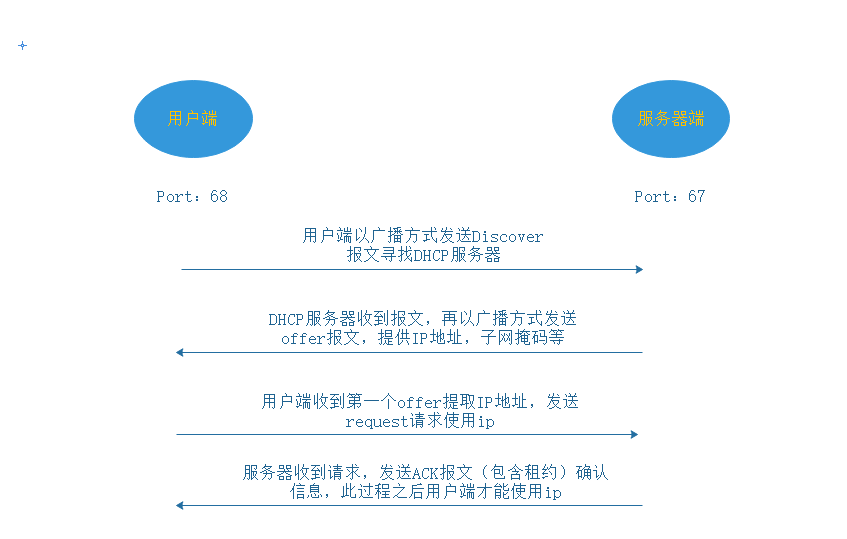
Update of DHCP lease
- When the IP address lease term reaches 50%, the client sends a Request to update the current IP address lease
- If the Request sent is a reply received, and the client continues to use the IP address until 87.5% of the lease term, send the Request again to follow the new lease
- If the server receives the request and replies, the client will first use the new IP address when the lease term of the original IP address runs out. If it still receives the reply from the server, it will release the IP address and resend the Discover message
Two, analog settings DHCP
Experimental equipment: a DHCP service is added to linux as a DHCP server, and win10 system and linux system are added to enable win10 and linux systems to dynamically obtain ip
[root@handsomeboy1 ~]# yum -y install dhcp / / download dhcp [root@handsomeboy1 ~]# vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf / / view this configuration file
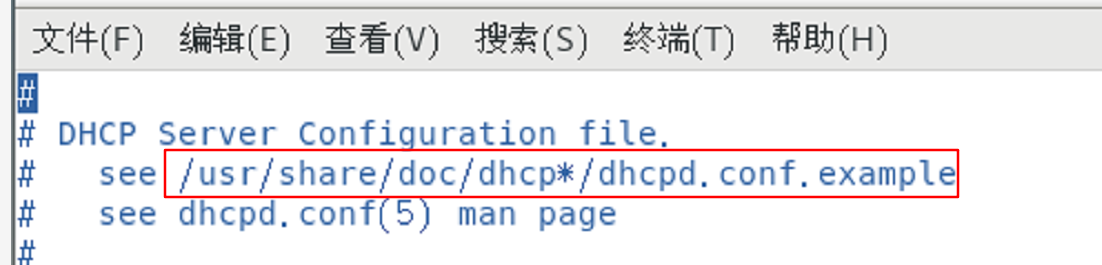
1. Set / etc / DHCP / chcpd Copy a copy of the file seen in conf to / etc / DHCP / chcpd In conf
[root@handsomeboy1 ~]# cp -p /usr/share/doc/dhcp*/dhcpd.conf.example /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf cp: Overwrite"/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf"? y [root@handsomeboy1 ~]# vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf / / copy the file before editing it
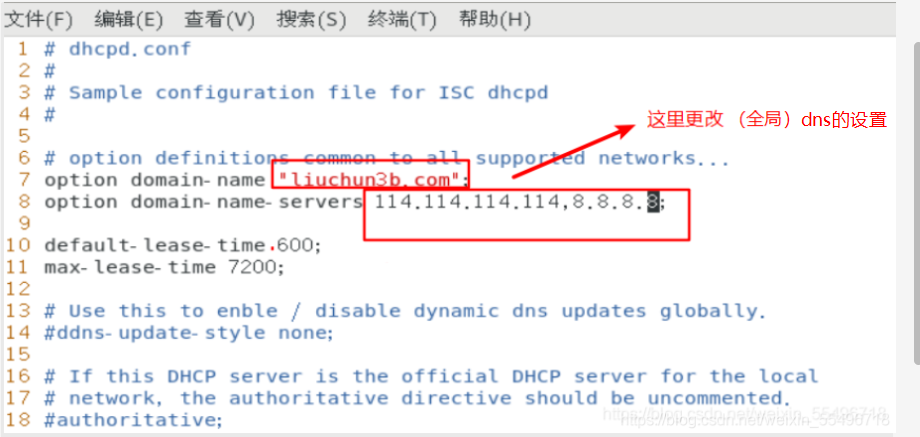
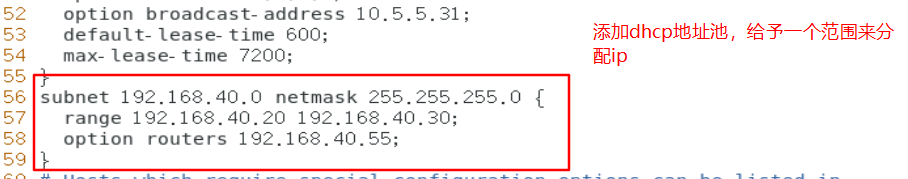
Then save and exit
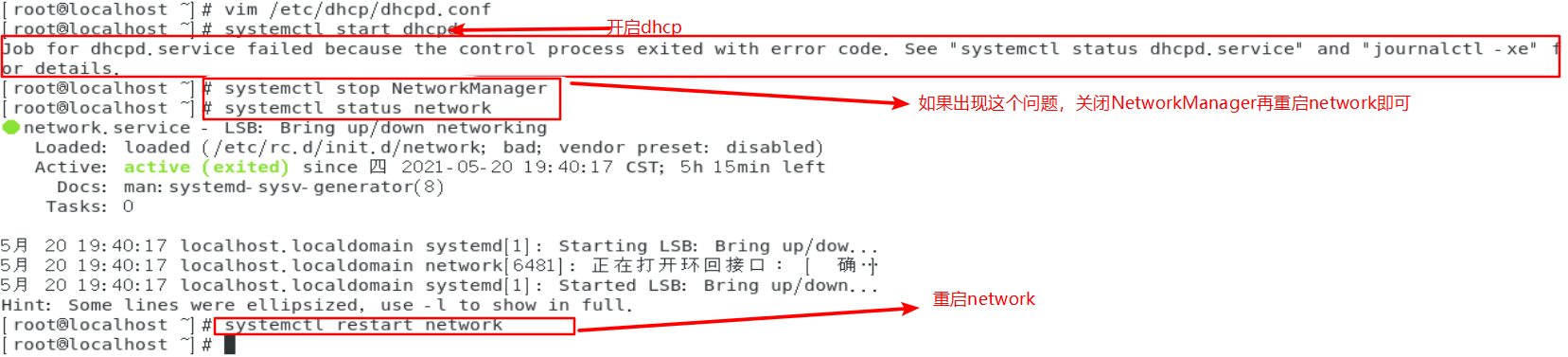
[root@localhost ~]# netstat -anup | grep dhcpd / / check whether dhcp is enabled udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:67 0.0.0.0:* 77457/dhcpd
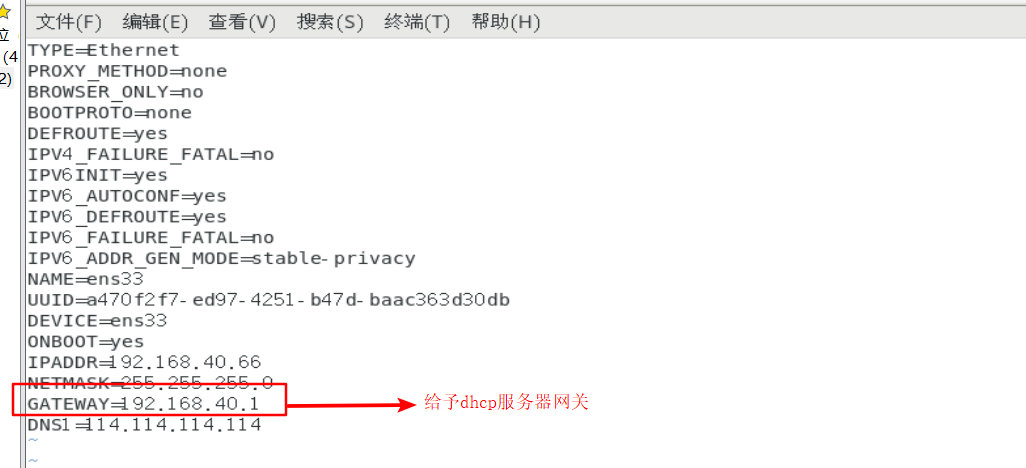
2. Set the ens33 network card of the DHCP server to a fixed ip according to the ip of VMnet1 (because VMnet1 host only mode will be used later), because as a DHCP server, DHCP can no longer be enabled to obtain addresses dynamically
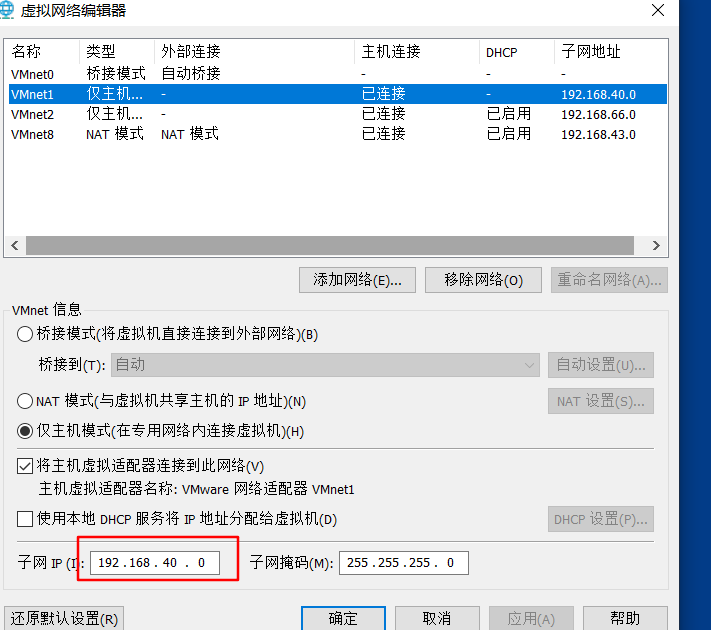
Note here that because DHCP of VMnet1 is not checked above, we need to create an IP address for VMnet1 of this machine, otherwise this machine cannot obtain vnnet1 IP address
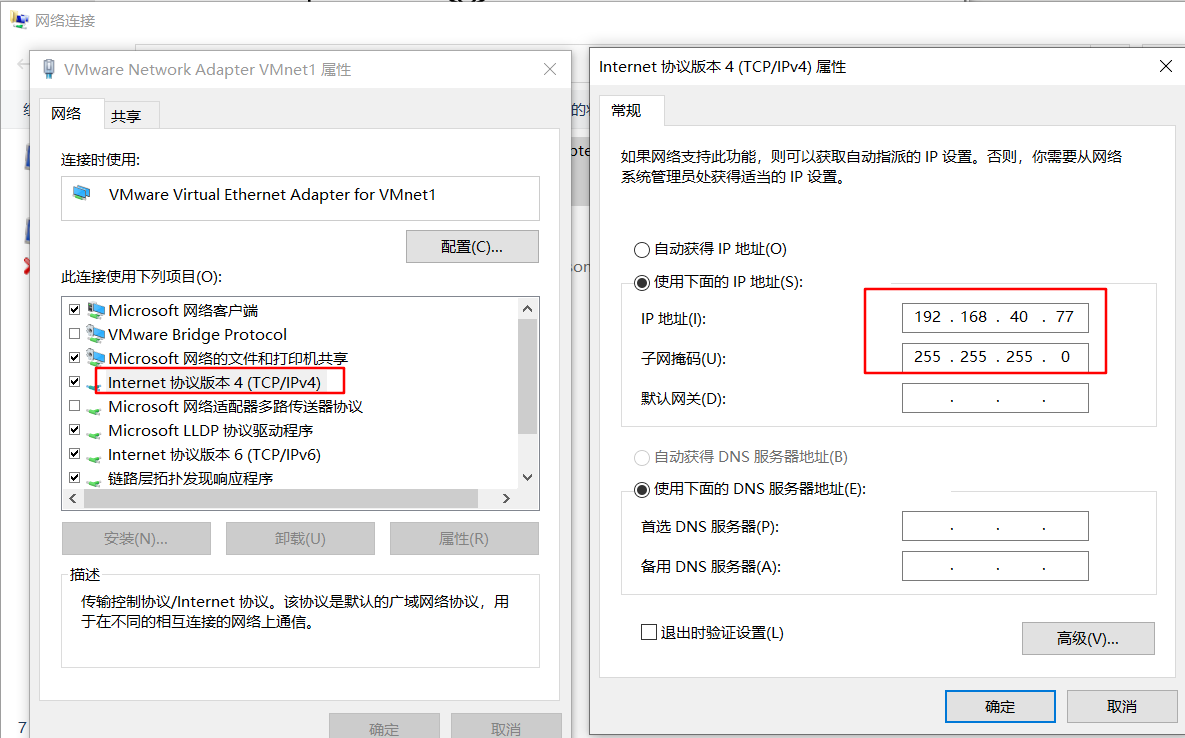
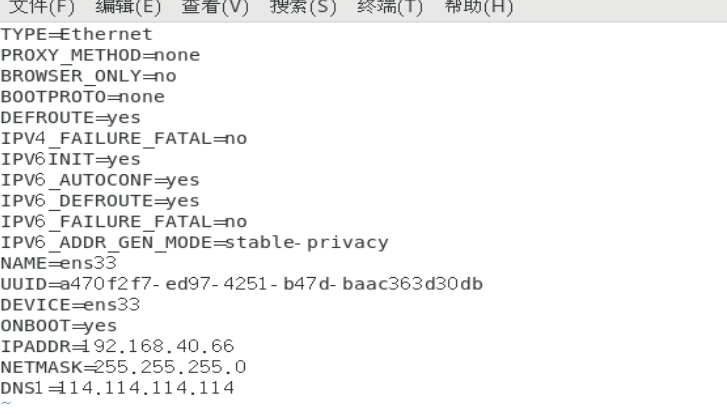
Set the network card configuration of dhcp server
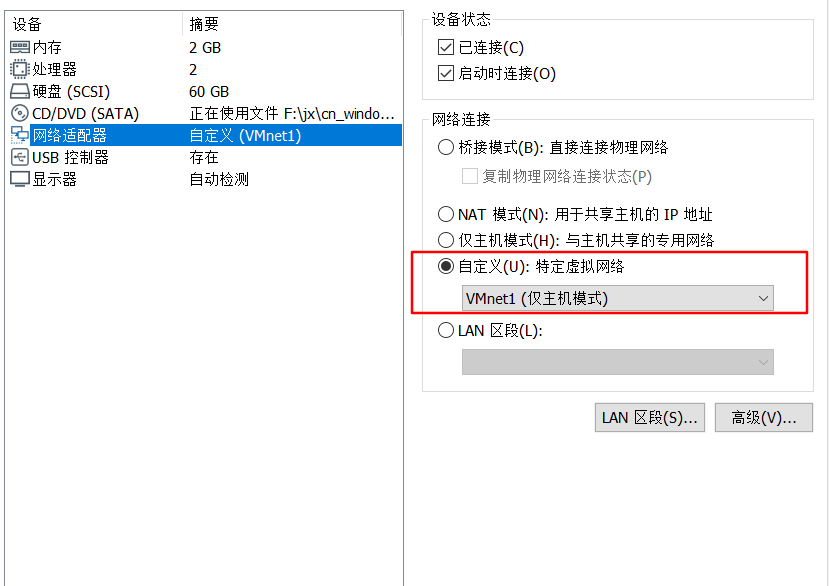
3. Then change its network adapter to host only VMnet1 (choose by yourself). Set the other two windows 10 and cengtos 7. The network adapter is also in host only mode of VMnet1
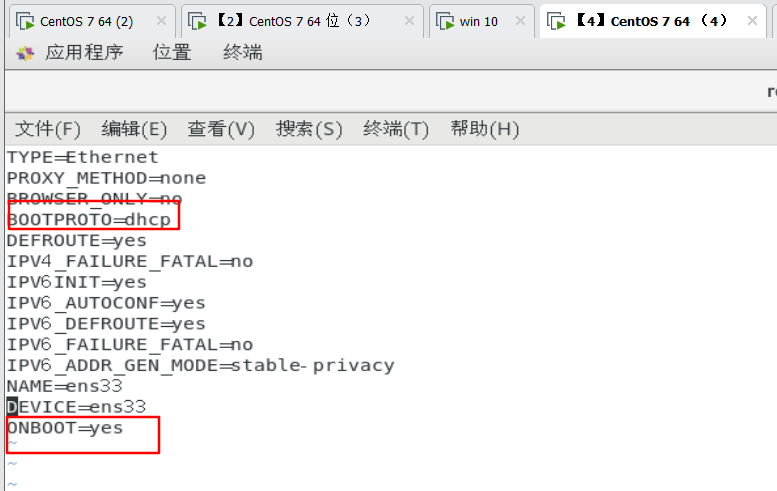
4. Set the network card configuration of another linux system to dhcp to obtain IP dynamically
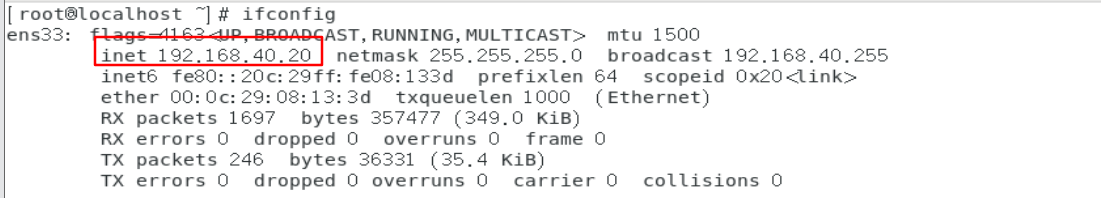
5. Check whether the other two win10 systems and linux systems obtain IP

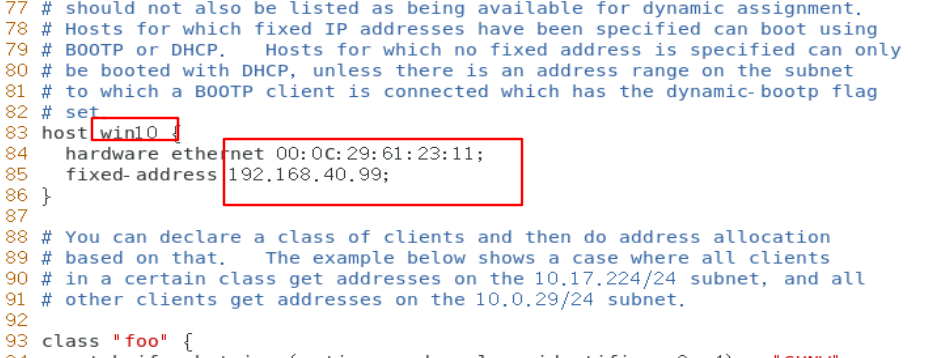
Small expansion: Based on the above, give fixed ip with win10 physical MAC address
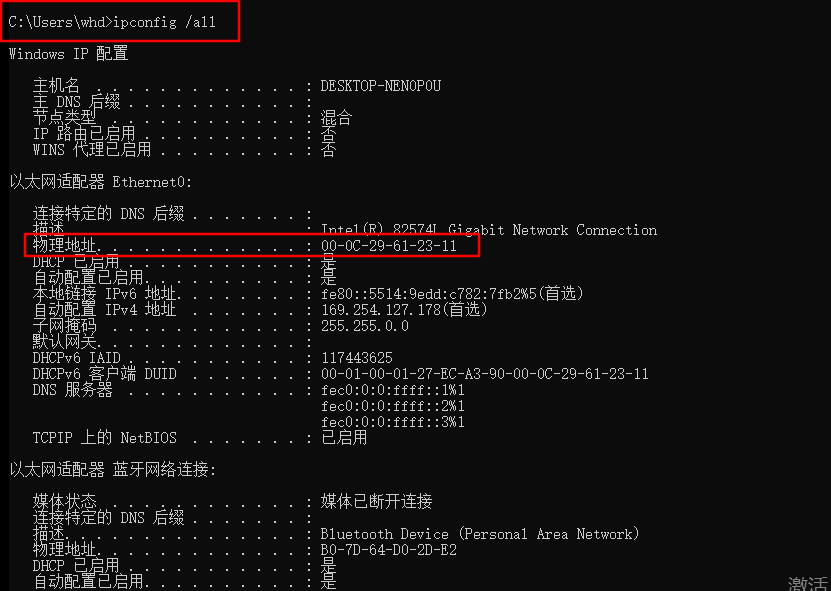
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
3, ensp connects the virtual machine to realize DHCP dynamic allocation of IP address
Preparation of experimental equipment: the dhcp server set above is used in linux, and the ensp equipment is as follows
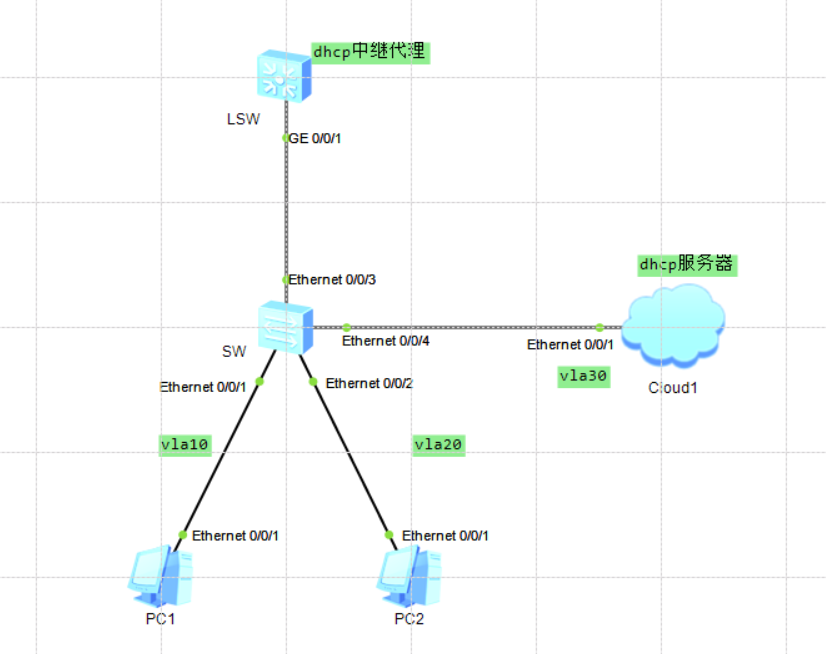
Configuration of each equipment:
1. PC1 and PC2 all enable dhcp to dynamically allocate ip addresses
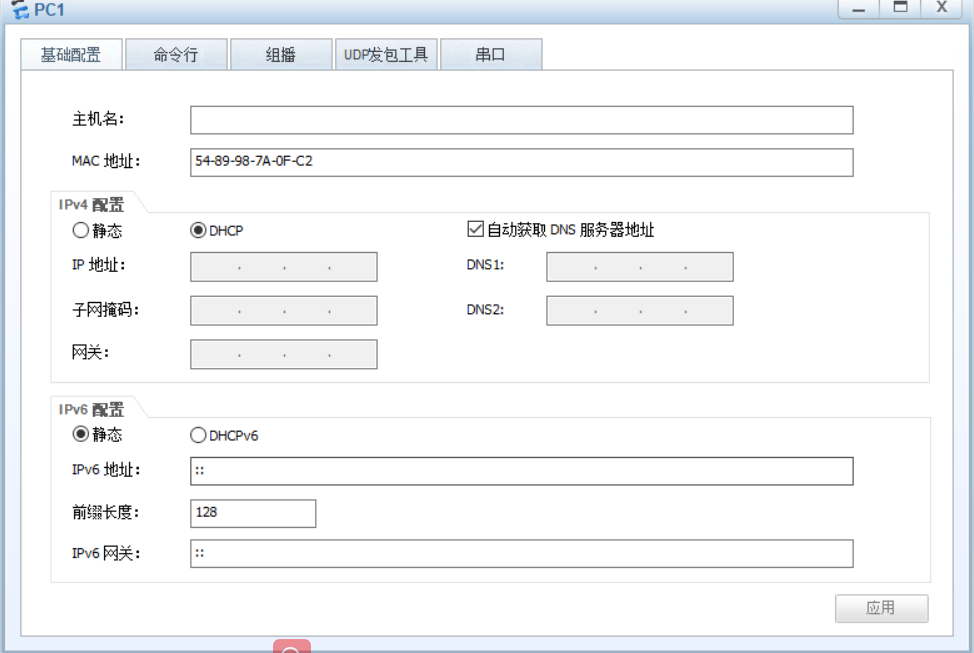

[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
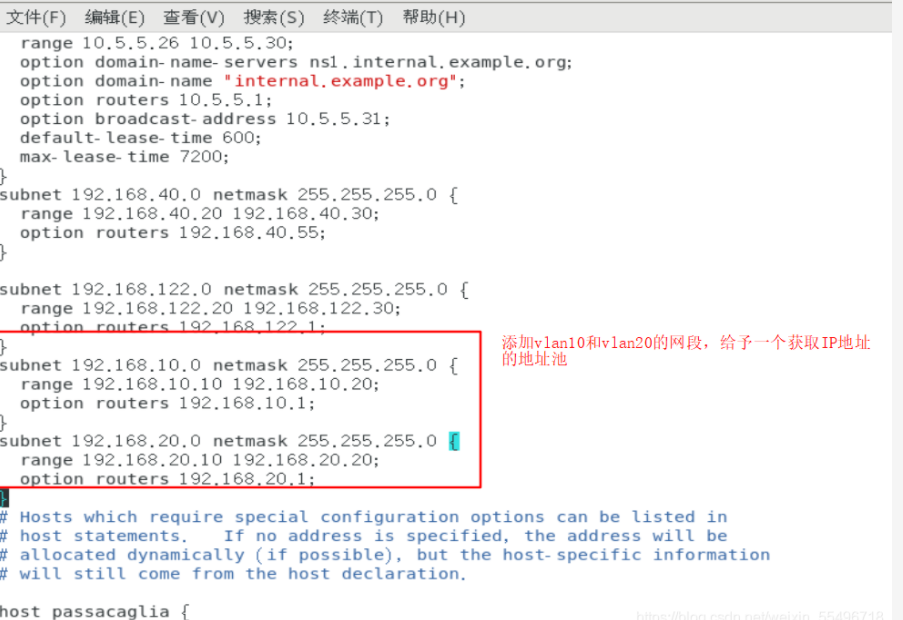
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart dhcpd. / / after modifying the service configuration, you need to restart [root@localhost ~]#systemctl restart network. / / after modifying the network card configuration, you need to restart the network
sw:
[sw]dis cu //View configuration vlan batch 10 20 30 interface Ethernet0/0/1 port link-type access port default vlan 10 # interface Ethernet0/0/2 port link-type access port default vlan 20 # interface Ethernet0/0/3 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 4094 # interface Ethernet0/0/4 port link-type access port default vlan 30 #
LSW:
[lsw]dis cu sysname lsw undo info-center enable vlan batch 10 20 30 dhcp enable interface Vlanif10 ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 dhcp select relay dhcp relay server-ip 192.168.40.66 //Specify dhcp server # interface Vlanif20 ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 dhcp select relay dhcp relay server-ip 192.168.40.66 # interface Vlanif30 ip address 192.168.40.1 255.255.255.0 dhcp select relay interface MEth0/0/1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 4094
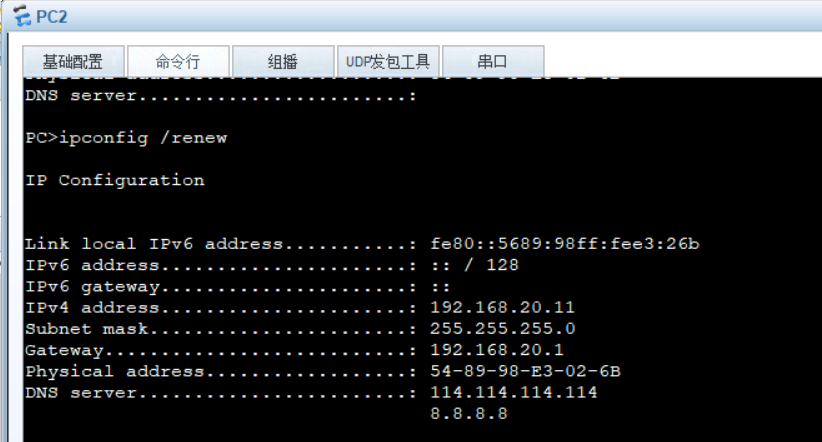
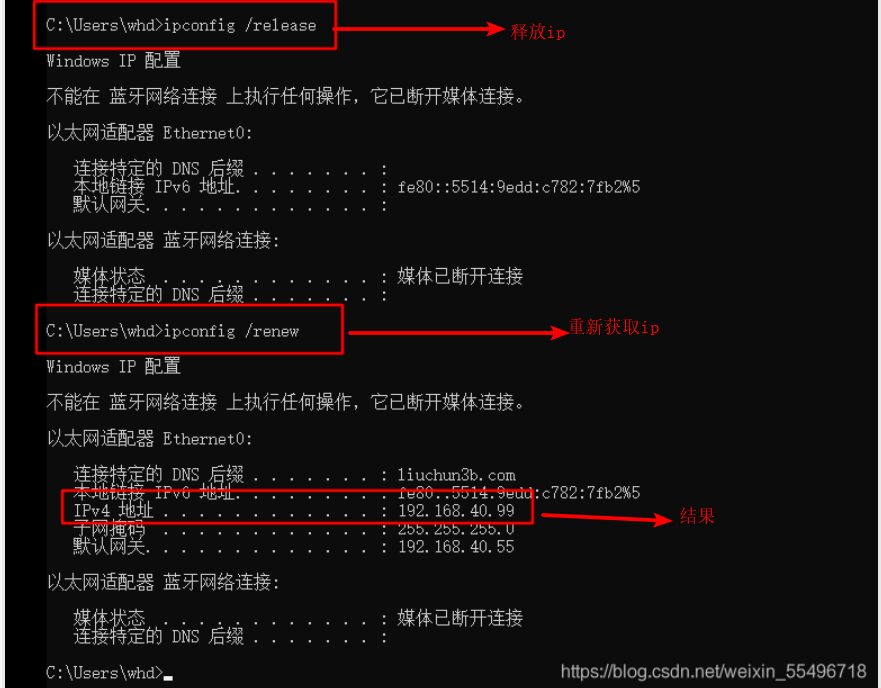
Release the IP address on the PC and get it again
ipconfig /release : release IP address ipconfig /renew : Reacquire IP address