What is DNS
The full name of DNS is Domain Name System, which means Domain Name Resolution System. It is the responsibility of translating a domain name into a recognizable IP for connecting different computer devices.
linux Configuration and Files for DNS Resolution
There are three files in linux about dns parsing:
- /etc/hosts Records ip address corresponding to hostname
- /etc/resolv.conf Set ip address of DNS server
- /etc/host.conf Specifies the order in which domain names are resolved (from local hosts files or from DNS)
The existence of /etc/hosts is that the early network is not very developed. It is just necessary to keep the corresponding relationship between hostname and ip address in hosts. With the development of network, distributed DNS services gradually appear, but the form of /etc/hosts remains.
/etc/resolv.conf is configured with a DNS domain name and an ip address. There is a lot of information on the Internet to refer to.
How a domain name is resolved
How the Domain Name System (DNS) Works This article roughly explains the process of domain name resolution, which can be divided into:
- Request the Domain Name Service where the top-level domain name is located from the Root Domain Name Service
- Request secondary domain name service from top-level domain name service
- Request a specific ip address from the secondary domain name service
Simple DNS configuration case (based on entOs7)
Server Side
1. Install bind
yum install bind
2. Modify/etc/named.conf configuration file
vim /etc/named.conf
options {
listen-on port 53 { any; }; //Open listening port 53 and accept any IP connection
listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; //Support IP V6
directory "/var/named"; //All forward and reverse zone files are created in this directory
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt";
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt";
allow-query { 0.0.0.0/0; }; //Allow any IP query
recursion yes;
dnssec-enable yes;
dnssec-validation yes;
dnssec-lookaside auto;
/* Path to ISC DLV key */
bindkeys-file "/etc/named.iscdlv.key";
managed-keys-directory "/var/named/dynamic";
};
logging {
channel default_debug {
file "data/named.run";
severity dynamic;
};
};
zone "." IN {
type hint;
file "named.ca";
};
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones"; //Main Profile
include "/etc/named.root.key";3. Modify the/etc/named.rfc1912.zones file to add a forward zone for duiyi.com
vim /etc/ named.rfc1912.zones
zone "localhost.localdomain" IN {
type master;
file "named.localhost";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "localhost" IN {
type master;
file "named.localhost";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "1.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.ip6.arpa" IN {
type master;
file "named.loopback";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "1.0.0.127.in-addr.arpa" IN {
type master;
file "named.loopback";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "0.in-addr.arpa" IN {
type master;
file "named.empty";
allow-update { none; };
};
//Forward Zone of duiyi.com
zone "duiyi.com" IN {
type master;
file "duiyi.com.zone";
allow-update { none; };
};4. Create a forward zone resource file
vim /var/named/duiyi.com.zone
$TTL 1D
@ IN SOA duiyi.com. rname.invalid. (
0 ; serial
1D ; refresh
1H ; retry
1W ; expire
3H ) ; minimum
NS @
A 127.0.0.1
AAAA ::1
www IN A 192.168.81.1
mail IN A 192.168.81.2
ftp IN A 192.168.81.35. Start the name service
systemctl start named
6. Start-up self-start
systemctl enable named
##Client
Operating system: both windows and linux
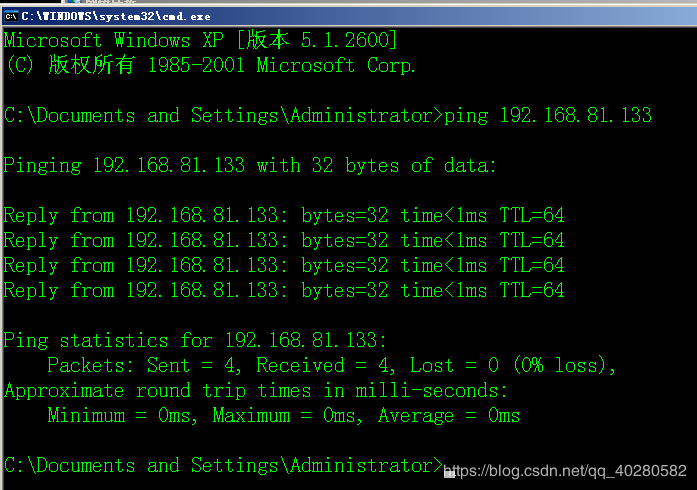
IP address: The IP (192.168.81.133) that can ping through the DNS server is fine.
Role: Tests whether the DNS server is functioning properly.
1. Modify DNS:
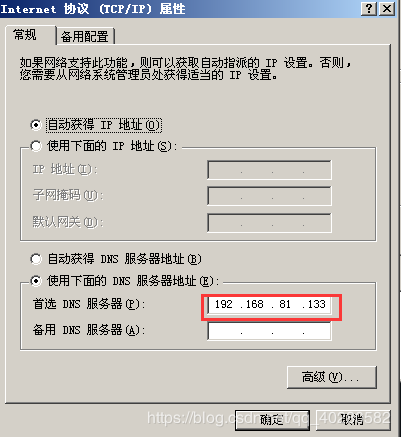
2.ping server ip(192.168.81.133), test access to the server
3. Use the nslookup command to test whether three DNS resolves successfully
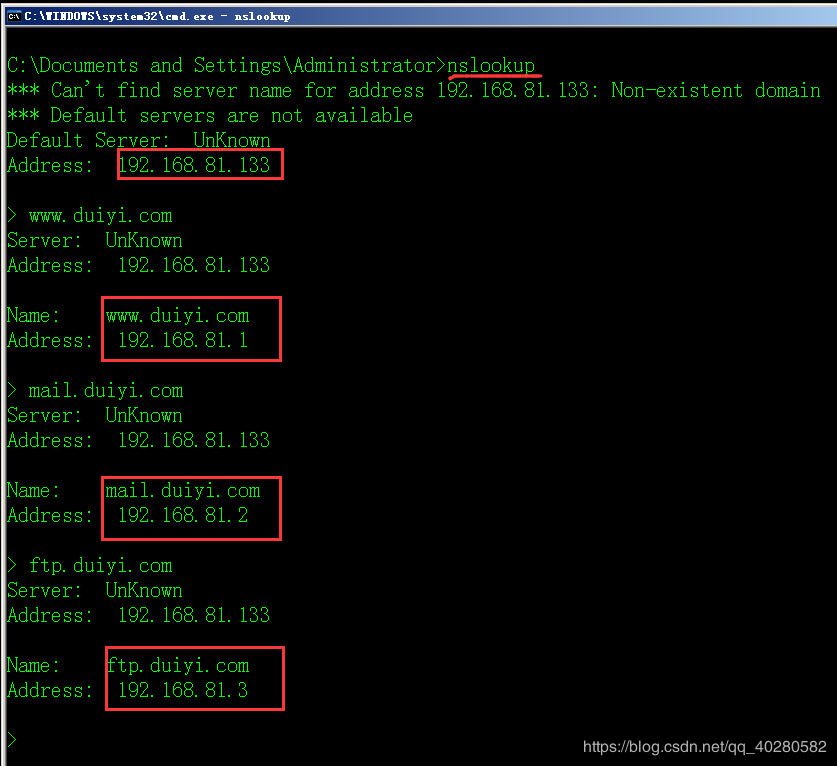
As shown, DNS forward resolution succeeded
Linux as a client test:
1. Install the bind-utils package so that you can use the nslookup, dig, and host tools
yum install bind-utils
2. Modify DNS configuration to use our DNS server
vim /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 192.168.81.133 nameserver 114.114.114.114 nameserver 8.8.8.8
3. Forward parsing test, using nslookup command (same as windows test)
nslookup