1. pod life cycle

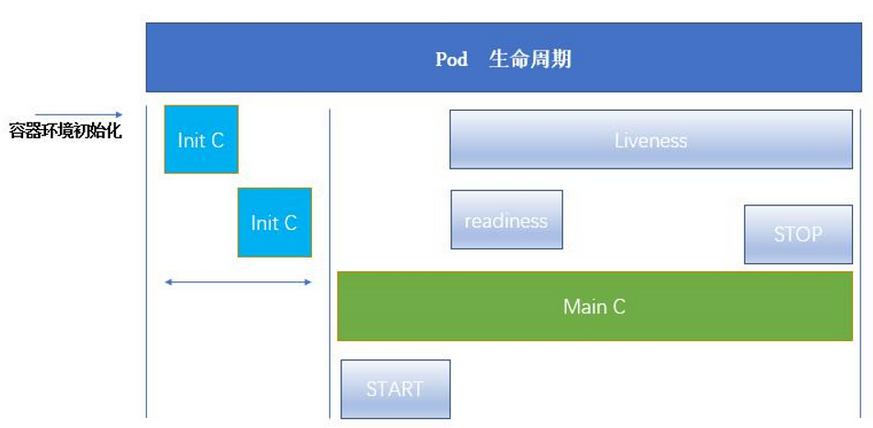
init container
 Case: when the service monitored by the init container is not configured, the main container and init container cannot start normally
Case: when the service monitored by the init container is not configured, the main container and init container cannot start normally
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: myapp-pod
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp-container
image: busyboxplus
command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo The app is running! && sleep 3600']
initContainers:
- name: init-myservice
image: busyboxplus
command: ['sh', '-c', "until nslookup myservice.default.svc.cluster.local; do echo waiting for myservice; sleep 2; done"]
- name: init-mydb
image: busyboxplus
command: ['sh', '-c', "until nslookup mydb.default.svc.cluster.local; do echo waiting for mydb; sleep 2; done"]
#---
#apiVersion: v1
#kind: Service
#metadata:
# name: myservice
#spec:
# ports:
# - protocol: TCP
# port: 80
# targetPort: 9376
#---
#apiVersion: v1
#kind: Service
#metadata:
# name: mydb
#spec:
# ports:
# - protocol: TCP
# port: 80
# targetPort: 9377
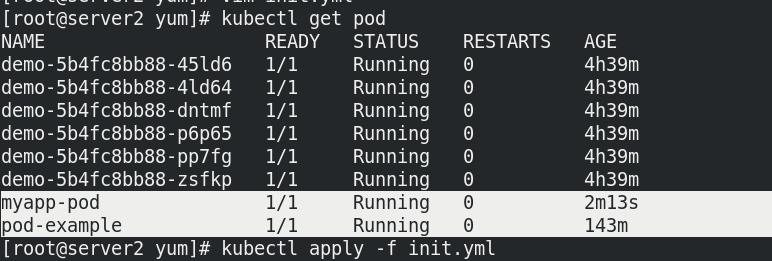
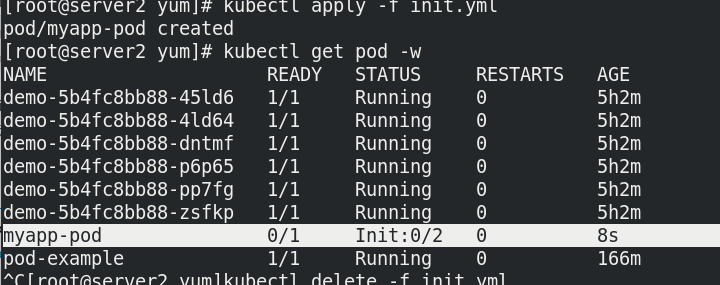 Delete the pod, cancel the comment, and reopen the container to run normally
Delete the pod, cancel the comment, and reopen the container to run normally
probe



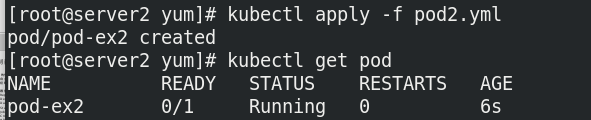
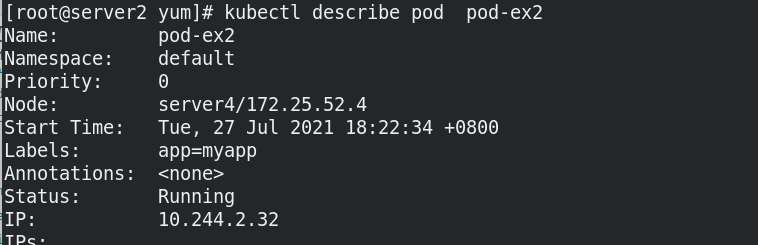
Case: the probe detects the container port and publishes files. When the conditions are not met, the container cannot be started.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-ex2
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: myapp:v1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
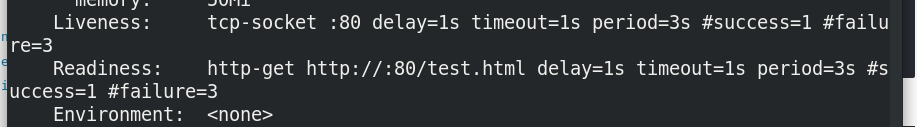
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket: #Monitor port 80
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 3
timeoutSeconds: 1
readinessProbe:
httpGet: #Monitor release files
path: /test.html
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 1
periodSeconds: 3
timeoutSeconds: 1
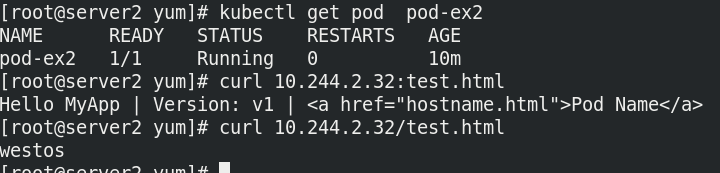
Test does not exist HTML, build the pod, and cannot run the pod successfully
 Add required files
Add required files
kubectl exec pod-ex2 sh -i -t / # echo westos> /usr/share/nginx/html/test.html
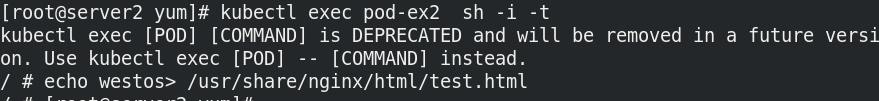 The pod successfully enters the ready state
The pod successfully enters the ready state
2. Controller
Replication Controller and ReplicaSet
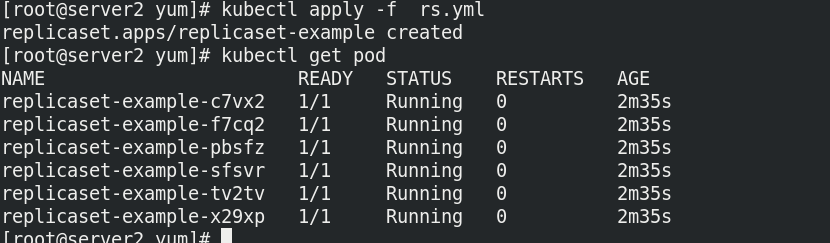
ReplicaSet replicaset is officially recommended to support the new set based selector requirements. ReplicaSet ensures that a specified number of Pod replicas are running at any time.
Although ReplicaSets can be used independently, today it is mainly used by Deployments as a mechanism to coordinate Pod creation, deletion and update.
Write a configuration file to verify the copy and establish the capacity expansion function. The version cannot be upgraded or rolled back using this controller
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: replicaset-example
spec:
replicas: 6#12
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: myapp:v1
When the number of copies is 6:
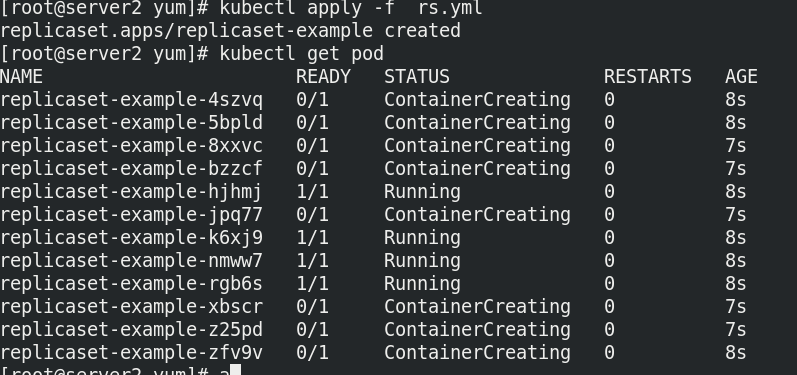
 When modified to 12:
When modified to 12:
Deployment
It is used to create Pod and ReplicaSet, scroll update and rollback, expand and shrink capacity
, pause and resume.
vim deployment.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp-deployment
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: myapp:v1 #Specify the mirror as v1
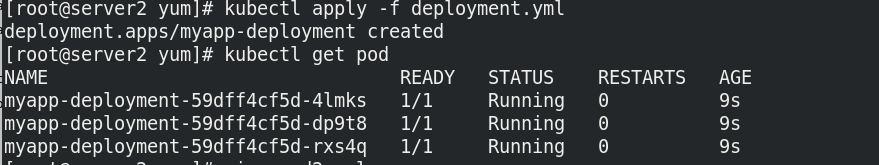
Run the deployment to view the container status
 Change the image to v2 and rebuild the pod
Change the image to v2 and rebuild the pod
image: myapp:v2 #Specify the mirror as v2
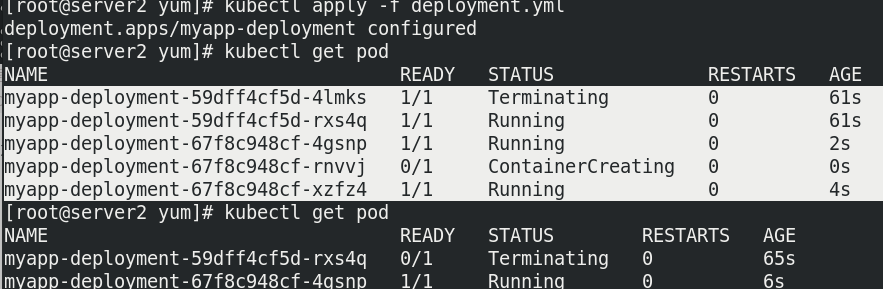 deployment will re-establish an rs controller to create a replica of v2. The rs of v1 will not be discarded and used for
deployment will re-establish an rs controller to create a replica of v2. The rs of v1 will not be discarded and used for
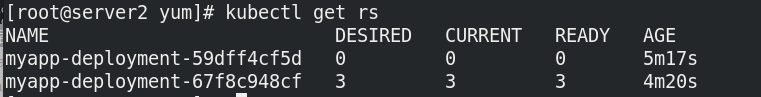
DaemonSet
The daemon set ensures that a copy of the Pod is running on all (or some) nodes. When nodes join the cluster, a Pod will also be added for them. When a node is removed from the cluster, these pods will also be recycled. Deleting a DaemonSet will delete all pods it creates. Generally, run the cluster storage DaemonSet, log collection DaemonSet, and monitoring DaemonSet on each node.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: daemonset-example
labels:
k8s-app: zabbix-agent
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: zabbix-agent
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: zabbix-agent
spec:
containers:
- name: zabbix-agent
image: zabbix/zabbix-agent
StatefulSet
StatefulSet is an API object used to manage workload of stateful applications. For applications where there are unequal relationships between instances and instances have dependencies on external data, StatefulSet is used to manage Deployment and extend a group of pods, and can provide sequence number and uniqueness guarantee for these pods
Job and CronJob
Job is used to execute batch tasks. It only executes the task once to ensure that one or more pods of the task end successfully.
Cron Job creates Jobs based on time scheduling. A CronJob object is like a line in a crontab (cron table) file. It is written in Cron format and executes Jobs periodically at a given scheduling time.
#job
$ vim job-example.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: pi
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: pi
image: perl
command: ["perl", "-Mbignum=bpi", "-wle", "print bpi(2000)"]
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 4
$ kubectl apply -f job-example.yaml
$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pi-6phk8 0/1 Completed 0 2m22s
$ kubectl logs pi-6phk8
$ kubectl delete job pi
#cornjob
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: cronjob-example
spec:
schedule: "* * * * *"
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: cronjob
image: busybox
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- date; echo Hello from k8s cluster
restartPolicy: OnFailure
HPA
Automatically adjust the number of pods in the service according to the resource utilization to realize the automatic scaling of Pod level.