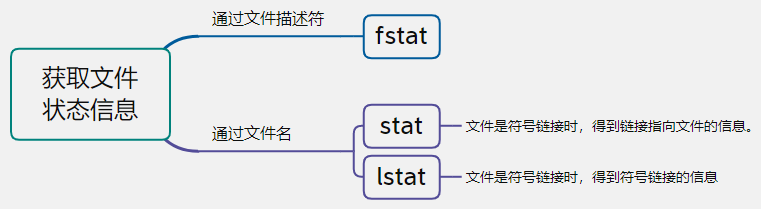
fstat,stat,lstat
Get file status information (status).
prototype
#include<unistd.h> #include<sys/stat.h> #include<sys/types.h> int fstat(int fildes, struct stat *buf); int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf); int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
Write the file status information into the stat structure pointed to by buf
stat structure
struct stat {
mode_t st_mode; /* File type and mode(permission) */
ino_t st_ino; /* Inode number */
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
dev_t st_rdev; /* Device ID (if special file) */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* Number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* User ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID of owner */
off_t st_size; /* Total size, in bytes */
struct timespec st_atim; /* Time of last access */
struct timespec st_mtim; /* Time of last modification */
struct timespec st_ctim; /* Time of last status change */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* Block size for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* Number of 512B blocks allocated */
};
- st_mode
mode_t st_mode; //unsigned int, only the lower 16 bits are used
[the external chain image transfer fails, and the source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the image and upload it directly (img-wevcphej-1644655890496) (C: \ users \ 14595 \ appdata \ roaming \ typora \ typora user images \ image-20220209231636612. PNG)]
-
file type
Macro (the parameter is st_mode) file type S_ISREG() Regular file S_ISDIR() Directory file S_ISLNK() Symbolic link S_ISCHR() Character special file S_ISBLK() Block special file S_ISSOCK() Socket S_ISFIFO() Pipeline or FIFO Example:
if(S_ISREG(buf.st_mode)) printf("Files are ordinary files"); -
Permission attribute
-
Saved text bit s_ ISVTX)
If the adhesive bit of an executable program is set, a copy of the program body (machine instruction) is saved in the exchange area when the first execution of the program terminates.
-
Set user ID and group ID when executing
//File type properties area #define S_ Bit mask for ifmt 0170000 file type #define S_IFSOCK 0140000 socket #define S_ Iflnk 012000 symbolic link #define S_ Ifreg 0100000 general documents #define S_ Ifblk 00600000 block device #define S_ Ifdir 0040000 directory #define S_ Ifchr 0020000 character device #define S_ IFO 0010000 first in first out (fifo) #define S_ ISSOCK(m) (((m) & S_ IFMT) == S_ Ifsock) / / some macros are provided to help users perform & operations. If yes, 1 is returned #define S_ISLNK(m) (((m) & S_IFMT) == S_IFLNK) #define S_ISREG(m) (((m) & S_IFMT) == S_IFREG) #define S_ISBLK(m) (((m) & S_IFMT) == S_IFBLK) #define S_ISDIR(m) (((m) & S_IFMT) == S_IFDIR) #define S_ISCHR(m) (((m) & S_IFMT) == S_IFCHR) #define S_ISFIFO(m) (((m) & S_IFMT) == S_IFIFO) //Special attribute area for permissions #define S_ (set user ID on execution) bit of isuid 0004000 file #define S_ (set group ID on execution) bit of isgid 0002000 file #define S_ sticky bit of isvtx 0001000 file //Permission attribute area //File owner #define S_IRWXU 00700 /* mask for file owner permissions */ #define S_IRUSR 00400 /* owner has read permission */ #define S_IWUSR 00200 /* owner has write permission */ #define S_IXUSR 00100 /* owner has execute permission */ //group user (group) #define S_IRWXG 00070 /* mask for group permissions */ #define S_IRGRP 00040 /* group has read permission */ #define S_IWGRP 00020 /* group has write permission */ #define S_IXGRP 00010 /* group has execute permission */ //other users #define S_IRWXO 00007 /* mask for permissions for others (not in group) */ #define S_IROTH 00004 /* others have read permission */ #define S_IWOTH 00002 /* others have write permission */ #define S_IXOTH 00001 /* others have execute permission */
access and faccessat
Test access with actual user ID and actual group ID.
#include<unistd> int access(const char *pathname,int mode); int faccessat(int fd,const char *pathname,int mode,int flag);
access is consistent with faccessat in the following two cases
- The pathname parameter is an absolute path
- pathname parameter is relative path, and fd parameter is AT_FDCMD
Factessat tests the pathname relative to the open directory (fd)
-
mode parameter
- Whether the test file exists: F_OK
- Test access: R_ OK, W_ OK, X_ The bitwise or of OK (read, write, and execute permissions, respectively).
-
flag parameter
Used to change the behavior of factessat.
Return value
It returns 0 on success and - 1 on error
umask system call
Controls the default permissions for files.
#include<sys/stat.h> mode_t umask(mode_t cmask);
cmask is the bitwise or composition of the following 9 constants. If the bit is 1, the corresponding permission is closed.
[the external chain image transfer fails, and the source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the image and upload it directly (img-bgnqhqtt-1644655890498) (C: \ users \ 14595 \ appdata \ roaming \ typora user images \ image-20220210212619807. PNG)]
chmod, fchmod and fchmodet
Change access to existing files.
#include<sys/stat.h> int chmod(const char *pathname,mode_t mode); int fchmod(int fd,mode_t mode); int fchmodat(int fd,const char *pathname,mode_t mode,int flag);
Return value
Return 0 when successful; Return - 1 in case of error
In the following two cases, fchmod is consistent with fchmodat
- The pathname parameter is an absolute path
- pathname parameter is relative path, and fd parameter is AT_FDCMD
fchmodat tests pathname. Relative to the open directory (fd)
flag parameter
Used to change the behavior of fchmodat.
When set to at_ SYMLINK_ When nofollow, dosen't follow symbolic links
chown, fchown, fchownat, and lchown
Change the user ID and group ID of the file
#include<unistd.h> int chown(const char *pathname,uid_t owner,gid_t group); int lchown(const char *pathname,uid_t owner,gid_t group); int fchown(int fd,uid_t owner,gid_t group); int fchownat(int fd,const char *pathname,uid_t owner,gid_t group,int flag);
If the owner or group parameter is - 1, the corresponding ID remains unchanged.
- When the referenced file is a symbolic link, the following function is used to change the symbolic link itself.
- lchown
- Set the parameter to hofcat, flag_ SYMLINK_ NOFOLLOW
gid_t group);
int fchownat(int fd,const char *pathname,uid_t owner,gid_t group,int flag);
owner or group Parameter is-1,Then the corresponding ID unchanged. - When the referenced file is a symbolic link, the following function is used to change the symbolic link itself. - lchown - fchownat, flag The parameter is set to AT_SYMLINK_NOFOLLOW