preface
1. Server and system version
Article based Tencent cloud Server linux centos7 nine
2. Why reinstall the system
When Tencent cloud first bought, the security group was fully open by default and the firewall was closed by default
When I operated redis, I allowed external access without setting a password. It was easy to be invaded. Authorized was modified through redis_ Keys file to achieve secret free login. After looking at the ip addresses of South Korea and the United States
Virtual currency is very rampant recently. What you know and don't know is unproductive and meaningless, but it wastes a lot of resources
Check your server / usr/share directory and open config_background.json file to see if it has been mined
They can't even connect me. They can't log in to the remote Tencent cloud. They can only log in through VNC. The VNC remote login of Tencent cloud engineers can't be solved. They simply reinstall the system directly
3. Article version
5-17-v1: build some necessary software, which are effective for personal testing
Chapter I construction of Linux basic environment
1.1 installation of zsh and oh my zsh
How many shell s are there in the viewing system
cat /etc/shells
Install zsh
sudo yum install zsh #Default installation location /bin/zsh
Set zsh as the system default shell for root user:
chsh -s /bin/zsh root sudo chsh -s /bin/zsh
View the default shell
echo $SHELL
If you want to go back to bash
chsh -s /bin/bash root
Installing the zsh frame oh my zsh
#You need to install git. Sometimes this domain name cannot be accessed in the mainland sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/robbyrussell/oh-my-zsh/master/tools/install.sh)" #Installation position /root/.oh-my-zsh #Powerful d command, which will list the history of the directory we recently entered d
Modify theme
# vim .zshrc #Default theme ZSH_THEME="robbyrussell" #Set it to "random". Each time you log in oh-my-zsh, you will randomly select a theme #[reference article]( https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/63585679)
Installation effect

1.2 update sudo
#Fix vulnerability number CVE-2021-3156 yum update sudo
1.3 installing git
yum install git #View installation location find . -name "git" |grep git #Default installation location /usr/bin/git #[reference article]( https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1640614)
Install jdk 1.4
Mode 1:
#View the version of jdk that can be installed yum list | grep java #The default installation location is / usr / lib / JVM / java-11-openjdk-11.0.11.0.9-1 el7_ 9.x86_ 64/bin/java yum install -y java-11-openjdk.x86_64
Mode 2:
#decompression tar -zxvf jdk-8u211-linux-x64.tar.gz #Configure environment variables vim /etc/profile export JAVA_HOME=/DATA/jdk/jdk1.8.0_211 export CLASSPATH=$:CLASSPATH:$JAVA_HOME/lib/ export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin #Refresh environment variables source /etc/profile #query java -version
1.5 set password free login of local computer
Password free login method 1:
#Locally generated rsa ssh-keygen #Upload the local public key to the server. Enter the root password here ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx #Password free login ssh root@xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx #[Key login]( https://goodgoodstudy.blog.csdn.net/article/details/113694654)
Password free login mode 2:
#Add ~ /. To your local computer ID in ssh directory_ rsa. Content in pub (i.e. public key) #Copy to ~ /. Of ECS Authorized in ssh directory_ Keys file
be careful:
docker and redis can easily be invaded in this way if they open ports and do not set passwords.
1.6 modify hostname
# Re login takes effect # 1. Method 1 vi /etc/hostname # cloudserver,: wq save exit hostname -F /etc/hostname # 2. Method 2 hostname -b cloudserver
1.7 increase connection timeout
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config #The following configuration items were found in this file: #ClientAliveInterval 0 #ClientAliveCountMax 3 #Remove the note and change to #These two lines mean #1. How many seconds does the server send heartbeat data to the client #2. How many times does the client fail to respond, and the server automatically disconnects ClientAliveInterval 30 ClientAliveCountMax 120 #Restart sshd service service sshd restart #Reference articles #https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1163845
1.8 flow monitoring gadget iftop
- Execute the following command to install iftop tool (iftop tool is a traffic monitoring gadget under Linux server).
#If it is an Ubuntu system, please execute the command 'apt get install iftop - y'. yum install iftop -y
- Execute the following command to install lsof.
yum install lsof -y
- Execute the following command to run iftop. As shown in the figure below:
iftop
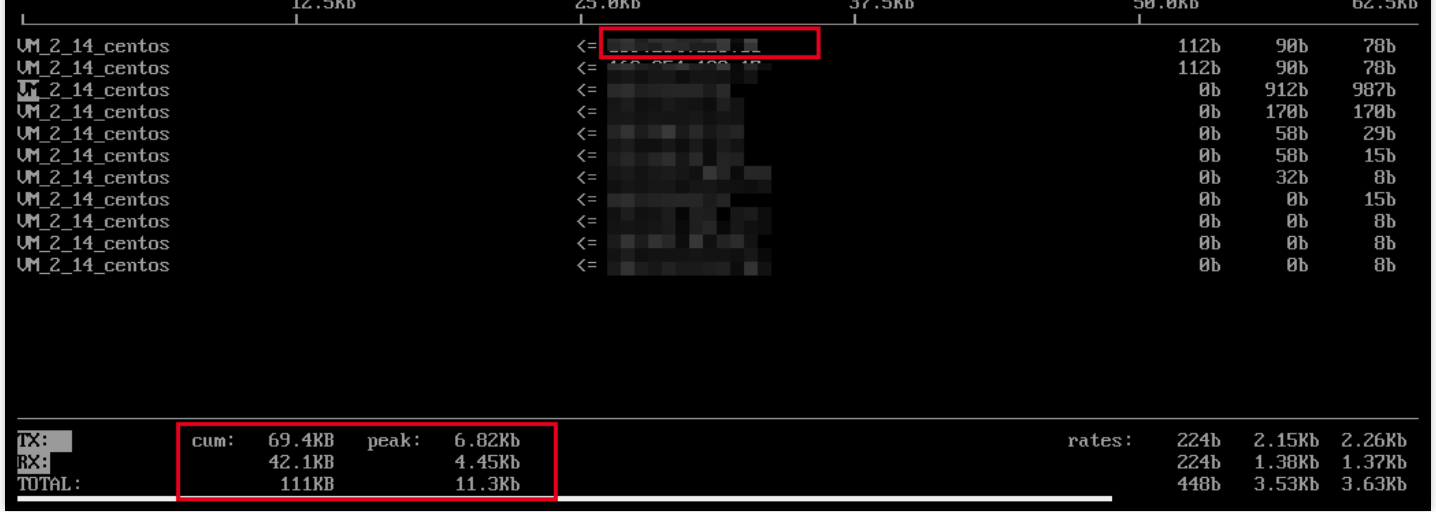
- According to the IP that consumes traffic in iftop, execute the following command to view the process connected to the IP.
lsof -i | grep IP
- If the IP that consumes traffic is 201.205.141.123, execute the following command:
lsof -i | grep 201.205.141.123
- According to the returned results, it is known that the bandwidth of this server is mainly consumed by the SSH process.
sshd 12145 root 3u IPV4 3294018 0t0 TCP 10.144.90.86:ssh->203.205.141.123:58614(ESTABLISHED) sshd 12179 ubuntu 3u IPV4 3294018 0t0 TCP 10.144.90.86:ssh->203.205.141.123:58614(ESTABLISHED)
1.9 configuring security groups
Configure the new security rules to open only some commonly used ports

1.10 configure firewall
View firewall status
firewall-cmd --state
Turn on the firewall
#open systemctl start firewalld #close systemctl stop firewalld
Add ports that need to be open
#In the running state, add the ports that need to be opened to the firewall #Permanently add the port. Removing -- permanent means temporary. firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp --permanent
Close open ports
firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=8080/tcp --permanent
Load the firewall configuration to make the modification effective
firewall-cmd --reload
Check whether a port of the firewall is open
firewall-cmd --zone=public --query-port=80/tcp #View all open ports firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --list-ports
1.11 installation nginx
#First, install PCREPCRE to enable Nginx to support Rewrite. #Download nginx wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.20.0.tar.gz #Download pcre wget https://ftp.pcre.org/pub/pcre/pcre-8.44.tar.bz2 #decompression tar zxvf nginx-1.20.0.tar.gz tar xvf pcre-8.44.tar.bz2 #Installation dependency yum -y install gcc zlib zlib-devel pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel yum install -y gcc-c++ #Compile and install pcre cd pcre-8.44 ./configure make && make install #Generate Makefile cd ../nginx-1.20.0 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-pcre=../pcre-8.44 # Compile and install make make install #Installation position usr/local/nginx #nginx three main commands # start-up /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ ./nginx # Stop Nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ ./nginx -s stop # Reload configuration file /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ ./nginx -s reload #[reference article]( https://www.runoob.com/linux/nginx-install-setup.html)
1.12 installing tomcat
wget https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/apache/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.46/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.46.tar.gz tar zxvf apache-tomcat-9.0.46.tar.gz
1.13 installing mysql
#centos7 doesn't have mysql by default. Download c7 from the yum source #https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/repo/yum/ #Download yum source wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm #You need to switch the root user for software installation: use the root account to install the yum source rpm -vih mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm #Check whether the yum source is successfully installed yum repolist enabled | grep "mysql.*-community.*" #View the default installation version yum repolist all | grep mysql #Select installation version ##Disable version 8.0 yum-config-manager --disable mysql80-community ##Enable version 5.7 yum-config-manager --enable mysql57-community #Start installation yum install mysql-community-server #mysql start systemctl start mysqld #Check whether mysql is started systemctl status mysqld #Restart mysql systemctl restart mysqld.service #View mysql temporary password cat /var/log/mysql.log #Or search mysql temporary password grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log #A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: A&0&cSh_F,AB #Log in to mysql mysql -uroot -p'A&0&cSh_F,AB' #If the password is not changed, an error will be reported #You must reset your password #You have an error in your SQL syntax; show databases; #The password must be changed ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'mysql5@Root'; flush privileges; #Re login mysql -uroot -pmysql5$Root
Create authorized user
create user "lane"@"IP" identified by "Mysql@1234"; #Create user xsge with password SQLxsge1 Any permission Library (*%), any permission Library (%), all permissions allowed (*) grant all on *.* to 'lane'@'%' identified by 'Mysql@1234'; ##Modify the xsge host access permission range (provided that the user lane already exists) #Modify the access scope of xsge account: localhost can only be accessed locally in Linux system update mysql.user set host='localhost' where user='lane'; #Modify permissions #Authorize lane to query and update all tables in the test database (test. *) Grant select,update on test.* to 'lane'@'%';
Prohibit MySQL from updating
#Put the following code in your / etc / yum.com Conf file exclude=mysql-community-client,mysql-community-common,mysql-community-libs,mysql-community-server
Set firewall open port
####Set firewall open port firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
Database garbled problem
#Log in to MySQL to check the encoding problem show variables like 'character_set%'; #Modify mysql configuration file / etc / my cnf vim /etc/my.cnf #Change to utf8 [mysqld] character-set-server=utf8 [client] default-character-set=utf8 [mysql] default-character-set=utf8
Set password free login
#/etc/my.cnf add the following [client] host=localhost user='root' password='youpassword' default-character-set=utf8 [mysql] default-character-set=utf8
Set startup
systemctl enable mysqld systemctl daemon-reload
Reference articles
CentOS7 install MySQL - Jianshu (jianshu.com) using yum or up2date
1.14 installing redis
#download wget https://download.redis.io/releases/redis-6.2.2.tar.gz #decompression tar zxvf redis-6.2.2.tar.gz #Jump cd redis-6.2.2 #compile make #create a file mkdir /usr/local/redis mkdir /usr/local/redis/bin mkdir /usr/local/redis/conf #move file mv redis.conf /usr/local/redis/conf mv src/redis-benchmark /usr/local/redis/bin mv src/redis-check-aof /usr/local/redis/bin mv src/redis-check-rdb /usr/local/redis/bin mv src/redis-cli /usr/local/redis/bin mv src/redis-sentinel /usr/local/redis/bin mv src/redis-server /usr/local/redis/bin mv src/redis-trib.rb /usr/local/redis/bin #Jump to bin file cd /usr/local/redis/bin #Start redis without occupying the window ./redis-server ../conf/redis.conf & ./redis-cli #test set aa aa get aa ##Close the server connection 127.0.0.1:6379> shutdown not connected> exit #Set password vim ./conf/redis.conf #Modify requirepass redispass #You can delete the source file rm -rf redis-6.2.2
1.15 installing docker
# install yum -y install docker # start-up systemctl start docker.service # Power on self start systemctl enable docker.service # verification docker info #Installation position /var/lib/docker #Reference articles ()
Chapter II Linux start state
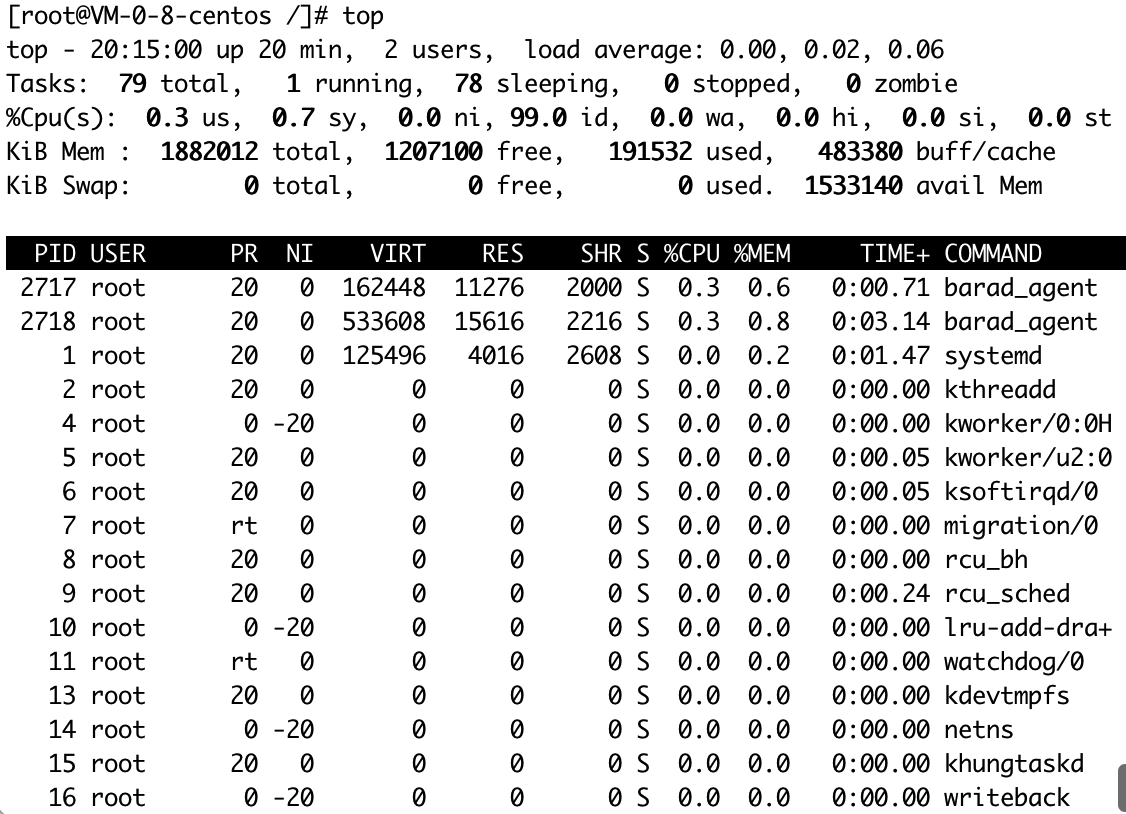
2.1 top command
2.2 free command

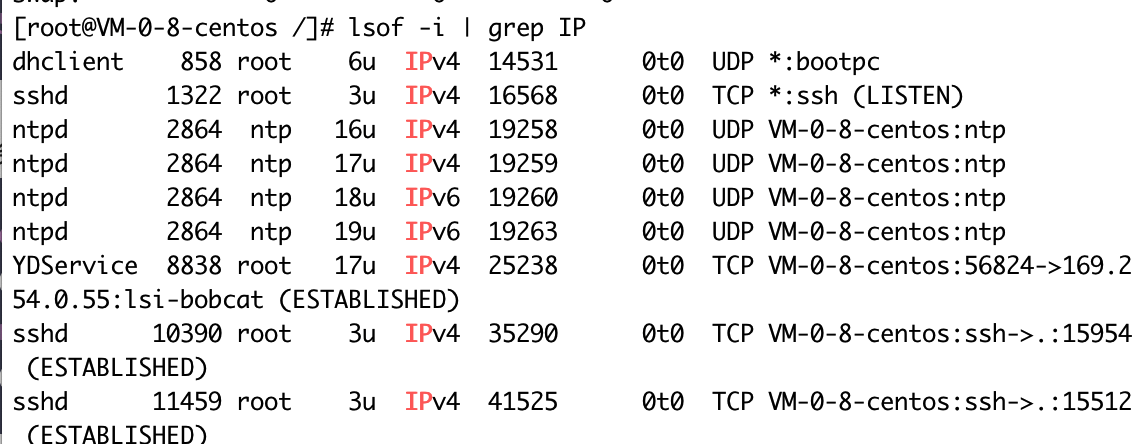
3.3 ip connection command
lsof -i | grep IP
3.4 initial folder
