Linux mysql5.7 installation - super detailed
Step: the installation of this article is version 5.7
Step reference video - ruoze explanation
The installation steps should be roughly described below during the interview
- check whether Mysql is installed or running in the system
- download mysql source package and decompression
- Create administrative user mysqladmin and user group dba
- Configuration * * / etc / my cnf**
- Assign permissions to 4's files and source folder (user, user group, RWX)
- Configure Mysql service and set automatic startup after startup
- Switch to mysqladmin, compile and install mysql
- service mysql start
- Log in using mysql command
- Configure environment variables
Official website: wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-5.7/mysql-5.7.27-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
Sohu image download: wget http://mirrors.sohu.com/mysql/MySQL-5.7/mysql-5.7.27-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
Download tar package from MySQL official website
There are two ways:
- Download the mysql official website to the local computer, and then upload it with the rz command
- wget + download link, download directly from linux
Novice recommended the first
If the bandwidth of linux server is fast, the second one is recommended, which is faster.
First:
The first mysql official website download should be registered. Just register in the email, and it will be very fast.
Select the first tar package to download
rz //Upload command
Enter rz to open windows and upload your download directory
ps: rpm is also OK. The following article is about the installation of rpm command. It is particularly well written and recommended.
Install mysql5.0 under CentOS 7 7(rpm)_ wudinaniya blog - CSDN blog_ mysql rpm
- Difference between rpm and tar
Personal understanding: in a nutshell, the main thing is that there are some differences in unloading. rpm is friendly to storing decompressed files in multiple folders. You can delete them all with one command. tar needs to be deleted manually. It is suitable for decompressed files to be in one path.
Second: wget
wget https://cdn.mysql.com/archives/mysql-5.7/mysql-5.7.11-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64.tar.gz
tar package decompression
- Decompression path / usr/local
[root@hadoop001 ~]# rz [root@hadoop001 ~]# ll -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1799250 Nov 23 08:39 mysql-5.7.11-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64.tar.gz [root@hadoop001 ~]# tar xzvf mysql-5.7.11-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/ [root@hadoop001 ~]# cd /usr/local/ [root@hadoop001 local]# mv mysql-5.7.11-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64 mysql / / change the name of this folder [root@hadoop001 local] mkdir mysql/arch mysql/data mysql/tmp // Create three folders under the / mysql path, arch, data and TMP
[MySQL/MySQL 5.7.11 Install.txt at master · Hackeruncle/MySQL (github.com)](https://github.com/Hackeruncle/MySQL/blob/master/MySQL 5.7.11 Install.txt#L224)
Create my cnf
vi /etc/my.cnf
[client] port = 3306 socket = /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql.sock default-character-set=utf8mb4 [mysqld] port = 3306 socket = /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql.sock skip-slave-start skip-external-locking key_buffer_size = 256M sort_buffer_size = 2M read_buffer_size = 2M read_rnd_buffer_size = 4M query_cache_size= 32M max_allowed_packet = 16M myisam_sort_buffer_size=128M tmp_table_size=32M table_open_cache = 512 thread_cache_size = 8 wait_timeout = 86400 interactive_timeout = 86400 max_connections = 600 # Try number of CPU's*2 for thread_concurrency #thread_concurrency = 32 #isolation level and default engine default-storage-engine = INNODB transaction-isolation = READ-COMMITTED server-id = 1739 basedir = /usr/local/mysql datadir = /usr/local/mysql/data pid-file = /usr/local/mysql/data/hostname.pid #open performance schema log-warnings sysdate-is-now binlog_format = ROW log_bin_trust_function_creators=1 log-error = /usr/local/mysql/data/hostname.err log-bin = /usr/local/mysql/arch/mysql-bin expire_logs_days = 7 innodb_write_io_threads=16 relay-log = /usr/local/mysql/relay_log/relay-log relay-log-index = /usr/local/mysql/relay_log/relay-log.index relay_log_info_file= /usr/local/mysql/relay_log/relay-log.info log_slave_updates=1 gtid_mode=OFF enforce_gtid_consistency=OFF # slave slave-parallel-type=LOGICAL_CLOCK slave-parallel-workers=4 master_info_repository=TABLE relay_log_info_repository=TABLE relay_log_recovery=ON #other logs #general_log =1 #general_log_file = /usr/local/mysql/data/general_log.err #slow_query_log=1 #slow_query_log_file=/usr/local/mysql/data/slow_log.err #for replication slave sync_binlog = 500 #for innodb options innodb_data_home_dir = /usr/local/mysql/data/ innodb_data_file_path = ibdata1:1G;ibdata2:1G:autoextend innodb_log_group_home_dir = /usr/local/mysql/arch innodb_log_files_in_group = 4 innodb_log_file_size = 1G innodb_log_buffer_size = 200M #Adjust the pool size according to production needs innodb_buffer_pool_size = 2G #innodb_additional_mem_pool_size = 50M #deprecated in 5.6 tmpdir = /usr/local/mysql/tmp innodb_lock_wait_timeout = 1000 #innodb_thread_concurrency = 0 innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 2 innodb_locks_unsafe_for_binlog=1 #innodb io features: add for mysql5.5.8 performance_schema innodb_read_io_threads=4 innodb-write-io-threads=4 innodb-io-capacity=200 #purge threads change default(0) to 1 for purge innodb_purge_threads=1 innodb_use_native_aio=on #case-sensitive file names and separate tablespace innodb_file_per_table = 1 lower_case_table_names=1 [mysqldump] quick max_allowed_packet = 128M [mysql] no-auto-rehash default-character-set=utf8mb4 [mysqlhotcopy] interactive-timeout [myisamchk] key_buffer_size = 256M sort_buffer_size = 256M read_buffer = 2M write_buffer = 2M
[special attention]
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 2G
My virtual machine itself is 8G, so the 2G setting is reasonable; If your virtual machine itself is 1G/2G, the size set to 2G will explode. Reasonable setting.
Create administrative user mysqladmin and user group dba
[root@hadoop001 ~]# groupadd -g 101 dba [root@hadoop001 ~]# useradd -u 514 -g dba -G root -d /usr/local/mysql mysqladmin [root@hadoop001 ~]# id mysqladmin uid=514(mysqladmin) gid=101(dba) groups=101(dba),0(root)
if user mysqladmin is existing,please execute the following command of usermod.
If the user already exists, change the path attribute with usermod
[root@hadoop001 ~]# usermod -u 514 -g dba -G root -d /usr/local/mysql mysqladmin
Configure environment variables
[root@hadoop001 ~]# cp /etc/skel/.* /usr/local/mysql #Prevent style loss when switching to mysqladmin user
# Configure environment variables
[root@hadoop001 ~]# vim /usr/local/mysql/.bashrc
# .bashrc
# Source global definitions
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bashrc
fi
# Uncomment the following line if you don't like systemctl's auto-paging feature:
# export SYSTEMD_PAGER=
# User specific aliases and functions
export MYSQL_BASE=/usr/local/mysql
export PATH=${MYSQL_BASE}/bin:$PATH
unset USERNAME
#stty erase ^H
set umask to 022
umask 022
PS1=`uname -n`":"'$USER'":"'$PWD'":>"; export PS1
## end
Configure permissions
[root@hadoop001 local]# chown mysqladmin:dba /etc/my.cnf [root@hadoop001 local]# chmod 640 /etc/my.cnf [root@hadoop001 local]# chown -R mysqladmin:dba /usr/local/mysql [root@hadoop001 local]# chmod -R 755 /usr/local/mysql
Configure services
Copy the service file under the mysql path to init D, and then add the service
[root@hadoop001 local]# cd /usr/local/mysql [root@hadoop001 mysql]# cp support-files/mysql.server /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql [root@hadoop001 mysql]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql [root@hadoop001 mysql]# chkconfig --del mysql [root@hadoop001 mysql]# chkconfig --add mysql [root@hadoop001 mysql]# chkconfig --level 345 mysql on
Configure startup and self startup
[root@hadoop001 ~]# cd /usr/local/mysql [root@hadoop001 mysql]# vi /etc/rc.local Add the last two sentences #!/bin/bash # THIS FILE IS ADDED FOR COMPATIBILITY PURPOSES # # It is highly advisable to create own systemd services or udev rules # to run scripts during boot instead of using this file. # # In contrast to previous versions due to parallel execution during boot # this script will NOT be run after all other services. # # Please note that you must run 'chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local' to ensure # that this script will be executed during boot. touch /var/lock/subsys/local su - mysqladmin -c "etc/init.d/mysql start --federated"
Install libaio
[root@hadoop001 mysql]# yum -y install libaio
initialization
[root@hadoop001 mysql]# sudo su - mysqladmin hadoop001:mysqladmin:/usr/local/mysql:>bin/mysqld \ --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf \ --user=mysqladmin \ --basedir=/usr/local/mysql/ \ --pid-file=/usr/local/mysql/data/hostname.pid \ --socket=/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql.sock \ --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data/ \ --initialize
View temporary password
hadoop001:mysqladmin:/usr/local/mysql:>cat data/hostname.err |grep password
start-up
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my.cnf &
Login and change password
Password is the password you just cat checked
hadoop001:mysqladmin:/usr/local/mysql:>mysql -uroot -p'password'
Change Password:
Every grant must have flush permission, otherwise it will not take effect
alter user root@localhost identified by 'newpasswd'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'newpasswd' ; flush privileges;
restart
service mysql restart
Error 1
This error was reported before:
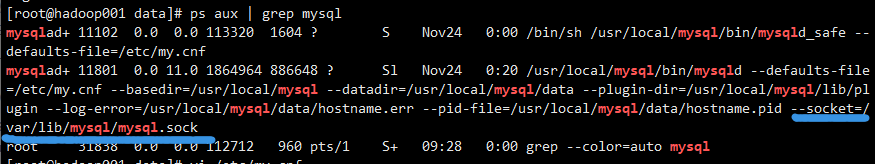

The reason for the mistake is that I started my The socket path of mysqld in CNF says something else, but the process keeps running
ps -ef | grep mysql
Check the mysql process and find 11801, so kill - 9 11801, cat / dev / null > data / hostname err
Then run service mysql start successfully
mysql -uroot -p input newpassword
Then enter the root user
Error 2
The initialization of the machine is not reflected during the second installation. There is no mistake in deleting users and groups and decompressing them again from beginning to end.
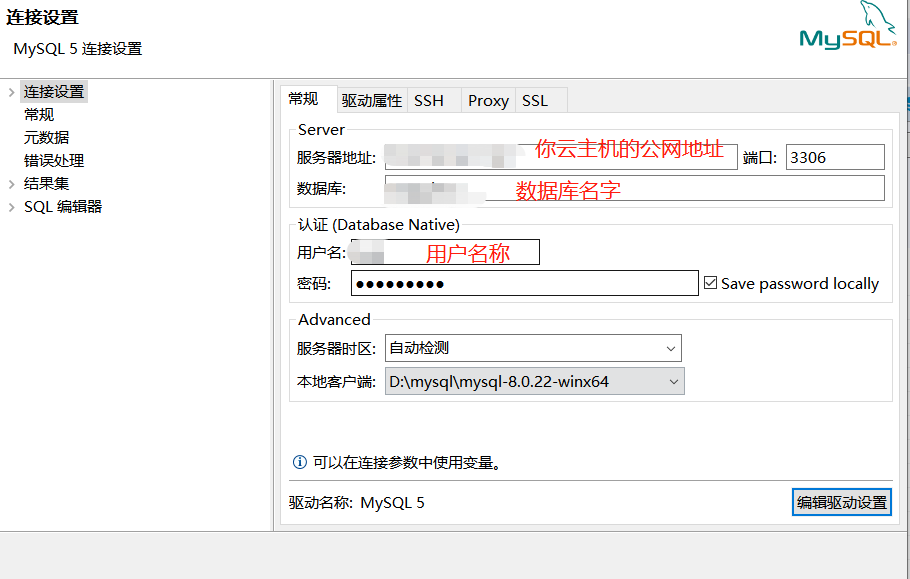
Create database for dbeaver connection
After the following command is changed, dbeaver can be used to connect
# Create database maggiecn create database maggiecn; # Give all permissions to the database, and log in with suju user name and login password newpassword # %IP addresses representing any client are allowed to use suju users for remote access grant all privileges on maggiecn.* to suju@'hadoop001' identified by '12345678' with grant option; grant all privileges on maggiecn.* to suju@'%' identified by 'newpassword'; # Update permissions flush privileges;
Reflect that there is nothing wrong with deleting users and groups and decompressing them again from beginning to end.
Create database for dbeaver connection
After the following command is changed, dbeaver can be used to connect
# Create database maggiecn create database maggiecn; # Give all permissions to the database, and log in with suju user name and login password newpassword # %IP addresses representing any client are allowed to use suju users for remote access grant all privileges on maggiecn.* to suju@'hadoop001' identified by '12345678' with grant option; grant all privileges on maggiecn.* to suju@'%' identified by 'newpassword'; # Update permissions flush privileges;