1. Longest common subsequence (discontinuous)
It refers to the subsequence formed by randomly removing some characters from a given sequence. (random means that some can be removed discontinuously or none can be removed)
For example, for the following two sequences
a: abcbdb
b: acbbabdbb
Their longest common subsequence: acbdb, length 5.
It is solved by dynamic programming, and f [I, J] is defined as( a 0 , a 1 , . . . a i − 1 a_0,a_1,...a_{i-1} a0,a1,... ai − 1) and( b 0 , b 1 , . . . b j − 1 b_0,b_1,...b_{j-1} b0,b1,... The longest common subsequence length of bj − 1).
Therefore, according to the definition, the search process is divided into the following three cases:
- When i=0 or j=0, f [I, J] = 0, corresponding to the boundary condition.
- When a [I-1] = B [J-1], further solve a sub problem and continue to find( a 0 , a 1 , . . . a i − 2 a_0,a_1,...a_{i-2} a0,a1,... ai − 2) and( b 0 , b 1 , . . . b j − 2 b_0,b_1,...b_{j-2} b0,b1,... The longest common subsequence length of bj − 2). State transition equation f [I, J] = f [I-1, J-1] + 1.
- When a [I-1] ≠ B [J-1], it is divided into two subproblems, which need to be found out separately( a 0 , a 1 , . . . a i − 1 a_0,a_1,...a_{i-1} a0,a1,... ai − 1) and( b 0 , b 1 , . . . b j − 2 b_0,b_1,...b_{j-2} b0,b1,... bj − 2) and( a 0 , a 1 , . . . a i − 2 a_0,a_1,...a_{i-2} a0,a1,... ai − 2) and( b 0 , b 1 , . . . b j − 1 b_0,b_1,...b_{j-1} b0,b1,... bj − 1), and take the maximum of the two. Corresponding state transition equation f [I, J] = max (f [I, J-1], f [I-1, J]).
public class LCS {
char[] a; // Storage sequence a
char[] b; // Storage sequence b
int[][] dp;
public LCS(String str1, String str2) {
a = str1.toCharArray();
b = str2.toCharArray();
dp = new int[a.length + 1][b.length + 1];
}
// Get maximum length
public int getLenth() {
for (int i = 1; i <= a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= b.length; j++) {
if (a[i - 1] == b[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[a.length][b.length];
}
// Finding subsequences according to dp array is actually the process of reverse restoring the length above
public StringBuilder getSubSequence() {
int i = a.length;
int j = b.length;
int len = dp[i][j];
StringBuilder subs = new StringBuilder("");
while (len > 0) {
if (dp[i][j] == dp[i - 1][j]) {
i--;
} else if (dp[i][j] == dp[i][j - 1]) {
j--;
} else {
// If the above two conditions are not satisfied, there must be dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1, corresponding to a[i-1]=b[j-1]
subs.append(a[i - 1]);
i--;
j--;
len--;
}
}
return subs.reverse();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abcbdb";
String str2 = "acbbabdbb";
LCS ls = new LCS(str1, str2);
System.out.println("Length:" + ls.getLenth());
System.out.println("Longest common subsequence:" + ls.getSubSequence());
}
}
dp array in solving process
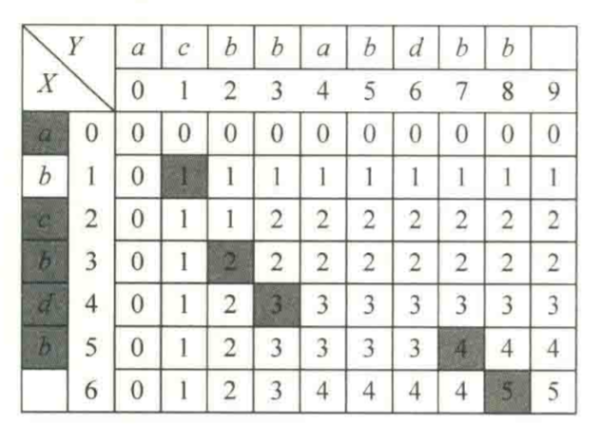
Because two layers of for loops are created and a two-dimensional array is created in the process of solving, the time and space complexity of solving two sequences with lengths of M and N are
O
(
m
n
)
Ο(mn)
O(mn).
2. Longest common subsequence (continuous)
The longest common continuous subsequence of the above two sequences is:
a: abcbdb
b: acbbabdbb
This time, f [I, J] is defined as( a 0 , a 1 , . . . a i − 1 a_0,a_1,...a_{i-1} a0,a1,... ai − 1) and( b 0 , b 1 , . . . b j − 1 b_0,b_1,...b_{j-1} b0,b1,... The longest common continuous subsequence length of bj − 1), and the last character of the subsequence is a i − 1 or b i − 1 a_{i-1} or b_{i-1} ai − 1 or bi − 1, that is, this continuous subsequence is the second half of the two sequences at the same time.
This can be divided into the following three cases:
- Boundary case f [I, J] = 0, when i=0 or j=0.
- A [I-1] = B [J-1], continue to look forward. There is f [I, J] = f [I-1, J-1] + 1.
- A [I-1] ≠ B [J-1], according to the definition, this continuous subsequence must end with a [I-1] or B [J-1]. Such subsequence does not exist, so there is f [I, J] = 0.
public class LCS {
char[] a; // Storage sequence a
char[] b; // Storage sequence b
int[][] dp;
int len; // Save maximum length
int index; // Save the starting subscript of the common subsequence
public LCS(String str1, String str2) {
a = str1.toCharArray();
b = str2.toCharArray();
dp = new int[a.length + 1][b.length + 1];
}
public int getLenth() {
for (int i = 1; i <= a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= b.length; j++) {
if (a[i - 1] == b[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
}
if (dp[i][j] > len) {
len = dp[i][j];
index = i - len;
}
}
}
return len;
}
public StringBuilder getSubSequence() {
StringBuilder subs = new StringBuilder("");
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
subs.append(a[index + i]);
}
return subs;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abcbdb";
String str2 = "acbbabdbb";
LCS ls = new LCS(str1, str2);
System.out.println("Length:" + ls.getLenth());
System.out.println("Longest continuous common subsequence:" + ls.getSubSequence());
}
}
dp array during solution:
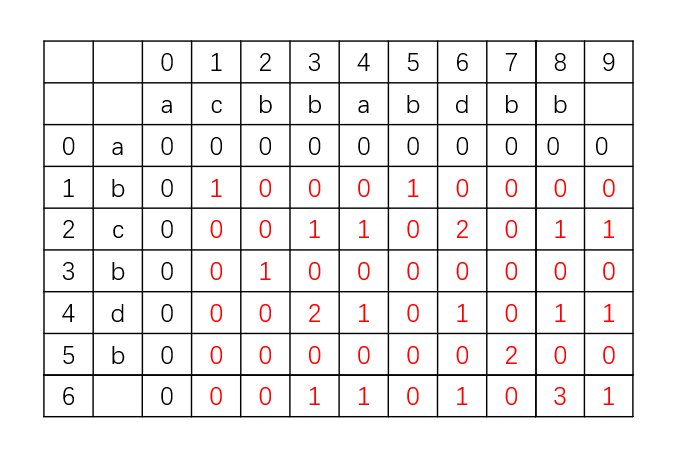
Space and time complexity are the same O ( m n ) Ο(mn) O(mn).