1. Application Scenario: We used to copy classmates'unwritten homework when we were in school. Sometimes bad luck was discovered by the teacher. Finally, he was handed over to him by the teacher who grabbed the copy of homework N.
Copying is about repeating something, and sometimes we have similar problems in our programs.
Loops are needed to quickly resolve such repetitive operations.
Think about it: We were punished 100 times by our teacher for "writing makes me happy!" What should I write?
General Writing:
i = 1 # Define Initial Value
print(f"No.{i}All over: Writing homework makes me happy!") # i = 1
i += 1 # Self-increasing
print(f"No.{i}All over: Writing homework makes me happy!") # i(1) + 1 = 2
i += 1
print(f"No.{i}All over: Writing homework makes me happy!") # i(2) + 1 = 3
i += 1
print(f"No.{i}All over: Writing homework makes me happy!") # i(3) + 1 = 4
i += 1
print(f"No.{i}All over: Writing homework makes me happy!") # i(4) + 1 = 5
i += 1
print(f"No.{i}All over: Writing homework makes me happy!") # i(5) + 1 = 6
i += 1
print(f"No.{i}All over: Writing homework makes me happy!") # i(6) + 1 = 7
# Repeat this 100 timesOutput: (I've written it seven times here, so if there's too much code in a hundred times, I won't show it all.)
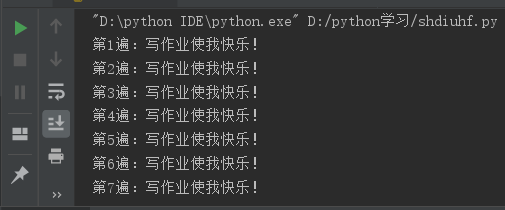
This can cause a lot of code.
2. Cyclic Role and Classification
Role: Simplify code, more efficient repeat execution, and improve code execution efficiency
Category: The loop is divided into while and for, and the end result is the same
break and continue
When a break condition is met, it exits the loop, does not execute subsequent duplicate code, and is only valid for the current loop.
When a continue condition is met, you do not want to execute the loop code, but you do not want to exit the loop. You can use continue
1.while Loop
initial value
Basic format: while + when the condition is satisfied
What to do
Increase by itself
i = 1 # Define Initial Value
while i<=100: # condition
print(f"No.{i}All over: Writing homework makes me happy!") # To do
i+=1 # Self-increasing 1Output results:
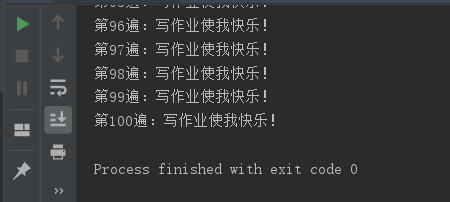
It's much less than the code above, and it takes only four lines to output 100 "Happy writing my homework!"
1.1 While Circulation Exercise:
"""
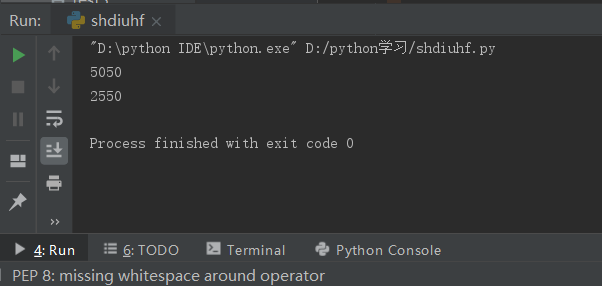
1. Calculate 1~100 The sum of (1 and 100))
"""
i = 1 # initial value
s = 0 # Result variable
while i<= 100: # Maximum range
s += i # 1+2+3+4......
i += 1 # Self-increasing
print(s) # Final result
"""
2. Calculate 1~100 The sum of even numbers between (1 and 100)
"""
a = 2 # initial value
b = 0 # Result variable
while a<= 100: # Maximum range
b += a # 2+4+6+8......
a += 1 # Self-increasing
print(b) # ResultOutput results:
1.2 while nesting
Basic format:
initial value
while condition:
What to do when conditions are met
while condition:
What to do when conditions are met
Increase by itself
Self-increasing
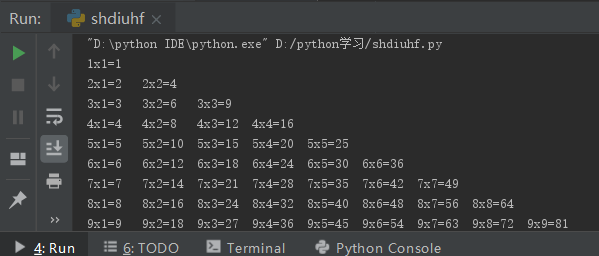
Exercise: while loop to implement the Nine-Nine Multiplication Table
x = 1 # initial value
while x <= 9: # condition
y = 1 # initial value
while y <= x: # condition
print(f"{x}x{y}={x * y}",end="\t")
y += 1 # Self-increasing
x += 1 # Self-increasing
print()Output results:
Exercise: Guess Numbers Game
"""
Guess Numbers Game
1,System random number generation random,randint
2,User 5 Guess Opportunities while
3,Detect Guess Size if
4,Guess right to exit the loop break
"""
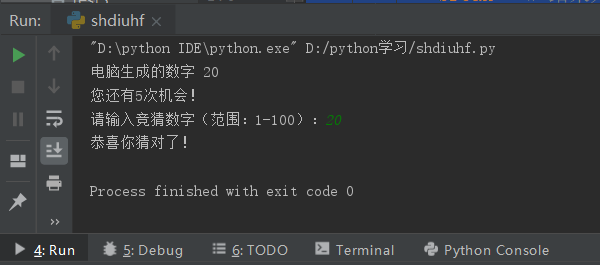
import random # Import Library
comput = random.randint(1,100) # Calling the library randint function
print("Computer generated numbers",comput) # View computer generated numbers (for hang-up behavior, do not imitate)
opporturity = 5 # There are five opportunities in total
while True : # Dead cycle
if opporturity > 0: # If Opportunity>5
print(f"You also have{opporturity}Second chance!") # Remaining Opportunities
user_input = int(input("Please enter a guess number (Range: 1)-100): ")) # User Input
if comput == user_input: # If the number is right
print("Congratulations on your guess!")
break # End Dead Cycle
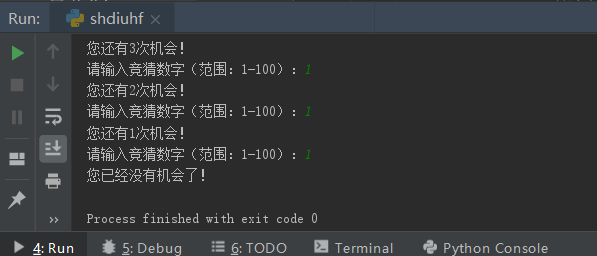
elif opporturity == 0: # If Opportunity=0
print("You have no chance!")
break # Exit Loop
opporturity -= 1 # Opportunity-1Output result 1:
Output result 2:
2.for loop
Basic format: for temporary variable in iterative object:
Code to execute when conditions are met
Range function prototype: range (start, end, step)
Start: The start position of the count, which starts at 0 by default.
End: The end of the count (the end requires writing the last digit of the target number, similar to a slice)
step: The spacing for each jump is not filled in by default of 1.
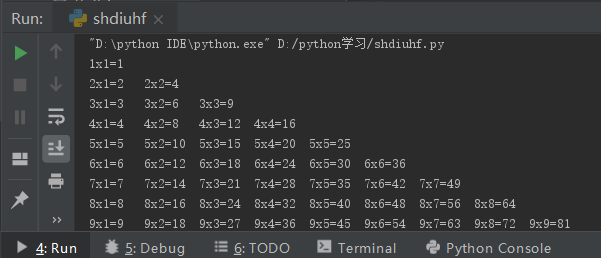
2.1 Exercise: for Loop Implements Nine-Nine Multiplication Table
for i in range(1,10):
for s in range(1,i+1):
print(f"{i}x{s}={i*s}",end="\t")
s+=1
i+=1
print()Output results:
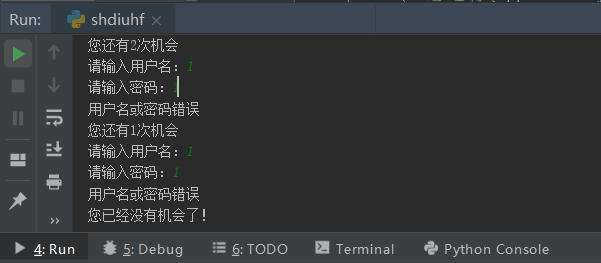
2.2 Exercise: Simulate user login
"""
User Login
1,User name and password entered correctly into the system if judge
2,Error Continue Input... for loop
3,Initial Opportunity Value is entered only three times
"""
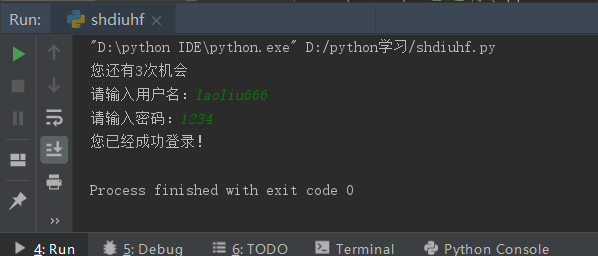
user_name = "laoliu666" # User name
passwd = 1234 # Password
opporturity = 3 # Opportunity
for i in range(4): # Number of loops
if opporturity == 0: # If Number=0
print("You have no chance!")
break # Exit Loop
print(f"You also have{opporturity}Second Opportunity")
if opporturity >= 1: # If Opportunity>0
use_name_input = input("Please enter a user name:") # User Enter User Name
user_passwd_input = int(input("Please input a password:")) # User Enter Password
if use_name_input == user_name and user_passwd_input == passwd: # If the user enters a username and password = username and password
print("You have successfully logged in!")
break # Exit Loop
else: # otherwise
print("ERROR Incorrect username or password")
opporturity -= 1 # Opportunity-1Output result 1:
Output result 2: