catalogue
2. Branch statement (select structure)
2.2.1 break in switch statement
3.1.1 break and continue in while
3.2.2. break and continue in the for loop
3.2.3 loop control variable of for statement
3.2.4 variants of the for loop
3.3.3 characteristics of do statement
1. What is a statement?
C statements can be divided into the following five categories:
1. Expression statement
2. Function call statement
3. Control statement
4. Compound statement
5. Empty statement
Control statements are used to control the execution process of the program to realize various structural modes of the program. They are composed of specific statement definer. There are nine kinds of control statements in C language.
It can be divided into the following three categories:
1. Conditional judgment statements are also called branch statements: if statements and switch statements;
2. Circular execution statements: do while statement, while statement and for statement;
3. Turn statements: break statements, goto statements, continue statements, and return statements.
2. Branch statement (select structure)
2.1 if statement
Syntax structure:
//Single branch
if(expression)
sentence;
if(expression)
Statement 1;
else
Statement 2;
//Multi branch
if(Expression 1)
Statement 1;
else if(Expression 2)
Statement 2;
else
Statement 3;Else matching: else matches the nearest if.
2.2. switch statement
switch is a multi branch statement
switch(Integer expression)
{
case Integer constant expression:
sentence;
}2.2.1 break in switch statement
The switch statement needs to be combined with break to realize the real branch
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int day = 0;
switch(day)
{
case 1:
printf("Monday\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("Tuesday\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("Wednesday\n");
break;
case 4:
printf("Thursday\n");
break;
case 5:
printf("Friday\n");
break;
case 6:
printf("Saturday\n");
break;
case 7:
printf("Sunday\n");
break;
}
return 0;
}When required:
1. Input 1-5 and output "weekday";
2. Input 6-7 and output "weekend"
So our code should be implemented in this way:
#include <stdio. h> / / switch code demonstration
int main()
{
int day = 0;
switch(day)
{
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
printf("weekday\n");
break;
case 6:
case 7:
printf("weekend\n");
break;
}
return 0;
}The actual effect of the break statement is to divide the statement list into different branch parts.
Good programming habits
Add a break statement after the last case statement.
(this is written to avoid forgetting to add a break statement after the last previous case statement.).
2.2.2ddefault clause
When all case conditions are not met, the default statement is executed
3. Circular statement
3.1. while cycle
while syntax structure
while(expression)
Circular statement;The process of executing the while statement:
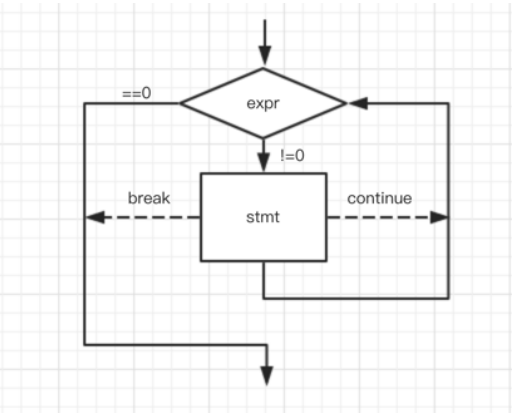
Print numbers from 0 to 10 on the screen.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
while(i<=10)
{
printf("%d ", i);
i = i+1;
}
return 0;
}3.1.1 break and continue in while
break: jump out of the whole loop
continue: skip a loop
3.2 for cycle
3.2.1 grammar
for(Expression 1; Expression 2; Expression 3)
Circular statement;Expression 1
Expression 1 is the initialization part, which is used to initialize the of the loop variable.
Expression 2
Expression 2 is a condition judgment part, which is used to judge the termination of the cycle.
Expression 3
Expression 3 is the adjustment part, which is used to adjust the loop conditions.
Execution process of for loop
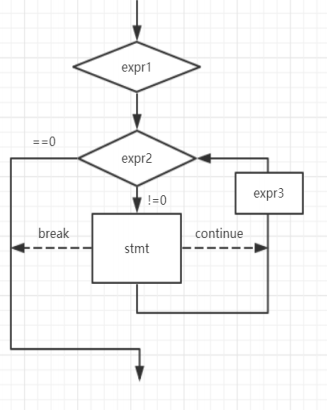
3.2.2. break and continue in the for loop
Same as while loop
3.2.3 loop control variable of for statement
1. Do not modify the circulation variable in the circulation body to prevent dead circulation
2. Adopt the interval writing method of front closing and rear opening
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{}3.2.4 variants of the for loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(;;)
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
//The initialization part, judgment part and adjustment part of the for loop can be omitted, but it is not recommended to omit them at the beginning of learning, which is easy to cause problems. return 0;
}3.3do... while() loop
3.3.1 grammar
do
Circular statement;
while(expression);3.3.2 implementation process
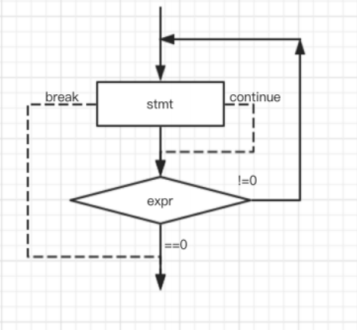
3.3.3 characteristics of do statement
Execute the loop body once first
3.3.4 break and continue
Same as for loop
4. goto statement
Syntax format:
again: goto again;
Usage scenario:
Jump out of multi-layer loop