What is a mail server?
E-mail is an information transmission behavior that uses the network to transmit information to remote servers. We can send files or information to any place on the earth where there is a network, and we can also connect to the internet to receive mail anywhere there is a network. However, there are some problems:
1. Email problem with virus
2. Hackers invaded through mail programs
3. Advertising information and spam information, etc
4. The host is full of unknown mail
The E-mail we usually receive is processed by using the "account @ host name". Due to the proliferation of malicious mail and spam, we are not allowed to directly use the host's IP address to send mail. Therefore, the mail server must have A legally registered host name. Since the host name is used, that is, your host name needs to have an A flag in DNS query. For general servers, just use the positive solution so that the client can correctly find the IP of our server. At present, the mail server at the receiving end will reverse solve the source IP of the mail. If the address of your mail server is not A fixed IP, This kind of IP is usually expressed as XXX in ISP dynamic. XXX and other host names. However, such host names will be regarded as spam by major large mail servers, so the mail sent by your mail server may be discarded. Therefore, we'd better apply to the ISP for IP reverse solution.
How does the mail server deliver mail through DNS information
When we send an email, the host will first analyze the DNS of the target host of the letter, first obtain the MX flag (Mail Exchanger), and then send the letter based on the highest priority MX host.
Suppose we find the target host DNS The following information is available: haha.com IN MX 10 mail1.haha.com haha.com IN MX 20 mail2.haha.com haha.com IN A ip address 1,When there is a letter to send to user@haha.com Due to MX The lowest record mark is preferred, so the letter will be sent to mail1.haha.com On this host. 2,If mail1.haha.com If you fail to accept this letter for various reasons, it will be given second priority MX Host to transmit, that is mail2.haha.com. 3,If all MX If the host is not responsible, the letter will A The logo is transmitted directly to yourself.
Mail components and related protocols
MUA: (Mail User Agent)
There are two ways for the client to send mail. The first is to log in directly to the mail server (such as ssh) to actively send mail; The second is to send the letter to the mail server through MUA. The main function of MUA is to receive e-mail from the mail host and provide users with browsing and writing e-mail. The client software used to receive mail, such as foxmail, outlook, Thunderbird (Thunderbird is a client tool under linux) and Mutt (a character interface client tool under linux). MUA communicates with the server using SMTP, IMAP, or POP3 protocols.
Webmail: a Web-based E-mail sending and receiving system, which plays the role of E-mail user agent. Generally speaking, webmail system provides mail sending and receiving, user online service and system service management. The interface of Webmail is intuitive and friendly. It does not need the help of the client, which eliminates the trouble when users configure the E-mail client software. As long as they can surf the Internet, they can use webmail to facilitate users to receive and send mail. The commonly used webmail include Openwebmail, Squirrelmail, Extmail and Extman.
MTA: (Mail Transfer Agent)
MUA sends the user's mail to the mail host. If the mail host can help the user send the mail, it is an MTA. Mail server is an MTA. The protocol used by the MTA is SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol). The software used by MTA includes sendmail, postfix and Exchange.
Functions of MTA:
(1) Receive mail:
MTA will receive emails from clients or other MTAS. At this time, the MTA uses the SMTP protocol and the port number is 25.
(2) Forward mail
If the destination of the email is not its own user, and the relevant data of the email complies with the right to use MTA, MTA will forward the email to the next host. This is the function of Relay.
MDA: (Mail Delivery Agent)
In fact, MDA is a small program hanging under the MTA. Its main function is to analyze the header or content of the mail received by the MTA to determine the destination of the mail. After MDA analysis, it is found that the target of this email is MTA, so MDA will put this email into the user's Mailbox; If not, be ready to forward it. MDA also has the function of analyzing and filtering mail:
(1) Filter spam
(2) Automatic reply
However, each major MTA program has its own MDA function.
The commonly used MDA includes ProcMail (the default mail delivery tool of postfix) and MailDrop (a relatively professional delivery agent tool).
Mailbox
E-mail is a special mail collection document for an account. The default system mailbox in linux is placed in / var/spool/mail / user account.
The process of sending mail to the email mailbox of the other party through the local MUA
1,Local end MUA Want to use MTA To send mail, you must first get MTA Permissions. In other words, we need to MTA Register an email account. 2,User in MUA After writing the above email, send it to MTA On, the data of the email mainly includes the email title and email content. When you press the send button, your email will be placed in the MTA And waiting to be sent. 2.1 If the destination of this message is the local side MTA Own account, then MDA This letter will be sent to the corresponding user Mailbox Go. 2.2 If the target of this message is another target MTA,Start the relay forwarding process. first, MTA It will first judge whether the packet is legal. If it has permission, it will MDA The email forwarding will start, that is, the email will pass through our website MTA Next MTA(SMTP(port 25))Send it out. If the message is sent successfully, delete the message in the queue. 3,Remote MTA We'll get it MTA And put the email in the correct mailbox for users to read or download. Note: this email is left on the other side MTA On, not on MUA Come on.
User receiving process
Users can MRA Server provided POP(Post Office Protocol,Postal service agreement) to receive your own mail, or through IMAP(Intenet Message Access Protocol,Interactive data message access protocol) protocol keeps its own mail on the mail host, and further carries out advanced work such as establishing mail data folders. use POP3 Protocol receive mail: (1)MUA adopt POP3 Protocol to connect to MRA of port110,And input the account number and password to obtain correct authentication and authorization. (2)MRA After confirming that there is no problem with the user's account and password, you will go to the user's account Mailbox Get the user's mail and send it to the user's MUA Software. (3)When all mail is delivered, the user's Mailbox The data in will be deleted. Due to use POP3 The protocol will delete the received mail. Therefore, the IMAP(Port number 143), this protocol allows you to mailbox The data is stored in the user's home directory on your host, that is, after the client receives the mail, the mail remains on the server. frequently-used MRA: dovecot Is an open source support IMAP and POP3 Protocol mail server (self-contained) SASL Function). SMTP,POP3,IMAP All three communication protocols are plaintext transmission, especially in POP3 and IMAP In these two communication protocols, users must enter an account and password to send and receive mail. So there is POP3s,IMAPs The emergence of communication protocols, they are through ssl Encryption is implemented. So is there any SMTPs And? Yes, but no one uses it. The reasons are as follows: because POP3,IMAP Only with MRA It is related to your own users, so as long as you set the parameters used by users and servers MRA The agreement is consistent, and will not affect other servers. however MTA It's different because MTA Must work with other MTA Communication, therefore, if you use SMTPs,Then the world wants to be with you MTA Communication, all need to be changed into SMTPs Communication protocol is OK, so there is no way to realize it at present. Of course, if it is a special case, you can also encrypt your data and then MTA Just hand it over.
Importance of Relay and authentication mechanism
When you need MTA to help you forward mail to the next MTA, this operation becomes mail Relay. When everyone can use this MTA to help Relay, this situation is called Open Relay operation. When an Open Relay occurs on an MTA and the MTA is connected to the Internet, the following problems are likely to occur:
(1) The normal connection speed of your host network will slow down, because the network bandwidth is consumed by advertising and spam.
(2) Your host may run out of resources due to a large number of emails, which is prone to downtime and other problems.
(3) Your MTA will be defined as a "blacklist" by the Internet society. From then on, many normal emails will not be sent or received.
Therefore, at present, almost all distributions start MTA by default to only listen to internal loop interfaces, and also cancel the function of Open Relay. Therefore, when you want to use the forwarding function of MTA, you must obtain the permission to legally use this MTA. There are several ways to set Relay:
(1) Specify that the IP or network segment of a specific client can use Relay.
(2) If the IP address of the client is not fixed, the authentication mechanism can be used
(3) Build MUA on MTA, such as the MUA function of Web interfaces such as OpenWebMail.
There are two common authentication mechanisms: SMTP mail authentication mechanism and SMTP after POP. No matter which mechanism, it basically determines that the user has the right to legally use the MTA by asking the user to enter the account and password for authentication, and then turns on relay support for authenticated users.
Construction of mail server
Primary profile
Provided by default postfix,Its main configuration file is/etc/postfix/Inside. Set the requirements for the master profile: "#”Symbols are notes; The first character of each line cannot be a blank character. Set the method parameter = There should be a space character on both sides of the equal sign of "set value"; Can use“ $"To reference variable values, for example myorigin = $myhostname; If the parameter supports more than two data, use the space character or comma to separate; Multiple lines can be used to represent the same setting value. As long as there is a comma in the first line and the beginning of the second line is a space character, the data can be extended to the second line to continue writing; If an item is set repeatedly, the later setting value shall prevail. /etc/postfix/main.cf major postfix Configuration file, almost all setting parameters are standardized in this file. The file has been modified and needs to be restarted postfix. /etc/postfix/master.cf Main provisions postfix The working parameters of each program are ready by default, and usually do not need to be changed. /etc/postfix/access(utilize postmap Processing) can be set to open Relay Or reject the external configuration file of the source or destination address of the connection, but the file is in/etc/postfix/main.cf It will not take effect until it is started, and after setting, you need to postmap To become a database file. /etc/aliases(utilize postalias or newaliases (both) can be used as a mail alias or as a mail group setting. /usr/sbin/postconf This command lists your postfix Detailed setting data, including system parameter values, with a large amount of data. If you only want to view the data of some modified default parameters and non default values, you can use postconf -n. /usr/sbin/postfix This is postfix You can use this command to start or reread the configuration file. postfix check inspect postfix Are the relevant files and permissions correct postfix start/stop/reload postfix flush Force mail currently in the mail queue to be sent out /etc/sbin/postalias Command to set alias database because MTA The efficiency of reading files in database format is better, so it is necessary to ASCII The file in format is rebuilt into a database. stay postfix In, this command is mainly used for conversion/etc/aliases Become a database file. postaliases hash:/etc/aliases(hash For a database format, and then/etc/aliases Will be automatically updated) /usr/sbin/postcat It is mainly used to check the mail content placed in the queue. Because the message content in the queue is for MTA Yes, so the format is not text data that we generally understand. /usr/sbin/postmap This command has the same usage and postaliases Similarly, its role is in transformation/etc/postfix/access Database of files. /usr/sbin/postqueue similar mailq Output results of, for example postqueue -p
Experiment 1 ordinary user email sending
preparation: 1.Software installation: installing MTA yum install postfix -y #Provide email service 2.Install a mailbox MUA yum install mailx -y #If you are not familiar with the mail command here, you can view it through the command manual 3.need dns Domain name resolution of the mailbox server configured in the server: mail.xian. As shown below:
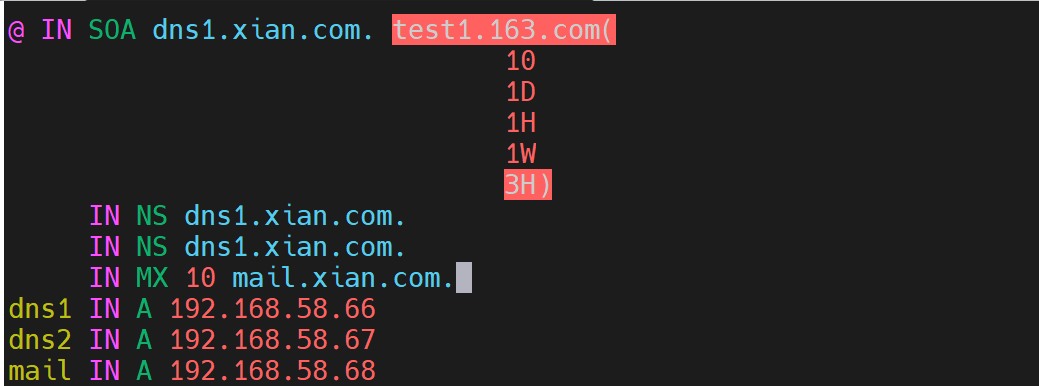
Step 1: configure the main configuration file (/ etc/postfix/mian.cf)
[root@localhost postfix]# vim /etc/postfix/main.cf mydestination = $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain, localhost, $mydomain #Set the host name that can receive mail, that is, what host name should be written when someone sends you an email. If the MX flag is set in DNS, it is best to write the host name in mydestination, otherwise error messages are easy to appear. mydomain = xian.com myhostname = mail.xian.com #Host name, FQDN is required. Because your mydomain setting project will take the name after the first decimal point of $myhostname by default. myorigin = $myhostname #The "sending source host" displayed when sending a letter, that is, the mail sent out on behalf of this MTA, will be subject to this setting value. inet_interfaces = all #Set the listening interface of postfix. By default, your postfix will only listen to the local interface lo (127.0.0.1). If all interfaces are open, it can be written as all. mynetworks = 192.168.58.0/24 #Specify trusted clients.
Step 2: create a user to send mail
Create user [root@rhce postfix]# useradd client1 [root@rhce postfix]# echo "123456" | passwd --stdin mailuser1 [root@rhce postfix]# useradd clientt2 [root@rhce postfix]# echo "123456" | passwd --stdin mailuser2 Send mail [root@rhce postfix]# echo "123" | mail -s "HELLO" client1@xian.com [root@rhce postfix]# echo "123" | mail -s "HELLO" client2@xian.com Turn on the service and turn off the firewall [root@localhost /]# systemctl restart postfix.service [root@localhost /]# systemctl stop firewall [root@localhost /]# setenforce 0
Step 3: client authentication
client1 user:

client2 user:

Experiment 2 mass email
Step 1: edit the group settings and translate them into database files
[root@localhost /]# vim /etc/aliases #root: marc workgroup: client1,client2 #Add mass sending user group [root@localhost /]#postalias /etc/aliases #Translate database files Turn on the service and turn off the firewall [root@localhost /]# systemctl restart postfix.service [root@localhost /]# systemctl stop firewall [root@localhost /]# setenforce 0
Step 2: mass email
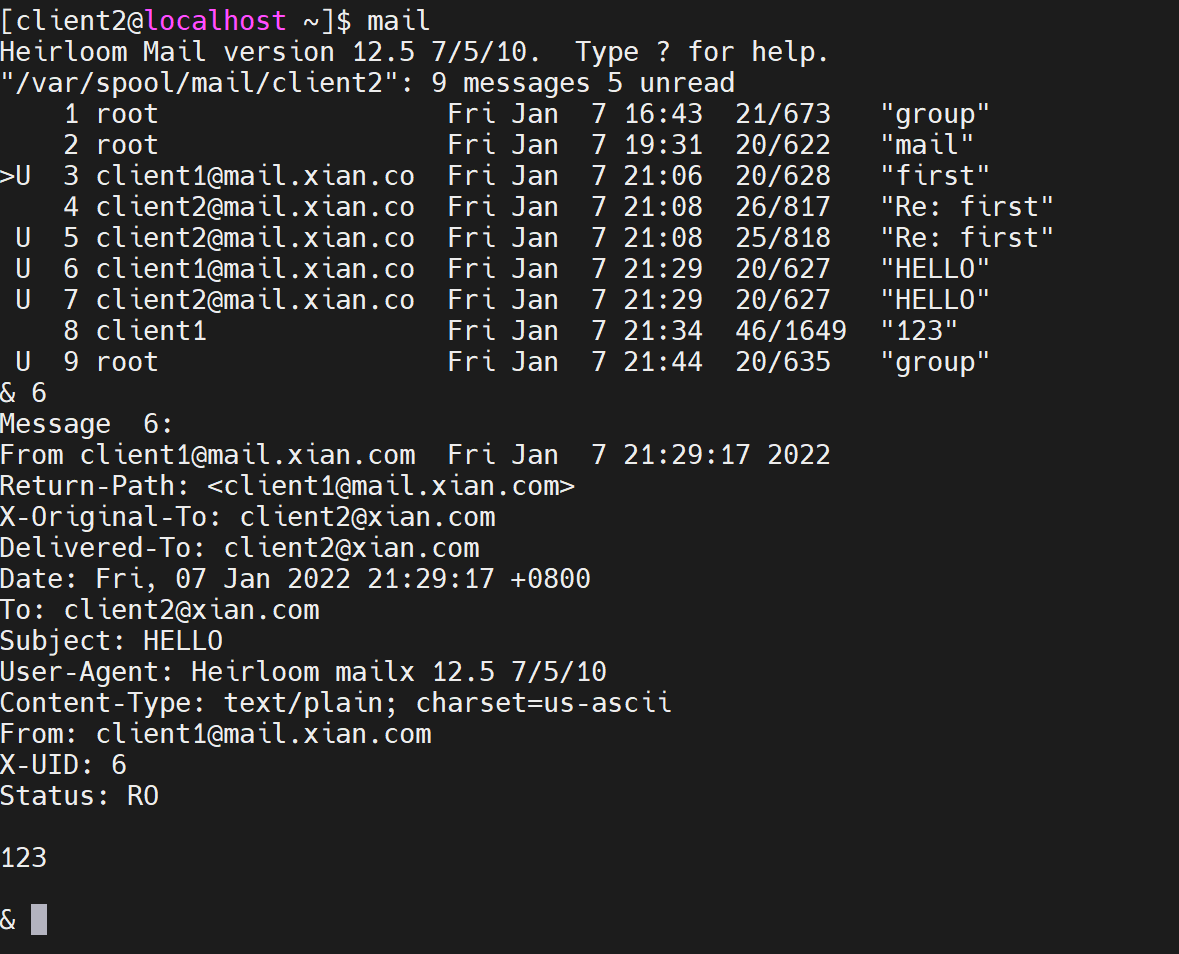
[root@localhost /]# echo "groupfile" | mail -s "group" workgroup
Step 3: verify the results

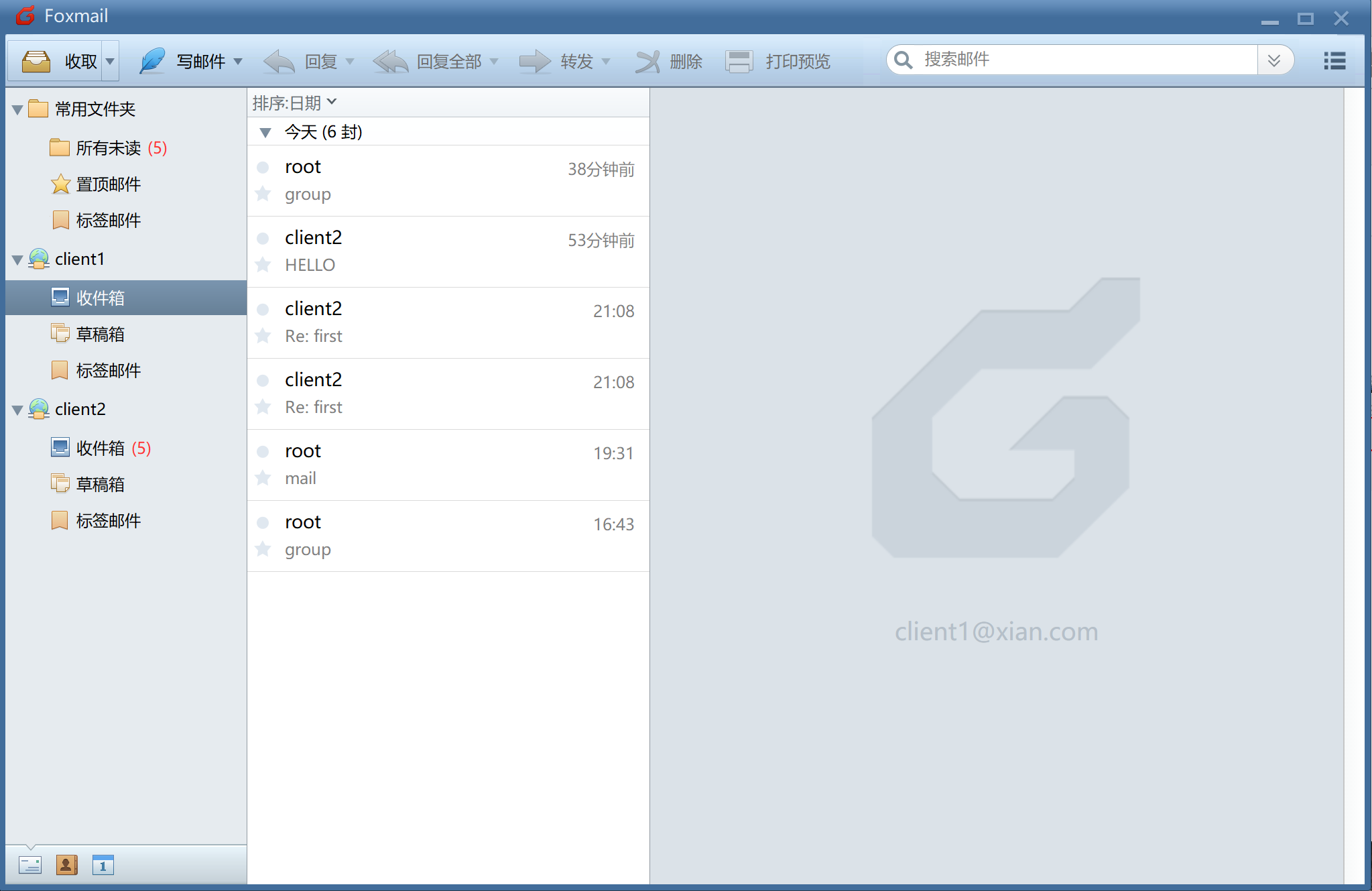
Experiment 3 login with foxmail
Install software: yum install dovecot -y #Provide incoming mail yum install cyrus-sasl* -y #Provide sasl services
Step 1: configure the parsing file
Configuration resolution file: one.First file: /etc/postfix main.cf root@localhost /]# vim /etc/postfix/main.cf Add at the end of the document sasl to configure: smtpd_client_restrictions = permit_sasl_authenticated #Restrictions on clients: allow sasl authentication smtpd_recipient_restrictions = permit_mynetworks, permit_sasl_authenticated, #Restrictions on the receiving side: allow mynetworks, allow sasl authentication, and reject the unauthenticated destination address_ unauth_ destination smtpd_sasl_auth_enable = yes #Enable sasl smtpd_sasl_local_domain = $mydomain #The region where sasl is enabled: $mydomain - > Xian com smtpd_sasl_security_options = noanonymous #Anonymity is not allowed inet_interfaces = all #Specify listening interface two.Second file:/etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf Send mail profile [root@localhost /]# vim /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf protocols = imap pop3 lmtp submission #Use email protocol login_trusted_networks = 192.168.58.0/24 #Set the ip segment allowed to log in three.Third file:/etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf [root@localhost conf.d]# vim 10-auth.conf disable_plaintext_auth = NO #Allow plaintext transmission four.Fourth file:/etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf [root@localhost conf.d]# vim /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf mail_location = mbox:~/mail:INBOX=/var/mail/%u #Set the directory where MRA stores mail: the directory where MRA stores mail after synchronizing mail from MTA five.Fifth document:/etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-ssl.conf [root@localhost conf.d]# vim /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-ssl.conf ssl = required Change to ssl = no #Do not use ssl six.Sixth document: /etc/sysconfig/saslauthd [root@localhost conf.d]# vim /etc/sysconfig/saslauthd MECH=pam Change to MECH=shadow #Log in and read / etc/shadow Turn on the service and turn off the firewall [root@localhost /]# systemctl restart postfix.service [root@localhost systemctl restart dovecot [root@localhost /]# systemctl restart saslauthd.service [root@localhost /]# systemctl stop firewall [root@localhost /]# setenforce 0
Step 2: modify the windows hosts file so that you can use mail
cmd enter the directory address of the host file, open it in text form and modify it.

Add the mail IP domain name at the end of the text

Step 3: create a user to store mail after foxmail login on Linux
[root@localhost /]#cd /home/client1/mail/.imap [root@localhost /]#mkdir INBOX [root@localhost /]#cd /home/client2/mail/.imap [root@localhost /]# mkdir INBOX
Step 4: windows opens foxmail software and logs in to create a new user
Open the software and click other mailboxes

Enter the user password. The IMAP and SMTP server addresses here are the same. Click create.

Click finish and log in to the user's email
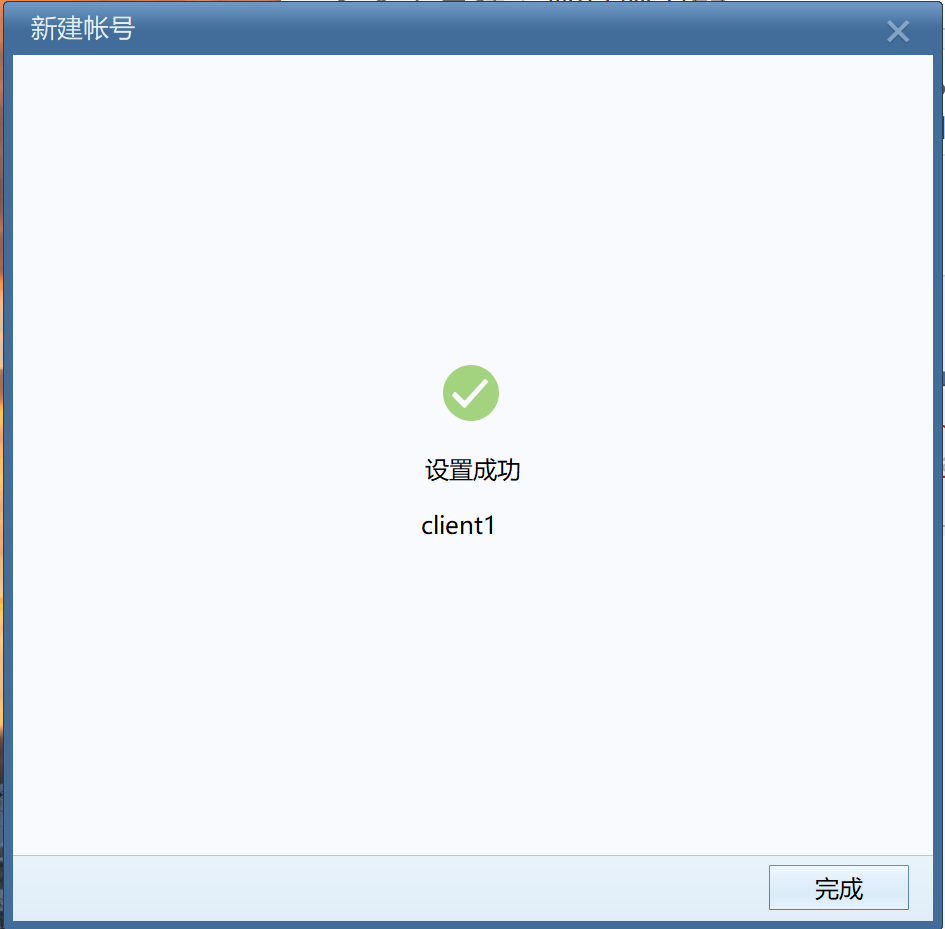
client1 user login succeeded
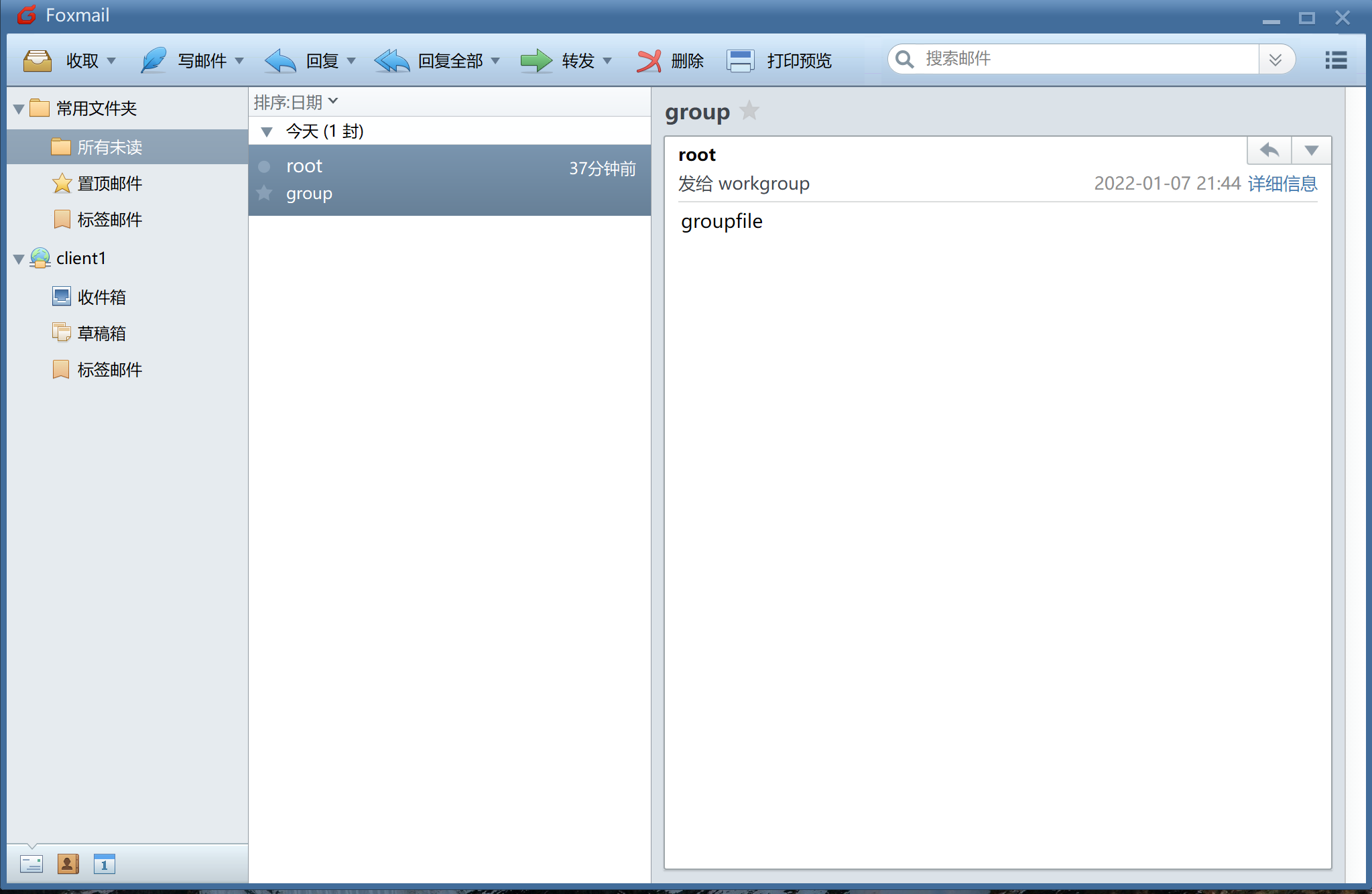
The client2 user is obtained by the same operation