preface
In the use of maps, especially in navigation scenes, GPS track recording is very necessary and useful. This article will share the track recording part under Android system.
system architecture
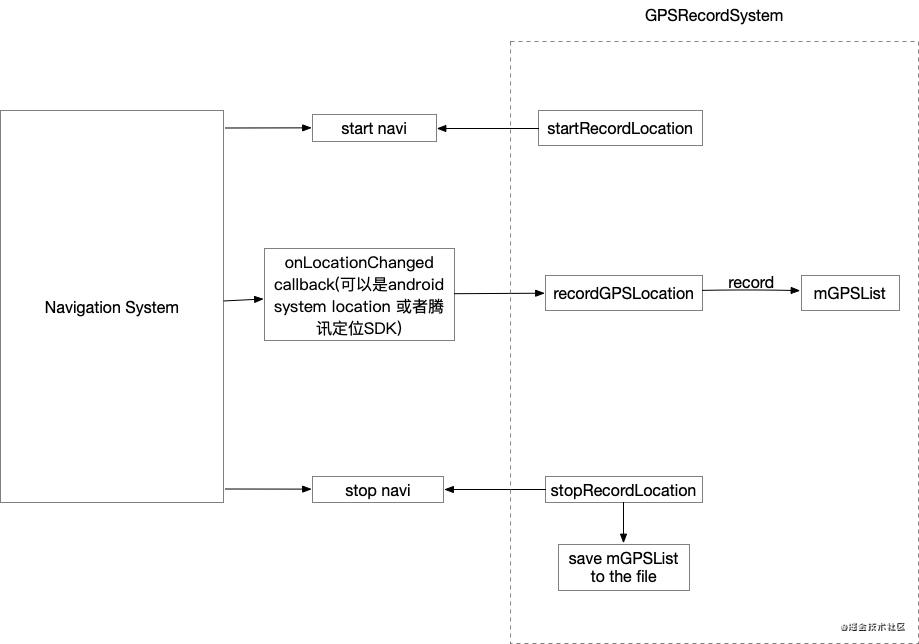
A GPS track recording system is mainly divided into three parts: start recording, record GPS positioning, end recording and storage, as shown on the right of the above figure. In practical application, take the navigation system as an example: (1) when starting Navi, configure the recording work; (2) Record the GPSLocation after receiving the callback of onLocationChanged from Android system; (3) At the end of the navigation (stop navi), stop recording and save the file.
Related code display
Relevant variables used
private LocationManager mLocationManager; // System locationManager private LocationListener mLocationListener; // System locationListener private boolean mIsRecording = false; // Are you recording private List<String> mGpsList; // list of gps records private String mRecordFileName; // gps file name
- start recording
Recording is generally started at the beginning of the whole system. For example, in the navigation scene, when "start navigation", you can start to configure "startRecordLocation"
public void startRecordLocation(Context context, String fileName) {
// Recording is already in progress
if (mIsRecording) {
return;
}
Toast.makeText(context, "start record location...", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// Initializing locationManager and locationListener
mLocationManager = (LocationManager) context.getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
mLocationListener = new MyLocationListener();
try {
// Add listener
mLocationManager.requestLocationUpdates(LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER, 0, 0, mLocationListener);
} catch (SecurityException e) {
Toast.makeText(context, "start record location error!!!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Log.e(TAG, "startRecordLocation Exception", e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
// The name of the record file is recorded in the form of "realLocationRecord + routeID"
mRecordFileName = fileName;
if (!mRecordFileName.endsWith(".gps")) {
mRecordFileName += ".gps";
}
mIsRecording = true;
}
- Track recorded during recording
The record location is usually called "recordGPSLocation" when obtaining the onLocationChanged callback of Android system
public void recordGPSLocation(Location location) {
if (mIsRecording && location != null) {
// location to list record
mGpsList.add(locationToString(location));
}
}
locationToString tool method
The GPS track points driving the navigation work generally include the following elements: longitude, latitude, accuracy, angle, speed, time and altitude. Therefore, it is recorded here to prepare for the later track playback.
private String locationToString(Location location) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
String timeStr = gpsDataFormatter.format(new Date(time));
sb.append(location.getLatitude());
sb.append(",");
sb.append(location.getLongitude());
sb.append(",");
sb.append(location.getAccuracy());
sb.append(",");
sb.append(location.getBearing());
sb.append(",");
sb.append(location.getSpeed());
sb.append(",");
sb.append(timeStr);
sb.append(",");
sb.append(df.format((double) time / 1000.0));
// sb.append(df.format(System.currentTimeMillis()/1000.0));
// sb.append(df.format(location.getTime()/1000.0));
sb.append(",");
sb.append(location.getAltitude());
sb.append("\n");
return sb.toString();
}
- End recording and save gps file
Ending recording generally works at the end of the whole system. For example, in the navigation scenario, stop recording when "end navigation" calls "stopRecordLocation"
public void stopRecordLocation(Context context) {
Toast.makeText(context, "stop record location, save to file...", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// Remove listener
mLocationManager.removeUpdates(mLocationListener);
String storagePath = StorageUtil.getStoragePath(context); // Stored path
String filePath = storagePath + mRecordFileName;
saveGPS(filePath);
mIsRecording = false;
}
GPS track storage tool and method
private void saveGPS(String path) {
OutputStreamWriter writer = null;
try {
File outFile = new File(path);
File parent = outFile.getParentFile();
if (parent != null && !parent.exists()) {
parent.mkdirs();
}
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
writer = new OutputStreamWriter(out);
for (String line : mGpsList) {
writer.write(line);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "saveGPS Exception", e);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (writer != null) {
try {
writer.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to flush output stream", e);
}
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to close output stream", e);
}
}
}
}
getStoragePath tool method of StorageUtil
// Stored in the following path / TencentMapSDK/navigation
private static final String NAVIGATION_PATH = "/tencentmapsdk/navigation";
// getStoragePath tool method
public static String getStoragePath(Context context) {
if (context == null) {
return null;
}
String strFolder;
boolean hasSdcard;
try {
hasSdcard = Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "getStoragePath Exception", e);
e.printStackTrace();
hasSdcard = false;
}
if (!hasSdcard) {
strFolder = context.getFilesDir().getPath() + NAVIGATION_PATH;
File file = new File(strFolder);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
} else {
strFolder = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getPath() + NAVIGATION_PATH;
File file = new File(strFolder);
if (!file.exists()) { // Directory does not exist, create directory
if (!file.mkdirs()) {
strFolder = context.getFilesDir().getPath() + NAVIGATION_PATH;
file = new File(strFolder);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
}
} else { // The directory exists. Create a file to test whether you have permission
try {
String newFile = strFolder + "/.test";
File tmpFile = new File(newFile);
if (tmpFile.createNewFile()) {
tmpFile.delete();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e(TAG, "getStoragePath Exception", e);
strFolder = context.getFilesDir().getPath() + NAVIGATION_PATH;
file = new File(strFolder);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
}
}
}
return strFolder;
}
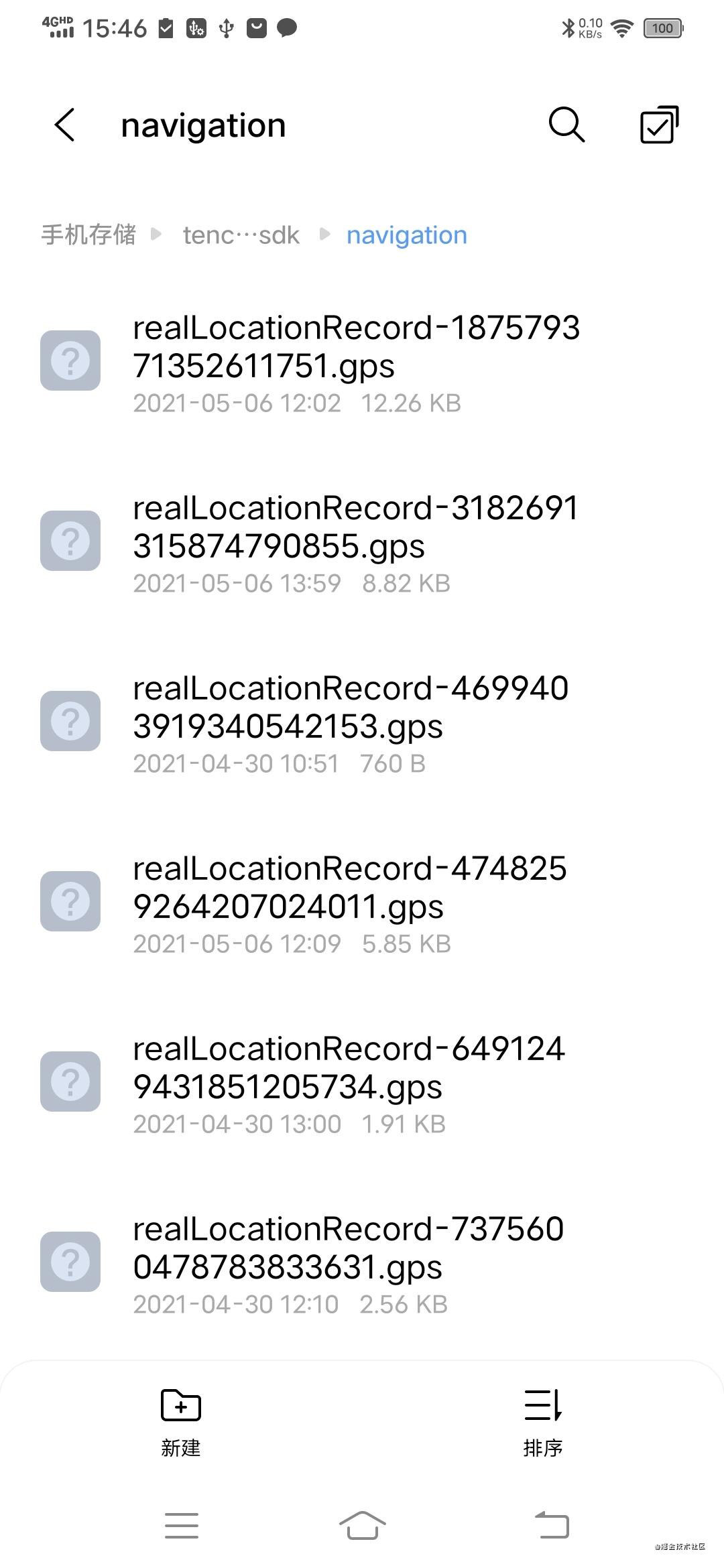
Result display
Finally, it is stored in the navigation directory under the mobile phone directory
follow-up work
Later, you can explain the recorded gps files and share the track playback in the navigation scene
Author: Tencent location service
Link: https://my.oschina.net/u/4209404/blog/5048899
Source: open source China
The copyright belongs to the author. For commercial reprint, please contact the author for authorization. For non-commercial reprint, please indicate the source.