Memory Forensics
- Forensics file suffix raw,. vmem,. img
- Common commands (imageinfo, pslist, dumpfiles, memdump)
- Suspicious process (notepad, cmd)
- Combined with disk Forensics
- Understand some operating system principles
- Common file suffixes dmg, img
Volatile basic commands
You can use the - h parameter to get the usage method and plug-in introduction, and list several commonly used commands
imageinfo: displays the summary information of the target image. This is often the first step. Obtain the operating system type and version of the memory. Then, you can bring the corresponding operating system in the – profile. This parameter is required for subsequent operations
pslist: the plug-in lists system processes, but it cannot detect hidden or unlinked processes. psscan can
pstree: view the process list in the form of a tree. Like pslist, hidden or unlinked processes cannot be detected
psscan: you can find previously terminated (inactive) processes and processes hidden or unlinked by rootkit
cmdscan: can be used to view terminal records
notepad: view the currently displayed notepad text (– low version of profile=winxp is OK, win7 is not OK, you can try to use editbox)
filescan: scan all file lists
linux performs directional scanning of relevant characters with grep command, such as grep flag, grep -E 'png|jpg|gif|zip|rar|7z|pdf|txt|doc'
dumpfiles: export a file (specify virtual address)
Offset - Q and output directory - D need to be specified
memdump: extract the specified process. foremost is often used to separate the files inside
Process - p [pid] and output directory - D need to be specified
editbox: displays information about the edit control (content that has been edited)
screenshot: save pseudo screenshots based on GDI windows
Clipboard: View clipboard information
iehistory: retrieve IE browser history
systeminfo: displays detailed configuration information (plug-ins) about the computer and its operating system
hashdump: view the password hash in the current operating system, such as the SAM file content of Windows (the mimikatz plug-in can obtain the system plaintext password)
mftparser: recover deleted files
svcscan: scan Windows services
connscan: View network connections
envars: view environment variables
dlllist: lists all dll files loaded by a process
hivelist: lists all registry keys and their virtual and physical addresses
timeliner: expands all operating system events in the form of a timeline
0x01 easy_dump.img
python vol.py -f easy_dump.img imageinfo
INFO : volatility.debug : Determining profile based on KDBG search...
Suggested Profile(s) : Win7SP1x64, Win7SP0x64, Win2008R2SP0x64, Win2008R2SP1x64_24000, Win2008R2SP1x64_23418, Win2008R2SP1x64, Win7SP1x64_24000, Win7SP1x64_23418
AS Layer1 : WindowsAMD64PagedMemory (Kernel AS)
AS Layer2 : FileAddressSpace (/home/ring04h/volatility/easy_dump.img)
PAE type : No PAE
DTB : 0x187000L
KDBG : 0xf8000403f070L
Number of Processors : 1
Image Type (Service Pack) : 0
KPCR for CPU 0 : 0xfffff80004040d00L
KUSER_SHARED_DATA : 0xfffff78000000000L
Image date and time : 2018-09-28 09:02:19 UTC+0000
Image local date and time : 2018-09-28 17:02:19 +0800
python vol.py -f easy_dump.img --profile=Win7SP1x64 pslist
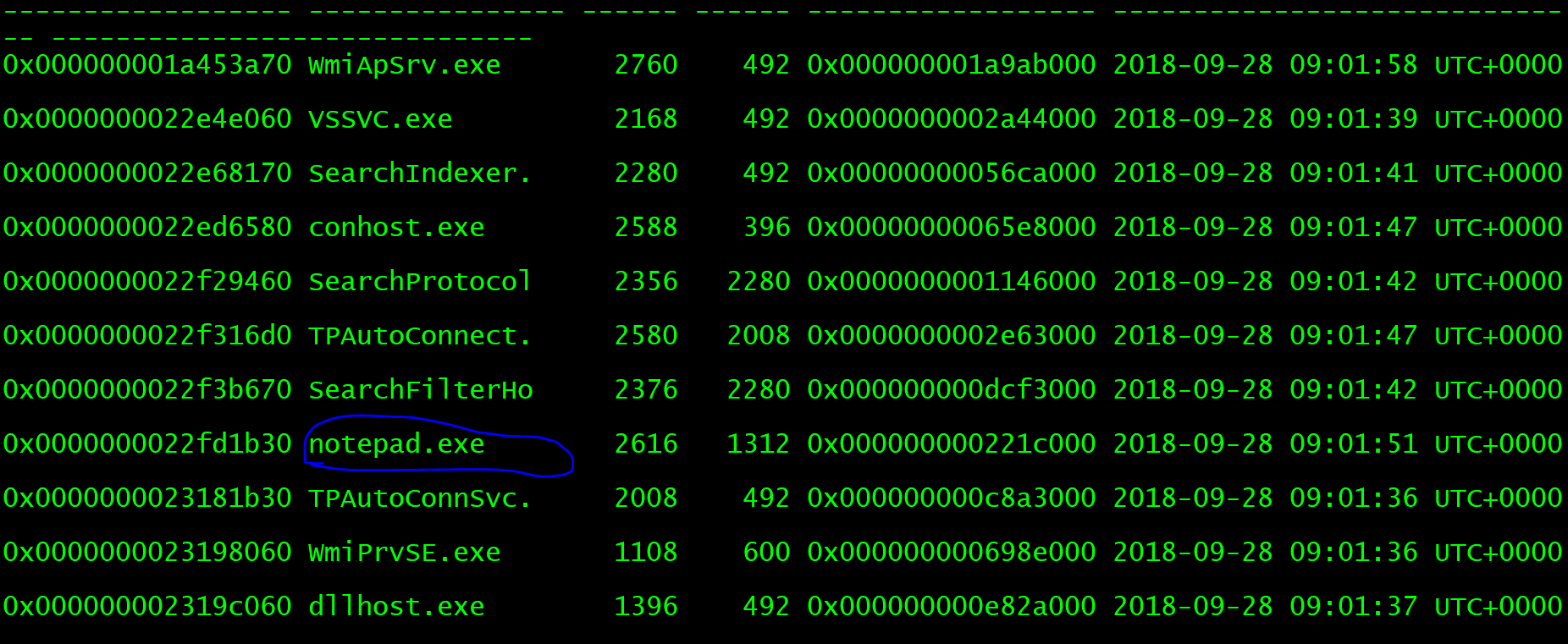
There is a notepad process, which obviously writes files and extracts them.
python vol.py -f easy_dump.img --profile=Win7SP1x64 memdump -p 2616 -D ./
However, the extracted strings cannot be viewed directly. You need to use the following command
strings -e l 2626.dmp | grep flag
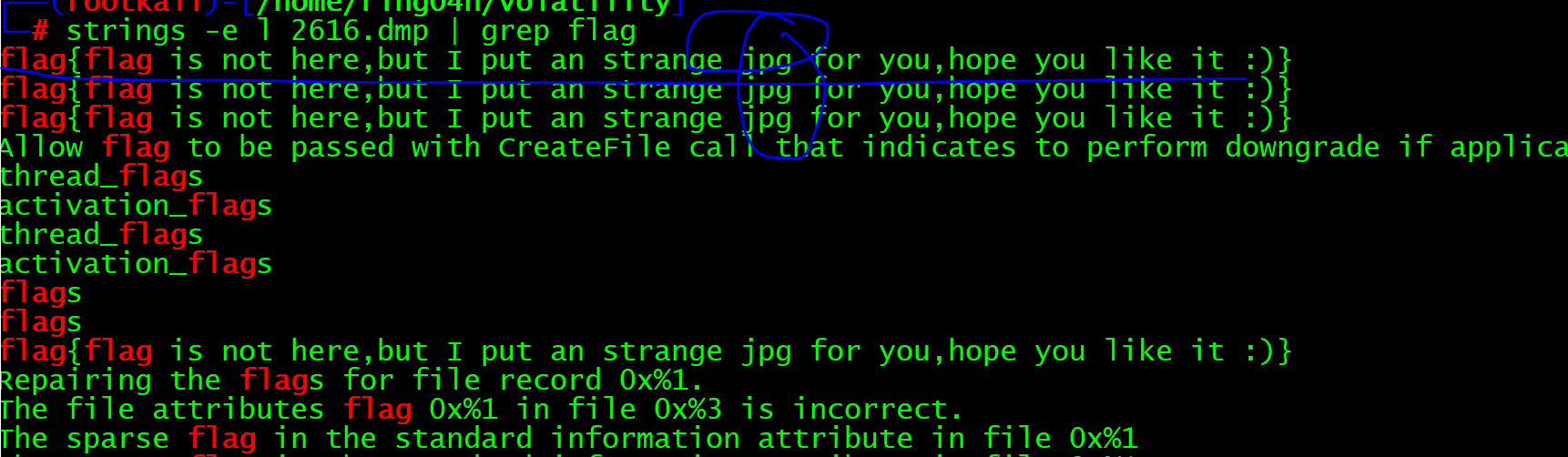
Continue looking for picture files
python vol.py -f easy_dump.img --profile=Win7SP1x64 filescan |grep -E 'jpg|gif|png'
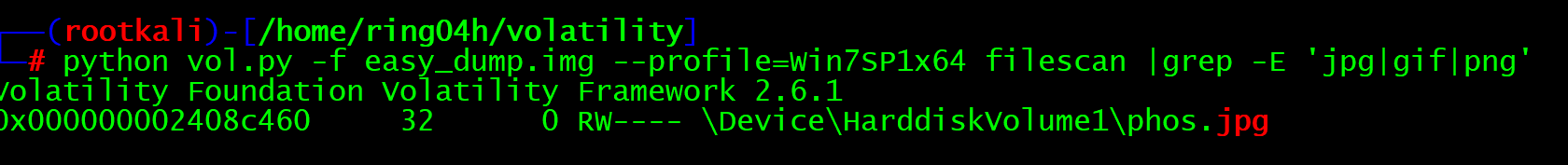
Extract picture file
python vol.py -f easy_dump.img --profile=Win7SP1x64 dumpfiles -Q 0x000000002408c460 -D ./
After the picture is claimed, use binwalk to test whether the picture carries zip files and other contents
binwalk file.None.0xfffffa8008355410.vacb
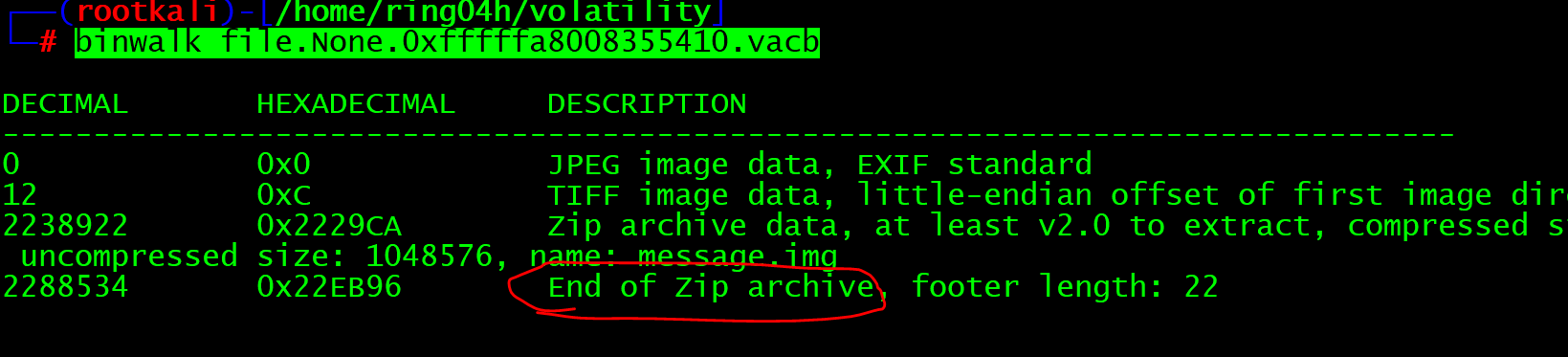
Use binwalk to separate files, or use foremost to separate files. We choose binwalk to separate files
binwalk -e file.None.0xfffffa8008355410.vacb
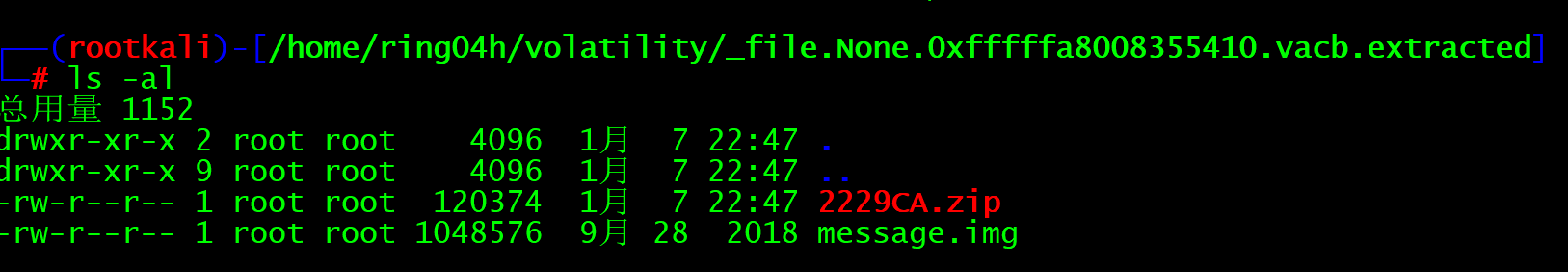
Obviously, there is a zip file and an img file. The IMG suffix may be an image file. You can check it with the file command or unzip the compressed package
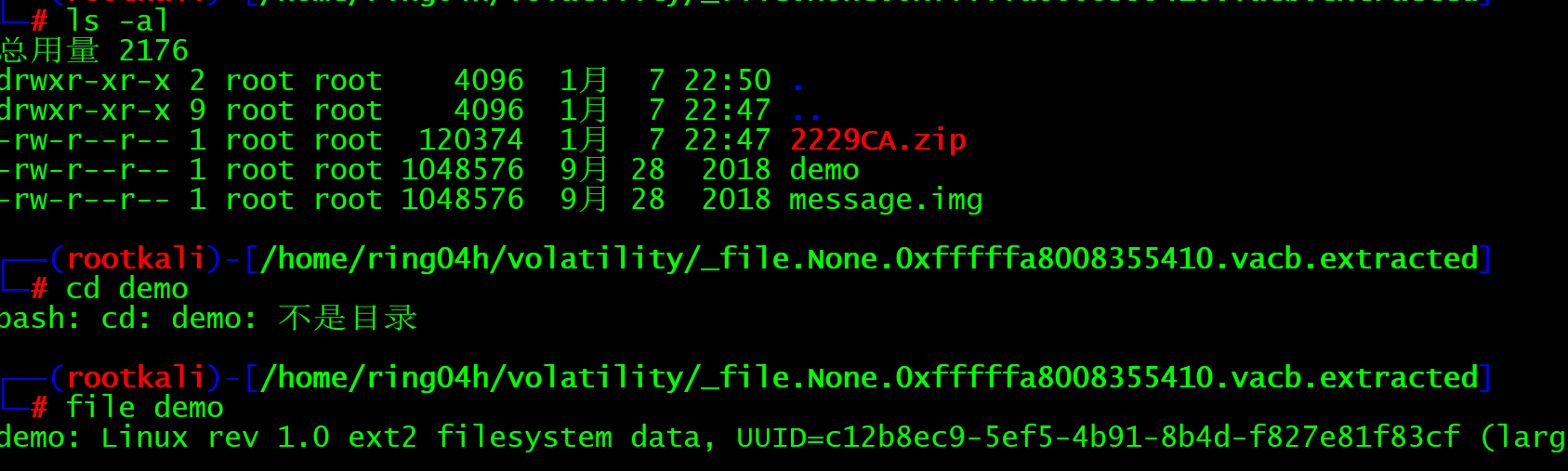
After decompression, we found that the zip folder is message IMG files. We use file to view linux files and mount them directly
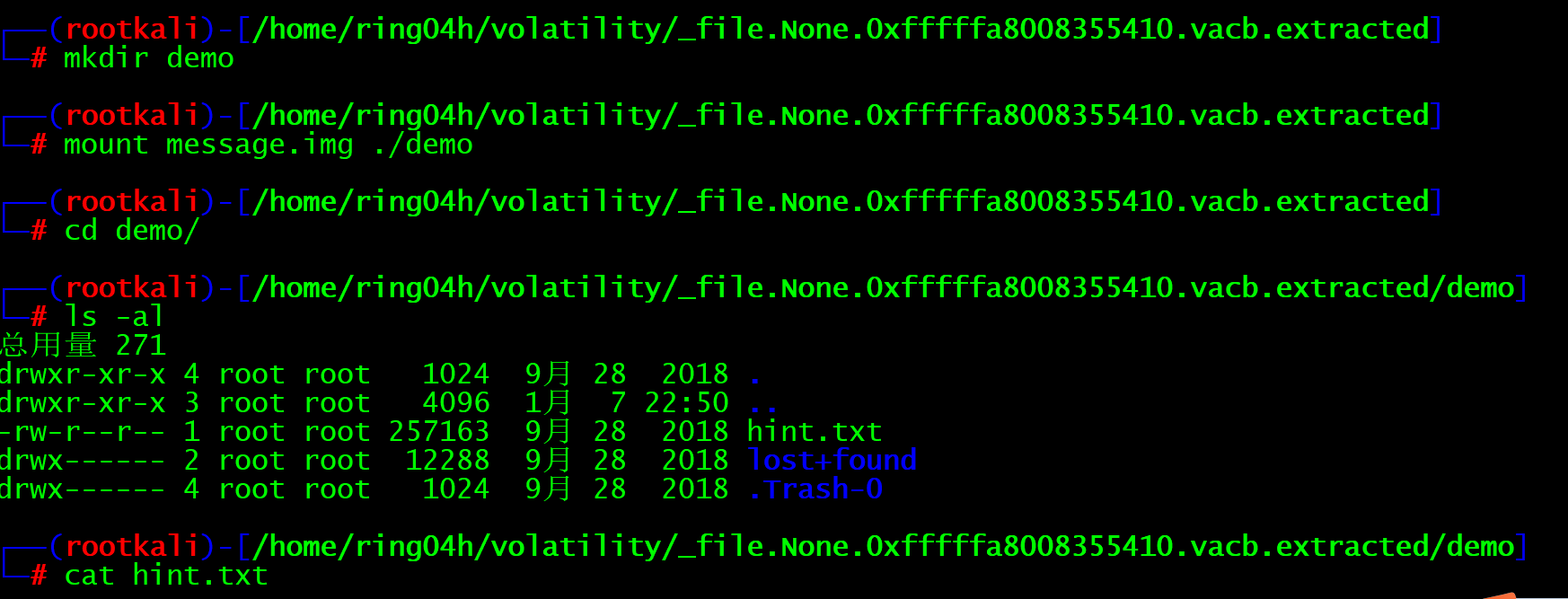
You can see that there are two folders and a TXT file. Let's check the txt file first
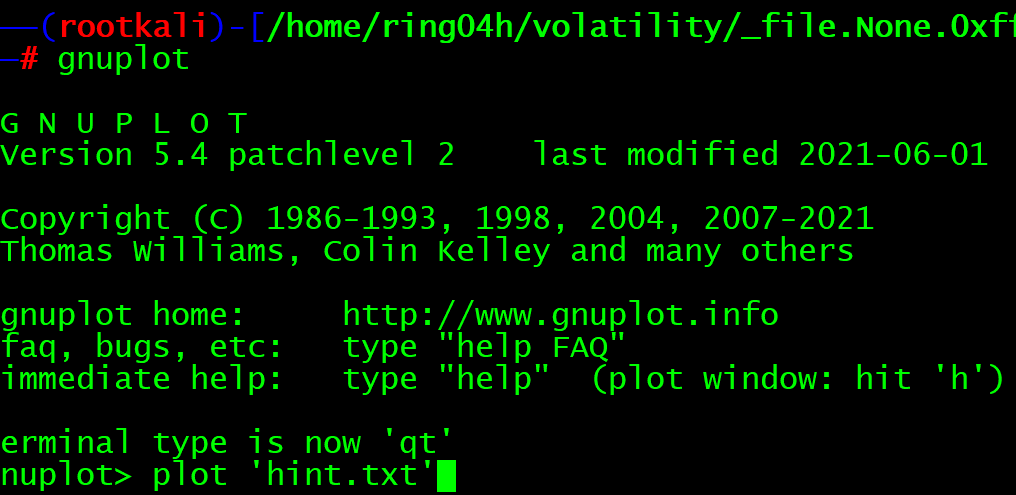
269 206 269 207 269 208 269 209 269 210 269 211 269 212 269 213 269 214 269 215 269 216 269 217 269 218 269 219 After checking, many numbers appear in pairs, which is similar to the coordinates Try converting numbers to coordinates, using gnuplot Draw a picture and find the QR code
After direct processing, a QR code is generated and scanned.
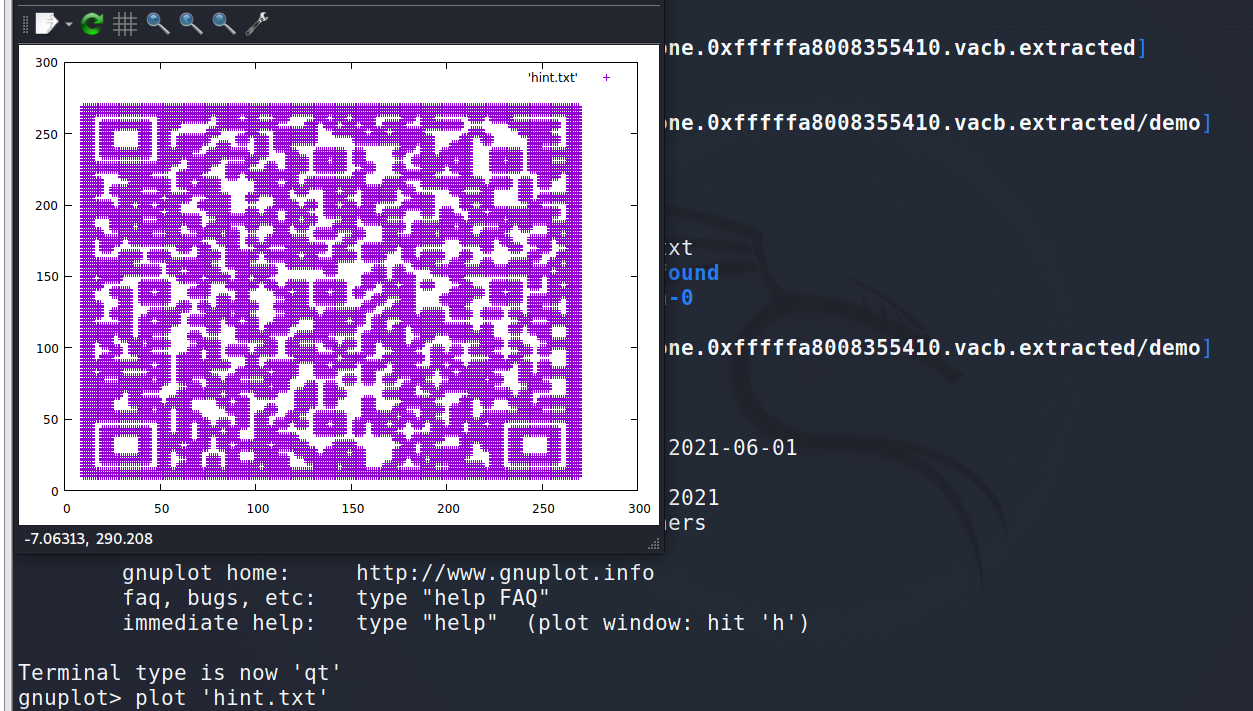
Prompt a string of English
Here is the vigenere key: aeolus, but i deleted the encrypted message.
This is a Virginia password. The secret key is aeolus. With encryption, with secret key, you need ciphertext. Continue to check the two folders just now and look for the ciphertext
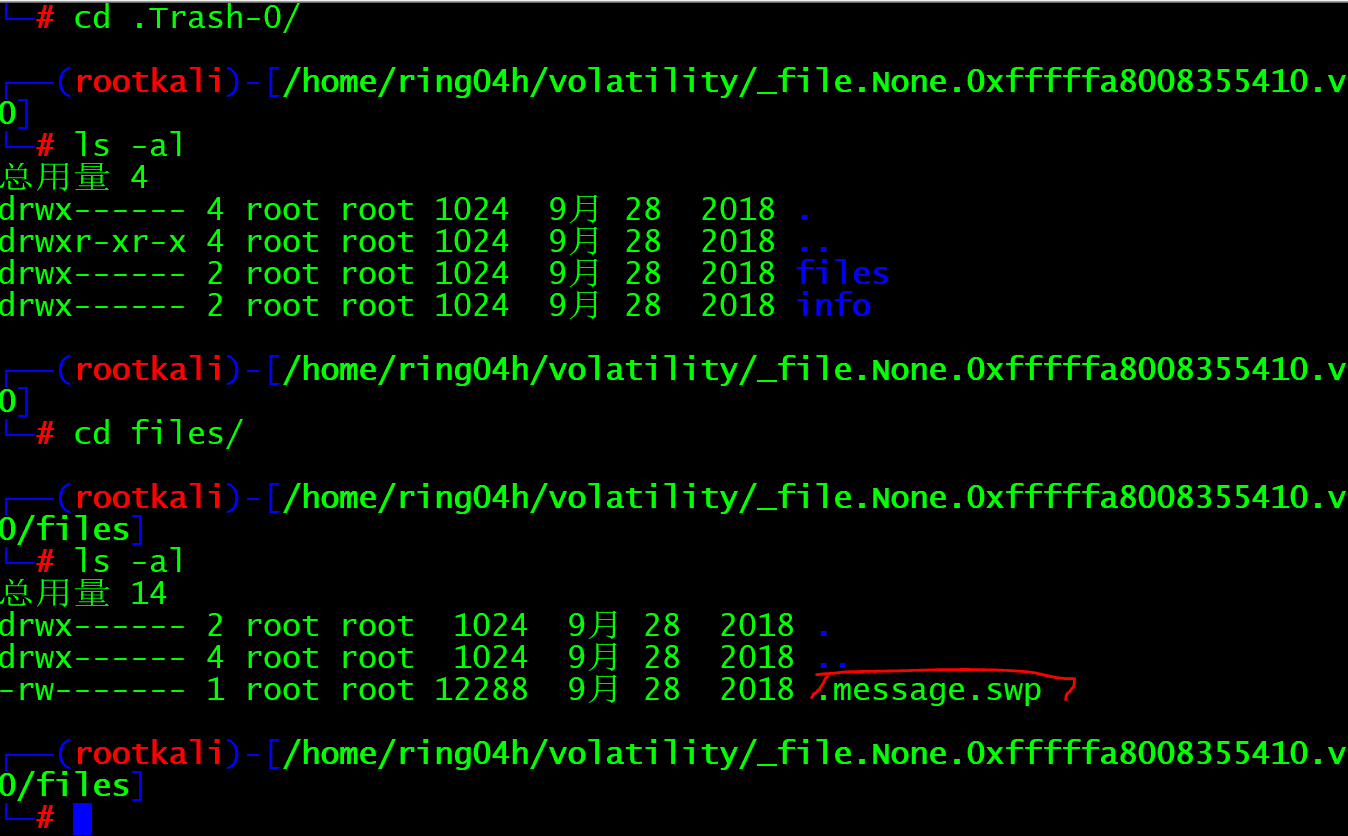
I found one swp file. If you are familiar with it and know that it is an interrupted file, you can recover it directly
vim -r .message.swp
Ciphertext appears
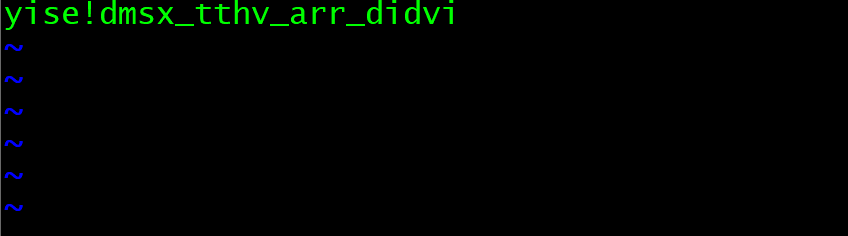
Direct online decryption
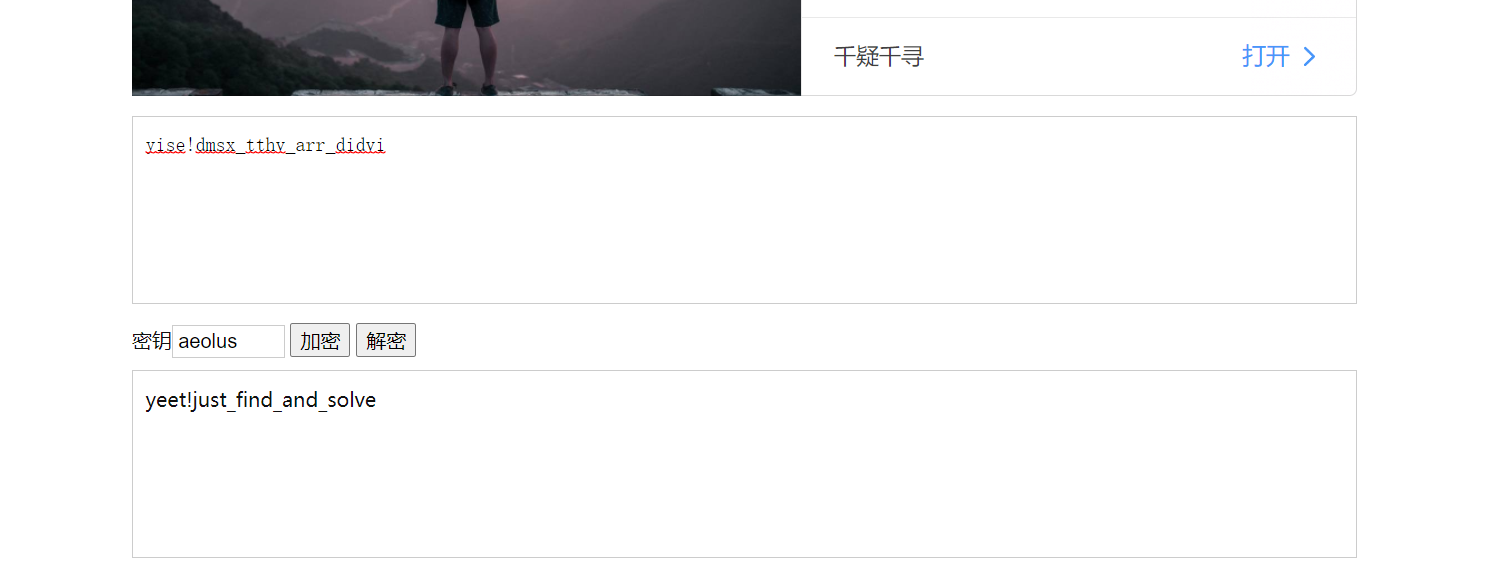
This is the end of the problem