There are many ways to merge multiple dataframes in pandas:
- merge merges are based on the same values in a column
- join is to merge multiple dataframes left and right, which is equivalent to merging multiple columns
- concat can merge multiple dataframes with the same column names. You can set whether to merge rows or columns
1. merge (join and merge based on the same column value)
how = connection mode
on = merge column names
The default internal connection mode is internal connection
Do not set only consider the common values in the key column
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'id':[1,2,3,4,5,6],'city':['wuhan','newyork','shanghai','paris','losangeles','london'],'country':['china','usa','china','france','usa','england'],'visits':[2,1,2,1,2,1]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'id':[1,2,3,4,5],'country':['china','france','usa','germany','japan'],'visits':[2,2,2,2,2]})
print(df1)
print(df2)

print('Internal links')
df3 = pd.merge(df1,df2,on='country')
print(df3)

Left join
Consider all the values in the key column of df1. If there is no corresponding value in the key column of df2, NaN will be filled
print('Left link')
df3 = pd.merge(df1,df2,on='country',how='left')
print(df3)

Right join
Consider all the values in the key column of df2. If there is no corresponding value in the key column of df1, NaN will be filled
print('Right link')
df3 = pd.merge(df1,df2,on='country',how='right')
print(df3)

Multiple column names are link keys
If you need to merge multiple columns, set on = ('column 1', 'column 2' )
print('Multiple column names are link keys')
df4 = pd.merge(df1,df2,on=('country','visits'))
print(df4)

Set column name suffix of new column after merging
If there are other columns with the same column names before and after merging, you can set the suffix of duplicate names in df1 and df2:
suffixes = ('left suffix', 'right suffix'))
If it is not set, the suffix is "X", "Y" by default
print('Set column name suffix of new column after merging')
df4 = pd.merge(df1,df2,on='country',suffixes=('_city','_country'))
print(df4)

Merge different column names in left and right tables
In some cases, the column names of the left and right tables that need to be merged are not necessarily the same. For example, country in df1 merges countryname in df2
print('Merge different column names in left and right tables')
df22.columns=['id','countryname','visits']
df5 = pd.merge(df1,df22,left_on=['country'],right_on=['countryname'],suffixes=('_city','_country'))
print(df5)

Delete extra columns
Delete the extra columns that just appeared (countryname)
print('Delete column')
df5.drop(columns=['countryname'],inplace=True)
print(df5)

2.join (merge two DFS of different column names)
Default left connection
Do not set how, default left connection, that is, consider all lines of df1, if the number of lines in df2 is not enough, Nan will make up
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'id':[1,2,3,4,5,6],'city':['wuhan','newyork','shanghai','paris','losangeles','london'],'country':['china','usa','china','france','usa','england'],'visits':[2,1,2,1,2,1]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'idy':[1,2,3,4,6],'cityy':['wuhan','newyork','shanghai','paris','losangeles'],'countryy':['china','usa','china','france','usa']})
print(df1)
print(df2)
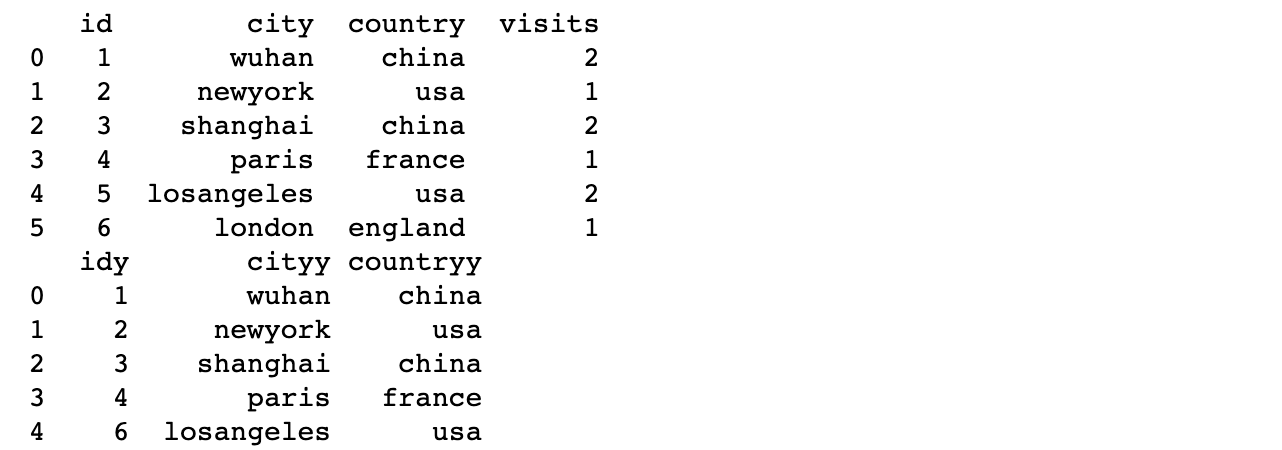

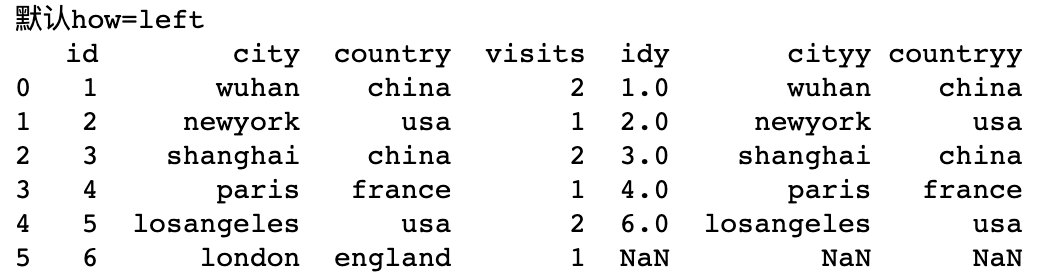
print('default how=left')
df3 = df1.join(df2)
print(df3)
Right join
Set how = 'right', consider all lines in df2, and if the number of lines in df1 is not enough, Nan will make up
print('Right link')
df3 = df1.join(df2,how='right')
print(df3)

Internal connection
how = 'inner', subject to the minimum number of lines in df1 and df2
print('Internal links')
df3 = df1.join(df2,how='inner')
print(df3)

External connection
how = 'outer', subject to the most lines in df1 and df2
print('External links')
df3 = df1.join(df2,how='outer')
print(df3)

Concat (specify the merged dimension to merge df)
Column connection
If axis=1, all columns will be spliced together. Column number = df1 column number + df2 column number
from pandas import concat
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'id':[1,2,3,4,5,6],'city':['wuhan','newyork','shanghai','paris','losangeles','london'],'country':['china','usa','china','france','usa','england'],'visits':[2,1,2,1,2,1]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'id':[1,2,3,4,6],'city':['wuhan','newyork','shanghai','paris','losangeles'],'country':['china','usa','china','france','usa'],'visits':[2,1,2,1,2]})
print(df1)
print(df2)
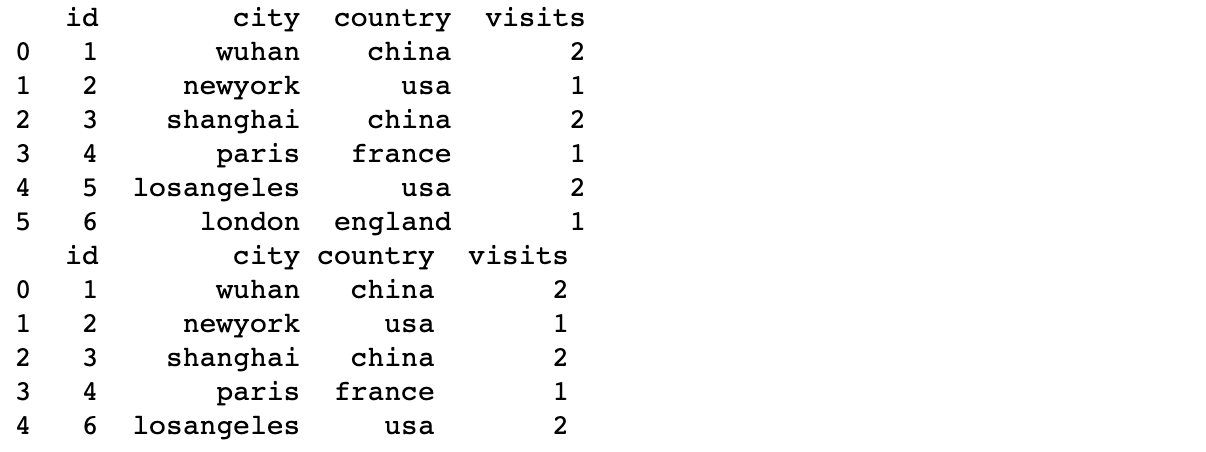

print('Column connection')
df3 = concat([df1,df2],join="inner",axis=1)
print(df3)

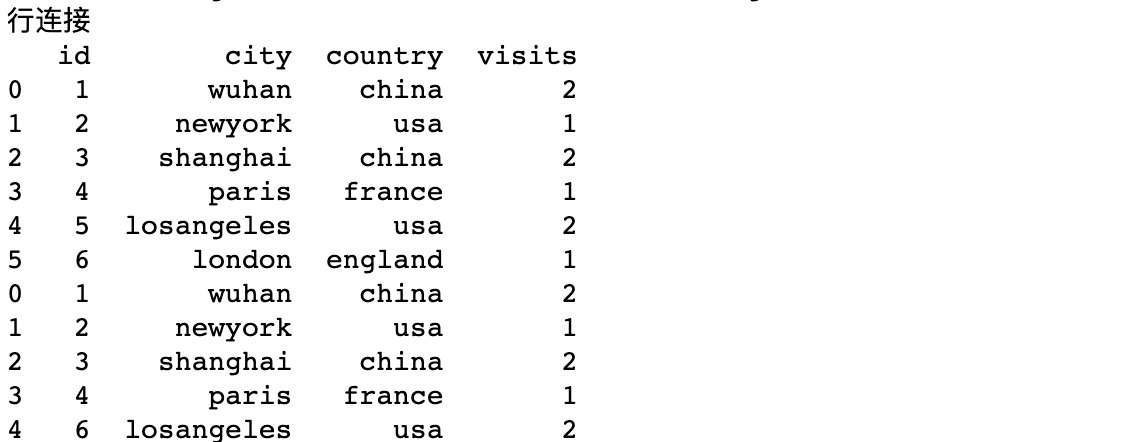
Row connection
If axis is not set, then axis=0. It is required that the same column name exists. According to the same column name, the rows are spliced. The number of rows = df1 rows + df2 rows
print('Row connection')
df3 = concat([df1,df2])
print(df3)

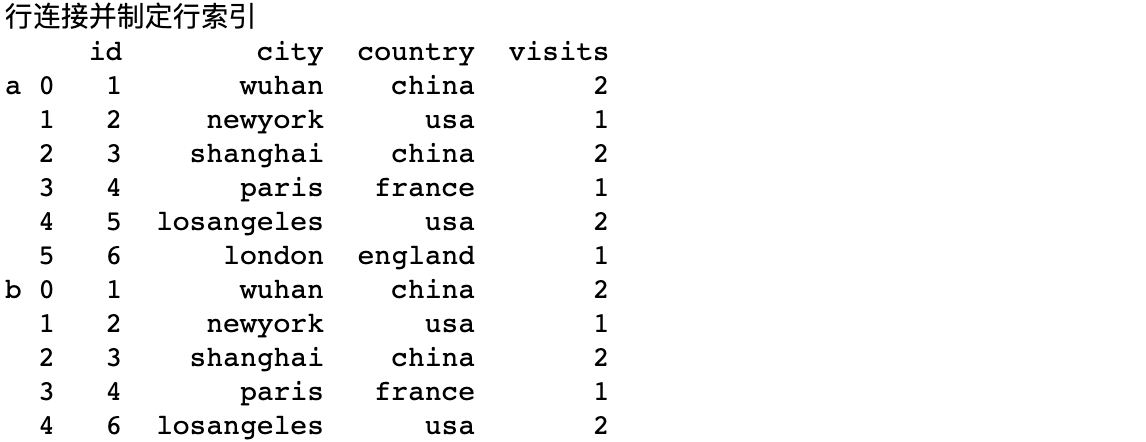
Row join and index
When connecting rows, you can specify the index
print('Row join and index')
df3 = concat([df1,df2],keys=['a','b'])
print(df3)
Duplicate removal
The same row information will appear after the row is connected, just delete duplicate rows by drop
print("Duplicate removal")
df3 = concat([df1,df2],ignore_index=True).drop_duplicates()
print(df3)


