Catalog
4.MHA cluster architecture diagram
Algorithms for failover alternate primary libraries:
1. Understanding MHA
1. Overview of MHA
MHA (MasterHigh Availability) is an excellent set of software for failover and master-slave replication in MySQL highly available environment.
The emergence of MHA is to solve the MySQL single point problem.
During MySQL failover, MHA can automatically complete the failover within 0-30 seconds.
MHA ensures maximum data consistency during failover to achieve true high availability.
2. Composition of MHA
# MHA Node (Data Node)
MHA Node runs on each MySQL server.
** MHA Manager (Management Node)
MHA Manager can be deployed on a separate machine to manage multiple master-slave clusters.You can also deploy on a slave node.
The MHA Manager periodically detects master nodes in the cluster.When the master fails, it can automatically promote the slave of the latest data to the new master, then redirect all other slaves to the new master.The entire failover process is fully transparent to the application.
3. Characteristics of MHA
During automatic failover, MHA tries to save binary logs from the downtime master server to ensure maximum data loss
With semi-synchronous replication, you can greatly reduce the risk of data loss. If only one slave has received the latest binary logs, MHA can apply the latest binary logs to all other slave servers, thereby ensuring data consistency across all nodes.
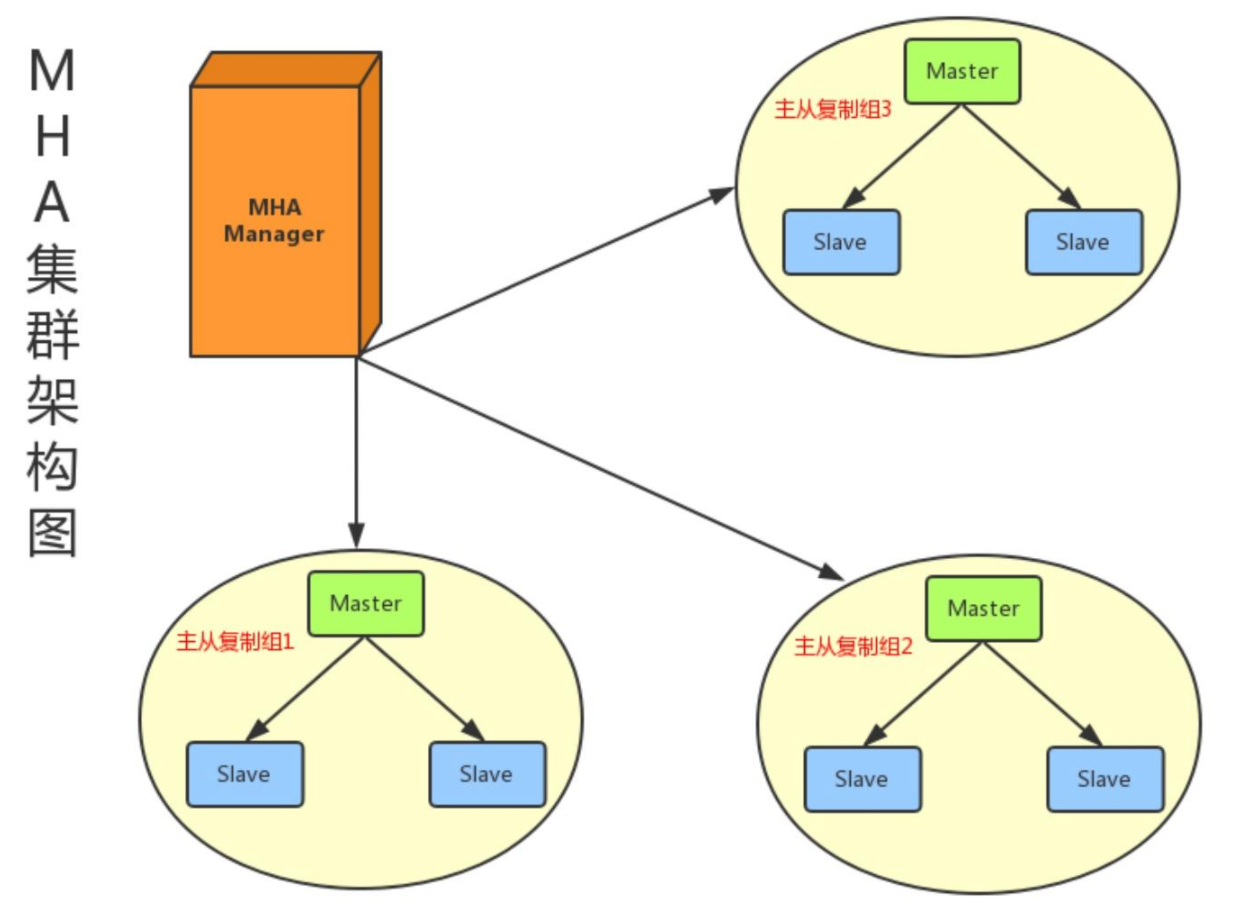
Currently, MHA supports a master-slave architecture with at least three services, one master-two-slave
4.MHA cluster architecture diagram
2. Build MySQL MHA
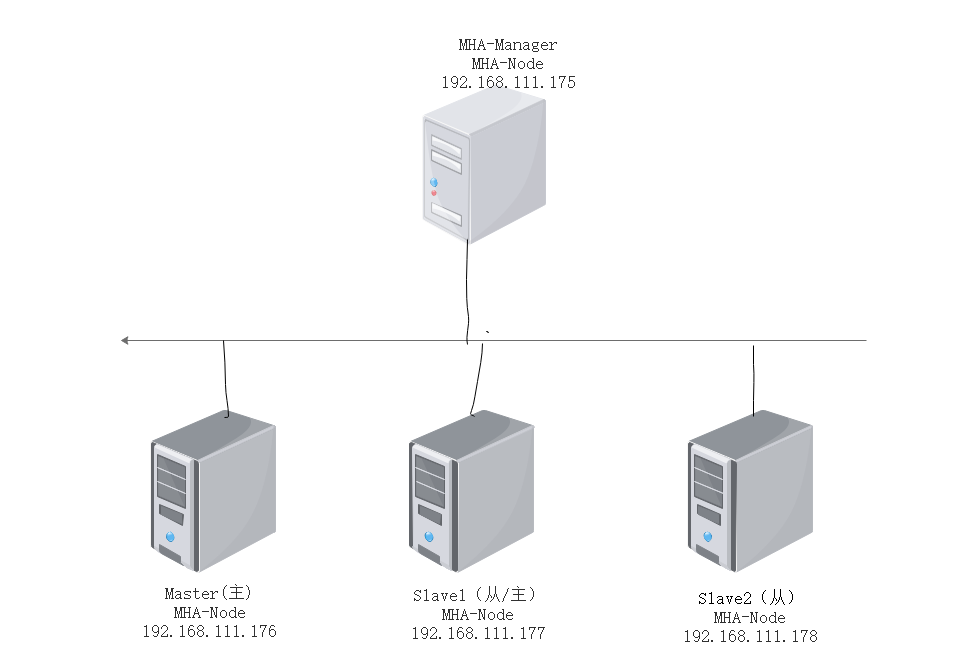
The schematic diagram used in the experiment
Experimental ideas:
1. MHA architecture
1) Database Installation
2) One master, two subordinates
3) MHA build
2. Fault simulation
1) Main warehouse failure
2) Alternate primary library becomes primary Library
3) Rejoining the original failure master library recovery to MHA as slave Library
Experimental preparation:
| Host | operating system | IP Address | Installation packages/software/tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| MHAmanager | CentOS7 | 192.168.111.175 | MHAnode component, MHAmanager component |
| Master | CentOS7 | 192.168.111.176 | mysql-boost-5.7.20.tar.gz, MHAnode components |
| Slave1 | CentOS7 | 192.168.111.177 | mysql-boost-5.7.20.tar.gz, MHAnode components |
| Slave2 | CentOS7 | 192.168.111.178 | mysql-boost-5.7.20.tar.gz, MHAnode components |
1. Construction of MHA
Turn off all server firewalls and security mechanisms
systemctl stop firewalld systemctl disable firewalld setenforce 0
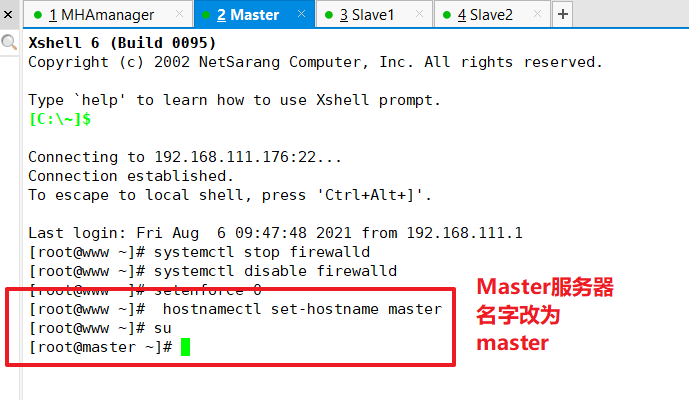
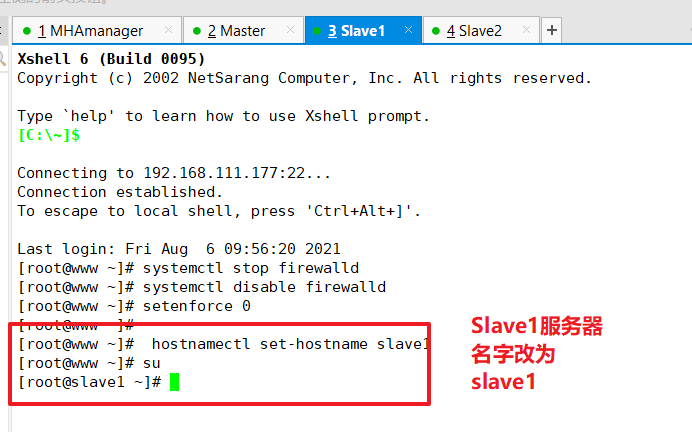
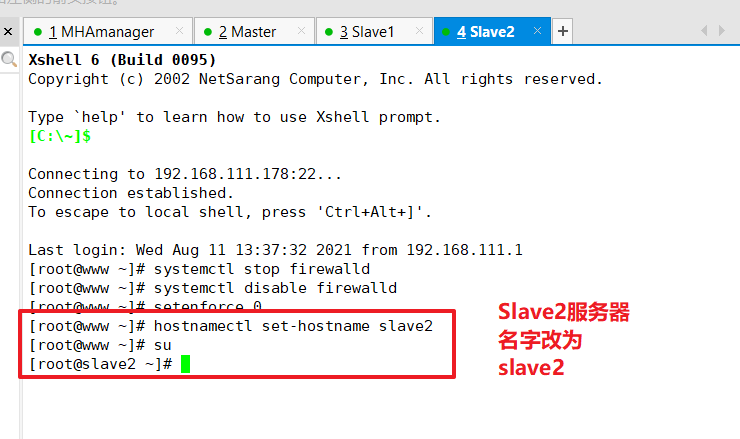
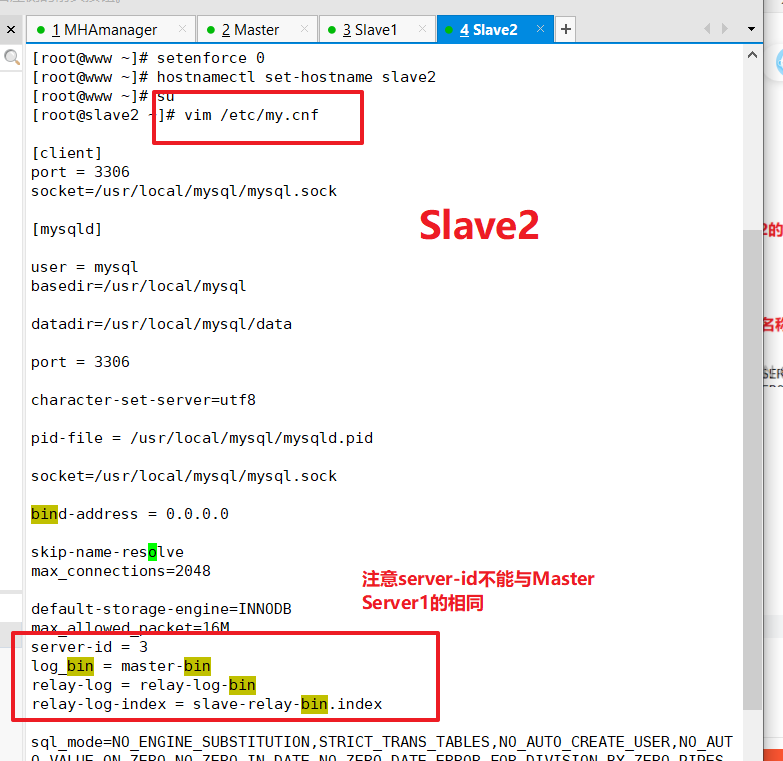
Modify the hostname of Master, Slave1, Slave2 nodes
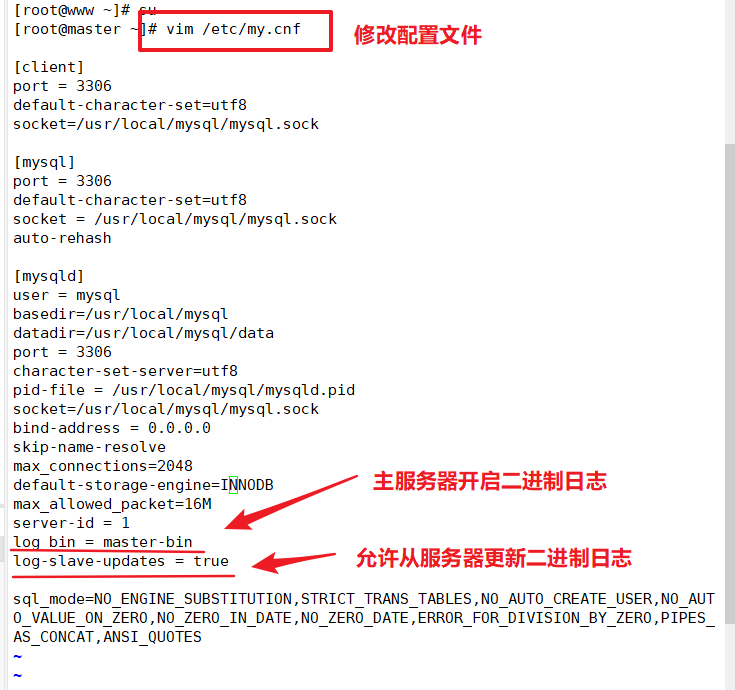
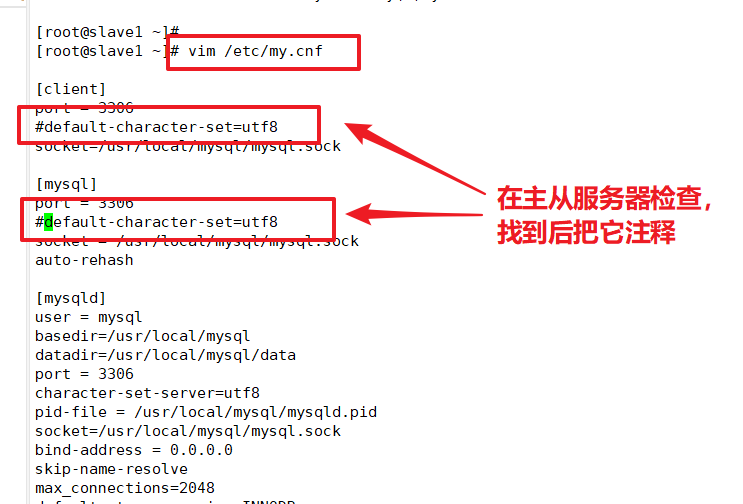
Modify Master's Mysql Master Profile/etc/my.cnf

Modify Mysql main profile/etc/my.cnf for Slave1
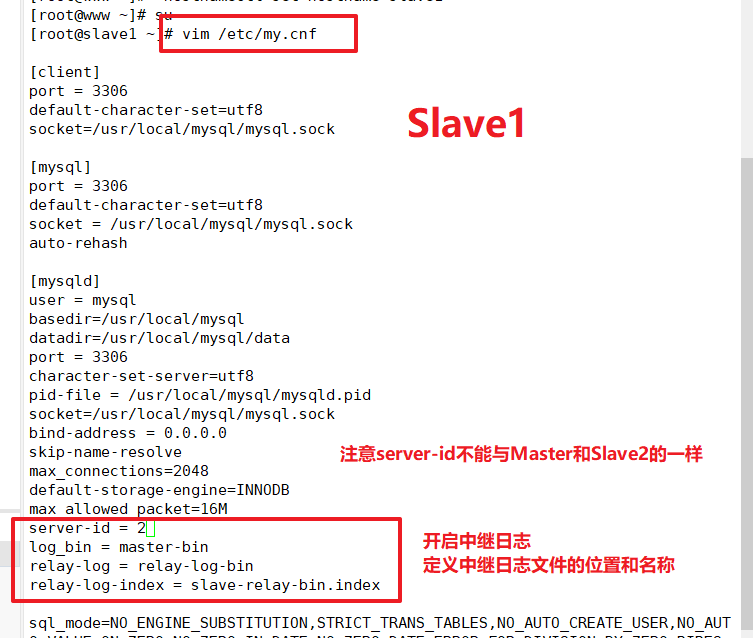

Modify Mysql main profile/etc/my.cnf for Slave2
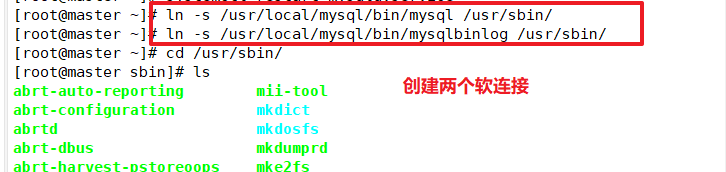
Create two soft links on the Master, Slave1, Slave2 nodes (Master, Slave1, Slave2 all need to be configured)
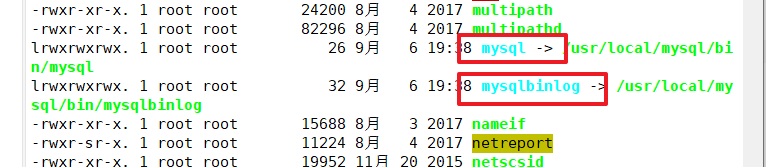
Configure mysql one master two slaves
(1) mysql authorization for all database nodes (Master, Slave1, Slave2 need to be configured)
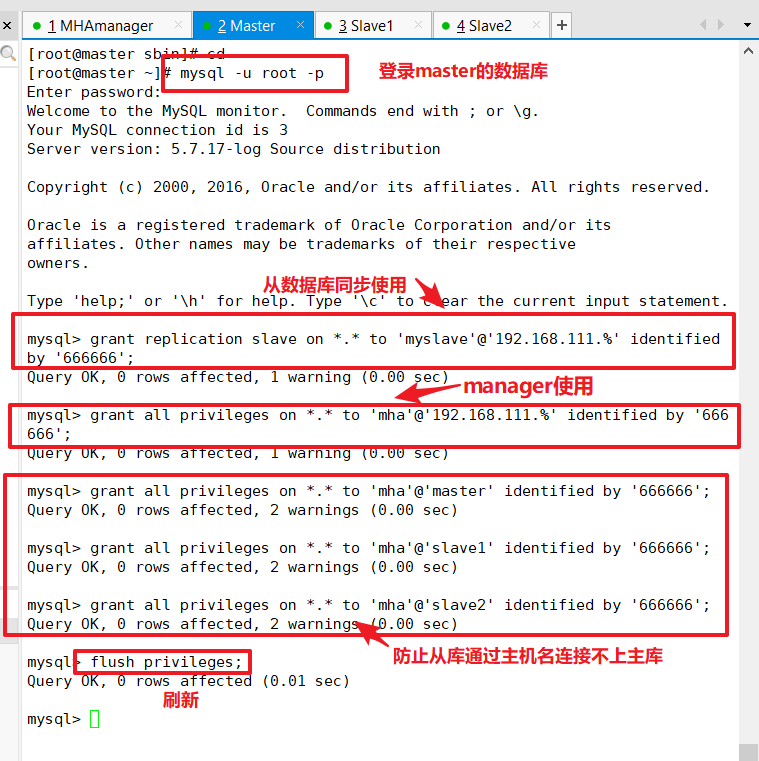
(2) View binaries and synchronization points on the Master node
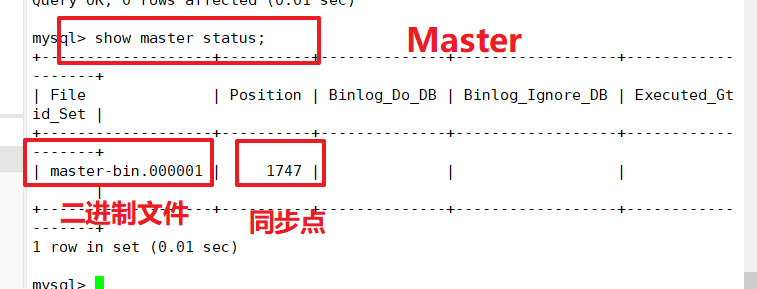
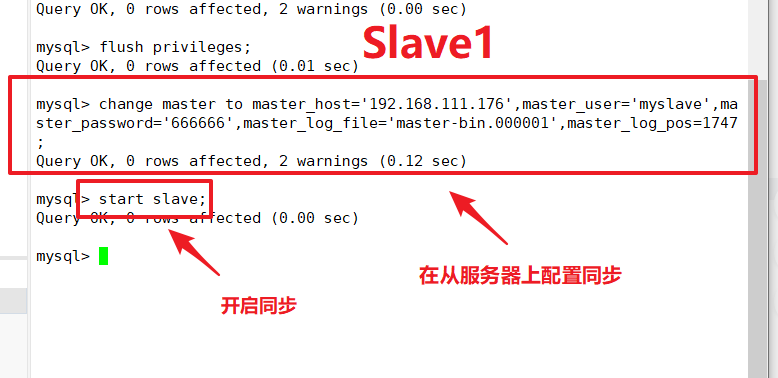
(3) Perform synchronization on Slave1, Slave2 nodes
change master to master_host='192.168.111.176',master_user='myslave',master_password='666666',master_log_file='master-bin.000001',master_log_pos=1747;
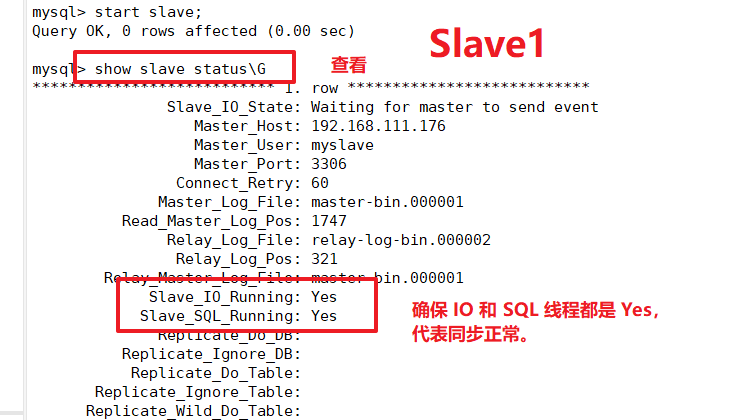
View data synchronization results on Slave1, Slave2 nodes
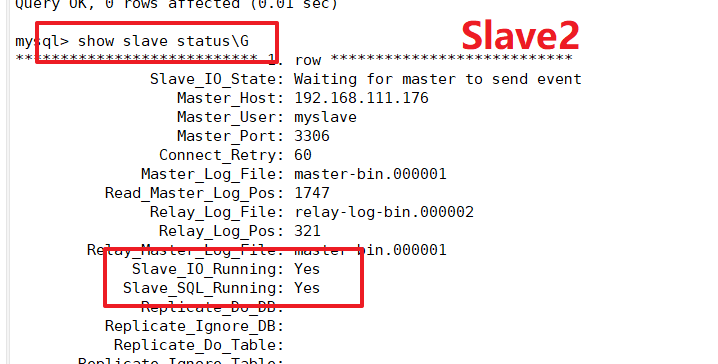
Two slave libraries must be set to read-only mode (Slave1, Slave2)

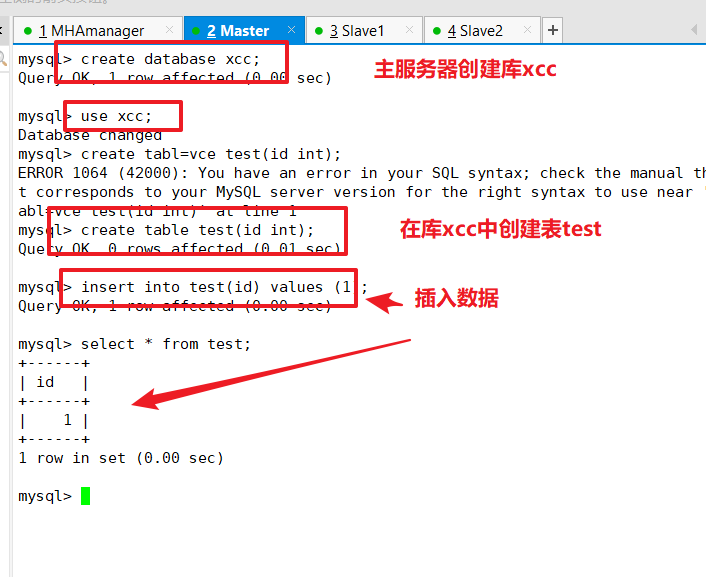
Insert Data Test Database Synchronization
Insert strip data into Master Library to test for synchronization
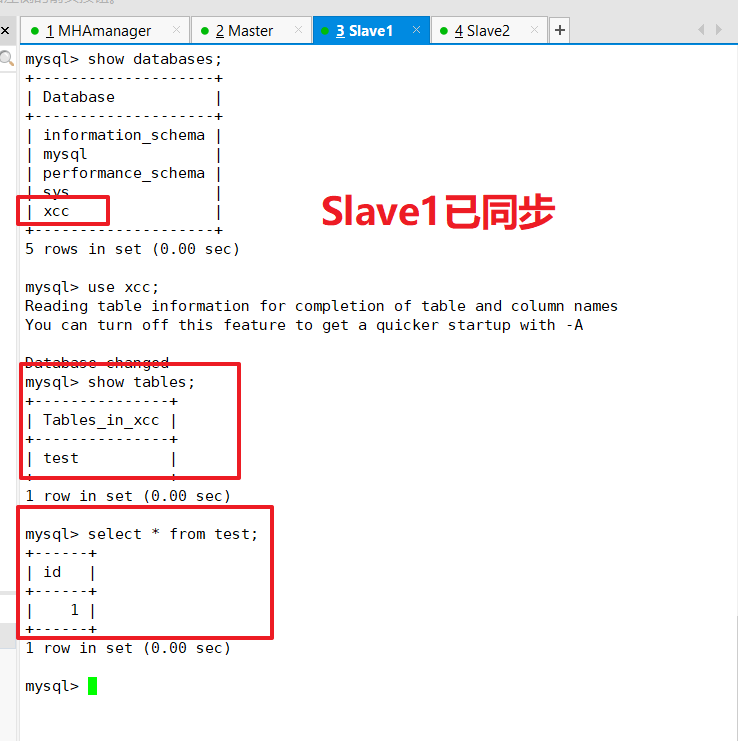
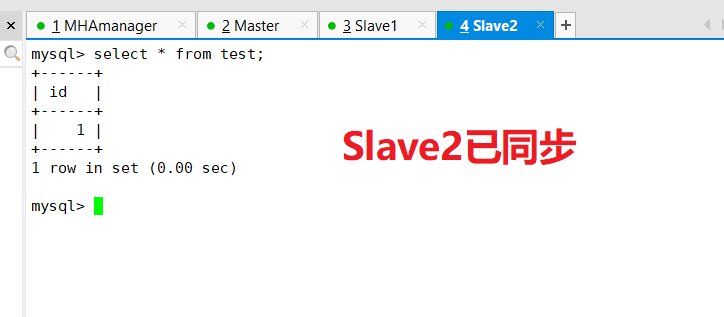
See if synchronization from server
Install MHA software
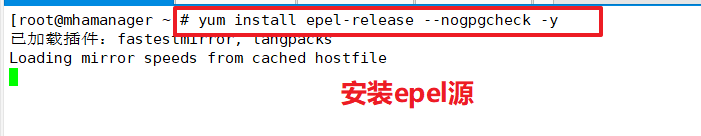
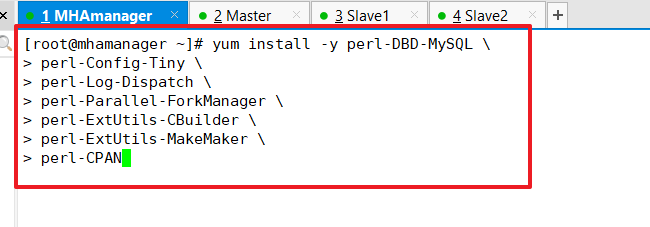
Install MHA-dependent environments on all servers, starting with epel source (4 servers)
yum install epel-release --nogpgcheck -y yum install -y perl-DBD-MySQL \ perl-Config-Tiny \ perl-Log-Dispatch \ perl-Parallel-ForkManager \ perl-ExtUtils-CBuilder \ perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker \ perl-CPAN
Install MHA package
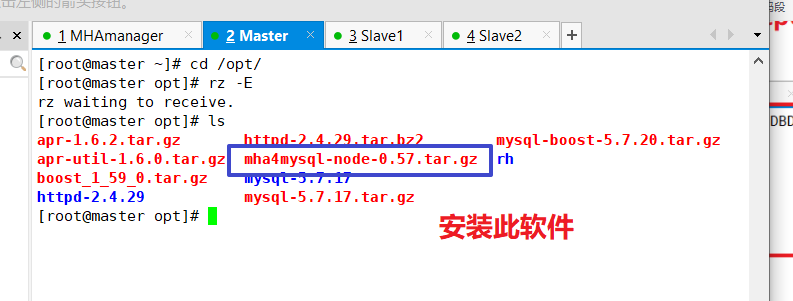
The node component must be installed on all servers first. For each operating system version, CentOS 7.4 must choose version 0.57.
The node component must be installed on all servers before the manager component can be installed on the MHA-manager node because the manager depends on the node component.
Install node components on all servers first
cd /opt tar zxvf mha4mysql-node-0.57.tar.gz cd mha4mysql-node-0.57 perl Makefile.PL make && make install

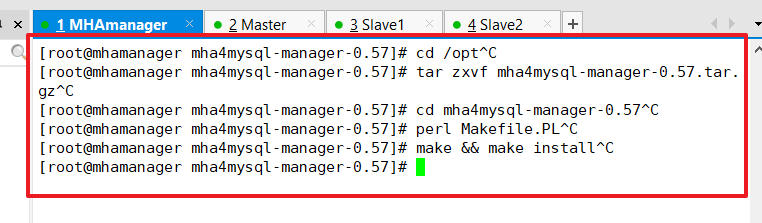
Install the manager component on the HA manager node
cd /opt tar zxvf mha4mysql-manager-0.57.tar.gz cd mha4mysql-manager-0.57 perl Makefile.PL make && make install
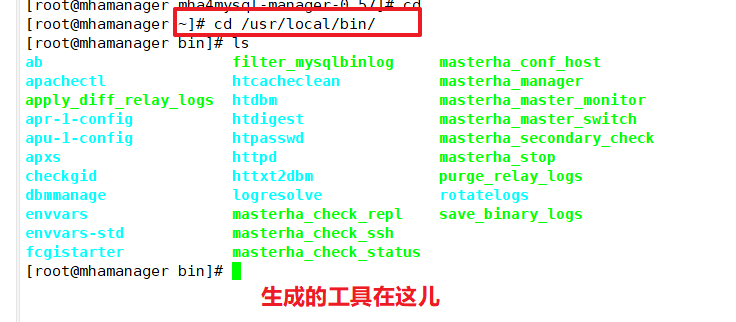
Several tools are generated under /usr/local/bin after the manager component is installed, including the following:
| masterha_check_ssh | Check SHH configuration of MHA |
|---|---|
| masterha_check_repl | Check MySQL replication status |
| masterha_manger | Script to start manager |
| masterha_check_status | Detecting the current MHA running state |
| masterha_master_monitor | Detect whether master is down |
| masterha_master_switch | Control failover (automatic or manual) |
| masterha_conf_host | Add or remove configured server information |
| masterha_stop | Close manager |
Several scripts will also be generated under/usr/local/bin after the node component is installed
Note: These tools are usually triggered by MHAManager scripts and do not require human action:
The main points are as follows:
| save_binary_logs | Save and copy master's binary log |
|---|---|
| apply_diff_relay_logs | Relay log events that identify differences and apply their differences to other slave s |
| filter_mysqlbinlog | Remove unnecessary ROLLBACK events (MHA no longer uses this tool) |
| purge_relay_logs | Clear relay logs (will not block SQL threads) |
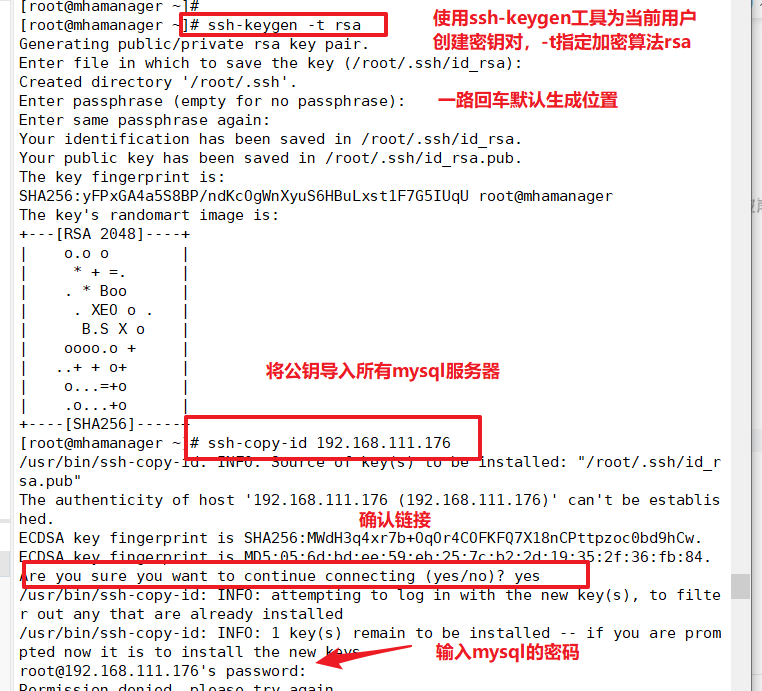
Configure Password-Free Authentication on All Servers
Password-free authentication configured on the manager node to all database nodes
ssh-keygen -t rsa #Press Enter all the way ssh-copy-id 192.168.111.176 ssh-copy-id 192.168.111.177 ssh-copy-id 192.168.111.178
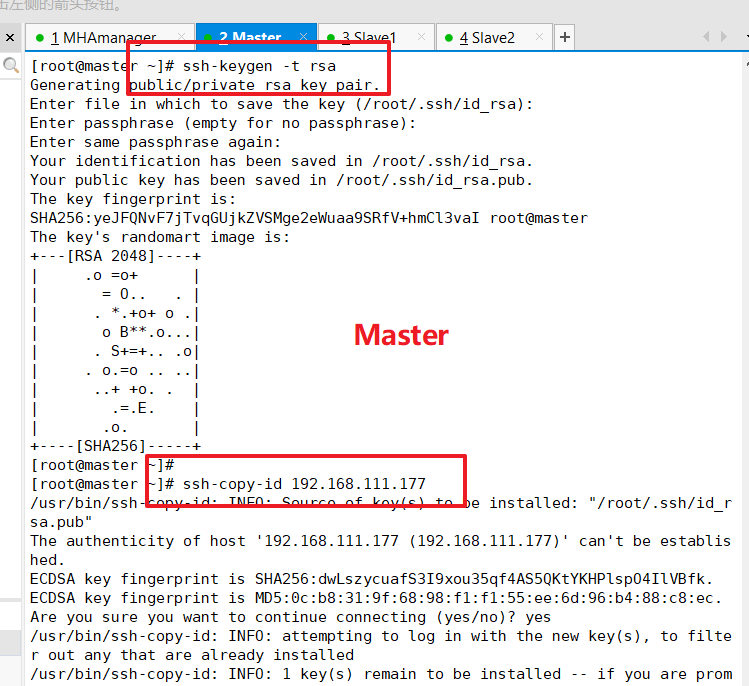
Password-free authentication configured on master to database nodes slave1 and slave2
ssh-keygen -t rsa ssh-copy-id 192.168.111.177 ssh-copy-id 192.168.111.178
Password-free authentication configured on slave1 to database nodes master and slave2
ssh-keygen -t rsa ssh-copy-id 192.168.111.176 ssh-copy-id 192.168.111.178
Password-free authentication configured to database nodes master and slave1 on slave2
ssh-keygen -t rsa ssh-copy-id 192.168.111.176 ssh-copy-id 192.168.111.177
Configure MHA on the manager node
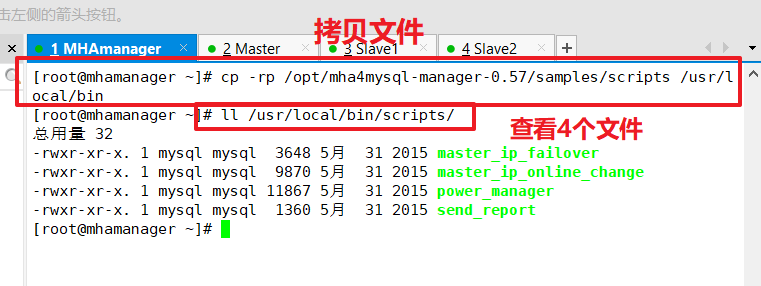
Copy the script on the manager node to the / usr/local/bin directory
cp -rp /opt/mha4mysql-manager-0.57/samples/scripts /usr/local/bin
Four execution files are copied
The role of scripts:
| master_ip_failover | Script for VIP management on automatic switch |
| master_ip_online_change | vip management during online switching |
| power_manager | Script to shut down the host after a failure occurs |
| send_report | Script to send an alert after failover |
Copy the above VIP-managed scripts for automatic switching to the / usr/local/bin directory, using master_ip_failover script to manage VIP and failover
cp /usr/local/bin/scripts/master_ip_failover /usr/local/bin
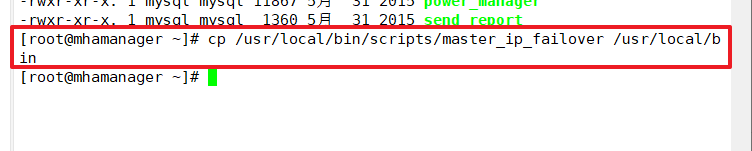
The modifications are as follows: (Delete the original content, copy the following directly and modify vip-related parameters)
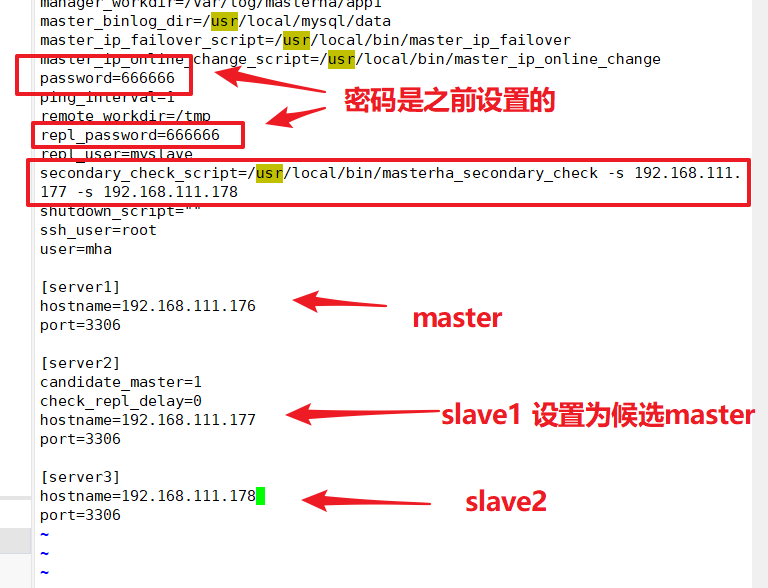
[server default] manager_log=/var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log #manager log manager_workdir=/var/log/masterha/app1.log #manager working directory master_binlog_dir=/usr/local/mysql/data/ #The location where Master saves the binlog, where the path matches that of the binlog configured in master so that MHA can find it master_ip_failover_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_failover #Set the switch script for automatic failover, which is the script above master_ip_online_change_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_online_change #Set switch script for manual switch password=666666 #Set the password for the root user in mysql, which is the password you created earlier to monitor the user ping_interval=1 #Set the time interval for monitoring the main library to send ping packets, default is 3 seconds, failover automatically when three attempts fail remote_workdir=/tmp #Set the location where binlog will be saved for remote mysql when a switch occurs repl_password=666666 #Set the password for the replication user repl_user=myslave #Set up users for replication users report_script=/usr/local/send_report #Set the script for alerts sent after a switch occurs secondary_check_script=/usr/local/bin/masterha_secondary_check -s 192.168.80.11 -s 192.168.80.12 #Specify the slave server IP address to check shutdown_script="" #Set up the fail host script to shut down after a failure occurs (the main purpose of this script is to shut down the host to prevent brain fissures, which are not used here) ssh_user=root #Set ssh login user name user=mha #Set monitoring user root [server1] hostname=192.168.111.176 port=3306 [server2] hostname=192.168.111.177 port=3306 candidate_master=1 #Set as candidate master, after setting this parameter, master-slave switching will promote this slave from the library to the master library even if it is not the latest slave in the cluster check_repl_delay=0 #By default, MHA will not choose a slave as a new master if it falls behind the master's relay logs exceeding 100M, because recovery of the slave will take a long time.By setting check_repl_delay=0, MHA triggered switch ignores replication delay when selecting a new master. This parameter sets candidate_forA host with master=1 is useful because this candidate must be a new master during the switching process [server3] hostname=192.168.111.178 port=3306
vim /usr/local/bin/master_ip_failover
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use strict;
use warnings FATAL => 'all';
use Getopt::Long;
my (
$command, $ssh_user, $orig_master_host, $orig_master_ip,
$orig_master_port, $new_master_host, $new_master_ip, $new_master_port
);
#############################Add Content Section#########################################
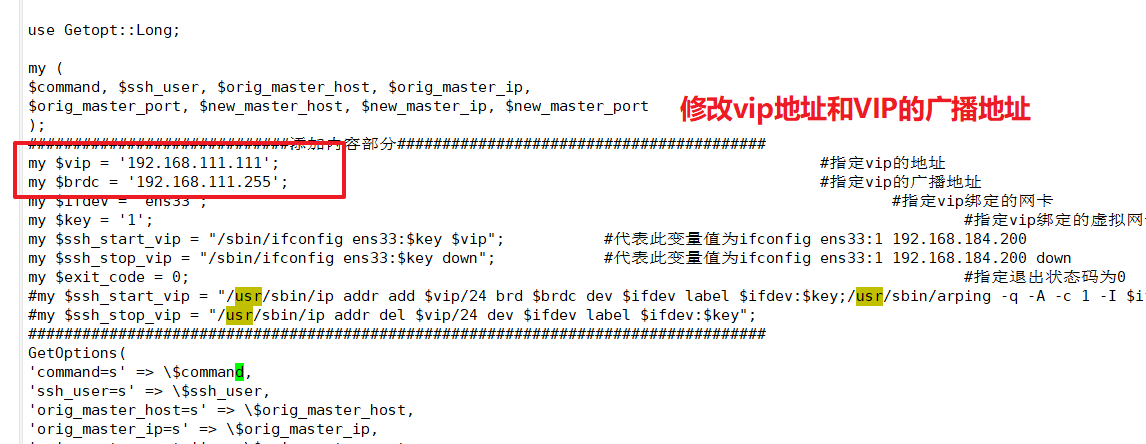
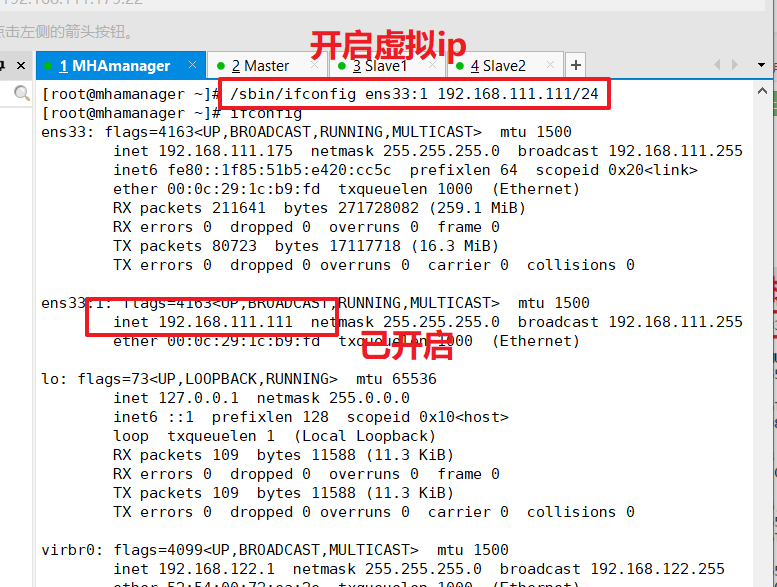
my $vip = '192.168.111.111'; #Specify the address of vip
my $brdc = '192.168.111.255'; #Specify vip broadcast address
my $ifdev = 'ens33'; #Specify vip-bound network card
my $key = '1'; #Specify vip-bound virtual network card serial number
my $ssh_start_vip = "/sbin/ifconfig ens33:$key $vip"; #Represents the value of this variable as ifconfig ens33:1 192.168.80.200
my $ssh_stop_vip = "/sbin/ifconfig ens33:$key down"; #Represents the value of this variable as ifconfig ens33:1 192.168.80.200 down
my $exit_code = 0; #Specify exit status code 0
#my $ssh_start_vip = "/usr/sbin/ip addr add $vip/24 brd $brdc dev $ifdev label $ifdev:$key;/usr/sbin/arping -q -A -c 1 -I $ifdev $vip;iptables -F;";
#my $ssh_stop_vip = "/usr/sbin/ip addr del $vip/24 dev $ifdev label $ifdev:$key";
##################################################################################
GetOptions(
'command=s' => \$command,
'ssh_user=s' => \$ssh_user,
'orig_master_host=s' => \$orig_master_host,
'orig_master_ip=s' => \$orig_master_ip,
'orig_master_port=i' => \$orig_master_port,
'new_master_host=s' => \$new_master_host,
'new_master_ip=s' => \$new_master_ip,
'new_master_port=i' => \$new_master_port,
);
exit &main();
sub main {
print "\n\nIN SCRIPT TEST====$ssh_stop_vip==$ssh_start_vip===\n\n";
if ( $command eq "stop" || $command eq "stopssh" ) {
my $exit_code = 1;
eval {
print "Disabling the VIP on old master: $orig_master_host \n";
&stop_vip();
$exit_code = 0;
};
if ($@) {
warn "Got Error: $@\n";
exit $exit_code;
}
exit $exit_code;
}
elsif ( $command eq "start" ) {
my $exit_code = 10;
eval {
print "Enabling the VIP - $vip on the new master - $new_master_host \n";
&start_vip();
$exit_code = 0;
};
if ($@) {
warn $@;
exit $exit_code;
}
exit $exit_code;
}
elsif ( $command eq "status" ) {
print "Checking the Status of the script.. OK \n";
exit 0;
}
else {
&usage();
exit 1;
}
}
sub start_vip() {
`ssh $ssh_user\@$new_master_host \" $ssh_start_vip \"`;
}
## A simple system call that disable the VIP on the old_master
sub stop_vip() {
`ssh $ssh_user\@$orig_master_host \" $ssh_stop_vip \"`;
}
sub usage {
print
"Usage: master_ip_failover --command=start|stop|stopssh|status --orig_master_host=host --orig_master_ip=ip --orig_master_port=port --new_master_host=host --new_master_ip=ip --new_master_port=port\n";
}
Create the MHA software directory and copy the configuration file, where the app1.cnf configuration file is used to manage the mysql node server
mkdir /etc/masterha
cp /opt/mha4mysql-manager-0.57/samples/conf/app1.cnf /etc/masterha
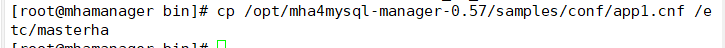
Also delete the original contents of this file and follow these steps to modify it
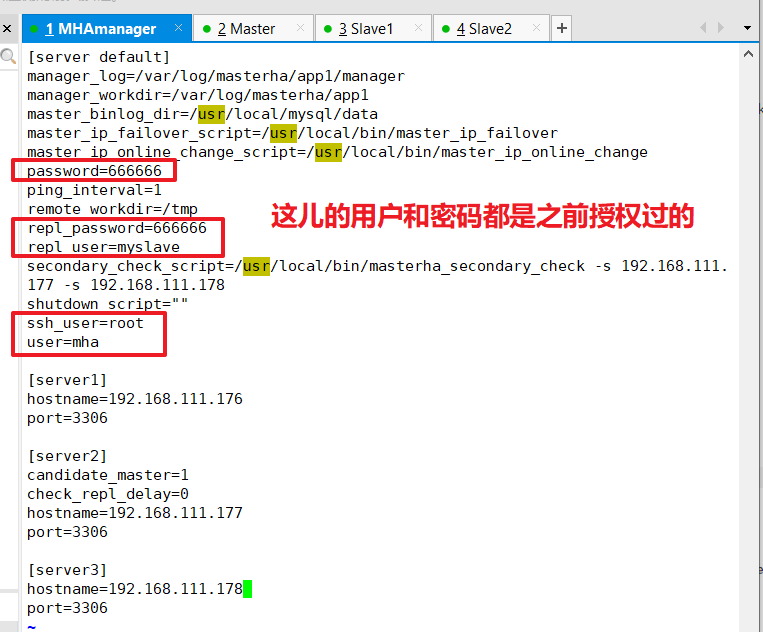
[server default] manager_log=/var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log #manager log manager_workdir=/var/log/masterha/app1.log #manager working directory master_binlog_dir=/usr/local/mysql/data/ #The location where Master saves the binlog, where the path matches that of the binlog configured in master so that MHA can find it master_ip_failover_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_failover #Set the switch script for automatic failover, which is the script above master_ip_online_change_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_online_change #Set switch script for manual switch password=666666 #Set the password for the root user in mysql, which is the password you created earlier to monitor the user ping_interval=1 #Set the time interval for monitoring the main library to send ping packets, default is 3 seconds, failover automatically when three attempts fail remote_workdir=/tmp #Set the location where binlog will be saved for remote mysql when a switch occurs repl_password=666666 #Set the password for the replication user repl_user=myslave #Set up users for replication users report_script=/usr/local/send_report #Set the script for alerts sent after a switch occurs secondary_check_script=/usr/local/bin/masterha_secondary_check -s 192.168.111.177 -s 192.168.111.178 #Specify the slave server IP address to check shutdown_script="" #Set up the fail host script to shut down after a failure occurs (the main purpose of this script is to shut down the host to prevent brain fissures, which are not used here) ssh_user=root #Set ssh login user name user=mha #Set monitoring user root [server1] hostname=192.168.111.176 port=3306 [server2] hostname=192.168.111.177 port=3306 candidate_master=1 #Set as candidate master, after setting this parameter, master-slave switching will promote this slave from the library to the master library even if it is not the latest slave in the cluster check_repl_delay=0 #By default, MHA will not choose a slave as a new master if it falls behind the master's relay logs exceeding 100M, because recovery of the slave will take a long time.By setting check_repl_delay=0, MHA triggered switch ignores replication delay when selecting a new master. This parameter sets candidate_forA host with master=1 is useful because this candidate must be a new master during the switching process [server3] hostname=192.168.111.178 port=3306
Copy the following directly
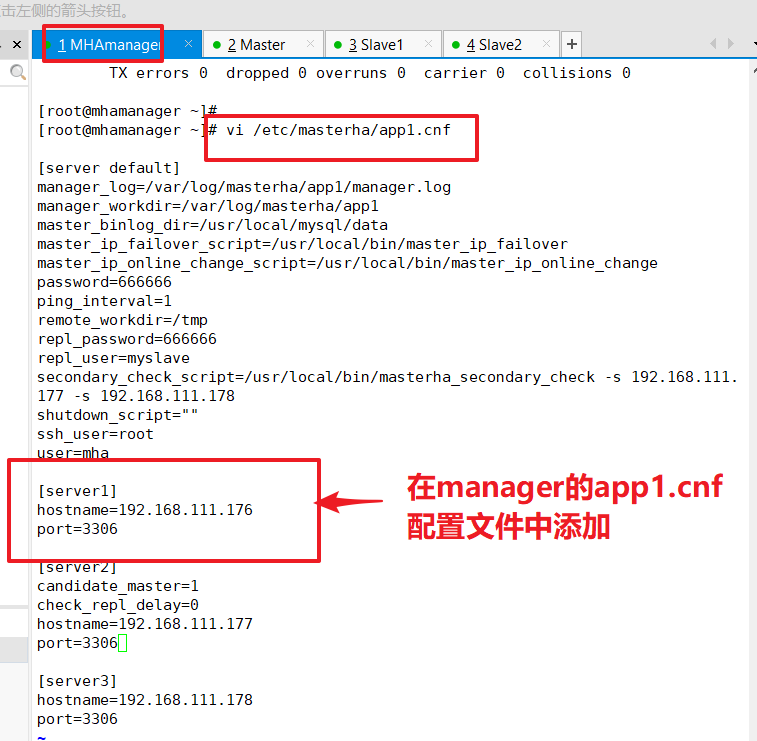
vim /etc/masterha/app1.cnf #Delete original content, copy and modify IP address of node server directly [server default] manager_log=/var/log/masterha/app1/manager manager_workdir=/var/log/masterha/app1 master_binlog_dir=/usr/local/mysql/data master_ip_failover_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_failover master_ip_online_change_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_online_change password=666666 ping_interval=1 remote_workdir=/tmp repl_password=666666 repl_user=myslave secondary_check_script=/usr/local/bin/masterha_secondary_check -s 192.168.111.177 -s 192.168.111.178 shutdown_script="" ssh_user=root user=mha [server1] hostname=192.168.111.176 port=3306 [server2] candidate_master=1 check_repl_delay=0 hostname=192.168.111.177 port=3306 [server3] hostname=192.168.111.178 port=3306
The first configuration requires the virtual IP to be manually turned on on the Master node
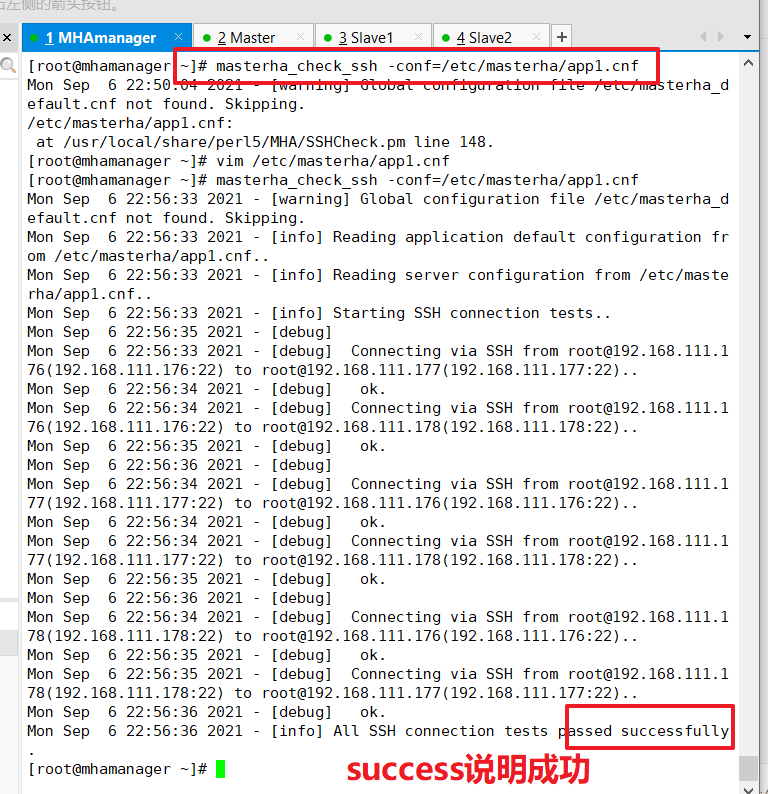
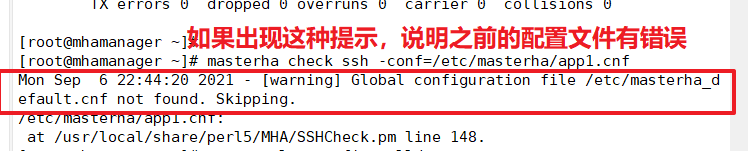
Tests ssh passwordless authentication on the manager node and outputs success if normal
masterha_check_ssh -conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf
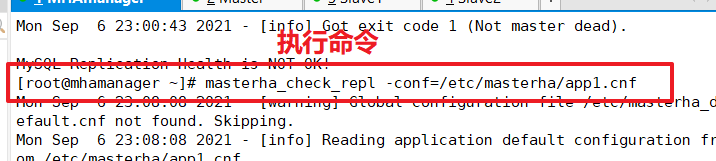
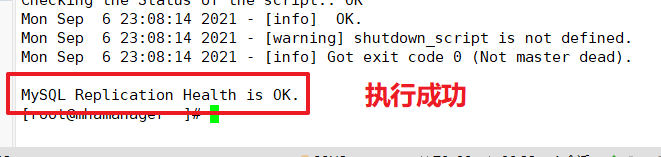
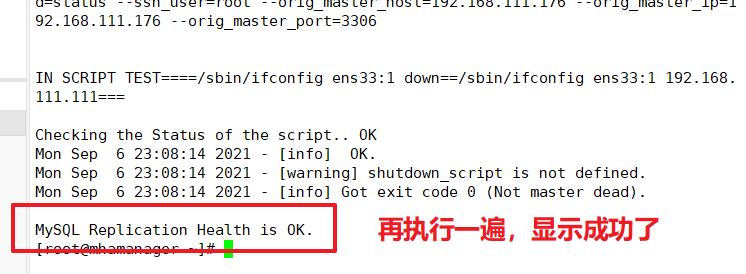
Testing the mysql master-slave connection on the manager node resulted in the word MySQL Replication Health is OK indicating normal.
masterha_check_ssh -conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf
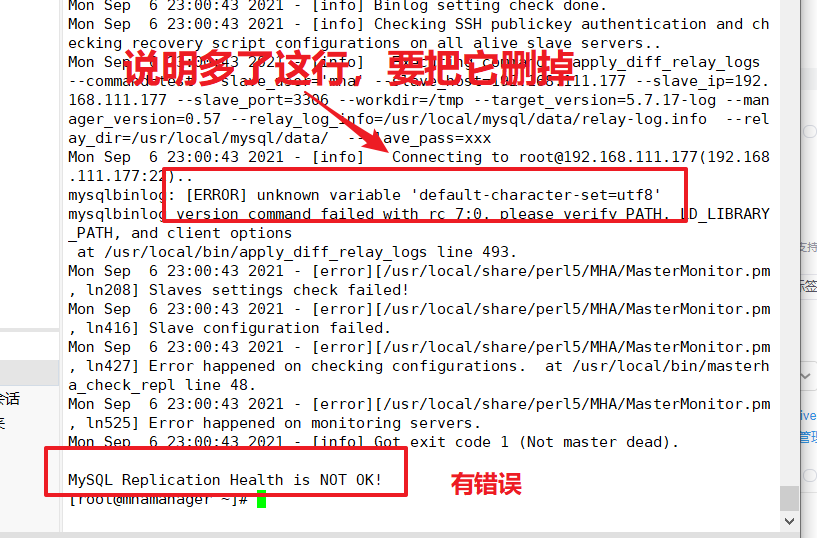
Note (troubleshooting)
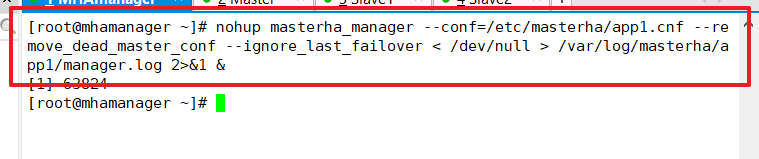
Start MHA on the manager node
nohup masterha_manager --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf --remove_dead_master_conf --ignore_last_failover < /dev/null > /var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log 2>&1 & --remove_dead_master_conf: This parameter represents the old master library's ip This will be removed from the configuration file. --manger_log: Log storage location. --ignore_last_failover: By default, if MHA Continuous downtime detected, and less than 8 hours between downtime, will not occur Failover, The reason for this limitation is to avoid ping-pong Effect.This parameter represents ignoring the last time MHA Triggers the file generated by the switch, and by default, MHA When a switch occurs, the log directory is set up above app1.failover.complete File, the next time you switch, you will not be allowed to trigger a switch if you find that the file exists in that directory, unless you receive the deletion of the file after the first switch. For convenience, set this to--ignore_last_failover.
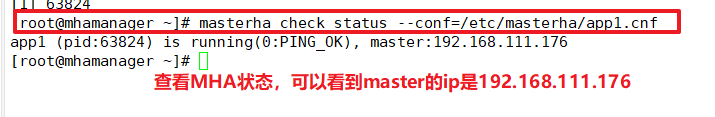
Looking at the MHA status, you can see that the current master is a Mysql1 node.
masterha_check_status --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf
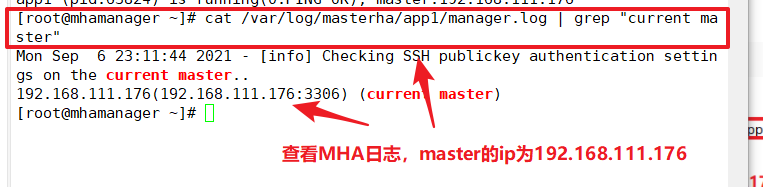
Looking at the MHA log, you can also see that the current master is 192.168.111.176
cat /var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log | grep "current master"
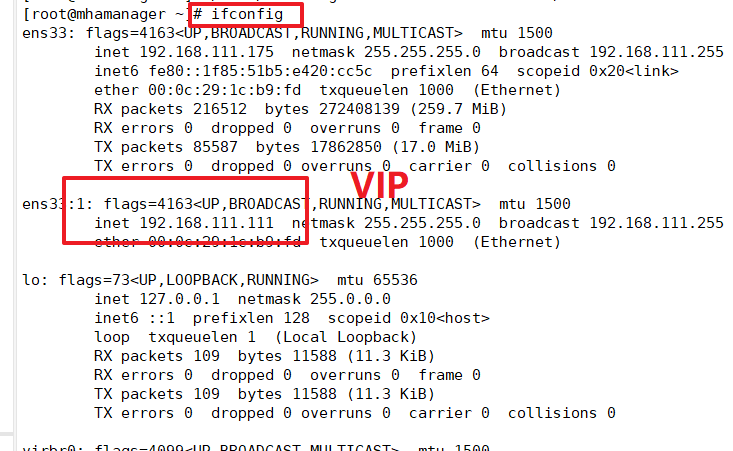
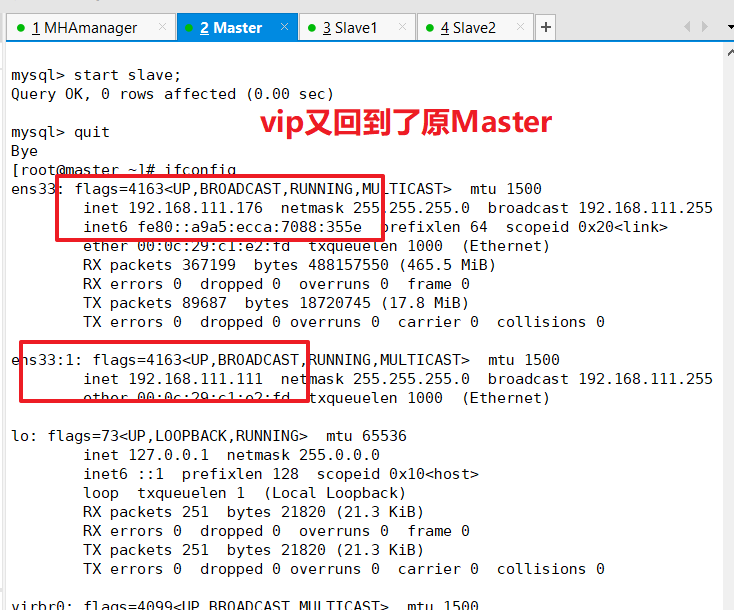
View Master's VIP address 192.168.168.111 If it exists, the VIP address will not disappear because the manager node stops the MHA service. (Make sure you turn it on manually before you see it)
MHA is now complete
To shut down the manager service, you can use the following command
masterha_stop --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf Or you can use it directly kill process ID Mode is off.
2. Fault simulation
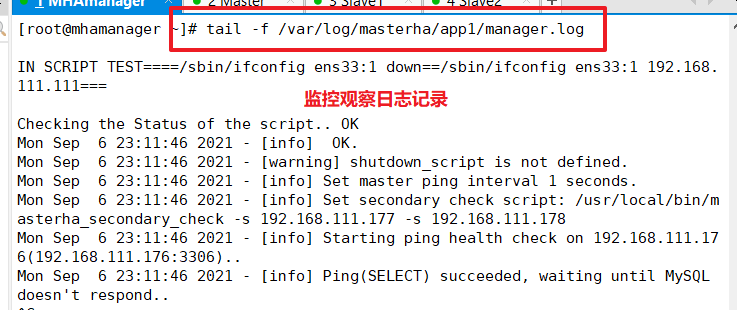
Monitor observation log records on the manager node
tail -f /var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log
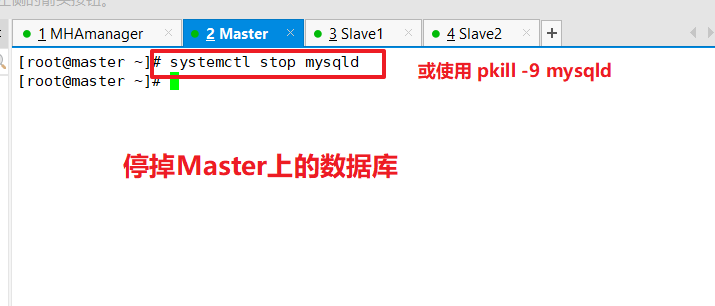
Stop mysql service on the Master node Mysql1
After a normal automatic switch, the MHA process exits.HMA automatically modifies the contents of the app1.cnf file and deletes the downtime mysql1 node.See if mysql2 takes over VIP
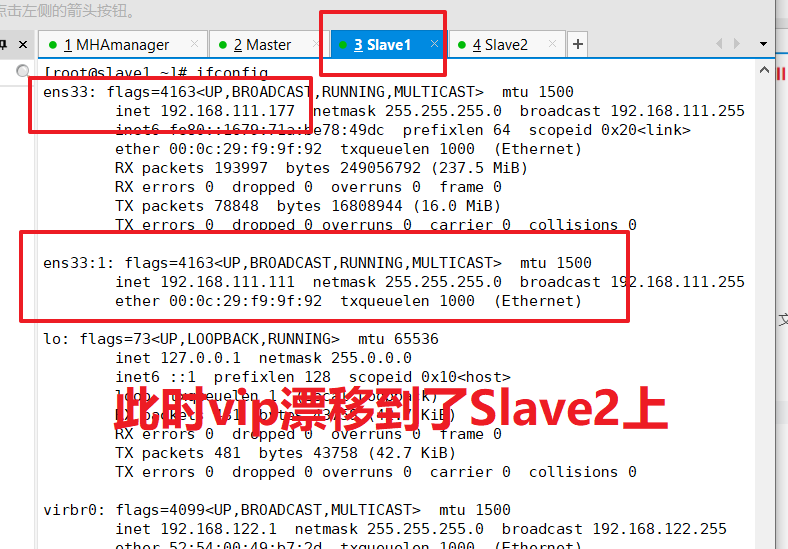
Algorithms for failover alternate primary libraries:
1 Generally, position/GTID is used to judge the quality of slave, which is closest to master and becomes the candidate.
2 If the data is consistent, select the alternate primary Library in the configuration file order.
3 Set weights (candidate_master=1), which forces the designation of alternatives by weight.
(1) By default, if a slave falls behind the relay logs of master 100M, it will fail even if it has weight.
(2) If check_Repl_If delay = 0, even logs are far behind, they are forced to be chosen as alternates.
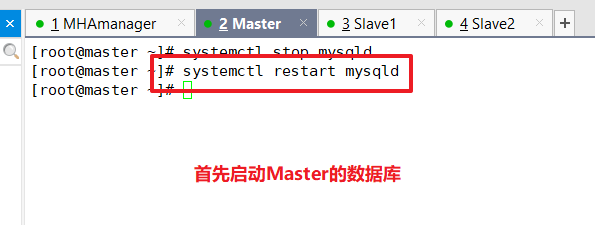
Failure Repair Steps:
1. Repair mysql
2. Repair master-slave
3. Modify the configuration file app1.cnf on the manager node (add this record again because it will disappear automatically when it detects failures)
4. Start MHA on the manager node
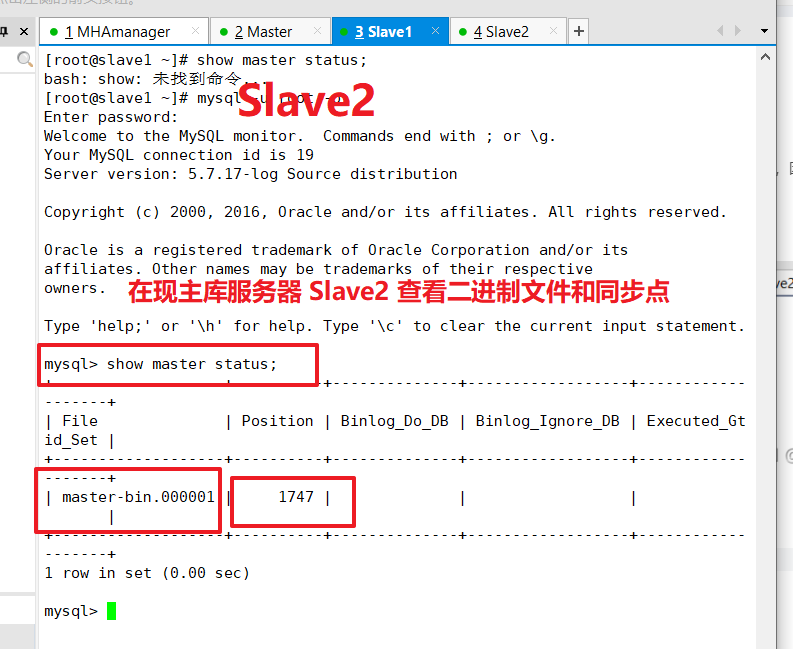
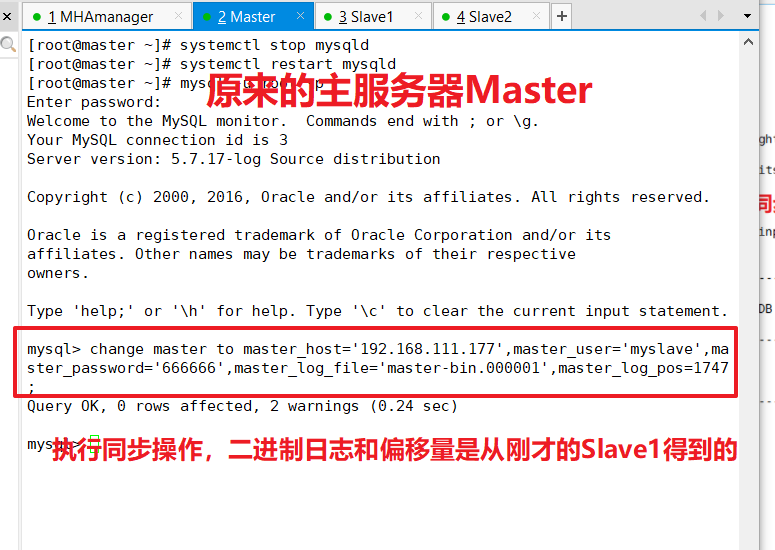
Perform synchronization on the original primary library server Master
change master to master_host='192.168.111.177',master_user='myslave',master_password='666666',master_log_file='master-bin.000001',master_log_pos=1747;
Start MHA on the manager node
nohup masterha_manager --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf --remove_dead_master_conf --ignore_last_failover < /dev/null > /var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log 2>&1 &
Solve the problem of incompatibility between Chinese and English
dos2unix /usr/local/bin/master_ip_failover