
- catalogue
Initialization of two checkerboards
Detailed explanation of recursive part
-
thinking
-
Clear logic.
For convenience, it is divided into three files: text C (test) game C (function implementation) game H (header file declaration)
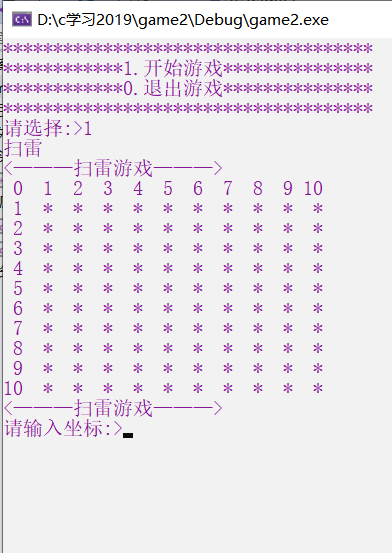
In order to facilitate demining, we need to print the number of rows and columns corresponding to each row and column.
#define LEI 10 #define ROW 10 #define LOW 10 #define ROWS ROW+2 #define LOWS LOW+2 //When defining the length and width of the chessboard, 2 is specially added to mark the number of rows and columns.
-
menu
The printed menu only needs to have the options of starting the game and exiting the game
void menu()
{
printf("*************************************\n");
printf("************1.Start the game***************\n");
printf("************0.Exit the game***************\n");
printf("*************************************\n");
}-
checkerboard
- Leipan
- checkerboard
Mine clearance needs to record mine information before demining. If using one chessboard is too complex, we use two chessboards, one for mine layout and one for player demining.
-
Initialization of two checkerboards
The chessboard initialization of the layout mine takes the character '0' as a non mine and the character '1' as a mine.
The player disk takes the character '*' as the place that has not been scanned
board(arr1, ROWS, LOWS, '0');//Leipan board(arr2, ROWS, LOWS, '*');//Player disk
Because the initialization methods of the two are different, we use the parameter ret initialization
//Initialize chessboard
void board(char arr1[ROWS][LOWS], int rows, int lows, char ret)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < lows; j++)
{
arr1[i][j] = ret;
}
}-
Lay thunder
The mine placement needs to be random, so two random numbers are used to locate the coordinates.
//Lay thunder
void Get_lei(char arr1[ROWS][LOWS], int row, int low)
{
int count = LEI;
while (count)
{
int x = rand() % row + 1;
int y = rand() % low + 1;
if (arr1[x][y] == '0')
{
arr1[x][y] = '1';
count--;
}
}
//displayboard(arr1, ROW, LOW);// For testing
}-
mine clearance
When we enter a coordinate, we need to know the number of mines around the coordinate and define a Get_num function to obtain the number of mines. However, at this time, only one coordinate information can be obtained. We know that general minesweeping will expand if the number of current coordinate mines is 0. This process is more complex, so we use recursive implementation
//Player disk
static int Get_num(char arr1[ROWS][LOWS],int x, int y)//Get the number of mines around the current coordinate
{
int count = 0;
int i = 0;
for (i = x - 1; i <= x + 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = y - 1; j <= y + 1; j++)
{
if (arr1[i][j] == '1')
{
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
//Judge whether to expand and implement the function
static void Judge(char arr2[ROWS][LOWS], char arr1[ROWS][LOWS], int x, int y)
{
if (x > 0 && x <= ROW && y > 0 && y <= LOW)
{
int ret = Get_num(arr1, x, y);
if (ret != 0)
arr2[x][y] = ret + '0';//Record the number of mines
//Recursive spreading
else if (arr1[x][y] != ' ')
{
arr2[x][y] = '0';
arr1[x][y] = ' ';
int i = 0;
for (i = x - 1; i <= x + 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = y - 1; j <= y + 1; j++)
{
Judge(arr2, arr1, i, j);
}
}
}
else
{
return;
}
}
}-
Judge whether to win or lose
Input: check the information corresponding to the mine disk once per row. If it is a mine, it will be killed. If not, continue to demine.
Win: when the player checks out all non mine areas, it is judged to win. (a counter is used here. The counter is used + + without discharging a mine. When the counter is the same as the total number of non mine areas, it is judged as winning)
void Out_lei(char arr2[ROWS][LOWS], int row, int low, char arr1[ROWS][LOWS])
{
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
while (1)
{
printf("Please enter coordinates:>");
scanf("%d,%d", &x, &y);
if (x >= 1 && x <= ROW && y >= 1 && y <= LOW)
{
if (arr1[x][y] == '1')
{
arr2[x][y] = '#';
displayboard(arr2, ROW, LOW);//mine clearance
printf("I'm sorry you lost\n");
break;
}
else
{
Judge(arr2, arr1, x, y);
displayboard(arr2, ROW, LOW);//mine clearance
}
}
else
{
printf("Input error!\n");
}
//Judge whether minesweeping wins
int i = 0, flag = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= ROW; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 1; j <= LOW; j++)
{
if (arr2[i][j] != '*')
{
flag++;
}
}
}
if (flag == ROW*LOW - LEI)
{
printf("You win!\n");
break;
}
}
}
-
text.c implementation
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "game.h"
//menu
void menu()
{
printf("*************************************\n");
printf("************1.Start the game***************\n");
printf("************0.Exit the game***************\n");
printf("*************************************\n");
}
void game()
{
//Initialize chessboard
char arr1[ROWS][LOWS] = { 0 };//Leipan
char arr2[ROWS][LOWS] = { 0 };//Player disk
board(arr1, ROWS, LOWS, '0');
board(arr2, ROWS, LOWS, '*');
//Print chessboard
//displayboard(arr1, ROW, LOW);// Lay thunder
displayboard(arr2, ROW, LOW);//mine clearance
//Lay thunder
Get_lei(arr1,ROW,LOW);
//mine clearance
Out_lei(arr2,ROW,LOW, arr1);
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
do
{
menu();
printf("Please select:>");
scanf("%d",&input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
{
printf("mine clearance\n");
game();
break;
}
case 0:
{
printf("Exit the game\n");
break;
}
default:
{
printf("Selection error\n");
break;
}
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}-
game.c implementation
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "game.h"
//Initialize chessboard
void board(char arr1[ROWS][LOWS], int rows, int lows, char ret)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < lows; j++)
{
arr1[i][j] = ret;
}
}
}
//Print chessboard
void displayboard(char arr1[ROWS][LOWS], int row, int low)
{
printf("<-—Minesweeper game -——>\n");
int i = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= row; i++)
{
int j = 0;
if (i == 1)
{
for (j = 0; j <= low; j++)
{
printf("%2d ", j);
}
printf("\n");
}
for (j = 1; j <= low; j++)
{
if (j == 1)
{
printf("%2d ", i);
}
printf("%2c ", arr1[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("<-—Minesweeper game -——>\n");
}
//Lay thunder
void Get_lei(char arr1[ROWS][LOWS], int row, int low)
{
int count = LEI;
while (count)
{
int x = rand() % row + 1;
int y = rand() % low + 1;
if (arr1[x][y] == '0')
{
arr1[x][y] = '1';
count--;
}
}
//displayboard(arr1, ROW, LOW);
}
//Player disk
static int Get_num(char arr1[ROWS][LOWS],int x, int y)
{
int count = 0;
int i = 0;
for (i = x - 1; i <= x + 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = y - 1; j <= y + 1; j++)
{
if (arr1[i][j] == '1')
{
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
//Determine whether to expand and implement the function
static void Judge(char arr2[ROWS][LOWS], char arr1[ROWS][LOWS], int x, int y)
{
if (x > 0 && x <= ROW && y > 0 && y <= LOW)
{
int ret = Get_num(arr1, x, y);
if (ret != 0)
arr2[x][y] = ret + '0';
//Recursive scatter
else if (arr1[x][y] != ' ')
{
arr2[x][y] = '0';
arr1[x][y] = ' ';
int i = 0;
for (i = x - 1; i <= x + 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = y - 1; j <= y + 1; j++)
{
Judge(arr2, arr1, i, j);
}
}
}
else
{
return;
}
}
}
void Out_lei(char arr2[ROWS][LOWS], int row, int low, char arr1[ROWS][LOWS])
{
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
while (1)
{
printf("Please enter coordinates:>");
scanf("%d,%d", &x, &y);
if (x >= 1 && x <= ROW && y >= 1 && y <= LOW)
{
if (arr1[x][y] == '1')
{
arr2[x][y] = '#';
displayboard(arr2, ROW, LOW);//mine clearance
printf("I'm sorry you lost\n");
break;
}
else
{
Judge(arr2, arr1, x, y);
displayboard(arr2, ROW, LOW);//mine clearance
}
}
else
{
printf("Input error!\n");
}
//Judge whether minesweeping wins
int i = 0, flag = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= ROW; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 1; j <= LOW; j++)
{
if (arr2[i][j] != '*')
{
flag++;
}
}
}
if (flag == ROW*LOW - LEI)
{
printf("You win!\n");
break;
}
}
}
-
game.h implementation
#pragma once #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define LEI 10 #define ROW 10 #define LOW 10 #define ROWS ROW+2 #define LOWS LOW+2 //Initialize chessboard void board(char arr1[ROWS][LOWS],int rows,int lows,char ret); //Print chessboard void displayboard(char arr1[ROWS][LOWS], int row, int low); //Lay thunder void Get_lei(char arr1[ROWS][LOWS], int row, int low); //Player disk void Out_lei(char arr2[ROWS][LOWS], int row, int low, char arr1[ROWS][LOWS]);
-
Detailed explanation of recursive part
Recursion condition: 1 There are conditions to stop. 2. Every recursion will approach this condition.
So what are the stop conditions here?
Recursion: when the number of returned mines is 0, it meets the condition of continuing recursion. We need to exclude all points around the current coordinate. And you need to mark the coordinates that have been checked, otherwise you will keep checking, and dead recursion will be formed. therefore
Stop condition: if the current coordinate has been checked, stop recursion.
Because each troubleshooting will be marked, this is the process of moving closer to the stop condition.
//Determine whether to expand and implement the function
static void Judge(char arr2[ROWS][LOWS], char arr1[ROWS][LOWS], int x, int y)
{
if (x > 0 && x <= ROW && y > 0 && y <= LOW)
{
int ret = Get_num(arr1, x, y);
if (ret != 0)
arr2[x][y] = ret + '0';
//Recursive spreading
else if (arr1[x][y] != ' ')
{
arr2[x][y] = '0';//Player disk
arr1[x][y] = ' ';//Leipan
int i = 0;
for (i = x - 1; i <= x + 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = y - 1; j <= y + 1; j++)
{
Judge(arr2, arr1, i, j);
}
}
}
else
{
return;
}
}
}
