MMM (Master-Master replication manager for MySQL) is a script that supports dual primary failover and dual primary day-to-day management.MMM is developed in Perl and is mainly used to monitor and manage MySQL Master-Master (dual master) replication, which can be referred to as mysql master replication manager.Although called dual master replication, only one master is allowed to write at the same time in the business, and a partial read service is provided on the other master to speed up the preheating of the alternate master at the master switch time. It can be said that the MMM script program achieves the function of failover on the one hand, and its additional tool scripts can also achieve load balancing of multiple slaves on the other hand.A scalable script suite for monitoring, failover, and management of mysql master replication configurations (only one node can be written at any time), which also reads load balancing to any number of secondary servers in a standard master-slave configuration, so you can use it to start virtual ip on a set of replicated servers, in addition toA script that enables data backup and resynchronization between nodes.
MMM provides automatic and manual removal of virtual IPS from a set of servers with high replication latency. It also backs up data, synchronizes data between two nodes, and so on.Since MMM does not fully guarantee data consistency, it is appropriate for scenarios where data consistency requirements are not high, but business availability is maximized.MySQL itself does not provide a replication failover solution. MMM solutions enable server failover, which makes MySQL highly available.MMM is a highly available architecture for businesses that require high data consistency.
MMM schema diagram:
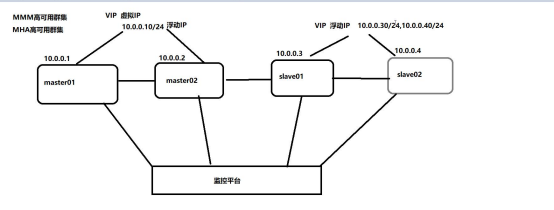
MMM is a mode in which master and slaver are easily charged with death, two or two
MHA mode, with high scalability, one main dual-device, one area.Expand one more main dual, one area
All node s need to be installed
First we have five virtual machines to plan for
Host Server 1 192.168.136.191 db1
Host Server 2 192.168.136.168 DB2
From server 1 192.168.136.185 db3
From server 2 192.168.136.184 DB4
Monitoring Server 192.168.136.135
Configure Ali Cloud Source.Install each server
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo httP://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
Install epel-release source, install on each server
yum -y install epel-release yum clean all && yum makecache
Set up local YUM source, all servers should be installed except monitoring server
yum install mariadb-server mariadb -y`
Modify the main configuration file to monitor the other four servers.Copy and paste.
vim /etc/my.cnf 9dd [mysqld] log_error=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.err log=/var/lib/mysql/mysql_log.log log_slow_queries=/var/lib/mysql_slow_queries.log binlog-ignore-db=mysql,information_schema character_set_server=utf8 log_bin=mysql_bin server_id=1 #Note that each id needs to be different log_slave_updates=true sync_binlog=1 auto_increment_increment=2 auto_increment_offset=1
Turn off firewalls, enhancements, and open databases on each server
systemctl stop firewalld.service setenforce 0 systemctl start mariadb.service
[root@localhost ~]# mysql #Enter M1 database //Enter M1 server to see the name and location value of the log file MariaDB [(none)]> show master status; #View the name and location value of the log file +------------------+----------+--------------+--------------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +------------------+----------+--------------+--------------------------+ | mysql_bin.000003 | 245 | | mysql,information_schema | +------------------+----------+--------------+--------------------------+
Enter M2 Server to view the name and location value of the log file
MariaDB [(none)]> show master status; +------------------+----------+--------------+--------------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +------------------+----------+--------------+--------------------------+ | mysql_bin.000003 | 245 | | mysql,information_schema | +------------------+----------+--------------+--------------------------+
Both primary servers execute, granting permissions
grant replication slave on *.* to 'replication'@'192.168.136.%' identified by '123456';`
M1 server points to M2 server, address, log file name, location parameter
change master to master_host='192.168.136.168',master_user='relication',master_password='123456',master_log_file='mysql_bin.000003',master_log_pos=245;
M2 server pointing to M1 server, address, log file name, location parameter
change master to master_host='192.168.136.167',master_user='relication',master_password='123456',master_log_file='mysql_bin.000003',master_log_pos=245; #Both servers perform the task of turning on synchronized data MariaDB [(none)]> slave start; #Both primary servers execute to see the status of synchronized data MariaDB [(none)]> show slave status\G; #It is correct to see that the following IO threads and states are YES Slave_IO_Running: Yes Slave_SQL_Running: Yes #Let's test if two primary servers can synchronize data M1 Create Data One Database MariaDB [(none)]> create database myschool; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) M2 MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | myschool | | mysql | | performance_schema | | test | +--------------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#s1 and s2 slave servers
[root@localhost ~]# mysql
#All point to the address, log files and parameters of the M1 master server
MariaDB [(none)]> change master to master_host='192.168.136.191',master_user='replication',master_password='123456',master_log_file='mysql_bin.000003',master_log_pos=245;
#Create a database in M1
MariaDB [(none)]> create database school;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
#Three other servers have this database
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| school |
| test |
+--------------------+
#All servers need to be installed
yum -y install mysql-mmm*
#Start configuring on the first primary server
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/mysql-mmm/
[root@localhost mysql-mmm]# ls
mmm_agent.conf mmm_common.conf mmm_mon.conf mmm_mon_log.conf mmm_tools.conf
[root@localhost mysql-mmm]# vim mmm_common.conf
<host default>
cluster_interface ens33
pid_path /run/mysql-mmm-agent.pid
bin_path /usr/libexec/mysql-mmm/
replication_user replication
replication_password 123456
agent_user mmm_agent
agent_password 123456
</host>
<host db1>
ip 192.168.136.191
mode master
peer db2
</host>
<host db2>
ip 192.168.136.168
mode master
peer db1
</host>
<host db3>
ip 192.168.136.185
mode slave
</host>
<host db4>
ip 192.168.136.184
mode slave
</host>
<role writer>
hosts db1, db2
ips 192.168.136.200 #Virtual Address
mode exclusive
</role>
<role reader>
hosts db3, db4
ips 192.168.136.210, 192.168.136.220 #Virtual Address
mode balancedTransfer files to other servers using scp
scp mmm_common.conf root@192.168.136.168:/etc/mysql-mmm/ scp mmm_common.conf root@192.168.136.185:/etc/mysql-mmm/ scp mmm_common.conf root@192.168.136.184:/etc/mysql-mmm/ scp mmm_common.conf root@192.168.136.135:/etc/mysql-mmm/
Configure Monitoring Server Account
[root@localhost mysql-mmm]# vim mmm_mon.conf
ping_ips 192.168.136.191,192.168.136.168,192.168.136.185,192.168.136.184 Enter all your addresses
auto_set_online 10 #Take-on time is 10s
monitor_password 123456 #Modify password to 123 456
//Authorize mmm_agent in all databases
grant super, replication client, process on *.* to 'mmm_agent'@'192.168.136.%' identified by '123456';
grant replication client on *.* to 'mmm_monitor'@'192.168.136.%' identified by '123456';Corresponds to modifying the configuration file (M2,S1,S2)
[root@localhost mysql-mmm]# vim mmm_agent.conf this db2 this db3 this db4 systemctl start mysql-mmm-agent.service systemctl enable mysql-mmm-agent.service #Back to Monitoring Server systemctl start mysql-mmm-monitor.service
View each node
[root@localhost mysql-mmm]# mmm_control show db1(192.168.136.191) master/ONLINE. Roles: writer(192.168.136.200) db2(192.168.136.168) master/ONLINE. Roles: db3(192.168.136.185) slave/ONLINE. Roles: reader(192.168.136.220) db4(192.168.136.184) slave/ONLINE. Roles: reader(192.168.136.210) #Change the virtual address of the binding [root@localhost mysql-mmm]# mmm_control move_role writer db2 #Test Monitoring Server Functionality [root@localhost mysql-mmm]# mmm_control checks all db4 ping [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db4 mysql [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db4 rep_threads [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db4 rep_backlog [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK: Backlog is null db2 ping [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db2 mysql [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db2 rep_threads [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db2 rep_backlog [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK: Backlog is null db3 ping [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db3 mysql [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db3 rep_threads [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db3 rep_backlog [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK: Backlog is null db1 ping [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db1 mysql [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db1 rep_threads [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK db1 rep_backlog [last change: 2019/11/25 16:38:25] OK: Backlog is null [root@localhost mysql-mmm]# mmm_control move_role writer db1 OK: Role 'writer' has been moved from 'db2' to 'db1'. Now you can wait some time and check new roles info! [root@localhost mysql-mmm]# mmm_control show db1(192.168.136.191) master/ONLINE. Roles: writer(192.168.136.200) db2(192.168.136.168) master/ONLINE. Roles: db3(192.168.136.185) slave/ONLINE. Roles: reader(192.168.136.220) db4(192.168.136.184) slave/ONLINE. Roles: reader(192.168.136.210) #First Host Server Shutdown Database Simulation Failure [root@localhost mysql-mmm]# systemctl stop mariadb.service #Back to the Monitoring Server test, the virtual web address changed [root@localhost mysql-mmm]# mmm_control show db1(192.168.136.191) master/HARD_OFFLINE. Roles: db2(192.168.136.168) master/ONLINE. Roles: writer(192.168.136.200) db3(192.168.136.185) slave/ONLINE. Roles: reader(192.168.136.220) db4(192.168.136.184) slave/ONLINE. Roles: reader(192.168.136.210) #Open the database on the first master server [root@localhost mysql-mmm]# systemctl start mariadb.service #Back to the Monitoring Server to see the status of the primary server [root@localhost mysql-mmm]# mmm_control show db1(192.168.136.191) master/ONLINE. Roles: db2(192.168.136.168) master/ONLINE. Roles: writer(192.168.136.200) db3(192.168.136.185) slave/ONLINE. Roles: reader(192.168.136.220) db4(192.168.136.184) slave/ONLINE. Roles: reader(192.168.136.210) #Monitoring Server [root@localhost mysql-mmm]# yum install mariadb-server mariadb -y #Again M1 server authorizes login for monitor address MariaDB [(none)]> grant all on *.* to 'testba'@'192.168.136.135' identified by '123456'; MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges;
Go back to the monitoring server and test if you can log in
mysql -utestdba -p -h 192.168.136.200 Enter password: Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 2562 Server version: 5.5.64-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]>
Create a table and go to another server to see if the data is synchronized
MariaDB [(none)]> create database chen; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | chen | | mysql | | performance_schema | | school | | test | +--------------------+ 6 rows in set (0.01 sec)
That's all we have. Thank you for watching