1, Basic knowledge
1.1. What is MongoDB
MongoDB is written in C + + language and is an [open source] database system (NoSQL) based on [distributed] file storage
characteristic
- Mass storage: convenient for expansion, multi node deployment and cluster formation
- Document database: the data structure consists of key value (key = > value) pairs
- Support RUBY, PYTHON, JAVA, C + +, PHP, c# and other languages
- JavaScript scripts can be allowed directly
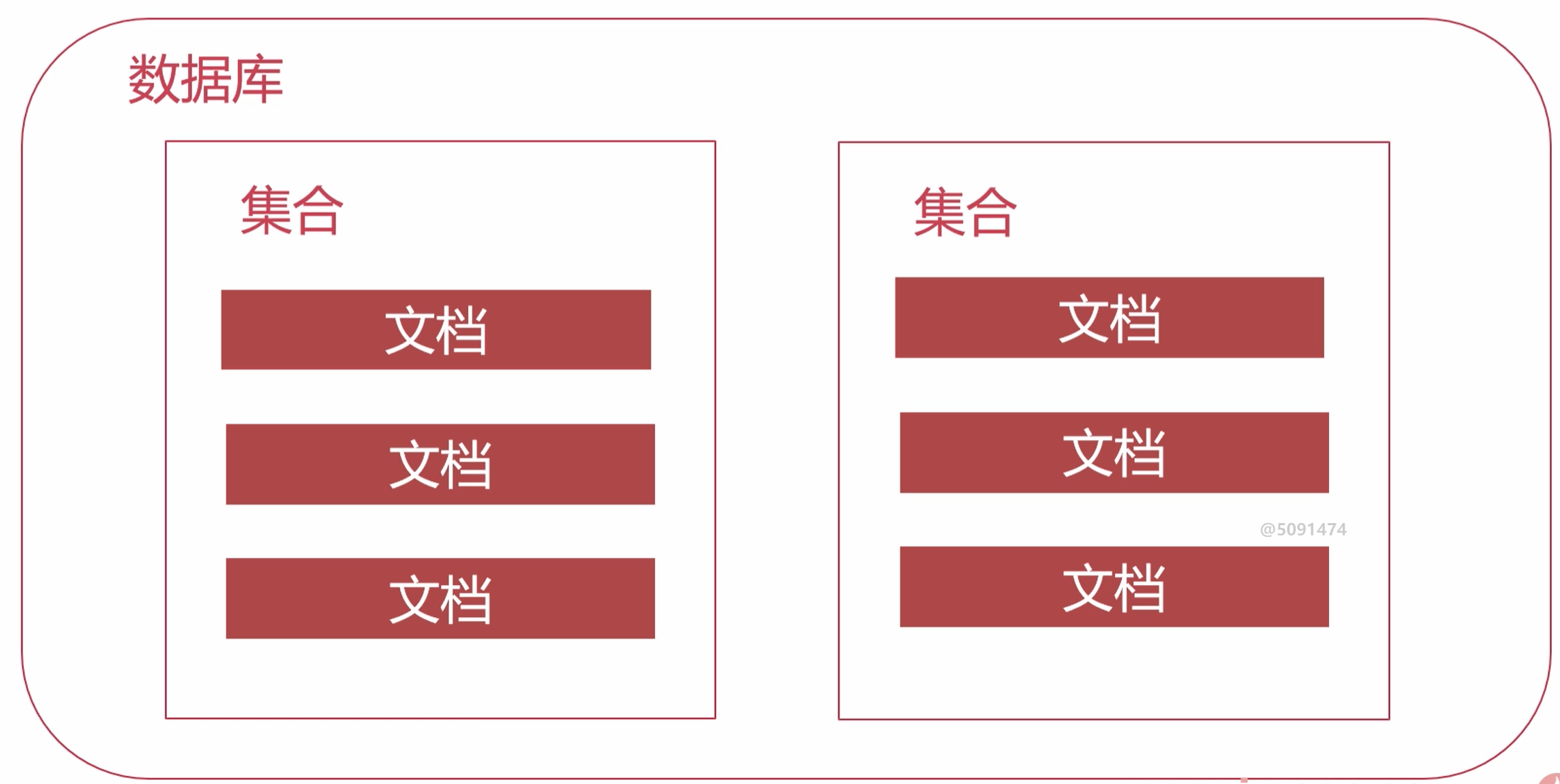
1.2 composition
1.3 documentation
Official definition
- A document is a key value pair
- Stored in binary JSON (BSON)
Example
{
"usernaem";"Li Ming",
"age": 21,
"sex": "male",
"email": "liming@example.com",
"address": "43 South Street",
"company": {
"name": "Technology company",
"industry": "internet"
}
}
Naming requirements for keys
- Cannot contain \ 0 (empty character)
- Avoid$_ x (beginning with underscore)
Document characteristics
- Key value pairs are ordered
- The key is unique and cannot be repeated
- Keys are type and case sensitive
- Documents can be nested
data type
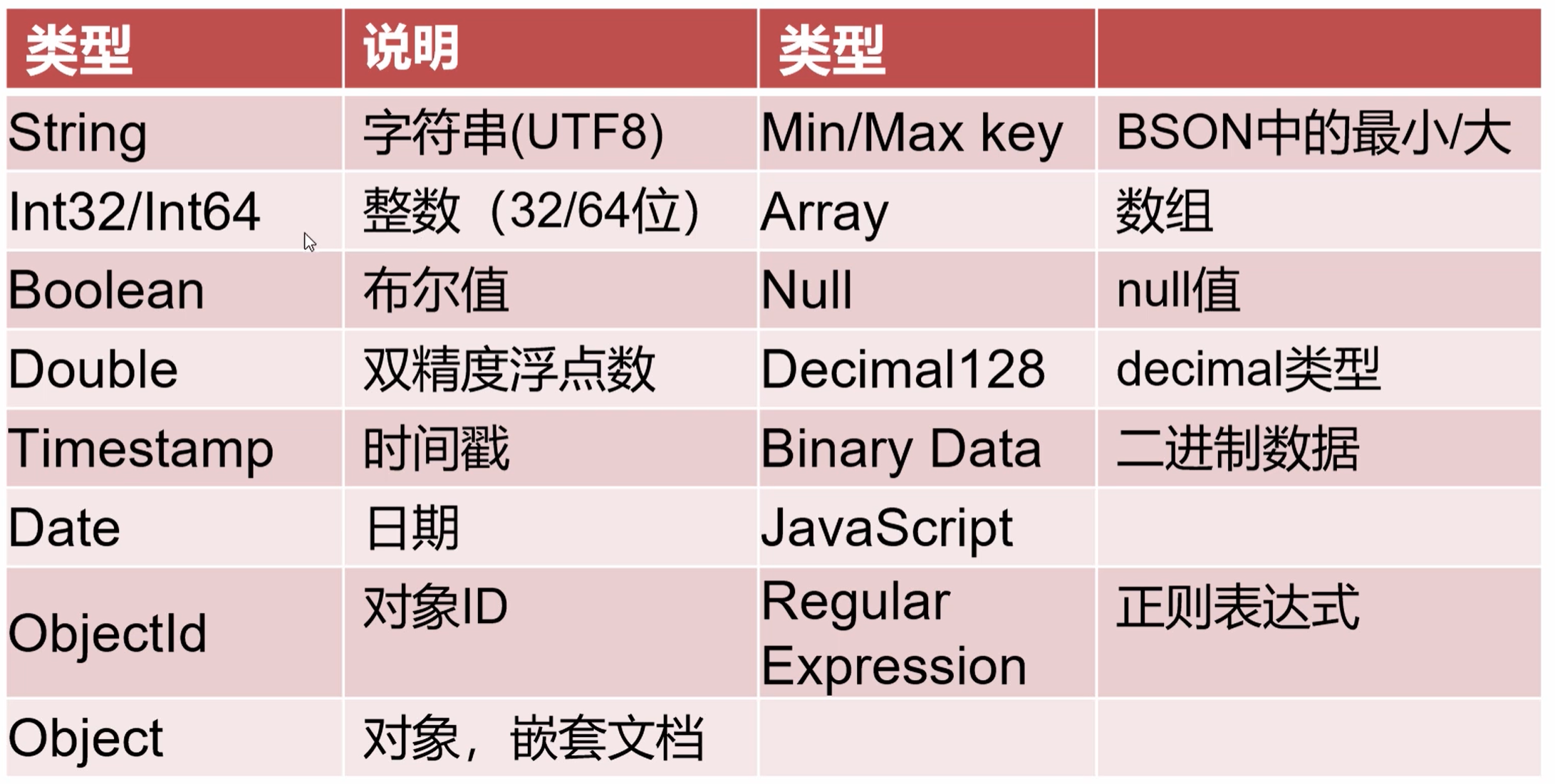
ObjectId
- Features and uses: small, almost unique, can be generated quickly and easy to sort (commonly used for the primary key of documents)
- Generation rule: current system time (seconds) + random number + self increment
- Common methods: getTimestamp(): get the time, str: get the string of ObjectId


1.4 collection
- Official definition: a collection is a document group in MongoDB
- Understanding sets: [sets] are similar to tables in relational data
- Compare relational databases: the documents in the collection have no fixed structure
Naming rules
- Cannot contain \ 0 characters (empty character '')
- Cannot use system Prefix of (system reserved)
- The reserved word "$" is not recommended
- Use Split subsets with different namespaces (e.g. blog.users, blog.posts)
1.5 database
- Multiple documents form a collection, and multiple collections form a database
- An instance can host multiple databases (logical libraries)
- Each database has independent permissions
- Reserved database name (admin, local, config)
1.6 comparison of MongoDB and MySQL terms

2, MongoDB installation and configuration
2.1 installation
- First, Download MongoDB Community Edition
https://www.mongodb.com/try/download/community - Step 2: installation

2.2 startup
System service startup

Command line startup (needs to be run as administrator)
net start/stop MongoDB
3, Database management
3.1,Mongo Shell
MongoDB's own command line management tool
- Step 1: enter the MongoDB installation directory / bin
- Step 2: open the command line window and enter mongo --host 127.0.0.1 --port 27017. If it is the default installation, you can directly enter mongo
You can directly add the MongoDB installation directory / bin to the environment variable Path. You can connect at any time by entering mongo on the command line.
3.2 graphical management tools
- Navicat
- Robo 3T (free)
- Studio 3T (charge)
3.3 database management
- View all databases: show dbs
- Create / switch database: use db_name
- Get the currently operating database: db
- Delete database: dB dropDatabase()
3.4 collection management
- View all collections: show collections
- Create collection (automatically created when data is inserted): dB createCollection("students")
- Delete collection: dB COLLECTION_NAME. drop(),COLLECTION_NAME, the name of the actual collection
- Rename collection: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. renameCollection("temp")
- Create indexes for some fields (columns) in the collection: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. createIndex(keys, <options>, <commitQuorum>)
4, Data management
4.1. Insert data
Insert a single piece of data
Syntax reference: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. insertOne(document)
Return result:
{ "acknowledged" : true, "insertedId" : ObjectId("60fe0c40fe9b36874a43644f") }
Insert multiple pieces of data
Syntax reference: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. insertMany([doc1, doc2])
Return result:
{ "acknowledged" : true, "insertedId" : [ObjectId("..."), ObjectId("...")] }
4.2. Query data
Data file grades Txt, extraction code: eh5t
Data file students Txt, extraction code: d4h3
4.2.1. Query one or more pieces of data
Query a piece of data
Syntax reference: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. findOne(<filter>, <projection>)
Parameter interpretation
- filter: query criteria (optional parameters)
- projection: the field (field) to be returned (optional parameter)
Example
//Query the first data
db.students.findOne();
//Specify the columns to display
db.students.findOne({},{"stu_no":1, "stu_name":1, "address":1});
//Specify the columns to display, specify_ id not displayed
db.students.findOne({},{"stu_no":1, "stu_name":1, "address":1, "_id":0});
Query all data
Syntax reference: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. find({})
Formatted display (with indent): dB COLLECTION_ NAME. find(). pretty()
4.2.2 query criteria
query criteria
-
Comparison operator
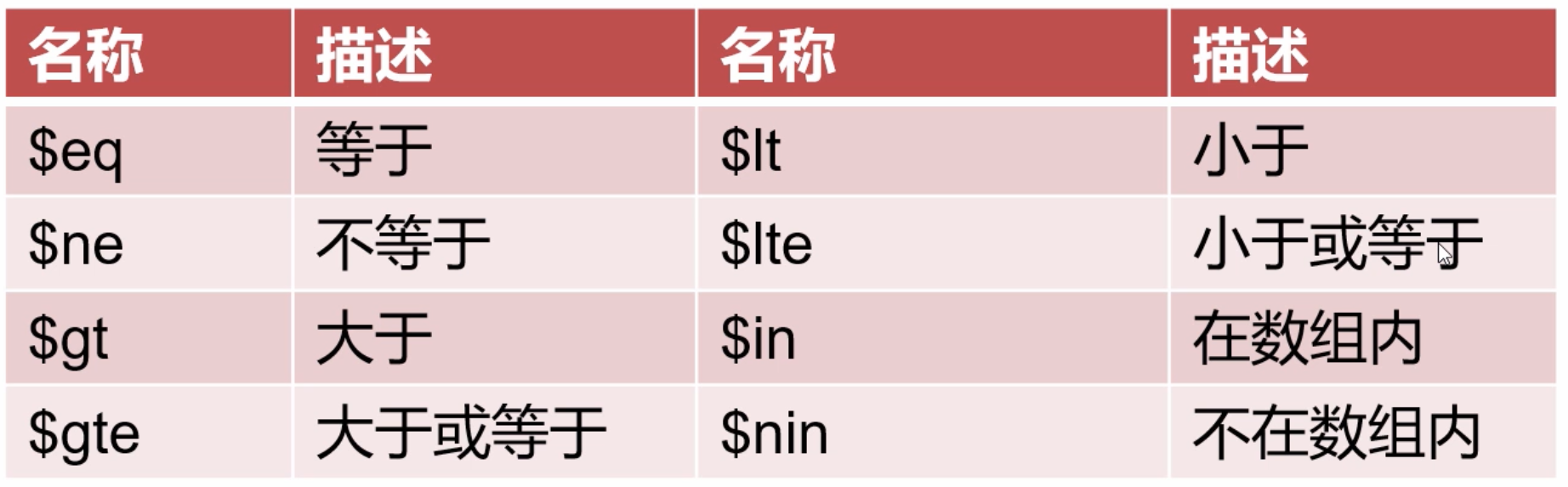
Sample code// Query all students over the age of 12 db.students.find({"age": {$gt: 12}}); // Query the information of students aged 9 ~ 12 (inclusive) db.students.find({"age": {$gte: 9, $lte: 12}}); // Query the information of students whose age is not set / set db.students.find({"age": null}); db.students.find({"age": {$ne: null}}); // Query the information of students aged 9 and 12 db.students.find({"age": {$in: [9, 12]}}); -
Logical operator
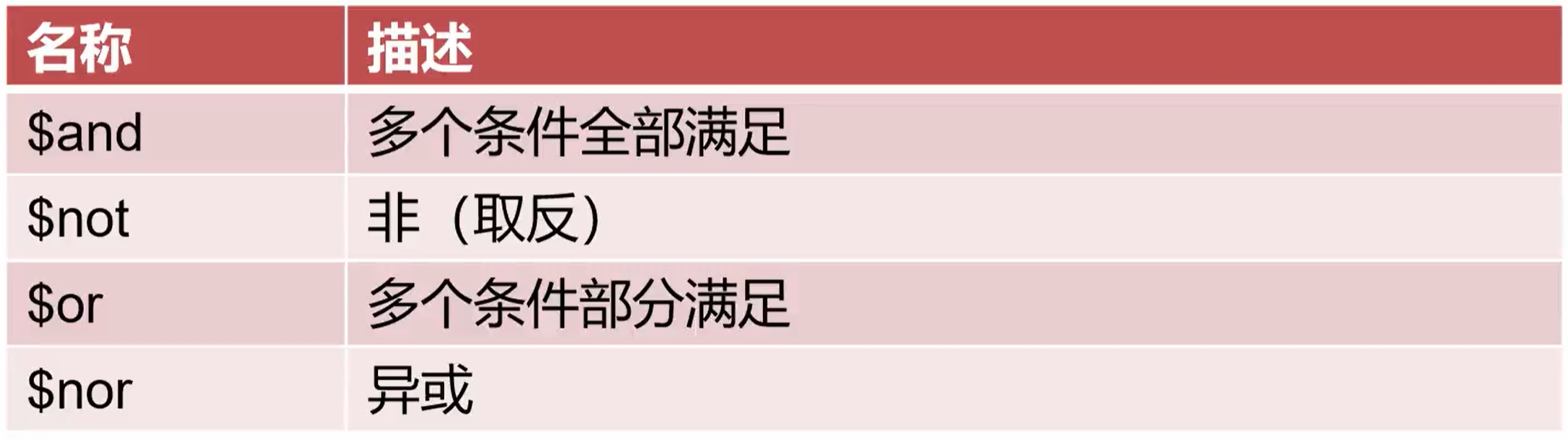
// Query all boys over the age of 12 and girls under the age of 9 db.students.find({ $or:[ {"sex": "male", "age": {"$gt": 12}}, {"sex": "female", "age": {"$lt": 9}} ] }); -
Support JavaScript regular expressions
// Find the information of all students surnamed "Li" db.students.find({stu_name: /^Lee/}); // Find the information of all students whose last name is "Li" and whose first name is only one word db.students.find({stu_name: /^Lee.$/}); // Find student information whose name contains the word "Snow" db.students.find({stu_name: /snow/}); -
Nested document query, using dot (.) Split key
Example code: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. find({"a.b": "c"})// Check the language scores of all students db.grades.find({"grade.course_name": "language"}); // Find the information of all students whose Chinese scores have passed db.grades.find({"grade.course_name": "language", "grade.score": {$gte: 60}}); db.grades.find({$and: [ {"grade.course_name": "language"}, {"grade.score": {$gte: 60}} ]}); -
Query within array

// Query student information with only two grades db.students.find({grades: {$size: 2}});
4.2.3 aggregation statistics
-
To view the number of documents in the collection, you can chain call
db.COLLECTION_NAME.count()
-
Remove duplicates
db.COLLECTION_NAME.distinct(field_name, <filter>)
Example
// Query student information with only two grades
db.students.find({grades: {$size: 2}});
// Count the total number of students
db.students.count();
// Query the total number of students with only two grades
db.students.find({grades: {$size: 2}}).count();
// Find the living area of students in class 1, grade 3
db.students.distinct("address", {"class_name": "Class 1, grade 3"});
Grammatical reference
db.COLLECTION_NAME.aggregate([
// where
{$match: {"grade.score":{$gte: 60}}},
// group by
{$group: {_id : "$stu_no", total: {$sum: 1}}},
// having
{$match: {total: {$eq: 3}}}
])
Built in aggregate statistics function

// Statistics of the highest / lowest / average score of Chinese scores
db.grades.aggregate([
// where
{$match: {"grade.course_name": "language"}},
// group by
{$group: {
_id: null,
maxSource: {$max: "$grade.score"},
minSource: {$min: "$grade.score"},
avgSource: {$avg: "$grade.score"},
}},
]);
// Statistics of the total scores of Zhang San's subjects
db.grades.aggregate([
// where
{$match: {"stu_name": "Zhang San"}},
// group by
{$group: {
_id: null,
maxSource: {$sum: "$grade.score"},
}},
]);
// Count the number of students in each class
db.students.aggregate([
// group by
{$group: {
_id: "$class_name",
total: {$sum: 1},
}},
]);
// Count the total number of boys and girls in each class
db.students.aggregate([
// group by
{$group: {
_id: {class_name: "$class_name", sex: "$sex"},
total: {$sum: 1},
}},
]);
// Find students who have passed all three grades (> = 60)
db.grades.aggregate([
// where
{$match: {"grade.score": {$gte: 60}}},
// group by
{$group: {
_id: "$stu_no",
total: {$sum: 1},
}},
// having
{$match: {total: {$eq: 3}}}
]);
4.3.4 sorting and paging
sort
Syntax reference: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. find(). sort({field: value})
Sorting rules
- 1: Ascending order
- -1: Descending order
Example
// Rank students' Chinese scores from high to low
db.grades.find({"grade.course_name": "language"}).sort({"grade.score": -1});
// Sort the students' Chinese scores according to their age and grades
db.grades.find({"grade.course_name": "language"}).sort({"grade.score": -1, "age": -1});
paging
Syntax reference: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. find(). skip(10). limit(10)
Method interpretation
- skip(N): skip N rows of data
- limit(N): take N rows of data
// Get the third page of student achievement information, 8 items per page db.grades.find().skip(16).limit(8);
4.3. Update data
The following three methods are similar in use. Take the updateMany method as an example
- updateOne(): updates a piece of data
- replaceOne(): replace a piece of data
- updateMany(): updates multiple pieces of data
Syntax reference: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. updateMany(<filter>, <update>, <options>)

Parameter interpretation
- The first parameter: < Filter >, query criteria, and modify the data that meets the criteria
- The second parameter: < update >, the data object to be modified
Update data expression

Example
// Create the users collection and insert document data
db.users.insertMany([{"username": "cjw", "age": 12},{"username": "cjw01", "age": 13},{"username": "cjw02", "age": 14},{"username": "cjw03", "age": 15}]);
db.users.insertMany([{"username": "cjw04", "age": 16, "hobby": ["Basketball", "Football"], "company": {"address": "Pearl Street"}}]);
// Set the user's age to 20
db.users.updateMany({}, {$set: {"age": 20}});
// Delete user's hobbies and company information
db.users.updateMany({}, {$unset: {"company": null, "hobby": null}});
// Add user created_at is the current time of the system
db.users.updateMany({}, {$currentDate: {"created_at": true}});
// Add user's age + 1
db.users.updateMany({}, {$inc: {"age": 1}});
4.4. Delete data
Delete a single piece of data
Syntax reference: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. deleteOne(<filter>)
Batch delete data
Syntax reference: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. deleteMany(<filter>)
Delete all data in the collection: dB COLLECTION_ NAME. deleteMayn({})
practice
//Query student information (student number, name, age and class) aged between 9 and 12 (inclusive)
db.students.find({"age": {$gte: 9, $lte: 12}},{"stu_no":1, "stu_name":1, "age":1, "class_name":1});