Twenty eight good people are like crisp people. They cut fools with swords at their waist. Although I don't see my head falling, I secretly teach you that your bone marrow is withered.
The previous chapter briefly introduced how to configure the jdbctemplate for multiple data sources (15). If you haven't seen it, Please watch the previous chapter
In the work, in the scenario of business development or business data isolation, it is usually necessary to introduce multiple data sources into a project,
However, the default automation configuration of SpringBoot is single data source, which can be processed through some additional configurations.
1, Preparation before configuring multiple data sources
1, Prepare two databases, springboot and springboot2
The user table is stored in the springboot database
The dept table is stored in the springboot 2 database table
-- stay springboot Create in the database user surface
use springboot;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(15) DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(6) DEFAULT NULL,
`description` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=0 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- stay springboot2 Create in the database dept surface
use springboot2;
CREATE TABLE `dept` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
1, 2. Prepare the corresponding entities User.java and Dept.java
User.java
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
/**
* @param id id number
* @param name full name
* @param sex Gender
* @param age Age
* @param description describe
*/
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private Integer age;
private String description;
}
Dept.java
@Data
public class Dept {
/**
* @param id id number
* @param name Department name
*/
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
1, III. use of Jpa
For the use of Jpa, see the articles written by old Butterfly: SpringBoot integrates JPA(6)
Project directory:
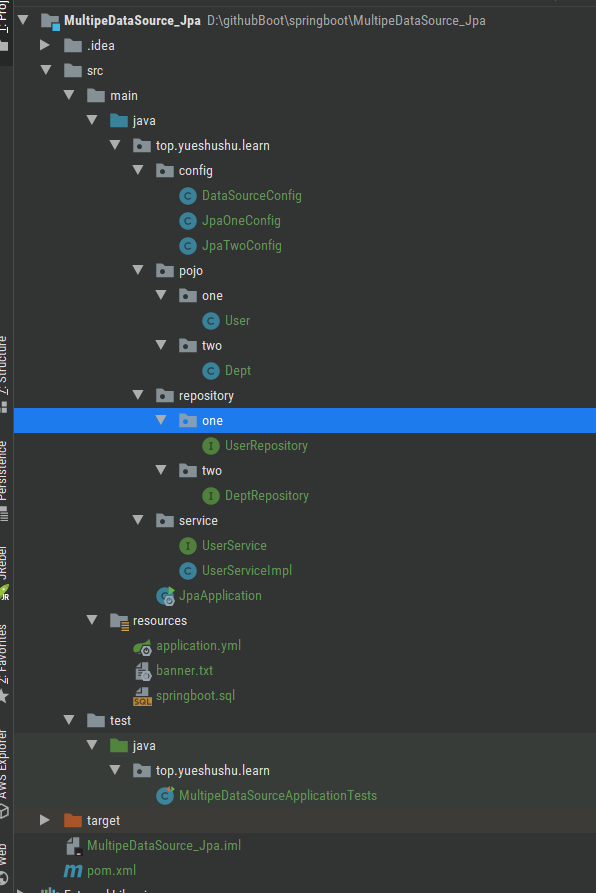
2, Jpa multi data source configuration
2, Add dependency to pom.xml
<!--introduce MySql Drive of-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--introduce springboot And jpa Integrated dependency-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.6</version>
</dependency>
2, II. Configure multiple data sources for application.yml
# Configure in the form of multiple data sources
spring:
datasource:
# Remove the previous configuration
#driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
#url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
#username: root
#password: abc123
# Configure the first database
one:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: abc123
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# Configure second database
two:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot2?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: abc123
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# Related configuration of JPA
jpa:
# Set database platform
database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
# Set up database
database: mysql
# Show SQL statements
show-sql: true
hibernate:
use-new-id-generator-mappings: false
# The persistence rule is update
ddl-auto: update
naming:
# The fully qualified name of the physical naming policy class
physical-strategy: org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.PhysicalNamingStrategyStandardImpl
2, Three entity configuration
Under the pojo package, create two packages, one and two.
The one package contains all the information about using the one database entity, and the two package contains all the information about using the two database entity
2, III. User.java user entity
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Table(name = "user")
@Entity
public class User implements Serializable {
/**
* @param id id number
* @param name full name
* @param sex Gender
* @param age Age
* @param description describe
*/
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name="sex")
private String sex;
@Column(name="age")
private Integer age;
@Column(name="description")
private String description;
}
2, III. Dept.java Department entity
@Data
@Table(name = "dept")
@Entity
public class Dept {
/**
* @param id id number
* @param name Department name
*/
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
}
2, IV. repository warehouse configuration
Under the repository package, create the one package and the two package
All information using the one database is placed under the one package, and all information using the two database is placed under the two package
2, IV. UserRepository interface
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer>,
JpaSpecificationExecutor<User>{
// For other methods, please refer to the chapter of Jpa for specific use
}
2, IV. II. Depositrepository interface
public interface DeptRepository extends JpaRepository<Dept, Integer>,
JpaSpecificationExecutor<Dept>{
// For other methods, please refer to the chapter of Jpa for specific use
}
2, V. multi data source configuration
It is mainly used to configure data sources, DataSource, scan libraries and scan entities.
2, V.1 DataSource data source configuration
package top.yueshushu.learn.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DruidDataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @ClassName:DataSourceConfig
* @Description Configuration of database source
* @Author zk_yjl
* @Date 2021/9/2 10:42
* @Version 1.0
* @Since 1.0
**/
@Component
public class DataSourceConfig {
/**
* Create the data source of the springboot database
* @return
*/
@Bean("dataSourceOne")
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.one")
@Primary //The @ Primary annotation indicates the default library
public DataSource dataSourceOne(){
return DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* Create the data source of the springboot2 database
* @return
*/
@Bean("dataSourceTwo")
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.two")
public DataSource dataSourceTwo(){
return DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
}
On the dataSourceOne() method, an additional annotation @ Primary is added to specify the default library. The default library is springboot
2, V. II configuration of scanning library and scanning entity
2, V. II. I configure the dataSourceOne data source of the main database
package top.yueshushu.learn.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.EntityManagerFactoryBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @ClassName:JpaOneConfig
* @Description Configuration information of Jpa main database of springboot database
* @Author zk_yjl
* @Date 2021/9/6 18:00
* @Version 1.0
* @Since 1.0
**/
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(
basePackages = "top.yueshushu.learn.repository.one", // Specify the location to scan the warehouse
entityManagerFactoryRef = "localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBeanOne", //Specifies the location of the scanned entity
transactionManagerRef = "platformTransactionManagerOne") //Specify transaction
public class JpaOneConfig {
@Resource(name="dataSourceOne")
DataSource dataSourceOne;
@Autowired
JpaProperties jpaProperties;
@Primary //Configure default
@Bean(name = "entityManagerPrimaryOne")
public EntityManager entityManagerOne(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBeanOne(builder).getObject().createEntityManager();
}
@Bean
@Primary //Configure default
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBeanOne(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return builder.dataSource(dataSourceOne)
// Set package for entity
.packages("top.yueshushu.learn.pojo.one")
//Set configuration information
.properties(jpaProperties.getProperties())
//Set the name of the persistence
.persistenceUnit("onePersistenceUnit")
.build();
}
@Bean
@Primary //Configure default
PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManagerOne(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean factoryBeanOne = localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBeanOne(builder);
return new JpaTransactionManager(factoryBeanOne.getObject());
}
}
2, V. II. Configuring the dataSourceOne data source from the database
package top.yueshushu.learn.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.EntityManagerFactoryBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @ClassName:JpaOneConfig
* @Description Jpa configuration information of database springboot
* @Author zk_yjl
* @Date 2021/9/6 18:00
* @Version 1.0
* @Since 1.0
**/
@Configuration
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "top.yueshushu.learn.repository.two", // Specify the location to scan the warehouse
entityManagerFactoryRef ="localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBeanTwo", //Specifies the location of the scanned entity
transactionManagerRef = "platformTransactionManagerTwo") //Specify transaction
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class JpaTwoConfig {
@Resource(name="dataSourceTwo")
DataSource dataSourceTwo;
@Autowired
JpaProperties jpaProperties;
@Bean(name = "entityManagerTwo")
public EntityManager entityManager(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBeanTwo(builder).getObject().createEntityManager();
}
@Bean
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBeanTwo(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return builder.dataSource(dataSourceTwo)
.packages("top.yueshushu.learn.pojo.two")
.properties(jpaProperties.getProperties())
//Set the name of the persistence
.persistenceUnit("twoPersistenceUnit")
.build();
}
@Bean
PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManagerTwo(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean factoryBeanTwo = localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBeanTwo(builder);
return new JpaTransactionManager(factoryBeanTwo.getObject());
}
}
2, Six interfaces and their implementation
UserService.java interface
public interface UserService {
void addUser(User user);
List<User> listUser();
void addDept(Dept dept);
List<Dept> listDept();
}
UserServiceImpl.java implementation class
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
// Data source 1 is placed in the springboot database
@Resource
private UserRepository userRepository;
//Data source 2 is placed in the springboot2 database
@Resource
private DeptRepository deptRepository;
/**
* The data source springboot is used
*/
@Override
public void addUser(User user) {
userRepository.save(user);
}
/**
* The data source springboot is used
*/
@Override
public List<User> listUser() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
/**
* The data source springboot2 is used
*/
@Override
public void addDept(Dept dept) {
deptRepository.save(dept);
}
/**
* The data source springboot2 is used
*/
@Override
public List<Dept> listDept() {
return deptRepository.findAll();
}
}
2, Seven tests
2, Vii.1 create test class
@SpringBootTest
@Log4j2
public class MultipeDataSourceApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void addUserTest(){
//1. Build object
User user=new User();
user.setName("Zhou Xiaohuan");
user.setAge(22);
user.setSex("female");
user.setDescription("A very lovely girl");
//2. Adding method
userService.addUser(user);
log.info("Employee added successfully");
}
@Test
public void listUserTest(){
List<User> userList=userService.listUser();
userList.forEach(n->log.info(n));
}
@Test
public void addDeptTest(){
//1. Build object
Dept dept=new Dept();
dept.setName("Information Management Department");
//2. Adding method
userService.addDept(dept);
log.info("Department added successfully");
}
@Test
public void listDeptTest(){
List<Dept> deptList=userService.listDept();
deptList.forEach(n->log.info(n));
}
/**
* Data source switching configuration
*/
@Test
public void allDataSourceTest(){
addUserTest();
listDeptTest();
addDeptTest();
listUserTest();
}
}
2, VII. II test data sources
Database source 1
add to
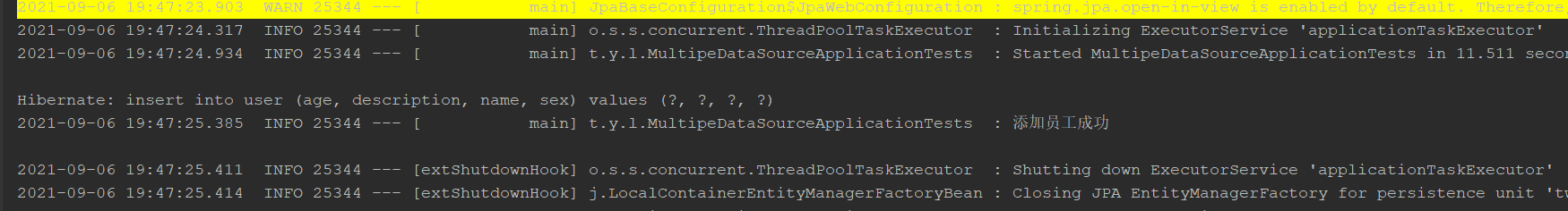
query
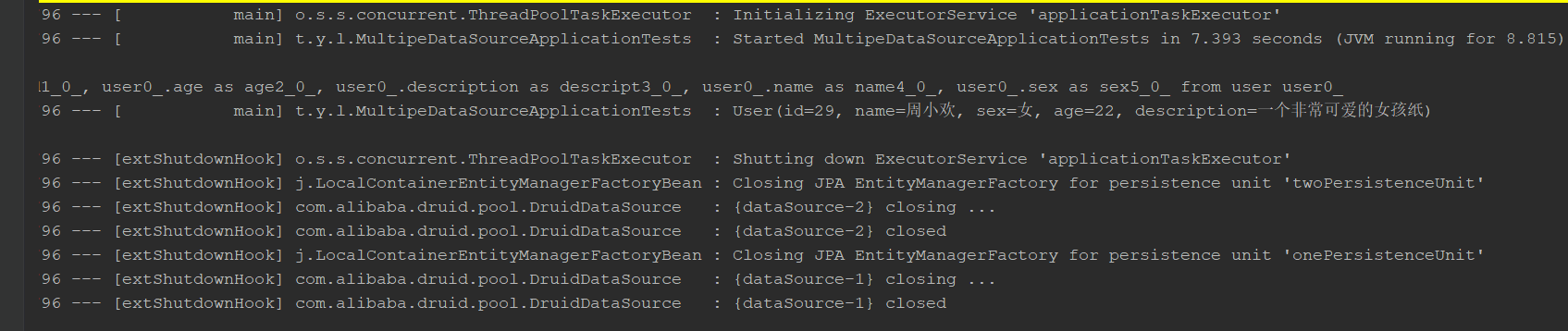
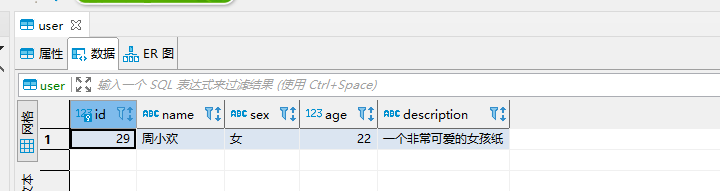
Only this data is stored in the user table of the springboot database
Database source 2
add to
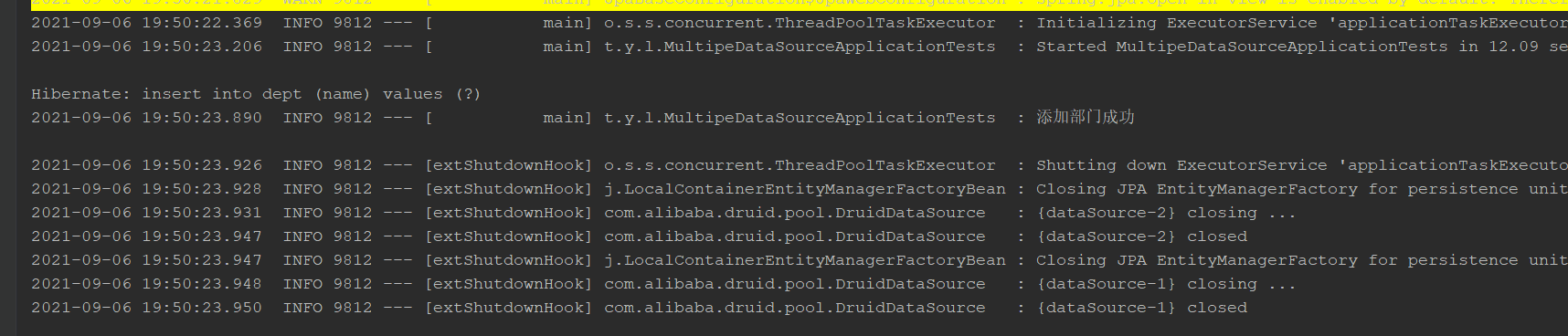
query
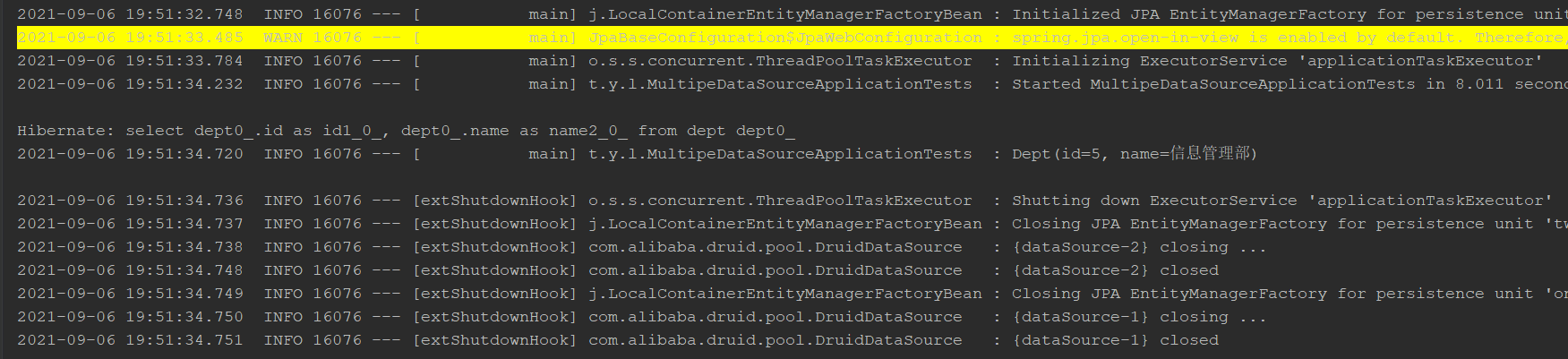
Only this data is stored in the dept table of springboot2 database
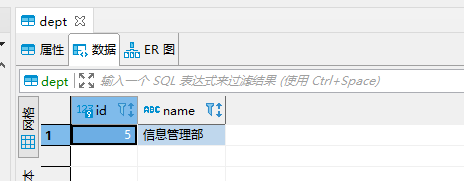
Data source switching configuration test
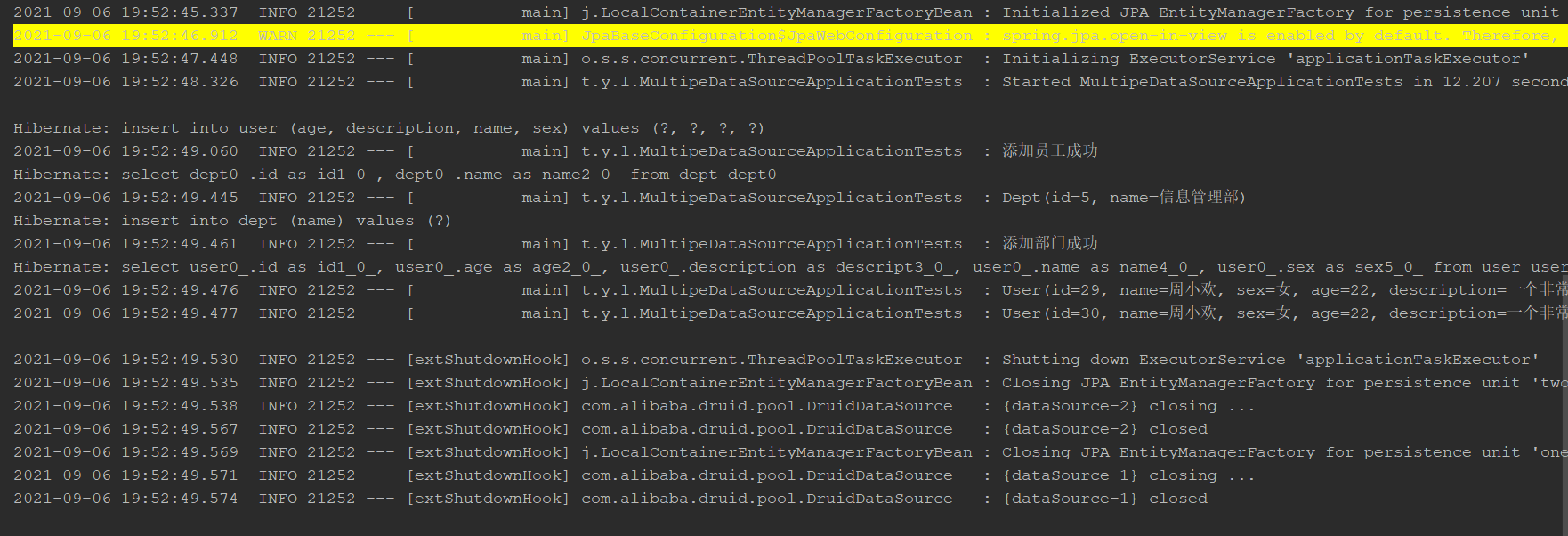
Query the database table again
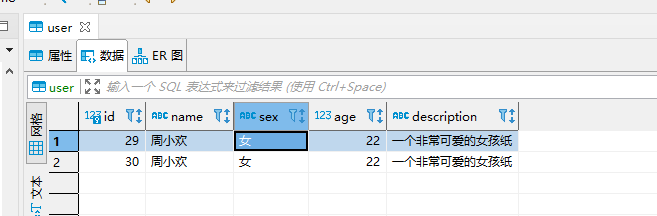
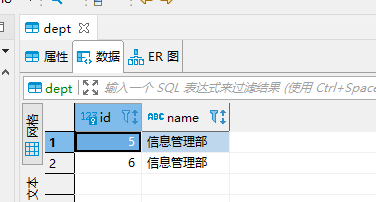
Data source switching configuration succeeded
The code in this chapter is placed on github:
https://github.com/yuejianli/springboot/tree/develop/MultipeDataSource_Jpa
Thank you for watching, if you like, please pay attention to me, thank you again!!!