10. Multi table query of mybatis
Relational database tables are divided into
* one-on-one * One to many * Many to many
give an example
- The ID number is one to one.
A person can only have one ID number.
An ID number can only belong to one person. - Users and orders are one to many, and orders and users are many to one
One user can place multiple orders
Multiple orders belong to the same user - Students and courses are many to many
A student can take multiple courses
A course can be taken by more than one student - special case
An order is subordinate to only one user, so mybatis regards many to one as one to one
1. One to one association query
- One to one query model
The relationship between user table and order table is that a user has multiple orders, and an order belongs to only one user
One to one query requirement: query all orders and find out the users of each order at the same time
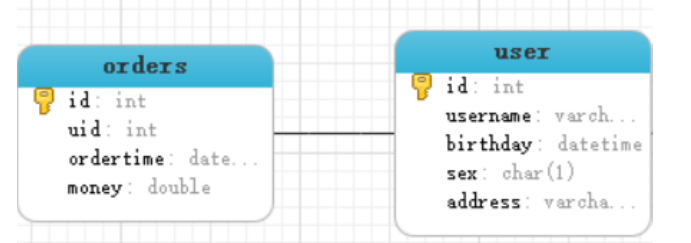
-
One to many query statement
SELECT *,o.id oid FROM USER u LEFT JOIN orders o ON u.`id` = o.`uid`;
1.1 code implementation
(1) Order entity
private Integer id;
private String orderTime;
private Double total;
private Integer uid;
//Import User object
private User user;
(2) OrderMapper interface
public interface OrdersMapper {
// Query user order
List<Orders> findOrder();
}
(3)OrderMapper.xml Mapping
- One to one (many to one) association using the association tag
<mapper namespace="com.lagou.mapper.OrdersMapper">
<resultMap id="orderMapper" type="orders">
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="orderTime" column="orderTime"></result>
<result property="total" column="total"></result>
<result property="uid" column="uid"></result>
<!--
One to one (many to one) use association Label Association
property="user" Encapsulates the attribute name of the entity
javaType="user" Encapsulates the attribute type of the entity
-->
<collection property="user" javaType="com.lagou.domain.User">
<id property="id" column="uid"></id>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="birthday" column="birthday"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="address" column="address"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findOrder" resultMap="orderMapper">
select *,u.id as uid from orders o left join `user` u on u.id =o.uid
</select>
</mapper>
(4) Test code
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
OrdersMapper ordersMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OrdersMapper.class);
List<Orders> orders = ordersMapper.findOrder();
for (Orders order : orders) {
System.out.println(order);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
-
test result
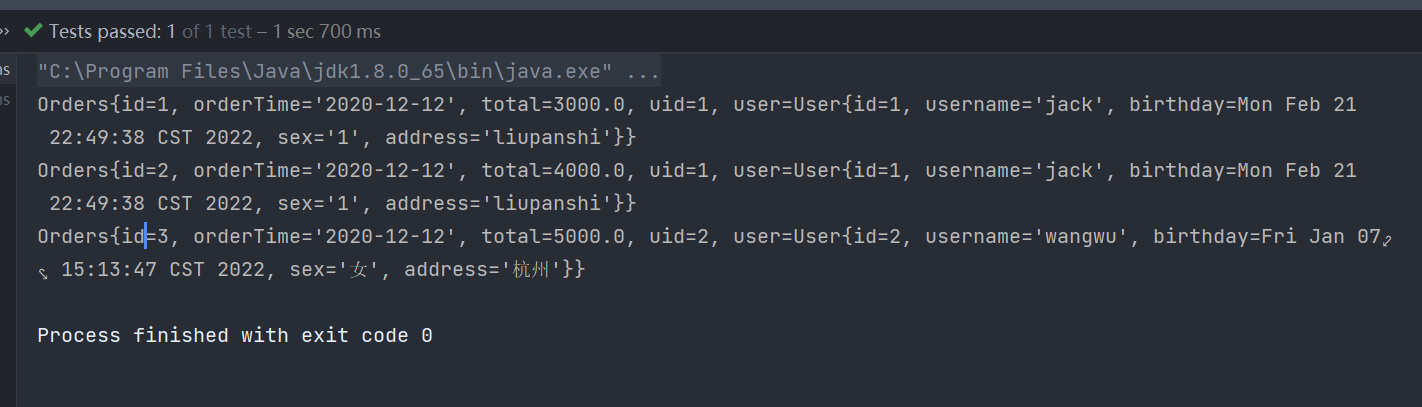
2. One to many association query
-
One to many model
The relationship between user table and order table is that a user has multiple orders, and an order belongs to only one user
One to many query requirements: query all users and find the orders that the user has at the same time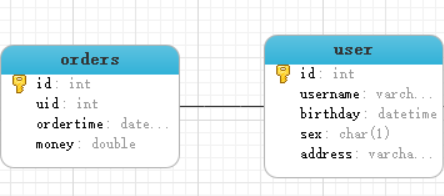
-
One to many query statement
SELECT *,o.id oid FROM USER u LEFT JOIN orders o ON u.`id` = o.`uid`;
2.1 code implementation
(1) User entity class
private Integer id;
private String username;
private Date birthday;
private String sex;
private String address;
Represents the order list of the current user
public List<Orders> ordersList;
(2) UserMapper interface
// Query user's order information
List<User> findUserOrder();
(3)UserMapper.xml Mapping
- Collection: one to many use of the collection tag
- Property = "ordersList": the property name encapsulated into the collection
- ofType = "order": encapsulates the generic type of the collection
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.lagou.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="userMapper" type="user">
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="birthday" column="birthday"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="address" column="address"></result>
<!-- collection:One to many use collection label
property="ordersList" : The property name encapsulated into the collection
ofType="order" : Encapsulates the generic type of the collection
-->
<collection property="ordersList" ofType="com.lagou.domain.Orders">
<id property="id" column="oid"></id>
<result property="orderTime" column="orderTime"></result>
<result property="total" column="total"></result>
<result property="uid" column="uid"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserOrder" resultMap="userMapper">
SELECT u.*,o.id oid , o.total, o.ordertime FROM USER u LEFT JOIN orders o ON u.`id` = o.`uid`;
</select>
</mapper>
(4) Test code
@Test
public void test3() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// Currently, the returned proxy object is actually generated based on UserMapper: bottom layer: JDK dynamic proxy, actual type: proxy
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> users = mapper.findUserOrder();
for (User people : users) {
System.out.println(people);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
3. Many to many association query
-
Many to many query model
The relationship between user table and role table is that a user has multiple roles and a role is used by multiple users.
Many to many query: query all users and find all roles of the user at the same time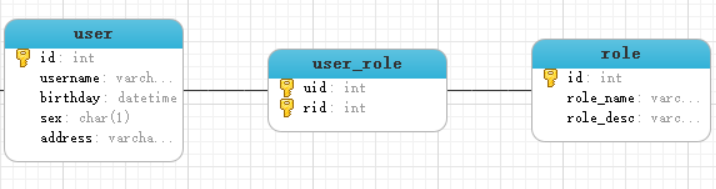
-
Query statement
SELECT u.*,r.id rid,r.rolename,r.roleDesc FROM `user` u LEFT JOIN sys_user_role ur on u.id = ur.userid LEFT JOIN sys_role r on ur.roleid = r.id ;
3.1 code implementation
(1) User and Role entities
public class Role {
private Integer id;
private String rolename;
private String roleDesc;
}
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private Date birthday;
private String sex;
private String address;
// Represents the order list of the current user
public List<Orders> ordersList;
//Represents the list of roles associated with the current user
private List<Role> roleList;
}
(2) UserMapper interface
// Query the corresponding roles of all users
List<User> findAllUserWithRole();
(3)UserMapper.xml Mapping
<resultMap id="getUserWithRole" type="user">
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="birthday" column="birthday"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="address" column="address"></result>
<collection property="roleList" ofType="com.lagou.domain.Role">
<id property="id" column="rid"></id>
<result property="rolename" column="rolename"></result>
<result property="roleDesc" column="roleDesc"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAllUserWithRole" resultMap="getUserWithRole">
SELECT u.*,r.id rid,r.rolename,r.roleDesc FROM `user` u LEFT JOIN sys_user_role ur on u.id = ur.userid LEFT JOIN sys_role r on ur.roleid = r.id ;
</select>
(4) Test code
@Test
public void test4() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// Currently, the returned proxy object is actually generated based on UserMapper: bottom layer: JDK dynamic proxy, actual type: proxy
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> users = mapper.findAllUserWithRole();
for (User people : users) {
System.out.println(people);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
(5) Test results
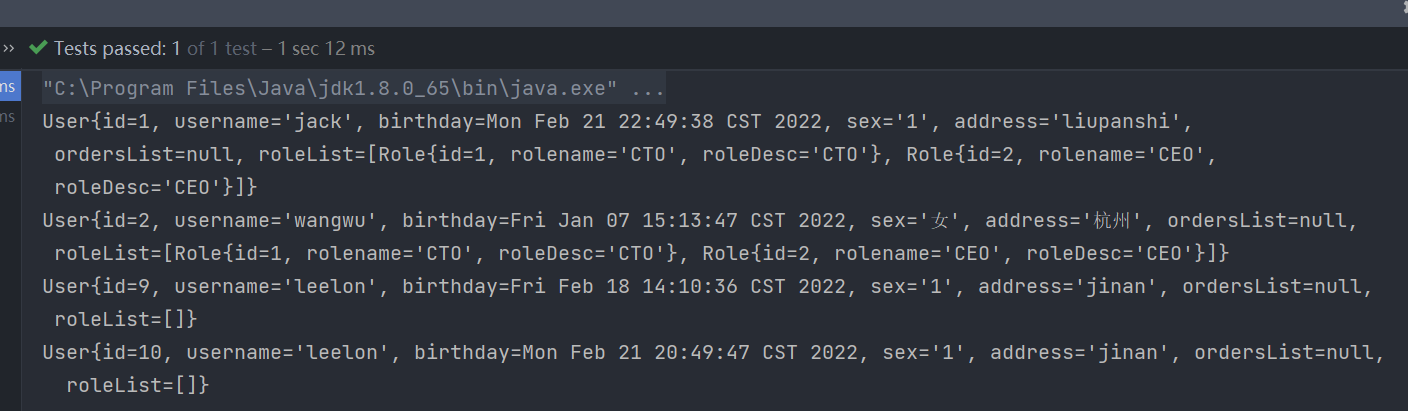
4. Summary
MyBatis multi table configuration mode
* Many to one (one to one) configuration: use<resultMap>+<association>Make configuration * One to many configuration: Using<resultMap>+<collection>Make configuration * Many to many configuration: Using<resultMap>+<collection>Make configuration * The many to many configuration is very similar to one to many, and the difficulty lies in SQL Statement writing.