In the actual development, we always use paging query. Different database paging SQL methods are different. We can use paging plug-ins to help us separate queries. We only need to care about the data itself, not the place
1. Plug in introduction
Configure the paging plug-in in the core configuration file SqlMapConfig.xml of mybatis, for example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <plugins> <!-- com.github.pagehelper by PageHelper Package name of class --> <plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper"> <!-- Set database type Oracle,Mysql,MariaDB,SQLite,Hsqldb,PostgreSQL Six databases--> <property name="dialect" value="mysql"/> </plugin> </plugins> </configuration>
2. use
There is a method startPage in PageHelper, as shown in the figure:
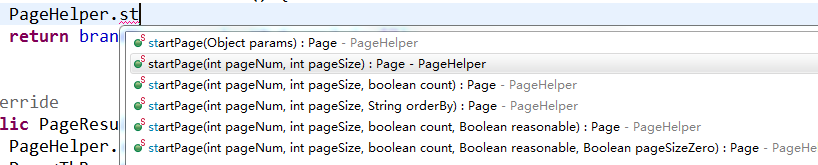
We found that it basically needs two parameters:
Parameter 1: pageNum current page.
Parameter 2: pageSize number of items displayed per page
These two parameters are generally passed to us by the front-end. In the front-end, there are no more than two data needed, one is the total number of records, the other is the result oriented list. Therefore, we can define a pageResult to encapsulate these two data (Map can also be used)
package entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Paging result class
* @author Administrator
* @param <T>
*/
public class PageResult<T> implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8744309372650296153L;
private Long total;
private List<T> rows;
public PageResult() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public PageResult(Long total, List<T> rows) {
super();
this.total = total;
this.rows = rows;
}
public Long getTotal() {
return total;
}
public void setTotal(Long total) {
this.total = total;
}
public List<T> getRows() {
return rows;
}
public void setRows(List<T> rows) {
this.rows = rows;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PageResult [total=" + total + ", rows=" + rows + "]";
}
}
PageHelper is easy to use. You only need to execute PageHelper.startPage before the SQL call statement, for example:
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pagesize);
At this time, when executing SQL query statements, the result of the query returns a page object, of course, it can also be a list < T > object, but we will force it to be a page object, because the page object encapsulates many methods for us to use. As shown in the picture:
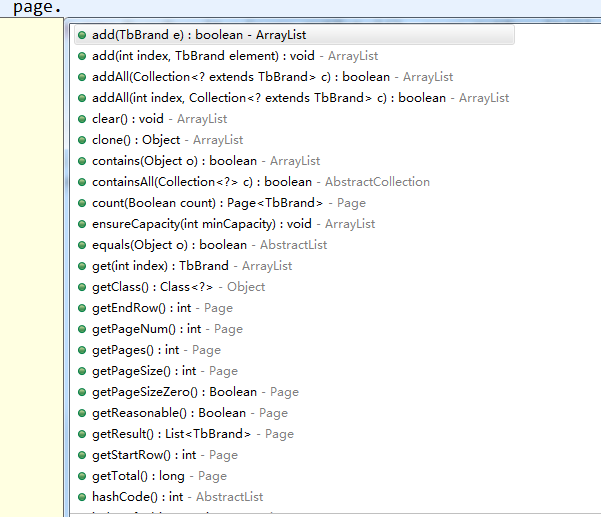
We only need two methods for paging, for example;
public PageResult<TbBrand> findPage(int pageNum, int pagesize) {
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pagesize);
Page<TbBrand> page = (Page<TbBrand>) brandMapper.selectByExample(null);
return new PageResult<>(page.getTotal(), page.getResult());
}

