MySQL (crazy God's notes)
1. Initial database
1.1 why learn databases?
1. Job requirements
2. In today's world, in the era of big data, those who get the database get the world.
3. Forced demand: save data
4. Database is the core existence of all software systems: DBA
1.2 what is a database?
DataBase (DB, DataBase)
Concept: data warehouse. The software is installed on the operating system (windows, Linux, mac...) and can store a large amount of data.
Function: store data and manage data.
1.3 database classification
Relational database
- MySQL ,Oracle,Sql Server,DB2, SQL Lite
- Data is stored through the relationship between tables and between rows and columns, including student information table and attendance table.
Non relational database: (NoSQL) Not Only
- Redis , MongDB
- Non relational database, object storage, is determined by the writing of the object itself/
DBMS (database management system)
- Database management software, scientific and effective management of our data. Maintain and obtain data.
- MySQL, database management system!
1.4 introduction to MySQL
install
Do not use exe files because they cannot be deleted cleanly
Use compressed files whenever possible
1.5MySQL installation tutorial
It is recommended that you use the compressed version, which is fast and convenient to install It's not complicated
Software download
mysql5.7 64 bit download address:
If the computer is 64 bit, download and use the 64 bit version!
Installation steps
1. Download and get the zip package
2. Unzip it to the directory where you want to install it. I unzip it to D:\Environment\mysql-5.7.19
3. Add environment variables: my computer - > properties - > Advanced - > environment variables
Select PATH and add the bin folder under your mysql installation file
4. Edit my INI file, pay attention to the replacement path location
[mysqld] basedir=D:\Program Files\mysql-5.7\ datadir=D:\Program Files\mysql-5.7\data\ port=3306 skip-grant-tables
5. Start CMD in administrator mode, switch the path to bin directory under mysql, and then enter mysqld – install
6. Then enter mysqld -- initialize secure -- user = Mysql to initialize the data file
7. Then start mysql again, and then use the command mysql – u root – p to enter the mysql management interface (the password can be blank)
8. Change the root password after entering the interface
update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('123456') where user='root'and Host = 'localhost';
9. Refresh permissions
flush privileges;
10. Modify my Delete the last skip grant tables from the INI file
11. Restart mysql to work normally
net stop mysql net start mysql
12. After the test on the connection shows the following results, it is installed
1.6 install visualization tool SQLyog
Brainless installation
1.7 connecting to database
mysql -uroot -p -- Connect to database
update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('123456') where user='root'and Host = 'localhost'; -- Change Password
flush privileges; -- Refresh permissions
-- All statements (except switching statements) use;ending
show databases; -- View all databases
use userdb -- Switch database use + Database name
show tables -- View all tables in the database
describe userdb -- View information about all tables in the database
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS myschool -- Delete database
create database westos -- Create a database
exit -- Exit link
-- Single line note( SQL Original notes)
/*
multiline comment
*/
Database xxx language
DDL definition
DML operation
DQL query
DCL control
2. Operation database
Operate database > operate tables in Database > operate data in tables in database
2.1 operation database (understand)
1. Create database
CREATE database if not EXISTS myschool
2. Delete database
drop database [if EXISTS] myschool
3. Use database
use myschool
4. Query database
SHOW DATABASES
2.2 column type of database
numerical value
- tinyint very small data a byte
- smallint smaller data 2 bytes
- mediumint medium size data 3 bytes
- Int standard integer 4 bytes common int
- bigint larger data 8 bytes
- float floating point number 4 bytes
- double floating point number 8 bytes
- decimal floating point numbers in string form are generally used in financial calculations
character string
- char character fixed size 0 ~ 255
- varchar variable String 0~65535 common String
- Tiny text 2 ^ 8 - 1
- Texttext string 2 ^ 16 - 1 save large text
Time date
java.util.Date
- date YYYY-MM-DD date format
- time HH: mm: ss time format
- datetime YYY-MM-DD HH: mm: ss the most commonly used time format
- Timestamp timestamp, the number of milliseconds from 1970.1.1 to now, is also commonly used
- Year means year
null
- Indicates no value, unknown
- Note: do not use NULL for operation. The result is NULL
2.3 field attributes of database (key points)
Unsigned:
- Unsigned integer
- Declared that the column cannot be negative
zerofill:
- 0 filled
- Insufficient digits, filled with 0
Self increasing:
- It is usually understood as self increment, which automatically adds 1 to the data of the previous record
- It is usually used to design a unique primary key ~ index, which must be integer data
- You can customize the start value and self increment value of the step size
Non NULL not null
- If it is set to not null, an error will be reported if it is not assigned a value!
- Null. If the value is not filled in, it is null by default!
Expand (just listen)
/*Each table must have the following five fields! For future projects, it indicates the significance of a record id Primary key `version` Optimistic lock is_delete Pseudo deletion gmt_create Creation time gmt_update Modification time */
2.4 creating tables
-- Note: use English(),Table names and fields should be used whenever possible ``Enclose -- AUTO_INCREMENT Self increasing -- String, enclosed in single quotes! -- All statements are followed by,(English),Don't add the last one -- PRIMARY KEY(`id`) Primary key. Generally, a table has only one unique primary key! CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `student`( `id` INT(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Student number', `name` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'anonymous' COMMENT 'full name', `pwd` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '123456' COMMENT 'password', `sex` VARCHAR(2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'female' COMMENT 'Gender', `birthday` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'date of birth', `address` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Home address', `email` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'mailbox', PRIMARY KEY(`id`) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
format
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] `Table name`(
`Field name` Column type [attribute] [Indexes] [notes]
`Field name` Column type [attribute] [Indexes] [notes]
......
`Field name` Column type [attribute] [Indexes] [notes]
)[Table type] [Character set settings][notes]
Common commands
SHOW CREATE DATABASE `myschool` -- View database creation statements SHOW CREATE TABLE student -- View the creation statement of the data table DESC student -- Displays the structure of the table
2.5 type of data sheet
-- About database engine /* INNODB Default use MYISAM Used in earlier years */
| MYISAM | INNODB | |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction support | I won't support it | support |
| Data row locking | I won't support it | support |
| Foreign key constraint | I won't support it | support |
| Full text index | support | I won't support it |
| Table space size | less | Larger, about 2 times |
General operation:
- MYISAM saves space and is fast
- INNODB: high security, transaction processing, multi table and multi-user operation
Where it exists in physical space
All database files are stored in the date directory. A folder is equivalent to a database.
Local or file storage!
Differences of MySQL engine in physical files
- InnoDB has only one *. In the database table frm file and ibdata1 file in the parent directory
- MYISAM corresponding file
- *Definition file of. frm table structure
- *. MYD data file (data)
- *. MYI index file (index)
Set the character set encoding of the database
CHARSET=utf8
If it is not set, it will be the default character set encoding of mysql ~ (Chinese is not supported)
The default code of MySQL is Latin1, which does not support Chinese
In my Ini to configure the default encoding
character-set-server=utf8
2.6 modifying and deleting tables
Modify table
-- Modify table information -- Modify table name ALTER TABLE Old table name RENAME AS New table name ALTER TABLE student RENAME AS student1 -- Add field name ALTER TABLE Table name ADD Field column properties ALTER TABLE student1 ADD grade INT(6) -- Modify fields (modify field names and constraints) -- Modify field constraints ALTER TABLE Table name MODIFY Field column properties ALTER TABLE student1 MODIFY grade VARCHAR(10) -- Modify field name ALTER TABLE Table name CHANGE Old field name new field column attribute ALTER TABLE student1 CHANGE grade grade1 INT(2) -- Delete field names in the table ALTER TABLE Table name DROP Field name ALTER TABLE student1 DROP grade1
Delete table
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS teacher
Create and delete tables with conditional statements as much as possible
Attention
- ``Use this as much as possible for field names
- Notes –/**/
- sql is case insensitive. Try to use lowercase
- All symbols are in English!
3.MySQL data management
3.1 foreign keys (just understand)
Method 1: perform foreign key connection when creating a table.
CREATE TABLE `grade` ( `gradeid` INT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Grade number', `gradename` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Grade name', PRIMARY KEY(`gradeid`) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- Foreign key joins are performed when the table is created CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `student`( `id` INT(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Student number', `name` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'anonymous' COMMENT 'full name', `pwd` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '123456' COMMENT 'password', `sex` VARCHAR(2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'female' COMMENT 'Gender', `birthday` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'date of birth', `gradeid` INT(8) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Grade number', `address` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Home address', `email` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'mailbox', PRIMARY KEY(`id`), KEY `FK_gradeid`(`gradeid`), CONSTRAINT `FK_gradeid` FOREIGN KEY (`gradeid`) REFERENCES `grade`(`gradeid`) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
When deleting a table, if the table contains foreign keys; Then, the table cannot be deleted. Tables that reference foreign keys must be deleted before they can be deleted.
Method 2: perform foreign key connection when creating a table
CREATE TABLE `grade` ( `gradeid` INT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Grade number', `gradename` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Grade name', PRIMARY KEY(`gradeid`) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- Foreign key joins are performed when the table is created CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `student`( `id` INT(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Student number', `name` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'anonymous' COMMENT 'full name', `pwd` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '123456' COMMENT 'password', `sex` VARCHAR(2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'female' COMMENT 'Gender', `birthday` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'date of birth', `gradeid` INT(8) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Grade number', `address` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Home address', `email` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'mailbox', PRIMARY KEY(`id`) )ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- When the table is created, add foreign keys ALTER TABLE student ADD CONSTRAINT `FK_gradeid` FOREIGN KEY (`gradeid`) REFERENCES `grade`(`gradeid`)
The above operations are physical foreign keys, database level foreign keys, which are not recommended! (to avoid the trouble caused by too many databases, just learn here)
Best practices
- A database is a simple table. It can only be used to store data, only rows (data) and columns (fields)
- We want to use the data of multiple tables and use foreign keys (programs to implement them)
3.2DML language (remember all)
The meaning of database: it is used to store and manage data.
-
insert
-
update
-
delete
3.3 add
insert
-- insert data INSERT INTO Table name (`Field name 1`,`Field name 2`,`Field name 3`) VALUES(`Value 1`),('Value 2')....
-- Others are either defaulted to NULL Or auto increment primary key
INSERT INTO grade (`gradename`) VALUES('Freshman')
-- If there is no corresponding field prompt, the fields and values must correspond one by one
INSERT INTO grade VALUES ('Sophomore') -- This is equivalent to execution INSERT INTO grade VALUES ('Sophomore',null)Mismatch
-- Insert multiple data
INSERT INTO grade (`gradename`) VALUES('Sophomore'),('Senior')
Syntax: INSERT INTO table name (field name 1, field name 2, field name 3) values (value 1), ('value 2')
matters needing attention:
- Fields must be separated by commas in English
- Fields can be omitted, but the following values must correspond to each other one by one
- Multiple pieces of data can be inserted at the same time. The VALUES after VALUES can be separated by English commas.
3.4 modification
Modify who (condition) set original value = new value
-- Modify who (condition) set Original value=New value -- Modification introduction UPDATE `student` SET `name`='Mad God' WHERE id=1 -- Whole column modification UPDATE `student` SET `name`='The Yangtze River seven' UPDATE `student` SET `email`='2398291@qq.com' WHERE id = 1 -- grammar -- UPDATE Table name SET column_name=value,[column_name=value] WHERE column_name=Specific value
Condition: where clause operator id is equal to a value, greater than a value and less than a value
Returns a Boolean value
| Operator | meaning | Range | result |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | be equal to | 5=6 | false |
| < > or= | Not equal to | 5<>6 | true |
| > | |||
| < | |||
| >= | |||
| <= | |||
| BETWEEN...AND... | [2,5] | ||
| AND | And&& | 5>1 AND 1<2 | false |
| OR | Or|| | 5>1 OR 1<2 | true |
-- Locate data through multiple conditions UPDATE student SET `sex`='female' WHERE `name`='The Yangtze River seven' AND `pwd`='12345'
Syntax: UPDATE table name SET column_name=value,[column_name=value] WHERE column_name = specific value
be careful:
-
column_name is a column in the database, which needs to be added``
-
Condition: if there is no filter condition, all columns will be modified
-
Value is a specific value or a variable
-
Multiple set attributes are separated by English commas
UPDATE student SET `birthday`=CURRENT_TIME WHERE `name`='The Yangtze River seven' AND `sex`='female'
3.5 deletion
delete command
Syntax: delete from table name [where condition]
-- delete Delete data (Delete all data in the table) Not recommended DELETE FROM `student`
-- Delete specified data DELETE FROM `student` WHERE `id`=1
TRUNCATE command
Function: completely empty the data in the table in the database
-- Delete all data in the database table TRUNCATE `student`
The difference between delete and TRUNCATE
-
Same point: you can clear the data in the table without affecting the structure and constraints of the table
-
difference:
- TRUNCATE zeroes the column set as the primary key
- TRUNCATE does not affect transactions
Just understand: delete the problem, restart the database, and solve the problem
- InnoDB auto incrementing will start from 1 (if it exists in memory, it will be lost after power failure)
- MyISAM will continue to start from the previous increment (those existing in the file will not be lost)
4.DQL query (most important)
4.1DQL
[Data Query Language]
-
All query operations use it select
-
Simple and complex queries use it
-
The core language and the most important statement in the database
-
Most frequently used statements
Order is important
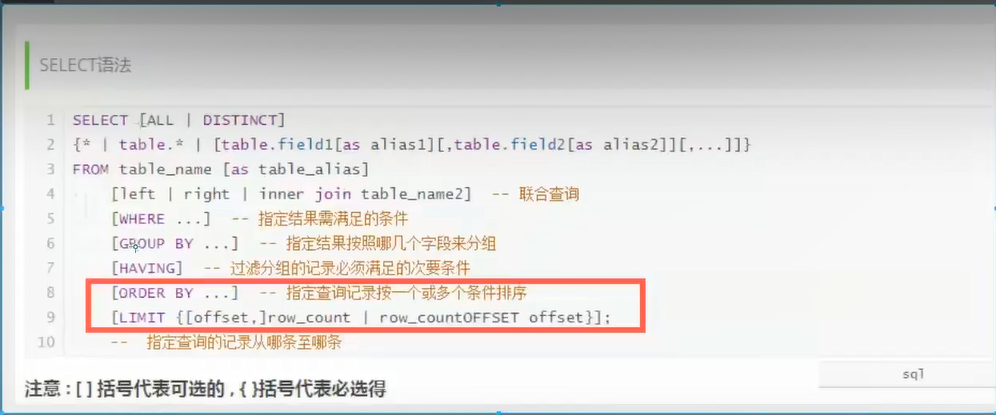
4.2 specifying query fields
-- All fields of the query table
SELECT * FROM student
-- Query the specified field of student information table
SELECT `studentno`,`studentname` FROM student
-- Alias AS Field name as New name table name as The new name alias only works in this statement, but does not actually change the field name and table name in the database
SELECT `studentno` AS Student number,`studentname` AS Student name FROM student AS s
-- function concat
SELECT CONCAT('full name:',`studentname`) AS New name FROM student
Syntax: SELECT field FROM table name
Sometimes, the list of names is not so obvious. So we will alias it as field name as new name
De duplication: distinct is directly added in front of the field name to be de duplicated to de duplicate it
-- De duplication of the queried data SELECT DISTINCT `studentno` FROM `student`
Database columns (expressions)
-- Query the version of the database(function) SELECT VERSION() -- Evaluate arithmetic expressions(expression) SELECT 100*3 - 1 AS Calculation results -- Display query step(variable) SELECT @@auto_increment_increment SELECT `studentno`,`studentresult` + 1 AS New achievements FROM `result` -- Variables can be calculated
Expressions in database: text value, column, NULL, function, calculation expression, system variable
select expression from table
4.3 where conditional clause
Function: query qualified values
operator
| operator | grammar | describe |
|---|---|---|
| and && | a and b a && b | Two for true is true |
| or || | a or b a ||b | Two false is false |
| Not ! | not a !a | Reverse |
Try to use English
-- Query student scores at 85~100 Between student number and student achievement SELECT `studentno`,`studentresult` FROM result WHERE `studentresult`>=85 AND `studentresult`<=100 SELECT `studentno`,`studentresult` FROM result WHERE `studentresult`>=85 && `studentresult`<=100 SELECT `studentno`,`studentresult` FROM result WHERE `studentresult` BETWEEN 85 AND 100 -- Query student numbers and student scores whose student scores are not equal to 60 SELECT `studentno`,`studentresult` FROM result WHERE `studentresult` != 68 SELECT `studentno`,`studentresult` FROM result WHERE NOT `studentresult`=60
Fuzzy queries: comparison operators
| operator | grammar | describe |
|---|---|---|
| is null | a is null | Returns true if a is empty |
| is not null | a is not null | Returns true if a is not empty |
| between | a between b and c | Returns true if a is between b and c |
| like | a like b | SQL matches. If a matches b, it returns true |
| in | a in (a1,a2,a3...) | If a is in one of a1 or a2, it returns true. |
like combined% (0 to any character)_ (one character)
SELECT * FROM student -- Query the information of students surnamed Zhao SELECT * FROM student WHERE `studentname` LIKE 'Zhao%' -- Query the information of students whose surname is Zhao and the number of names is 2 SELECT * FROM student WHERE `studentname` LIKE 'Zhang_' -- Query the information of students whose address contains chaozi SELECT * FROM student WHERE `address` LIKE '%towards%' -- Query the information of students whose student ID is one of the two numbers (10001001) SELECT * FROM student WHERE `studentno` IN (1000,1001) -- Query date of birth is NULL Student information SELECT * FROM student WHERE `borndate` IS NULL -- Query date of birth is not NULL Student information SELECT * FROM student WHERE `borndate` IS NOT NULL
4.4 associated table query
join comparison
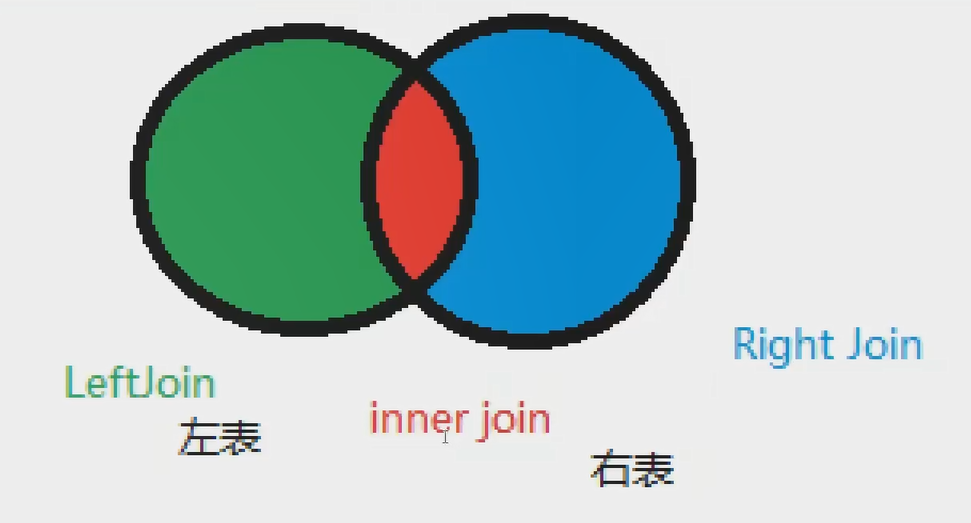
Idea:
- Analyze the requirements and which tables the fields of the analysis query come from (connection query)
- Determine which connection query to use? (7 kinds)
Determine the intersection (which data is the same in the two tables)
Conditions for judgment: studentNo of student table = studentNo of grade table
-- ===========Join table query=========== -- Query the names of the students who took the exam studentno studentname subjectno studentresult /* 1. Analyze the requirements and which tables the fields of the analysis query come from (connection query) 2. Determine which connection query to use? (7 kinds) Determine the intersection (which data is the same in the two tables) Conditions for judgment: studentNo of student table = studentNo of grade table */ -- INNER JOIN It implements the union between two tables SELECT s.studentno,studentname,subjectno,studentresult FROM student s INNER JOIN result r ON s.studentno=r.studentno -- LEFT JOIN Focusing on the left table will return all the information of the left table SELECT s.studentno,studentname,subjectno,studentresult FROM student s LEFT JOIN result r ON s.studentno=r.studentno -- RIGHT JOIN All information in the right table will be returned based on the right table SELECT s.studentno,studentname,subjectno,studentresult FROM student s RIGHT JOIN result r ON s.studentno=r.studentno -- join on join query -- where Equivalent query
Fields are union
| operation | describe |
|---|---|
| Inner join | If there is at least one match in the table, the row will be returned (redundant fields and empty fields will not be found, which are most frequently used) |
| left join | All values will be returned from the left table, even if there is no match in the right table |
| right join | All values will be returned from the right table, even if there is no match in the left table |
-- Query all the students who took the exam studentno studentname subjectname studentresult SELECT s.studentno,studentname,subjectname,studentresult FROM result r LEFT JOIN student s ON r.studentno=s.studentno INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.subjectno=sub.subjectno -- subjectname There is no ambiguity -- What data do I want to query select... -- From which tables from surface xxx join Connected tables on Cross condition -- Suppose there is a query with multiple tables. Take your time. First query two tables and then add them slowly -- from a left join b -- from a right join b
Self connection
The core is to as like as two peas of two tables.
Parent class:
| categoryid | categoryname |
|---|---|
| 2 | information technology |
| 3 | software development |
| 5 | Art design |
Subclass:
| pid | categoryid | categoryname |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | database |
| 3 | 6 | web development |
| 5 | 7 | ps Technology |
| 2 | 8 | Office information |
Join table of parent and child classes
| pcategoryname | categoryname |
|---|---|
| software development | database |
| software development | web development |
| Art technology | ps Technology |
| information technology | Office information |
-- Self connection SELECT a.categoryname AS 'Parent column',b.categoryname AS 'Sub column' FROM category a ,category b WHERE a.categoryid=b.pid -- where Equivalent query
4.5 paging and sorting
sort
-- Sort ascending asc Descending order desc -- ORDER BY Field name sort by SELECT * FROM result ORDER BY studentresult DESC
paging
Why do I need pagination?
Ease the pressure on the database, give people a better experience, waterfall flow
-- paging SELECT * FROM result LIMIT 1,2 -- Syntax: limit (Starting value,Page size) -- [n : PageCount ] -- [(n - 1) * pagesize : Starting value] -- [pagesize : Page size] -- [PageCount = total / pagesize]
Syntax: limit (starting value, page size)
4.6 sub query
where (this value is calculated)
Essence: nest a subquery statement within a where statement
where(select * from table name)
-- The query score is not less than 80 and the course name is advanced mathematics-1 Student number and name of the student -- Join table query SELECT s.`studentno`,`studentname` FROM student s INNER JOIN result r ON s.`studentno`=r.`studentno` INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.`subjectno`=sub.`subjectno` WHERE `studentresult`>80 AND `subjectname`='Advanced mathematics-1 ' SELECT s.`studentno`,`studentname` FROM student s INNER JOIN result r ON s.`studentno`=r.`studentno` WHERE `studentresult`>80 AND `subjectno` = ( SELECT `subjectno` FROM SUBJECT WHERE `subjectname`='Advanced mathematics-1 ' ) -- Subquery in transformation(From inside to outside) SELECT `studentno`,`studentname` FROM student WHERE `studentno` IN ( SELECT `studentno` FROM result WHERE `studentresult`>80 AND `subjectno` = ( SELECT `subjectno` FROM `subject` WHERE `subjectname`='Advanced mathematics-1 ' ) )
4.7 select summary
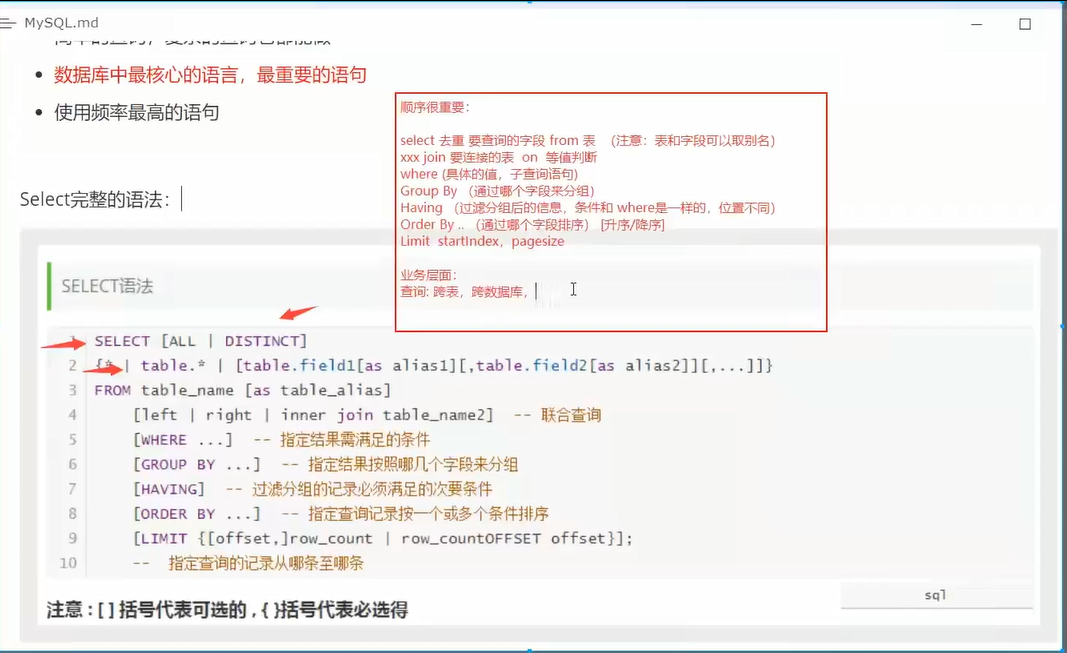
5. MySQL common functions
5.1 common functions
-- ==========Common functions========
-- Mathematical operation
SELECT ABS(-8) -- absolute value
SELECT CEILING(9.4) -- Round up
SELECT FLOOR(9.8)-- Round down
SELECT RAND() -- 0~1 Random number between
SELECT SIGN(10) -- Sign 0 for judging a number-0 Negative return-1,A positive number returns 1
-- String function
SELECT CHAR_LENGTH('Crazy God said that hard work will succeed') -- Return string length
SELECT CONCAT('I','love','You') -- Splice string
SELECT INSERT('I love programming helloworld',1,2,'Super love') -- Replace string from a location
SELECT LOWER('KUANGSHEN')
SELECT UPPER('kuangshen') -- Convert case
SELECT INSTR('kaungshen','sh') -- Returns the index of the first occurrence string
SELECT REPLACE('Crazy God says persistence can succeed','insist','strive') -- Replace the specified string that appears
SELECT SUBSTR('Crazy God says persistence can succeed',4,6) -- Intercepts the specified string (The location and length of the source string interception)
SELECT REVERSE('I got on my horse in the morning') -- Reverse string
-- Time date function
SELECT CURRENT_DATE() -- Get current date
SELECT CURDATE() -- Get current date
SELECT NOW() -- Get current time
SELECT LOCALTIME() -- Local time
SELECT SYSDATE() -- Get system time
SELECT YEAR(NOW())
SELECT MONTH(NOW())
SELECT DAY(NOW())
SELECT HOUR(NOW())
SELECT MINUTE(NOW())
SELECT SECOND(NOW())
-- system
SELECT SYSTEM_USER()
SELECT USER()
SELECT VERSION()
5.2 aggregate function (common)
| Function name | describe |
|---|---|
| COUNT() | count |
| SUM() | Sum |
| AVG() | Average |
| MAX() | Find the maximum value |
| MIN() | Find the minimum value |
-- =======Aggregate function==== SELECT COUNT(subjectno) FROM result -- COUNT(Specify field) Will ignore null value SELECT COUNT(*) FROM result -- COUNT(*) Will not ignore all null Value essence: count rows SELECT COUNT(1) FROM result -- COUNT(1) Will not ignore all null Value essence: count rows SELECT SUM(`studentresult`) FROM result SELECT AVG(`studentresult`) FROM result SELECT MAX(`studentresult`) FROM result SELECT MIN(`studentresult`) FROM result -- group by What fields are grouped by -- HAVING Equivalent to where however where Indicates before grouping HAVING After grouping
5.3 MD5 encryption (extension) at database level
What is MD5?
It mainly enhances the complexity and irreversibility of the algorithm.
MD5 is irreversible, and the specific value of MD5 is the same
The principle of MD cracking the website is that there is a dictionary behind it. The value after MD5 encryption and the value before encryption
CREATE TABLE `test05`(
`id` INT(4) NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
`pwd` VARCHAR(60) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(`id`)
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
-- enable password
INSERT INTO `test05` VALUES(1,'Zhang San','123456'),
(2,'Li Si','123456'),
(3,'Wang Wu','123456')
DROP TABLE test05
-- encryption
UPDATE test05 SET pwd=MD5(pwd) WHERE id=1 -- Encrypt the specified password
UPDATE test05 SET pwd=MD5(pwd) -- Encrypt all passwords
-- Encrypt when inserting
INSERT INTO test05 VALUES(4,'Zhao Si',MD5('567899'))
-- twice MD5 After encryption, the password is the same
-- How to verify: first encrypt the password entered by the customer, and then compare it
SELECT * FROM test05 WHERE `name`='Zhang San' AND pwd=MD5('123456')
6. Services
6.1 what is a transaction?
Either succeed or fail.
Put an SQL into a batch for execution.
Transaction principle: ACID principle atomicity consistency persistence isolation dirty read non repeatable read unreal read
Atomicity
Either all succeed or all fail.
uniformity
The integrity before and after the transaction shall be consistent. For example, the total amount of money before and after the money transfer shall be consistent
Isolation
Transaction isolation is that when multiple users access the database concurrently, the transactions opened by the database for each user cannot be disturbed by the operation data of other transactions, and the transactions should be isolated from each other.
persistence
Once the transaction is committed, it is persisted to the database.
Dirty read:
A transaction reads uncommitted data from another transaction.
Non repeatable:
A row of data in a table is read in a transaction, and the results are different multiple times. (this is not necessarily a mistake, but it is wrong on some occasions)
Unreal reading:
It means that the data inserted by another transaction is read in one transaction, resulting in inconsistent reading.
Execute transaction
-- ======transaction processing======= -- mysql Transaction auto commit is enabled by default SET autocommit = 0 -- close SET autocommit = 1 -- Turn on auto submit -- Manual transaction processing SET autocommit = 0 -- Turn off auto submit -- Transaction on START TRANSACTION -- Mark the beginning of a transaction, starting from the beginning sql All in one transaction INSERT xx INSERT xx -- Commit: persistent (successful!) COMMIT -- Rollback: return to the original state (failed!) ROLLBACK -- End of transaction SET autocommit = 1 -- Turn on auto submit -- understand SAVEPOINT Save roll call -- Savepoint name sets the savepoint of a transaction ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT Save roll call -- Rollback to savepoint RELEASE SAVEPOINT Save roll call -- Undo savepoint
Simulation scenario
-- =====Simulation scenario=========
CREATE DATABASE `shop` CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci
USE `shop`
CREATE TABLE `account`(
`id` INT(3) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
`money` DECIMAL(9,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
DROP TABLE `account`
INSERT INTO `account` (`name`,`money`)VALUES('A',2000.00),('B',10000.00)
SET autocommit = 0 -- Turn off auto submit
START TRANSACTION -- Open transaction
UPDATE `account` SET money = money - 500 WHERE `name` = 'A' -- A Minus 500
UPDATE `account` SET money = money + 500 WHERE `name` = 'B' -- B Plus 500
COMMIT -- Commit successfully committed to the database (persisted!)
ROLLBACK -- RollBACK
SET autocommit = 1 -- Turn on auto submit
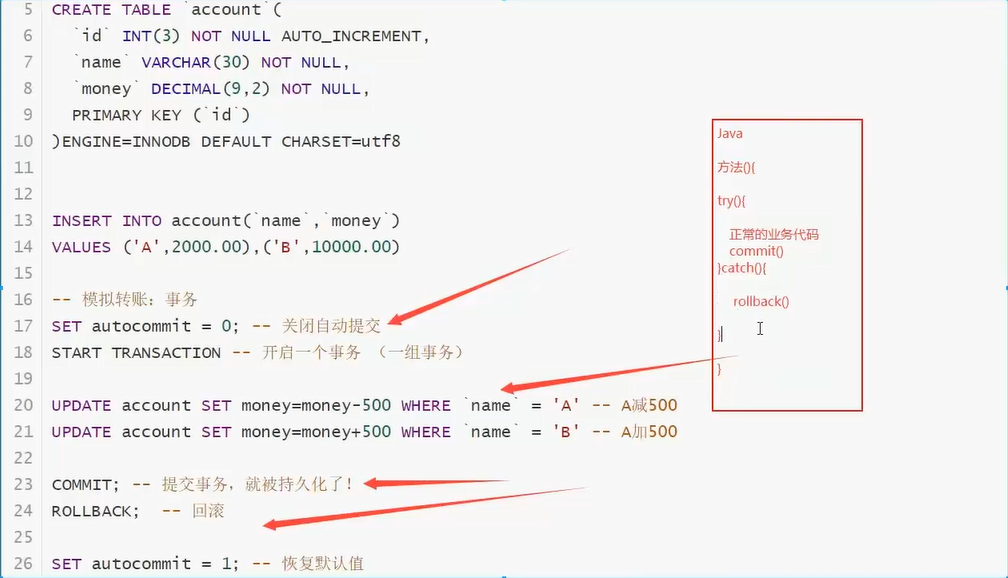
7. Index
MySQL's official definition of index is: index is a data structure that helps MySQL obtain data efficiently.
The essence of index: index is a data structure.
7.1 classification of index
In a table, the primary key index is unique, and the unique index can be multiple
- PRIMARY KEY (PRIMARY KEY)
- Unique identifier. The primary key cannot be repeated. There is only one column as the primary key
- UNIQUE KEY
- To avoid duplicate columns, unique indexes can be repeated, and multiple columns can be identified as unique indexes of identification bits
- General index (KEY/INDEX)
- default
- Full text index (FullText)
- Only under a specific database engine, MYISAM
- Quickly locate data.
-- =======Indexes==== SHOW INDEX FROM student -- Show all index information ALTER TABLE student ADD FULLTEXT INDEX `studentname`(`studentname`) -- Add index to table -- EXPLAIN see sql Statement execution -- EXPLAIN + Corresponding sql sentence
7.2 test index
Test index
-- P31 establish app_user form
CREATE TABLE `app_user` (
`id` BIGINT(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT '',
`eamil` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`phone` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT '',
`gender` TINYINT(4) UNSIGNED DEFAULT '0',
`password` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`age` TINYINT(4) DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time` DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`update_time` TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
-- Insert 1 million data.
DELIMITER $$
-- The flag must be written before writing a function
CREATE FUNCTION mock_data ()
RETURNS INT
BEGIN
DECLARE num INT DEFAULT 1000000;
DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;
WHILE i<num DO
INSERT INTO `app_user`(`name`,`eamil`,`phone`,`gender`)VALUES(CONCAT('user',i),'19224305@qq.com','123456789',FLOOR(RAND()*2));
SET i=i+1;
END WHILE;
RETURN i;
END;
SELECT mock_data() -- Execute this function to generate one million pieces of data
SELECT * FROM app_user WHERE `name`='User 99999' -- 1.175 sec
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM app_user WHERE `name`='User 99999'
-- 2.Another way to create an index: create index Index name on Table name (field name)
CREATE INDEX id_app_user ON app_user(`name`) -- General index
SELECT * FROM app_user WHERE `name`='User 99999' -- 0.035 sec
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM app_user WHERE `name`='User 99999'


When the data is still small, the index is of little use. In the case of big data, the index can speed up the query speed.
7.3 indexing principle
- The more indexes, the better
- Do not index the process
- Tables with small amounts of data do not need to be indexed
- Indexes are usually added to fields commonly used for queries
Indexed data structure
Hash type index
Btree: InnoDB default
Reference blog: Codinglabs - data structure and algorithm principle behind MySQL index
8. Rights management and backup
8.1 user management
SQLyog visual management
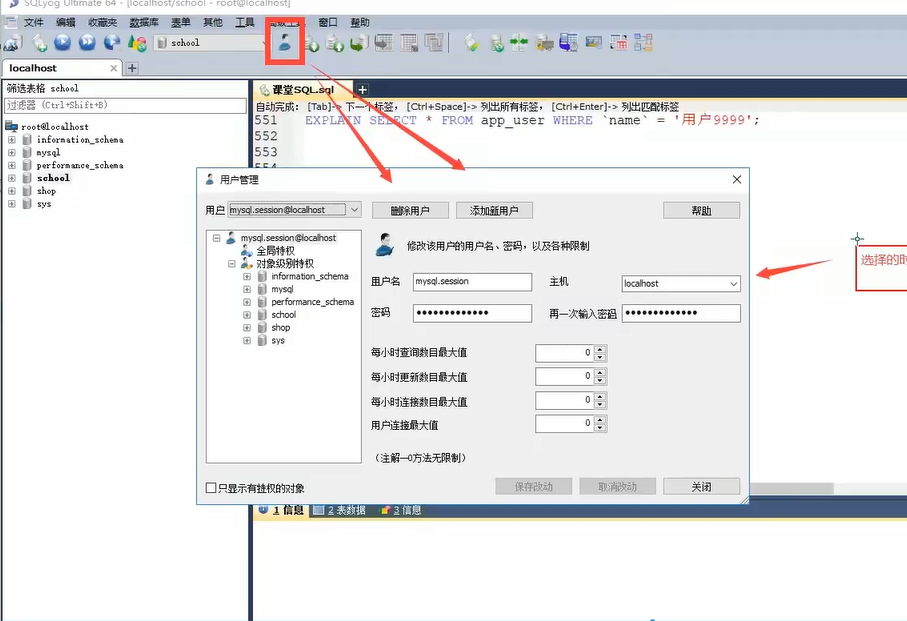
SQL command
-- Create user CREATE USER user name IDENTIFIED BY 'password'
CREATE USER kuangshen IDENTIFIED BY '123456'
-- Modify password (modify current user password)
SET PASSWORD = PASSWORD('123456')
-- Modify password (modify specified user password)
SET PASSWORD FOR kuangshen = PASSWORD('123456')
-- rename RENAME USER Original name TO New name
RENAME USER kuangshen TO kuangshen2
-- User authorization ALL PRIVILEGES All permissions, library.surface
-- ALL PRIVILEGES Except for authorizing others, others are capable
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO kuangshen2
-- Query authority
SHOW GRANTS FOR kuangshen2
SHOW GRANTS FOR root@localhost
-- root User rights: GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION
-- Revoke permissions REVOKE Which permissions, in which library, and to whom
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* FROM kuangshen2
-- delete user
DROP USER kuangshen2
8.2MySQL backup
Why backup?
- Ensure no data loss
- Data transfer
MySQL database backup method
- Copy physical files directly
- Manually import in a visualizer like SQLyog
- Right click the table and library you want to export and select backup or export
- Export using the SQL command line mysqldump
#mysqldump -h host - u user name - p password database name table name > export location mysqldump -hlocalhost -uroot -p123456 myschool student >D:/a.sql #mysqldump -h host - u user name - p password database name table 1 Table 2 Table 3 > export location mysqldump -hlocalhost -uroot -p123456 myschool student result >D:/b.sql #mysqldump -h host - u user name - p password database name > export location mysqldump -hlocalhost -uroot -p123456 myschool >D:/c.sql #Import #In the case of login, switch to the specified database #source backup file source D:/a.sql #Without logging in mysql -u user name -p Password library name<Backup file
9. Standardize database design
When the database is more complex, we need to design
Poor database design:
- Data redundancy, waste of space
- Database insertion and deletion will be troublesome, exception [shielding the use of physical foreign keys]
- Poor program performance
Good database design:
- Save memory space
- Ensure the integrity of the database
- It is convenient for us to develop the system
In software development, database design:
- Analysis requirements: analyze the requirements of the business and the database to be processed
- Outline design: design relationship diagram E-R diagram
Steps to design database: (personal blog)
- Collect information and analyze requirements
- User table (user login and logout, user's personal information, blogging, creating categories)
- Classification table (article classification, who created it)
- Article table (information about articles)
- Comment form
- Friend chain list (friend chain information)
- Custom table (system information, a key word, or some fields) key: value
- Talk about the table (post mood id... content... create_time)
- Identify the entity (implement the requirements to each field)
- Identify relationships between entities
- Blog: user -- > blog
- Create category: user -- > category
- Attention: user -- > User
- Friend chain: links
- Comments: user -- > user – > blog
9.2 three paradigms
Why data normalization?
- Duplicate information
- Update exception
- Insert exception
- Unable to display information normally
- Delete exception
- Missing valid information
Three paradigms (understanding)
First paradigm
Each column of the database is required to be a non separable atomic item
Second paradigm
Premise: meet the first paradigm
Each table describes only one thing
Third paradigm
Premise: meet the first paradigm and the second paradigm
The third paradigm needs to ensure that each column of data in the data table is directly related to the primary key, not indirectly.
(standardize the design of database)
Normative and performance issues
The associated query table cannot exceed three tables
- Considering the needs and objectives of commercialization (cost and user experience), the performance of database is more important
- When standardizing performance, we need to properly consider standardization!
- Deliberately add some redundant fields to some tables. (from multi table query to single table query)
- Deliberately add some calculated columns (query with large data volume reduced to small data volume: index)
10.JDBC (key)
10.1 database driver
Driver: sound card, graphics card, database
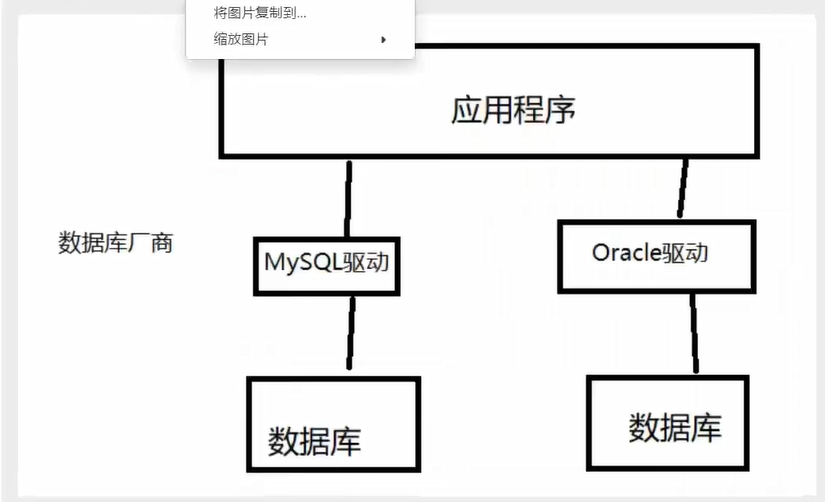
Our program will deal with the database through database driver.
10.2 JDBC
In order to simplify the (unified database) operation of developers, sun company provides a (java database operation) specification, commonly known as JDBC.
The implementation of these specifications has specific manufacturers to do.
For developers, we only need to master the operation of JDBC interface!
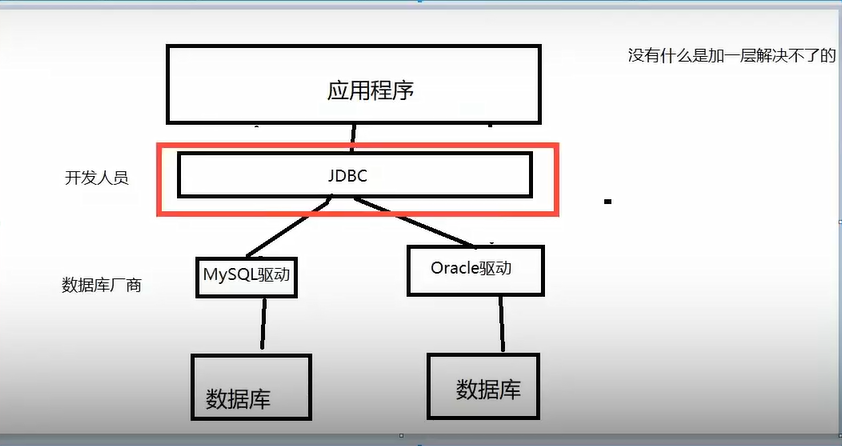
java.sql
javax.sql
You also need to import a database driver package. mysql-connector-java-5.1.47
10.3 first JDBC program
Create test database
CREATE DATABASE jdbcStudy CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; USE jdbcStudy; CREATE TABLE `users`( id INT PRIMARY KEY, NAME VARCHAR(40), PASSWORD VARCHAR(40), email VARCHAR(60), birthday DATE ); INSERT INTO `users`(id,NAME,PASSWORD,email,birthday) VALUES(3,'zhansan','123456','zs@sina.com','1980-12-04'), (2,'lisi','123456','lisi@sina.com','1981-12-04'), (3,'wangwu','123456','wwu@sina.com','1979-12-04')
1. Create a common project
2. Import database driver
Create a lib directory under the project directory, import the jar package, and then right-click.
3. Write test code
package study;
import java.sql.*;
public class JdbcFirstDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//1. Load drive
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2. Obtain user information and password
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";
String username="root"; //First error reason: wrong user name.
String password = "123456";
// 3. Connect to the database connection represents the database
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//4. Get the object that executes the sql statement. The statement represents the sql object
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//5. Execute sql statement to obtain result set
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while(resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("id=" + resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.println("name=" + resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.println("password=" + resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("email=" + resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.println("birth=" + resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
System.out.println("=====================");
}
//6. Release the connection
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
DriverManager
//1. Load drive
//DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); // Fixed writing, load driven
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// connection represents the database
// Database submission
//Database rollback
// Automatic database submission
connection.commit();
connection.rollback();
connection.setAutoCommit();
URL
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true"; // Protocol: / / host address: port number / database name? Parameter1 & parameter2 & parameter3 // Oralce -- 1521 // jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:sid
statement implement SQL Object of
connection.prepareStatement()
statement.executeQuery();// Executing a query statement
statement.execute();// Arbitrary SQL statements can be executed, which is inefficient
statement.executeUpdate(); // Updates, inserts, and deletes are performed
resultSet is a result set that encapsulates all the results.
resultSet.getObject() // Use without knowing the column type // Use specific when you know the column type resultSet.getString() resultSet.getInt(); resultSet.getFloat(); resultSet.getDouble();
Traversal: pointers
resultSet.beforeFirst();// Move to the front resultSet.afterLast();// Move to the back resultSet.previous();// Move to previous line resultSet.next(); // Move to the next line resultSet.absolute(row); // Move to specified row
Release resources
//6. Release the connection resultSet.close(); statement.close(); connection.close();//Very resource consuming
10.4 statement object
The statement object in jdbc is used to send SQL statements to the database. To complete the addition, deletion, modification and query of the database, you only need to send the addition, deletion, modification and query statements to the database through this object.
The executeUpdate method of the Statement object is used to send SQL statements of addition, deletion, modification and query to the database. After executeUpdate is executed, an integer will be returned (that is, the addition, deletion, modification and query statements cause changes to several rows of data in the database).
Statement. The executeQuery method is used to send query statements to the database, and the executeQuery method returns the ResultSet object representing the query results.
CRUD operation - create
Use the executeUpdate (String sql) method to add data. The instance operation is as follows:
Statement st = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "INSERT INTO Table name (`Field name 1`,`Field name 2`,`Field name 3`) VALUES(`Value 1`),('Value 2').... ";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num > 0){
System.out.println("Successfully added!");
}
CRUD operation - delete
Use the executeUpdate (String sql) method to delete data. The instance operation is as follows:
Statement st = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "DELETE FROM `student` WHERE `id`=1 ";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num > 0){
System.out.println("Delete succeeded!");
}
CRUD operation - update
Use the executeUpdate (String sql) method to complete the data update operation. The instance operation is as follows:
Statement st = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "UPDATE Table name SET column_name=value,[column_name=value] WHERE column_name=Specific value";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num > 0){
System.out.println("Delete succeeded!");
}
CRUD operation - Query
Use the executeQuery (String sql) method to complete the data query operation. The instance operation is as follows:
//4. Get the object that executes the sql statement. The statement represents the sql object
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//5. Execute sql statement to obtain result set
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while(resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("id=" + resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.println("name=" + resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.println("password=" + resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("email=" + resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.println("birth=" + resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
System.out.println("=====================");
}
1. Extraction tools
package study01;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
private static String driver = null;
private static String url = null;
private static String username = null;
private static String pwd = null;//String type
static {
try {
InputStream in = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");//Get the input stream from the corresponding file
Properties properties = new Properties();//Get resources
properties.load(in);//Get resources
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
pwd = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driver);//The driver only needs to be loaded once
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Get connection
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,pwd);
}
//The release connection parameter is passed by the caller
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement st, ResultSet rt){
if(rt != null){
try {
rt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(st != null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn != null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- executeUpdate test addition, deletion and modification
package study;
import study01.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JdbcDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rt = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();// Get connection
st = connection.createStatement();//Get SQL object
String sql = "INSERT INTO `users`(id,NAME,PASSWORD,email,birthday)" +
"VALUES(4,'mazi','456728','zs@sina.com','1989-11-14')";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num > 0){
System.out.println("Insert succeeded!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,st,rt);//Release resources
}
}
}
package study;
import study01.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestDelete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rt = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();// Get connection
st = connection.createStatement();//Get SQL object
String sql = "DELETE FROM users WHERE `id` = 4";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num > 0){
System.out.println("Delete succeeded!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,st,rt);//Release resources
}
}
}
package study;
import study01.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestUpdate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rt = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();// Get connection
st = connection.createStatement();//Get SQL object
String sql = "UPDATE users SET `name` = 'kuangshen' where `id` = 1";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num > 0){
System.out.println("Update succeeded!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection,st,rt);//Release resources
}
}
}
3.executeQuery implements query
package study;
import study01.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestQuery {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rt = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
st = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users";
rt = st.executeQuery(sql);
while(rt.next()){
System.out.println(rt.getInt("id"));
System.out.println(rt.getString("NAME"));
System.out.println(rt.getString("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println(rt.getString("email"));
System.out.println(rt.getDate("birthday"));
System.out.println("====================");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rt);
}
}
}
SQl injection problem
SQL has vulnerabilities, which will lead to data disclosure, which is essentially caused by or
package study;
import study01.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//login("kuangshen","123456"); Login successful
login("' or '1=1","' or '1=1");//SQL injection causes
/*
kuangshen
123456
====================
zhangsan
123456
====================
lisi
123456
====================
*/
}
public static void login(String username,String pwd){
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rt = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
st = conn.createStatement();
//SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME` = 'kuangshen' AND `PASSWORD` = '123456'
//SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME` = '' or '1=1' AND `PASSWORD` = '' or '1=1'
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME` = '"+ username +"' AND `PASSWORD` = '"+ pwd +"'";
rt = st.executeQuery(sql);
while(rt.next()){
System.out.println(rt.getString("NAME"));
System.out.println(rt.getString("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("====================");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rt);
}
}
}
10.5 PreparedStatement object
PreparedStatement can prevent SQL injection and is more efficient.
1. Addition, deletion and modification
package study02;
import study01.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Date;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement st = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//Get connection
String sql = "INSERT INTO `users`(id,NAME,PASSWORD,email,birthday)" +
"VALUES(?,?,?,?,?)";//use? Representative parameters
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);//Parameter requires a precompiled SQL statement
st.setInt(1,4);
st.setString(2,"Madness");
st.setString(3,"234516");
st.setString(4,"23457125@qq.com");
st.setDate(5,new java.sql.Date(new Date().getTime()));//Fill in parameters
int i = st.executeUpdate();//implement
if(i > 0){
System.out.println("Insert successful");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,null);
}
}
}
package study02;
import study01.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Date;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement st = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//Get connection
String sql = "delete from users where `id`=?";//use? Representative parameters
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);//Parameter requires a precompiled SQL statement
st.setInt(1, 4);//Fill in parameters
int i = st.executeUpdate();//implement
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("Delete succeeded");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, null);
}
}
}
package study02;
import study01.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement st = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//Get connection
String sql = "update users set `NAME`=? where `id`=?";//use? Representative parameters
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);//Parameter requires a precompiled SQL statement
st.setString(1,"Madness");
st.setInt(2,1);//Fill in parameters
int i = st.executeUpdate();//implement
if (i > 0) {
System.out.println("Update succeeded");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn, st, null);
}
}
}
2. Query
package study02;
import study01.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement st = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "Select * from users where `id`=?";
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
st.setInt(1,1);
rs = st.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getInt("id"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("NAME"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("email"));
System.out.println(rs.getDate("birthday"));
System.out.println("=====================");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3. Prevent SQL injection
The essence is to treat the input parameters as characters
Then, those containing escape characters are automatically filtered.
package study02;
import study01.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.*;
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//login("lisi","123456"); // Login successful
login("' or '1=1","' or '1=1");//SQL injection causes
}
public static void login(String username,String pwd){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement st = null;
ResultSet rt = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME` = 'kuangshen' AND `PASSWORD` = '123456'
//SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME` = '' or '1=1' AND `PASSWORD` = '' or '1=1'
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE `NAME` = ? AND `PASSWORD` = ?";
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
st.setString(1,username);
st.setString(2,pwd);
rt = st.executeQuery();
while(rt.next()){
System.out.println(rt.getString("NAME"));
System.out.println(rt.getString("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("====================");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rt);
}
}
}
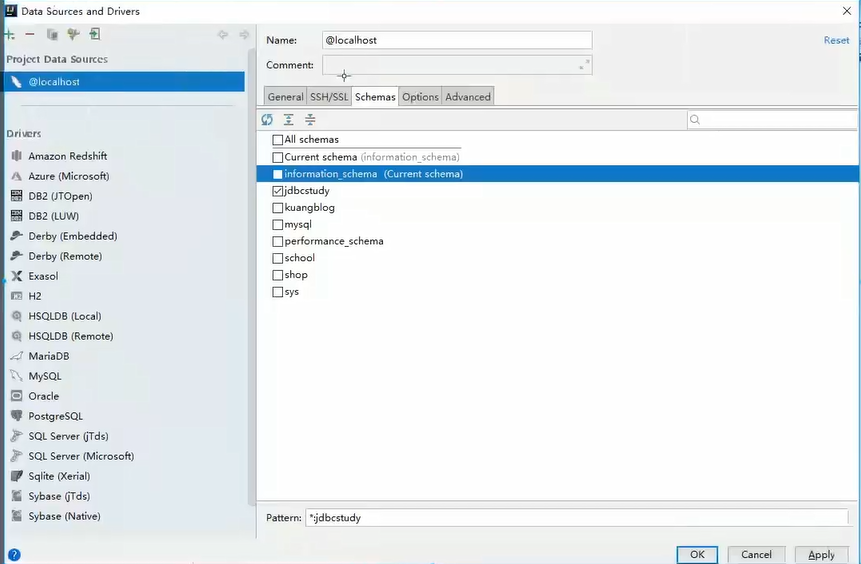
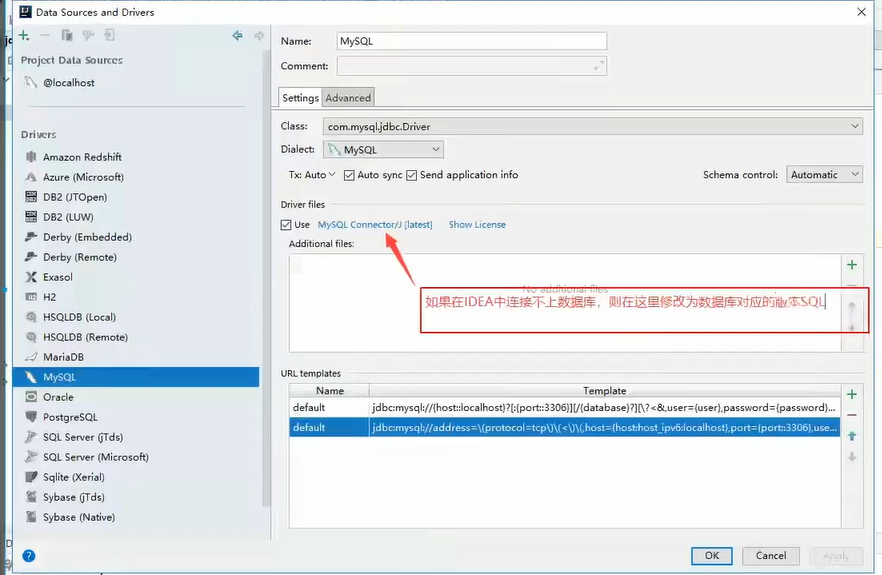
10.6 using IDEA to connect to database
Connect to database
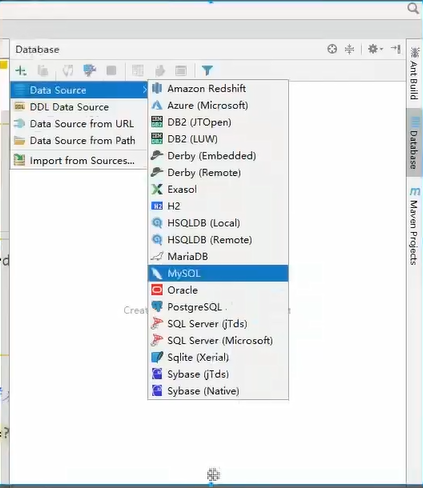
After the connection is successful, select the database
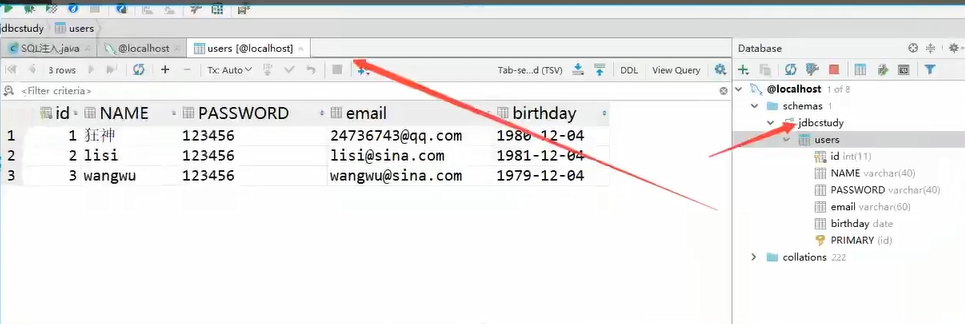
Double click the database to view the data
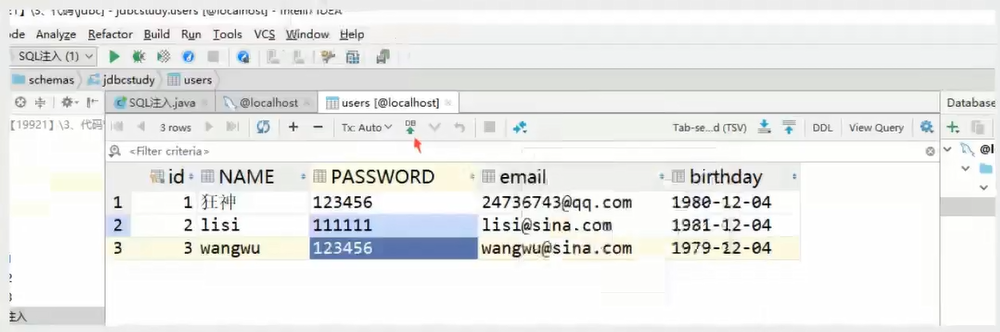
Update data
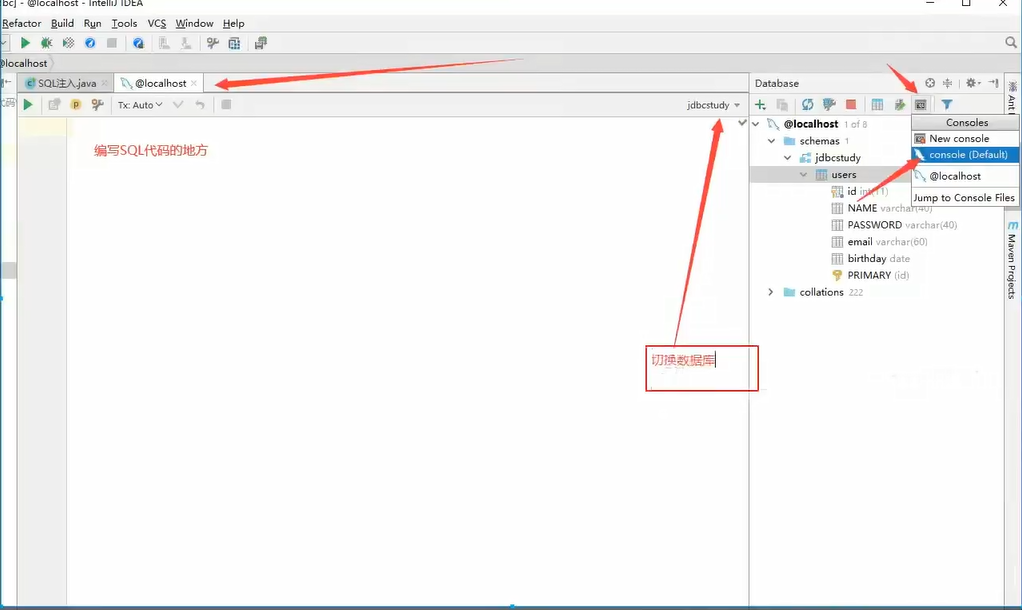
Connection failed. Check the reason
10.7 affairs
Either succeed or fail.
Put an SQL into a batch for execution.
Transaction principle: ACID principle atomicity consistency persistence isolation dirty read non repeatable read unreal read
Atomicity
Either all succeed or all fail.
uniformity
The integrity before and after the transaction shall be consistent. For example, the total amount of money before and after the money transfer shall be consistent
Isolation
Transaction isolation is that when multiple users access the database concurrently, the transactions opened by the database for each user cannot be disturbed by the operation data of other transactions, and the transactions should be isolated from each other.
persistence
Once the transaction is committed, it is persisted to the database.
Dirty read:
A transaction reads uncommitted data from another transaction.
Non repeatable:
A row of data in a table is read in a transaction, and the results are different multiple times. (this is not necessarily a mistake, but it is wrong on some occasions)
Unreal reading:
It means that the data inserted by another transaction is read in one transaction, resulting in inconsistent reading.
code implementation
1. Turn off auto commit and start the transaction automatically. conn.setAutoCommit(false);
2. Submit data to database conn.commit();
3. If it fails, rollback conn.rollback();
package study;
import study01.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TestTransaction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//Connect to database
conn.setAutoCommit(false);// Turn off auto commit and turn on transactions
st = conn.createStatement();
String sql1 = "update account set `money` = `money` - 100 where `NAME`='A'";
st.executeUpdate(sql1);
String sql2 = "update account set `money` = `money` + 100 where `NAME`='B'";
st.executeUpdate(sql2);
conn.commit();// Submit data to database
System.out.println("success");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
try {//If it fails, roll back
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rs);
}
}
}
10.8 database connection pool
Database connection - execution complete - release
Connect – free up wasteful resources
Pooling Technology: prepare some pre prepared resources and connect the pre prepared resources.
-------Open the door - salesman: wait - Service -
10 common connections
Minimum number of connections: 10
Maximum number of connections: 15 service maximum bearing limit
Queue up
Waiting timeout: 100ms
Write a connection pool to implement an interface DataSource
Open source data source implementation
DBCP
C3P0
Druid: Alibaba
After using these database connection pools, we don't need to write database connection code in project development.
DBCP
Required jar package
commons-dbcp-1.4 commons-pool-1.6
C3P0
Required jar package
c3p0-0.9.5.5 mchange-commons-java-0.2.19
conclusion
No matter what data source is used, the essence is the same. If the DataSource interface remains unchanged, the method will not change.