15. Mysql database - multi table query case
During company development, we often need to query the required data through two or more tables according to different business needs. Therefore, it is necessary for us to learn the query of 2 or more tables. In fact, no matter how many tables are queried, there are rules to follow.
1. Prepare data
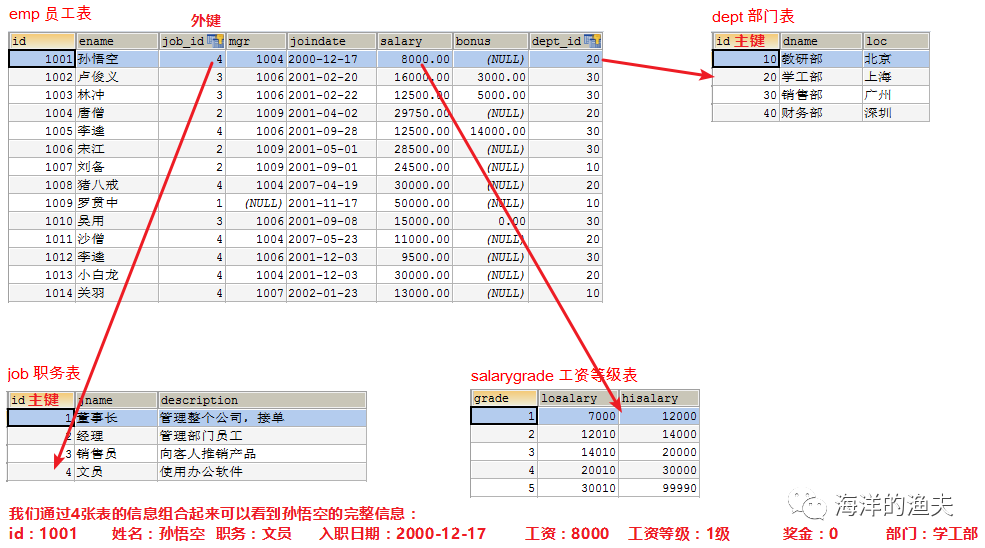
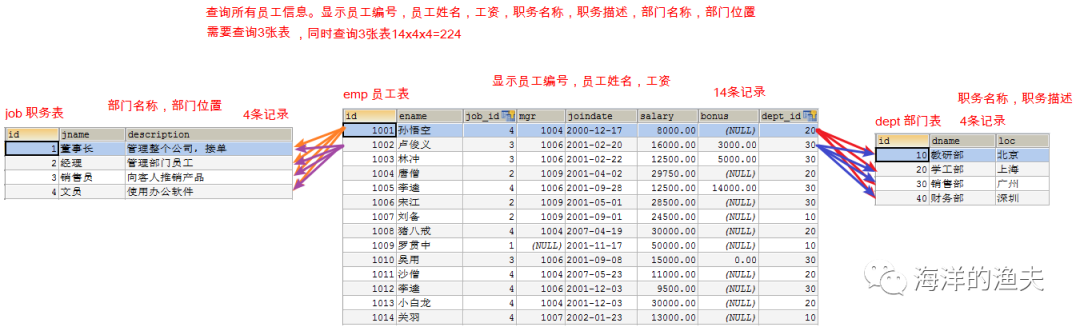
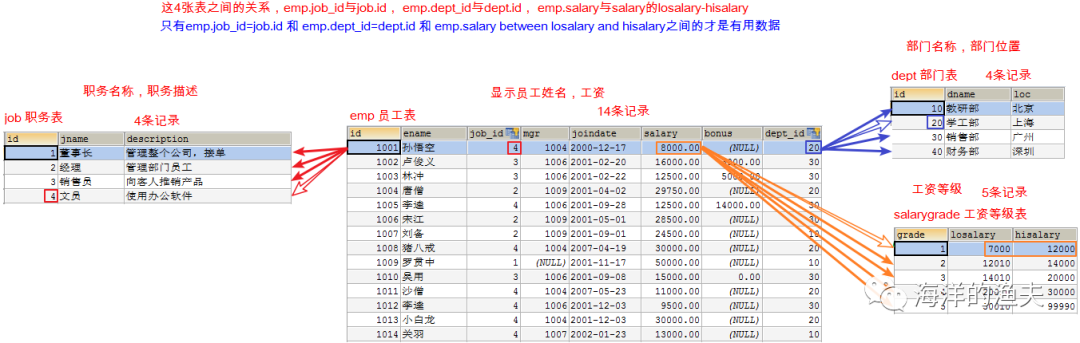
-- Department table CREATE TABLE dept ( id INT PRIMARY KEY PRIMARY KEY, -- department id dname VARCHAR(50), -- Department name loc VARCHAR(50) -- Department location ); -- Add 4 departments INSERT INTO dept(id,dname,loc) VALUES (10,'Teaching and Research Department','Beijing'), (20,'School Work Department','Shanghai'), (30,'Sales Department','Guangzhou'), (40,'Finance Department','Shenzhen'); -- Job table, job name, job description CREATE TABLE job ( id INT PRIMARY KEY, jname VARCHAR(20), description VARCHAR(50) ); -- Add 4 jobs INSERT INTO job (id, jname, description) VALUES (1, 'chairman', 'Manage the whole company and receive orders'), (2, 'manager', 'Management staff'), (3, 'salesperson', 'Promote products to customers'), (4, 'Clerk', 'Use office software'); -- Employee table CREATE TABLE emp ( id INT PRIMARY KEY, -- staff id ename VARCHAR(50), -- Employee name job_id INT, -- post id mgr INT , -- Superior leaders joindate DATE, -- Entry date salary DECIMAL(7,2), -- wages bonus DECIMAL(7,2), -- bonus dept_id INT, -- Department No CONSTRAINT emp_jobid_ref_job_id_fk FOREIGN KEY (job_id) REFERENCES job (id), CONSTRAINT emp_deptid_ref_dept_id_fk FOREIGN KEY (dept_id) REFERENCES dept (id) ); -- Add employee INSERT INTO emp(id,ename,job_id,mgr,joindate,salary,bonus,dept_id) VALUES (1001,'Sun WuKong',4,1004,'2000-12-17','8000.00',NULL,20), (1002,'Lu Junyi',3,1006,'2001-02-20','16000.00','3000.00',30), (1003,'Lin Chong',3,1006,'2001-02-22','12500.00','5000.00',30), (1004,'Tang Monk',2,1009,'2001-04-02','29750.00',NULL,20), (1005,'Li Kui',4,1006,'2001-09-28','12500.00','14000.00',30), (1006,'Song Jiang',2,1009,'2001-05-01','28500.00',NULL,30), (1007,'Liu Bei',2,1009,'2001-09-01','24500.00',NULL,10), (1008,'Zhu Bajie',4,1004,'2007-04-19','30000.00',NULL,20), (1009,'Luo Guanzhong',1,NULL,'2001-11-17','50000.00',NULL,10), (1010,'Wu Yong',3,1006,'2001-09-08','15000.00','0.00',30), (1011,'Monk Sha',4,1004,'2007-05-23','11000.00',NULL,20), (1012,'Li Kui',4,1006,'2001-12-03','9500.00',NULL,30), (1013,'Little white dragon',4,1004,'2001-12-03','30000.00',NULL,20), (1014,'Guan Yu',4,1007,'2002-01-23','13000.00',NULL,10); -- Wage scale CREATE TABLE salarygrade ( grade INT PRIMARY KEY, losalary INT, hisalary INT ); -- Add 5 salary levels INSERT INTO salarygrade(grade,losalary,hisalary) VALUES (1,7000,12000), (2,12010,14000), (3,14010,20000), (4,20010,30000), (5,30010,99990);
Analyze the relationship between the four tables: all the information of an employee can be found through the four tables
2. Practice
2.1 exercise 1
Query all employee information. Display employee number, employee name, salary, job name and job description
Specific operation:
1. Determine which tables to query: emp e, job j
SELECT * FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j;
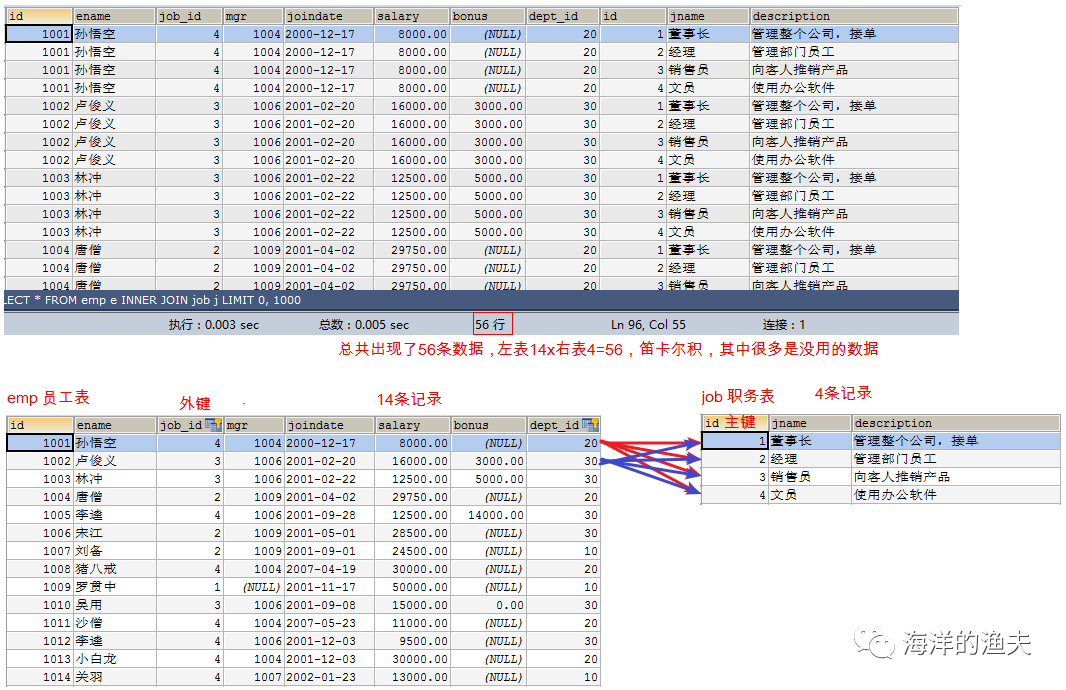
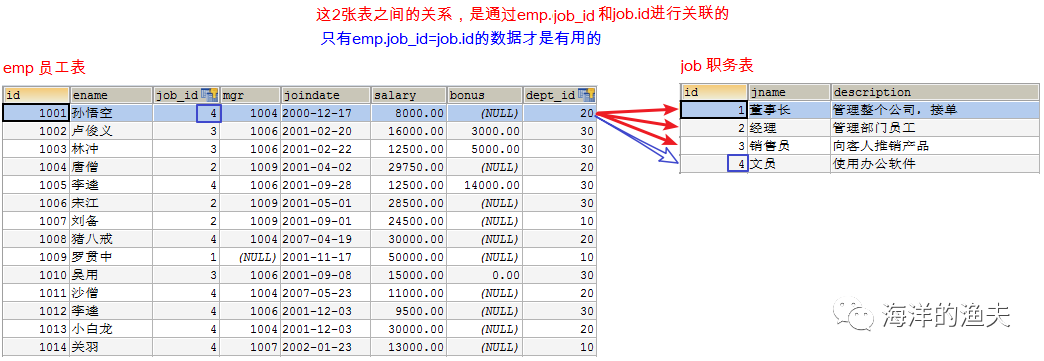
2. Determine the table connection condition: e.job_id=j.id
SELECT * FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j ON e.job_id=j.id;
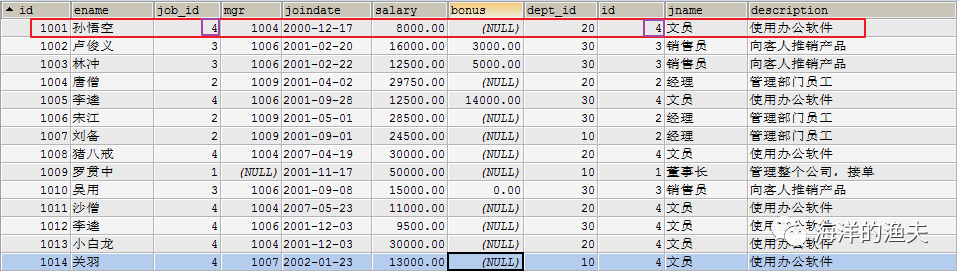
3. Confirm the query fields: employee number, employee name, salary, job name and job description
SELECT e.`id`, e.`ename`, e.`salary`, j.`jname`, j.`description` FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j ON e.job_id=j.id;
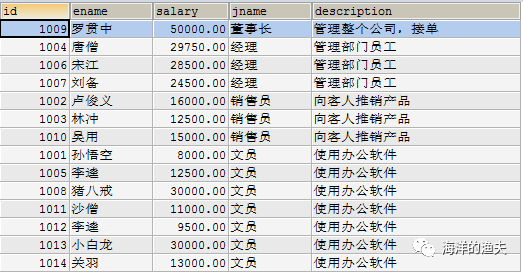
2.2 exercise 2
Query all employee information. Display employee number, employee name, salary, job name, job description, department name and department location
Specific operation:
1. Determine which tables to query, emp e, job j, dept d
SELECT * FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j INNER JOIN dept d;
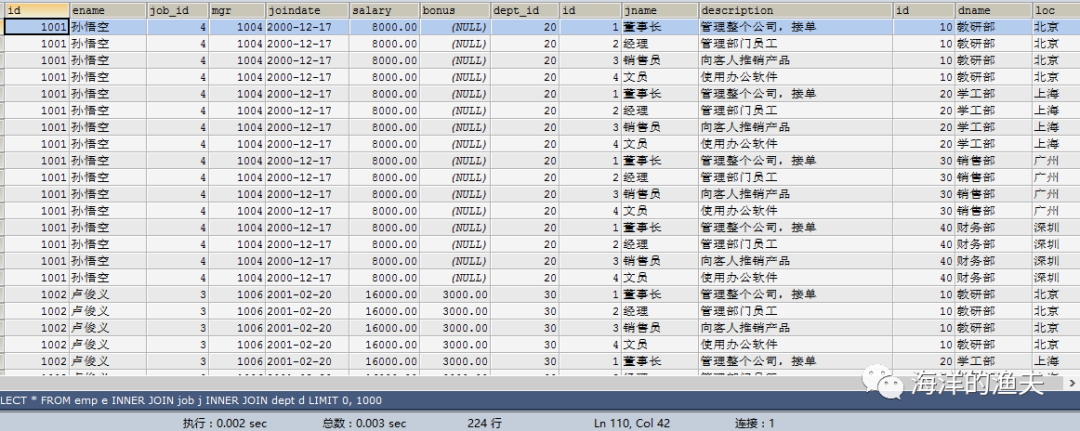
2. Determine table connection conditions e.job_id=j.id and e.dept_id=d.id
SELECT * FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j INNER JOIN dept d ON e.job_id=j.id AND e.dept_id=d.id;
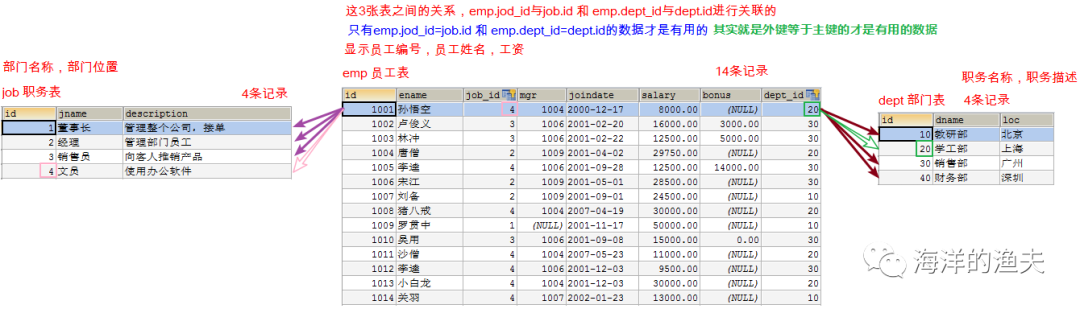
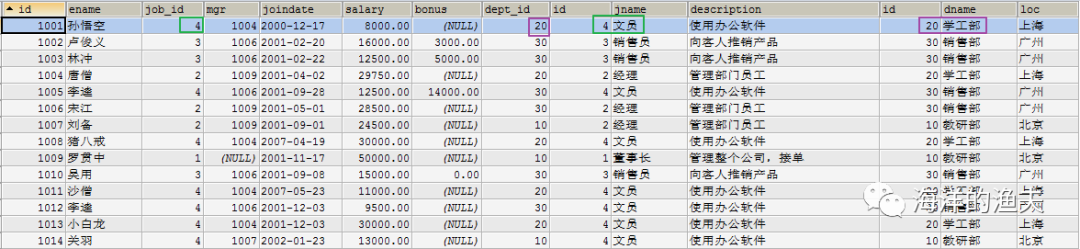
3. Confirm query fields: employee No., employee name, salary, job name, job description, department name, Department location
SELECT e.`id`, e.`ename`, e.`salary`, j.`jname`, j.`description`, d.`dname`, d.`loc` FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j INNER JOIN dept d ON e.job_id=j.id AND e.dept_id=d.id;
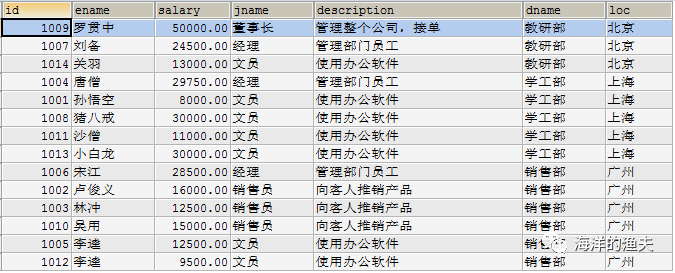
2.3 exercise 3
Query all employee information. Display employee name, salary, job name, job description, department name, Department location and salary grade
Specific operation:
1. Determine which tables to query, emp e, job j, dept d, salarygrade s
SELECT * FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j INNER JOIN dept d INNER JOIN salarygrade s;
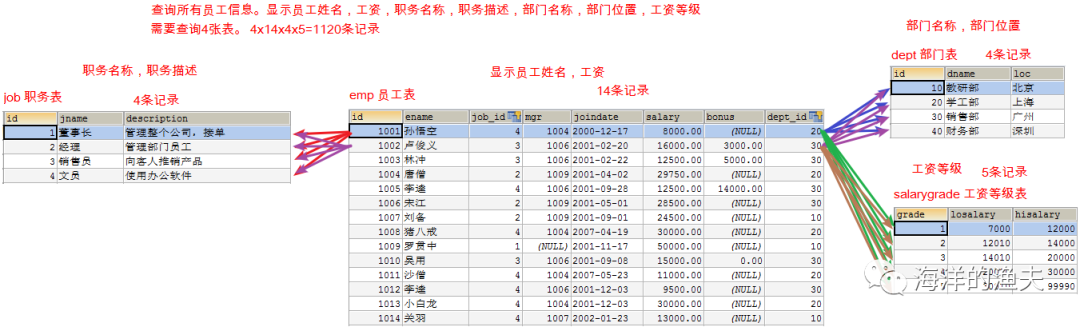
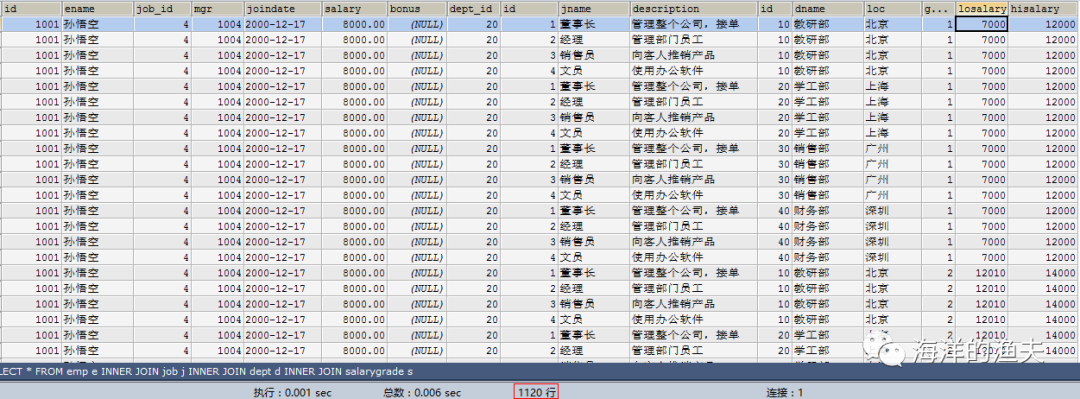
2. Determine table connection conditions e.job_id=j.id and e.dept_id=d.id and e.salary between s.losalary and hisalary
SELECT * FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j INNER JOIN dept d INNER JOIN salarygrade s ON e.job_id=j.id AND e.dept_id=d.id AND e.salary BETWEEN s.losalary AND hisalary;
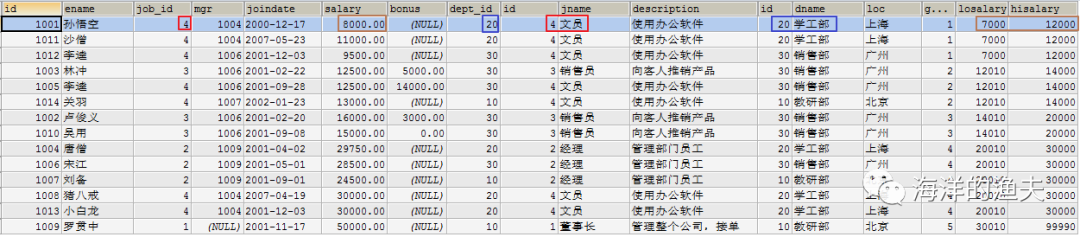
3. Confirm query fields: employee name, salary, job name, job description, department name, Department location and salary grade
SELECT e.`ename`, e.`salary`, j.`jname`, j.`description`, d.`dname`, d.`loc`, s.`grade` FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j INNER JOIN dept d INNER JOIN salarygrade s ON e.job_id=j.id AND e.dept_id=d.id AND e.salary BETWEEN s.losalary AND hisalary;
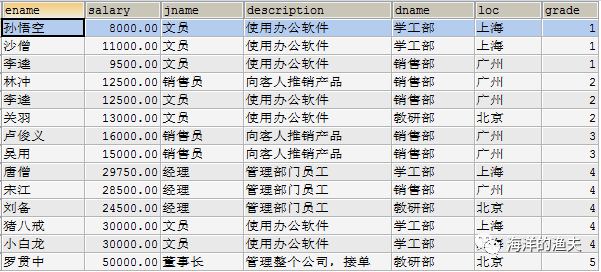
Summary of multi table query rules
- No matter how many tables we query, the table join query will produce Cartesian product. We need to eliminate Cartesian product and get the correct data. We need to find which field is associated between tables (usually foreign key = primary key)
- Eliminate Cartesian product law: two tables need one condition, three tables need two conditions, and four tables need three conditions. (condition quantity = table quantity - 1), each table should participate
- Multi table join query steps: 3.1 Determine which tables to query 3.2 Table 3.3.3 determination of connection conditions Determine query fields
2.4 exercise 4
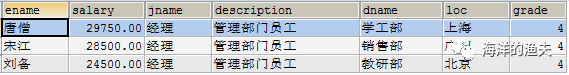
Query manager information. Display employee name, salary, job name, job description, department name, Department location and salary grade
Specific operation:
- Determine which tables to query, emp e, job j, dept d, salarygrade s
SELECT * FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j INNER JOIN dept d INNER JOIN salarygrade s;


- Determine the table connection condition e.job_id=j.id and e.dept_id=d.id and e.salary between s.losalary and hisalary
SELECT * FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j INNER JOIN dept d INNER JOIN salarygrade s ON e.job_id=j.id AND e.dept_id=d.id AND e.salary BETWEEN s.losalary AND hisalary;


Additional conditions: you only need to query the manager's information (j.jname = 'manager')

- Confirm query fields: employee name, salary, job name, job description, department name, Department location and salary grade
SELECT e.`ename`, e.`salary`, j.`jname`, j.`description`, d.`dname`, d.`loc`, s.`grade` FROM emp e INNER JOIN job j INNER JOIN dept d INNER JOIN salarygrade s ON e.job_id=j.id AND e.dept_id=d.id AND e.salary BETWEEN s.losalary AND hisalary AND j.jname='manager';
2.5 exercise 5
Query the department number, department name, Department location and department number
Specific operation:
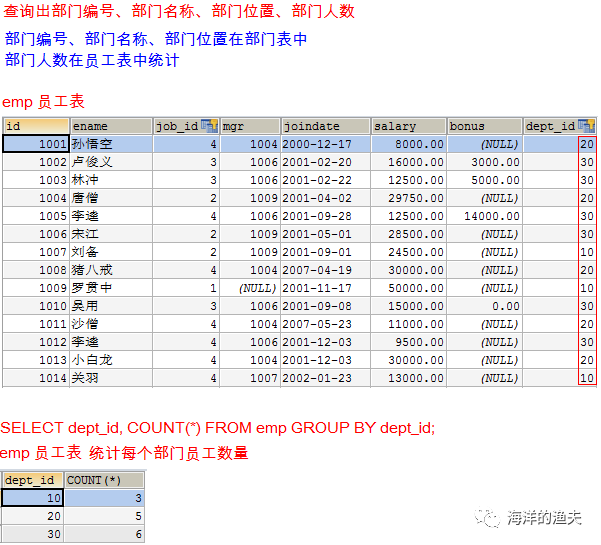
- Go to the employee table to find the number and department id of each department
SELECT dept_id, COUNT(*) FROM emp GROUP BY dept_id;
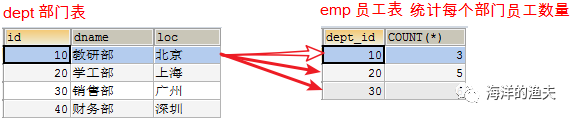
- Then connect and query with the Department table
SELECT * FROM dept d INNER JOIN (SELECT dept_id, COUNT(*) FROM emp GROUP BY dept_id) e ON e.dept_id=d.`id`;
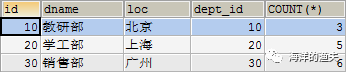
- Display corresponding fields
SELECT d.`id`, d.dname, d.`loc`, e.total Number of departments FROM dept d INNER JOIN (SELECT dept_id, COUNT(*) total FROM emp GROUP BY dept_id) e ON e.dept_id=d.`id`;
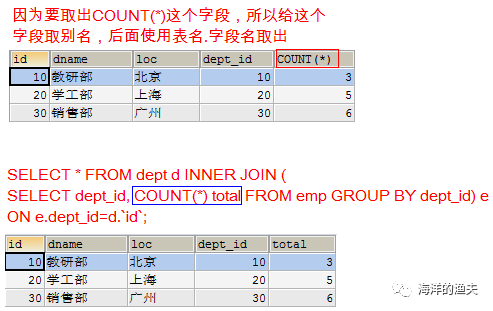
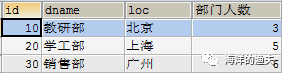
Final effect: