1, Log management of MySQL
The default location of MySQL logs is / usr/local/mysql/data
1. Log classification of MySQL
- Error log
- General query log
- Binary log
- Slow query log
2. MySQL log on
By modifying the MySQL configuration file
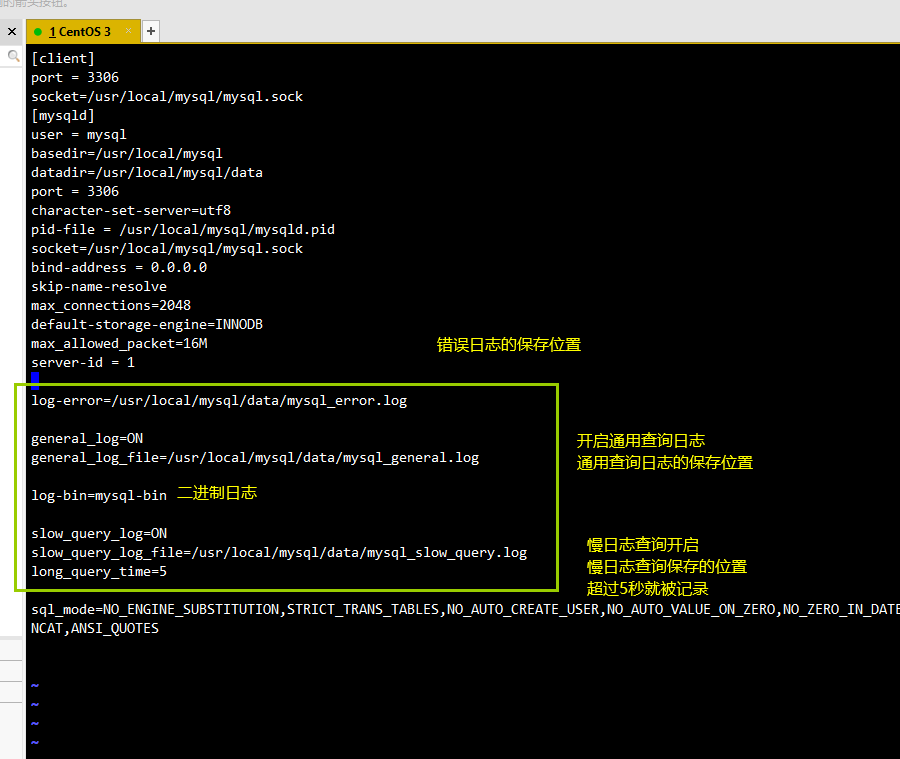
vim /etc/my.cnf [mysqld] ##The error log is used to record error messages that occur when MySQL is started, stopped, or running. It is enabled by default log-error=/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql_error.log #Specify the save location and file name of the log
##The general query log is used to record all MySQL connections and statements. It is closed by default
general_log=ON
general_log_file=/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql_general.log
##Binary log is used to record all statements that have updated data or have potentially updated data, record data changes, and can be used for data recovery. It is enabled by default
Log bin = MySQL bin # or log_bin=mysql-bin
##Slow query log, used to record all execution times exceeding long_ query_ For the statement of time seconds, you can find which query statements take a long time to execute for optimization. It is closed by default
slow_query_log=ON
slow_query_log_file=/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql_slow_query.log
long_ query_ When time = 5 # is set, statements executed for more than 5 seconds are recorded. The default is 10 seconds
systemctl restart mysqld
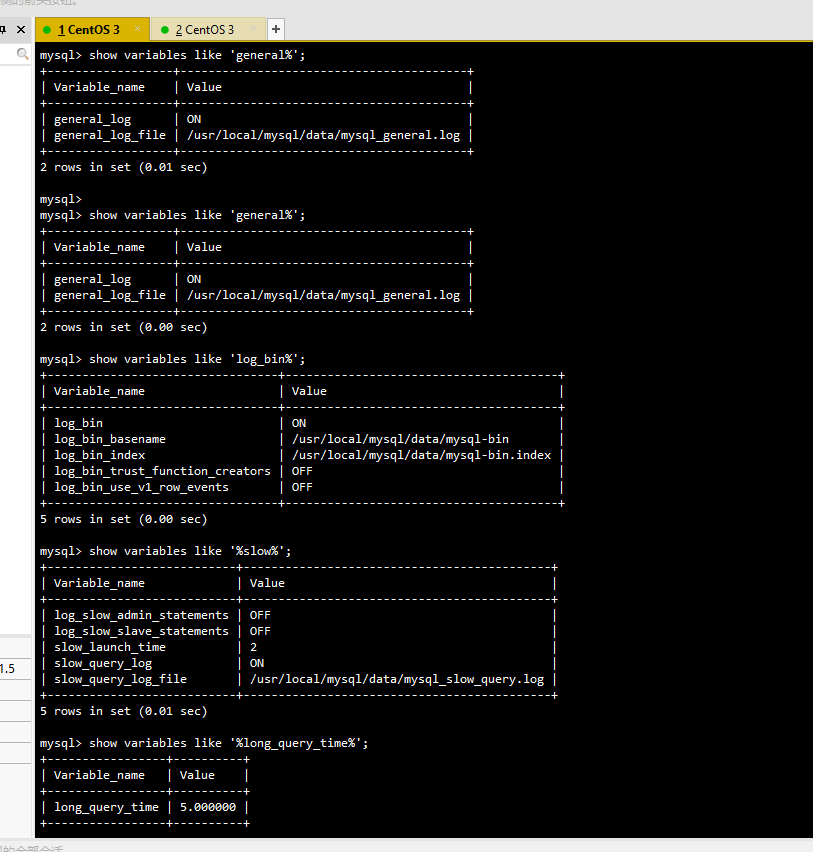
Enter the database to check whether the corresponding log is enabled
mysql -u root -p show variables like 'general%'; #Check whether the general query log is enabled
show variables like ‘log_bin%’; # Check whether the binary log is enabled
show variables like ‘%slow%’; # Check whether the slow query day function is enabled
show variables like ‘long_query_time’; # View slow query time settings
set global slow_query_log=ON; # Set the method of starting slow query in the database
2, MySQL full backup and recovery
1. Importance of data backup
- The primary purpose of backup is disaster recovery
- In a production environment, data security is critical
- Any loss of data can have serious consequences
- Causes of data loss
- Program error
- Human operation error
- Arithmetic error
- Disk failure
- Disasters (e.g. fire, earthquake) and theft
2. Classification of database backup
2-1 from the physical and logical point of view, backup can be divided into:
Physical backup: backup of physical files (such as data files, log files, etc.) of database operating system
Methods of physical backup
- Cold backup (offline backup): it is performed when the database is closed
- Hot backup (online backup): the database is running and depends on the log file of the database
- Warm backup: the backup operation is performed when the database is locked in a table (not writable but readable)
Logical backup: backup of database logical components (such as tables and other database objects)
2-2 from the perspective of database backup strategy, backup can be divided into
Full backup: perform a full backup of the database each time
Differential backup: backs up files that have been modified since the last full backup
Incremental backup: only files modified after the last full backup or incremental backup will be backed up
3. Common backup methods
Physical cold standby
- The database is closed during backup, and the database files are packaged directly
- Backup is fast and recovery is the simplest
Special backup tools mydump or mysqlhotcopy
- mysqldump is a common logical backup tool
- mysqlhotcopy only has backup MyISAM and ARCHIVE tables
Enable binary logs for incremental backups
- For incremental backup, you need to refresh the binary log
Third party tool backup
- Free MySQL hot backup software Percona XtraBackup
4. MySQL full backup
4-1 concept
It is a backup of the entire database, database structure and file structure
Save the database at the completion time of backup
It is the basis of differential backup and incremental backup
4-2 advantages and disadvantages of full backup
Advantages: simple and convenient backup and recovery operation
shortcoming
- There is a lot of duplication in the data
- Takes up a lot of backup space
- Long backup and recovery time
4-3 classification of database full backup
(1) Physical cold backup and recovery
- Close MySQL database
- Use the tar command to package the database folder directly
- Simply replace the existing MySQL directory
(2) mysqldump backup and recovery - MySQL has its own backup tool, which can facilitate the backup of MySQL
- You can export the specified libraries and tables as SQL scripts
- Use the mysql command to import the backed up data
3, Basic commands for database cold backup and recovery and full backup and recovery
1. Physical cold backup and recovery
systemctl stop mysqld yum -y install xz #xz is a compression tool #Compressed backup tar Jcvf /opt/mysql_all_$(date +%F).tar.xz /usr/local/mysql/data/ #Decompression recovery tar Jxvf /opt/mysql_all_2021-01-28.tar.xz -C /usr/local/mysql/data
systemctl start mysqld
2. mysqldump backup and recovery
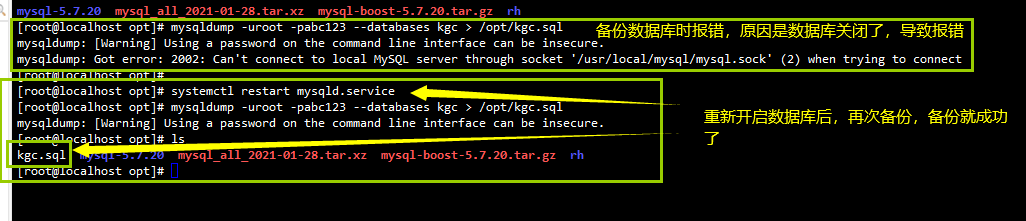
(1) Full backup of one or more complete libraries (including all tables therein)
mysqldump -u root -p[password] --databases Library name 1 [Library name 2] ... > /Backup path/Backup file name.sql #The exported is the database script file Example: mysqldump -u root -p --databases kgc > /opt/kgc.sql mysqldump -u root -p --databases mysql kgc > /opt/mysql-kgc.sql
(2) Fully back up all libraries in the MySQL server
mysqldump -u root -p[password] --all-databases > /Backup path/Backup file name.sql Example: mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases > /opt/all.sql

(3) Fully backs up some tables in the specified library
mysqldump -u root -p[password] Library name [Table name 1] [Table name 2] ... > /Backup path/Backup file name.sql Example: mysqldump -u root -p [-d] kgc info1 info2 > /opt/kgc_info1.sql #Use the "- d" option to explain that only the table structure of the database is saved #If the "- d" option is not used, the table data will also be backed up
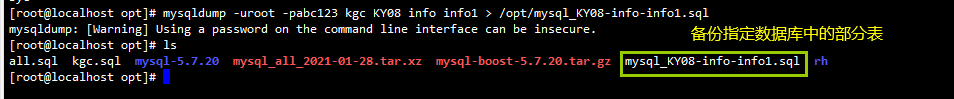
(4) View backup files
cat /opt/Backed up files |grep -v "^--" | grep -v "^/" | grep -v "^$"
- 1
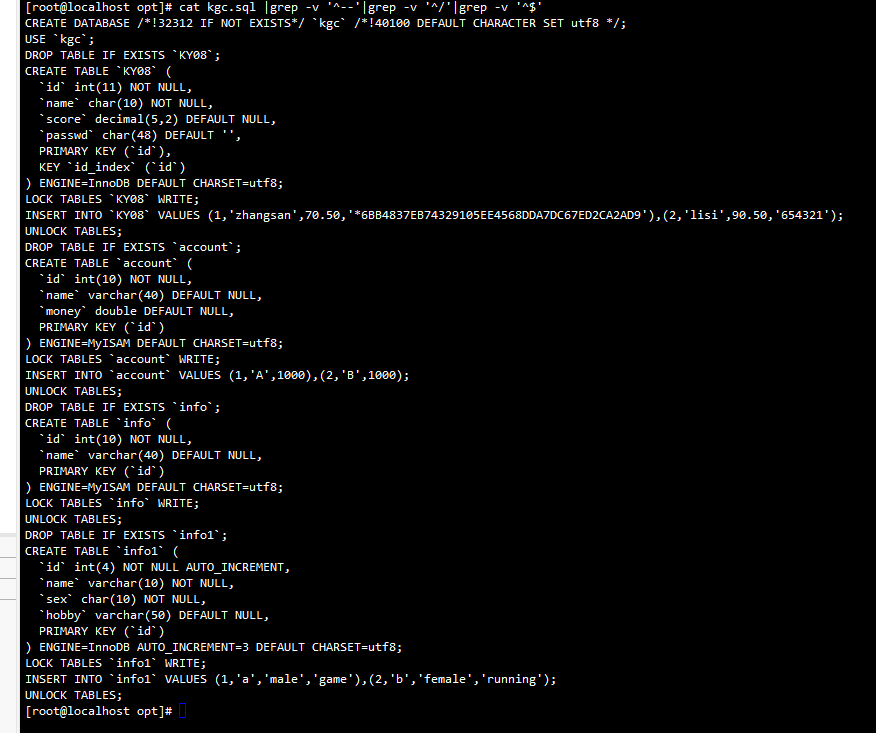
3. MySQL full backup
(1) Restore database
mysql -u root -p -e 'drop database kgc;' #The "- e" option is used to specify the command to be executed after connecting to MySQL. After the command is executed, it will exit automatically mysql -u root -p -e 'SHOW DATABASES;'
mysql -u root -p < /opt/kgc.sql
mysql -u root -p -e 'SHOW DATABASES;'
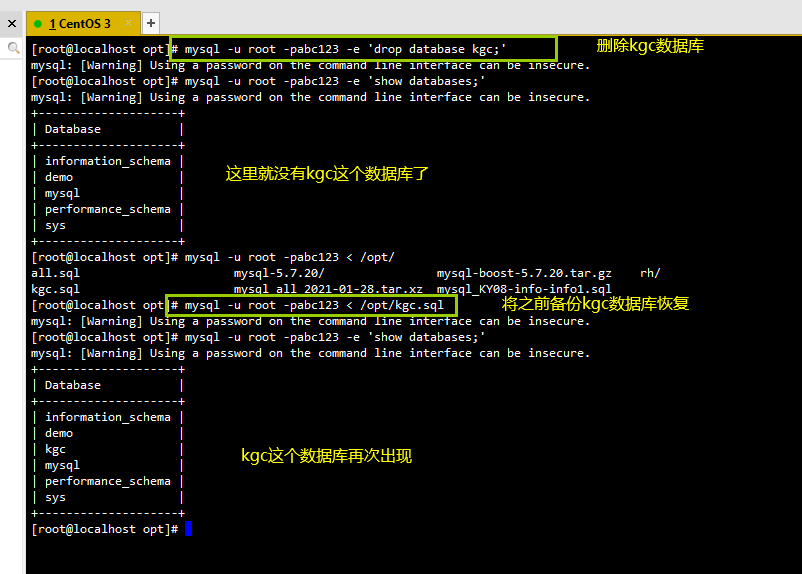
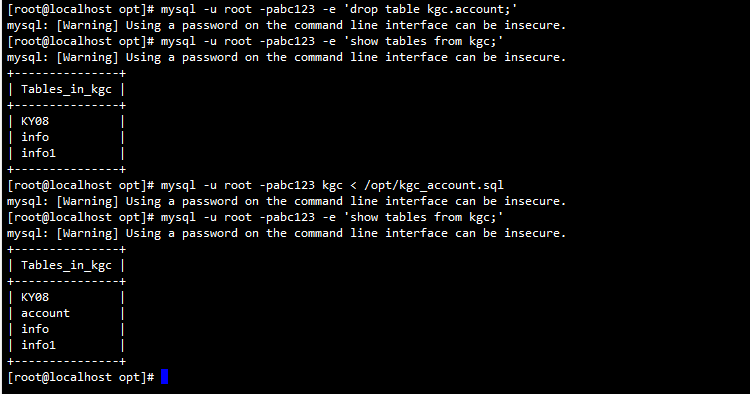
(2) Restore data table
When the backup file contains only the backup of the table, but not the statement of the created library, the library name must be specified when performing the import operation, and the target library must exist.
mysqldump -u root -p kgc info1 > /opt/kgc_info1.sql
mysql -u root -p -e 'drop table kgc.info1;'
mysql -u root -p -e 'show tables from kgc;'
mysql -u root -p kgc < /opt/kgc_info1.sql
mysql -u root -p -e 'show tables from kgc;'
4, Method of MySQL incremental backup and recovery
1. MySQL incremental backup
1. Enable binary log function
vim /etc/my.cnf [mysqld] log-bin=mysql-bin binlog_format = MIXED Specify binary log(binlog)The record format is MIXED server-id = 1
#There are three different recording formats for binary log: state (based on SQL STATEMENT), row (based on row) and mixed (mixed mode). The default format is state
systemctl start mysqld ls -l /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql-bin.*
- 1
- 2
2. The database or table can be fully backed up every week
Such scheduled tasks can be executed in combination with crontab -e scheduled tasks
mysqldump -u root -p kgc info1 > /opt/kgc_info1_$(date +%F).sql mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases kgc > /opt/kgc_$(date +%F).sql
- 1
- 2
3. Incremental backup can be performed every day to generate new binary log files (e.g. MySQL bin. 00000 2)
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-logs
4. Insert new data to simulate the addition or change of data
use kgc; insert into info1 values(3,'user3','male','game'); insert into info1 values(4,'user4','female','reading');
5. Generate a new binary log file again (for example, MySQL bin. 00000 3)
mysqladmin -u root -p flush-logs #The database operation in step 4 above will be saved to MySQL bin In the 00000 2 file, if the database data changes again, it is saved in MySQL bin 00000 3 document
6. View the contents of the binary log file
cp /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql-bin.000002 /opt/ mysqlbinlog --no-defaults --base64-output=decode-rows -v /opt/mysql-bin.000002 #--Base64 output = decode rows: use the 64 bit encoding mechanism to decode and read by line #-v: Show details
2. MySQL incremental recovery
1. General recovery
(1) Simulate recovery steps for lost changed data
use kgc; delete from info1 where id=3; delete from info1 where id=4;
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults /opt/mysql-bin.000002 | mysql -u root -p
(2) Simulate recovery steps for all lost data
use kgc; drop table info1;
mysql -u root -p kgc < /opt/kgc_info1_2020-11-22.sql
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults /opt/mysql-bin.000002 | mysql -u root -p
2. Breakpoint recovery
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults --base64-output=decode-rows -v /opt/mysql-bin.000002 Example: # at 302 #201122 16:41:16 Inserted“ user3"User data for
# at 623
#201122 16:41:24
User data for 'user4' was inserted
(1) Location based recovery
#Only recover the data before operation ID "623", that is, do not recover the data of "user4" mysqlbinlog --no-defaults --stop-position='623' /opt/mysql-bin.000028 | mysql -uroot -p
#Only recover the data of "user4" and skip the data recovery of "user3"
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults --start-position='623' /opt/mysql-bin.000002 | mysql -uroot -p
(2) Point in time based recovery
#Only the data before 16:41:24 is recovered, that is, the data of "user4" is not recovered mysqlbinlog --no-defaults --stop-datetime='2020-11-22 16:41:24'/opt/mysql-bin.000002 |mysql -uroot -p
#Only recover the data of "user4" and skip the data recovery of "user3"
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults–start-datetime='2020-11-22 16:41:24' /opt/mysql-bin.000002 |mysql -uroot -p
Summarize breakpoint recovery
If you restore all data before an SQL statement, stop at the location node or time point of the statement
If you restore an SQ statement and all subsequent data, start from the location node or time point of the statement