The master-slave replication of Mysql requires at least two Mysql services. Of course, Mysql services can be distributed on different servers or multiple services can be started on one server.
First, make sure that the Mysql versions on the master and slave servers are the same.
1, Installing and deploying mysql
1. Install server side:
yum install mysql-server yum install mysql-devel
Install client:
yum install mysql
2. Start service
service mysqld start
3. After installation, execute the following command to initialize the configuration, and the password will be required:
/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
4. Setting allows remote connection to the mysql server
Log in to mysql: mysql -uroot -ptest123
[root@zhoujietest ~]# mysql -uroot -ptest123 #Account root, password test123 Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 18 Server version: 5.5.35-log MySQL Community Server (GPL) by Remi Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql>
At this time, for example, the connection through navicat fails. You need to set the following user table of the mysql database:
mysql> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | cmdb | | mysql | | performance_schema | | test | +--------------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> use mysql; Database changed mysql> update user set host='%' where user='root'; ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '%-root' for key 'PRIMARY' mysql>
Although the prompt indicates that the update fails, the update is actually successful. Settings allow any host connection.
If you enter mysql, you will get this error: Access denied for user (using password: YES)
Then solve as follows:
1) , close mysql
service mysqld stop
2) . shielding permission
mysqld_safe --skip-grant-table
3) . start another terminal to execute the following steps:
[root@zhoujietest ~]#mysql -u root mysql>delete from user where user=''; mysql>flush privileges; #This must be executed, otherwise the terminal error before shutdown will reappear mysql>\q
2, Configure mysql master-slave synchronization
Prepare two virtual machines for testing, install the mysql environment as above, and start the mysql service
Master: 192.168.8.10
Slave: 192.168.8.11
1. Configure master library:
1) , authorized to slave database server
mysql>GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* to 'rep1'@'192.168.8.11' identified by 'test123456'; mysql>FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
2) Modify the master database configuration file, open binlog, and set the server ID. the mysql service will not take effect until the configuration file is modified each time
vim /etc/my.cnf
Add the following content under the configuration file [mysqld]:
[mysqld] log-bin=/var/lib/mysql/binlog server-id=1 binlog-do-db = cmdb datadir=/var/lib/mysql socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock ......
Server ID: the ID number of the master side;
Log Bin: synchronous log path and file name. Please note that if mysql has permission to write this directory (I'm lazy here and put it directly under the datadir below);
Binlog do DB: the name of the database to be synchronized
You can also display databases that are not synchronized:
Binlog ignore DB = mysql does not synchronize mysql database and test database
binlog-ignore-db = test
After modifying the configuration file, restart the service: service mysqld restart
If startup fails, use cat / var / log / mysqld Log | tail - 30 view the log of mysql startup failure and find a solution from the log content.
3) . view the current binary log name and offset of the primary server. The purpose of this operation is to recover data from this point after starting the database
mysql> show master status; +---------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +---------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | binlog.000001 | 1304 | cmdb | | +---------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
The primary server is configured.
2. Configure slave Library
1) , of course, start with the configuration file in / etc / my CNF add the following configuration:
[mysqld] server-id=2 master-host=192.168.8.10 master-user=rep1 master-password=test123456 master-port=3306 replicate-do-db=cmdb ......
Error when restarting: mysqld: unknown variable 'master host=
It shows that mysql doesn't know these variables. I searched online because mysql 5 The master-slave replication in version 5 + does not support these variables. You need to set them with a command on the slave Library:
mysql> CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='192.168.8.10', MASTER_PORT=3306, MASTER_USER='rep1', MASTER_PASSWORD='test123456', MASTER_LOG_FILE='binlog.000001', MASTER_LOG_POS=1304; #The values of the latter two parameters are consistent with the main library
2) . start the slave process
mysql> slave start; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)
3) . check the status of the slave. If the following two values are YES, the configuration is correct:
Slave_IO_Running: Yes
Slave_SQL_Running: Yes
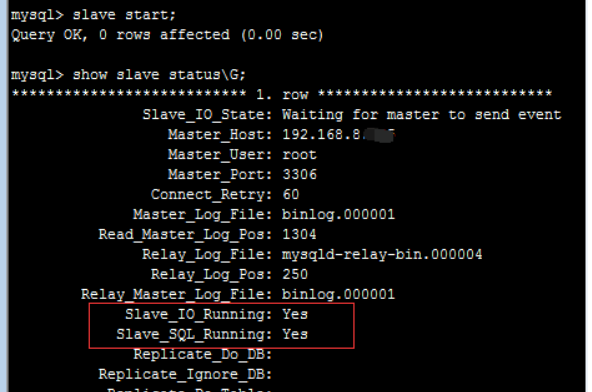
Slave database is waiting for master database to update data... Waitin for master to send event…
3, Synchronize existing data from the master database to the slave database
Main library operation:
1. Stop the data update operation of the main library
mysql>flush tables with read lock;
2. Open a new terminal and generate a backup of the main database (export database)
[root@zhoujietest ~]# mysqldump -uroot -ptest123 cmdb > cmdb.sql
3. Transfer backup files to slave Library
[root@zhoujietest ~]# scp cmdb.sql root@192.168.8.11:/root/
4. Master library unlock
mysql>unlock tables;
Operation from library:
1. Stop slave from library
mysql>slave stop;
2. New database cmdb
mysql> create database cmdb default charset utf8;
3. Import data
[root@ops-dev ~]# mysql -uroot -ptest123 cmdb<cmdb.sql
4. View the existing database and data from the library
mysql> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | cmdb | | mysql | | performance_schema | | test | +--------------------+
At this time, the data of the master and slave databases are completely consistent. If you add, delete or modify the master database, the slave database will automatically synchronize the operation.