We have learned the basic query statements. Next, we set foot in the query of conditional statements and keep up with me!
Advanced level 2: condition query
grammar
SELECT query list FROM table name WHERE filter criteria;
classification
1. Filter by conditional expression: > < = < > =<=
2. Filter by logical expression: & | & | and or not
3. Fuzzy query: like, between and, in, is null
Filter by conditional expression
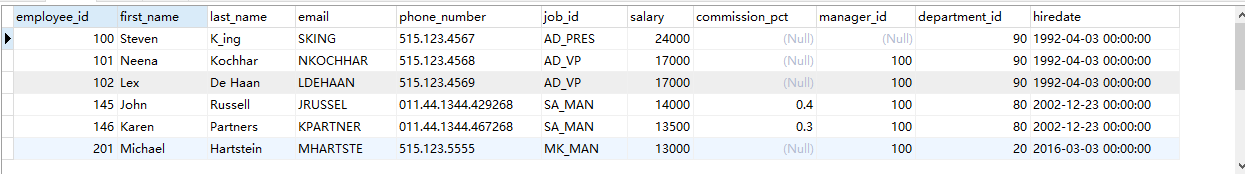
Case 1: query employee information with salary > 12000
Query code
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary>12000
Query results
Case 2: query the employee name and department number whose department number is not equal to 90
Query code
SELECT first_name,last_name,department_id FROM employees WHERE department_id <> 90
Query results

Filter by logical expression
It is essentially a connection condition expression
&&And: both conditions are true, and the result is true, otherwise it is false
||And or: as long as one of the conditions is true, the result is true, and vice versa
! And not, if the connection condition itself is false, the result is true, otherwise it is false
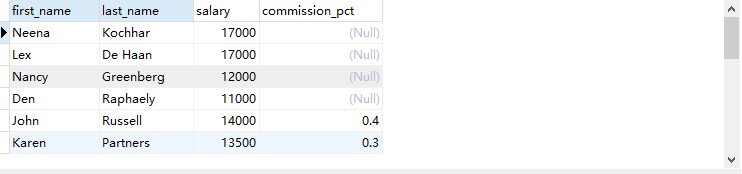
Case 1: query the name, salary and bonus of employees whose salary is between 10000 and 20000
Query code
SELECT first_name,last_name,salary,commission_pct FROM employees WHERE salary>10000 AND salary<20000
Query results
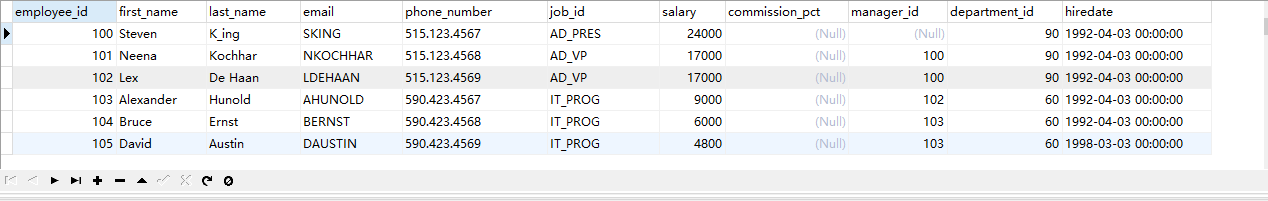
Case 2: query the information of employees whose department number is not between 90 and 110 or whose salary is higher than 15000
Query code
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary>15000 OR !(department_id>90 AND department_id<110);
Query results
Like, between and, in, is null
Vagueness, as the name suggests, is unclear. It means that the given conditions are unclear, such as including words
characteristic
Generally used with wildcards
%Any number of characters, including 0 characters
_ Any single character
like keyword
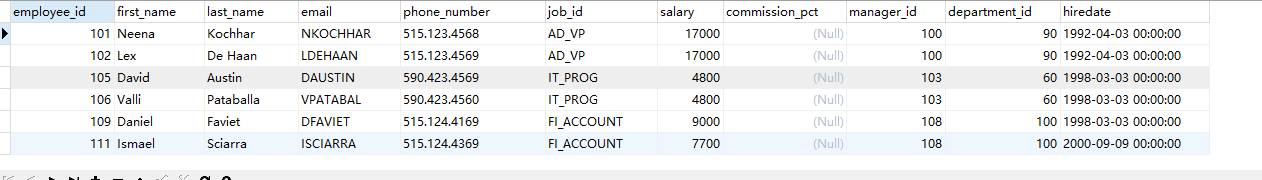
Case 1: query employee information with character a in employee name
Query code
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE '%a%';
Query results
Case 2: query the employee name and salary with the third character e and the fifth character a in the employee name
Query code
SELECT last_name,salary FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE '__e_a%';
Query result: data without this condition
The second character in the query employee name is_ Employee name
Note: the method of representing wildcard. Adding \ in front of wildcard is the default. You can also customize the ESCAPE character yourself. The example is ESCAPE '*'
Pay special attention to the need for single quotation marks
Query code
SELECT last_name FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE '_\_%';
SELECT last_name FROM employees WHERE last_name LIKE '_*_%' ESCAPE '*';
Query results
between and keyword
Note:
1. Using between and can improve the brevity of statements
2. Including critical value
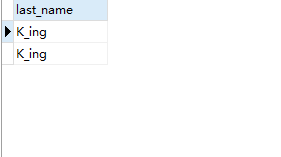
Case 1: query employee information with employee number between 100 and 120
Query code
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE employee_id BETWEEN 100 AND 120;
Query results
in keyword
Meaning: judge whether the value of a field belongs to an item in the in list
characteristic:
1. Use in to improve sentence conciseness
The value type of the 2.in list must be consistent or compatible with '123' 123
3. Wildcards cannot be used
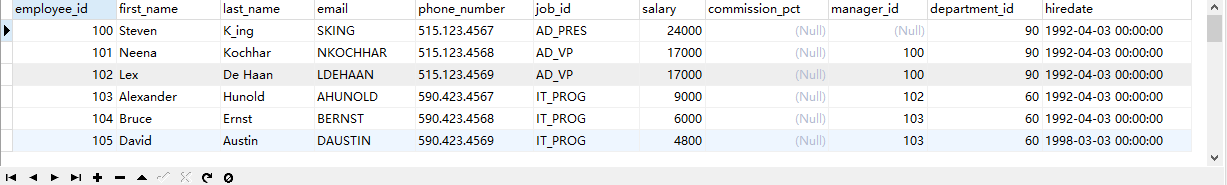
Case 1: the job number of the employee is it_ PROG,AD_ An employee name and type of work number in VP
Query code
SELECT
last_name,job_id
FROM
employees
WHERE
job_id IN('IT_PROG','AD_VP');
SELECT last_name,job_id FROM employees WHERE job_id ='IT_PROG' OR job_id ='AD_VP';
Query results
is null keyword
Note: = or < > cannot be used to judge null values
is null or is not null can determine the null value
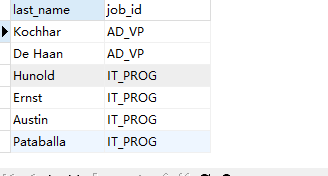
Case 1: query employees without bonus and bonus rate
Query code
SELECT last_name,commission_pct FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NULL;
Query results
Supplementary safety is equal to < = >
Note: when equal to, it can be used to judge null or data equivalence=
however
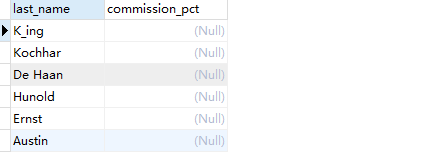
Case 1: query employee name and bonus rate without bonus
Query code
SELECT last_name,commission_pct FROM employees WHERE commission_pct <=> NULL;
Case 2: query employee information with salary of 12000
Query code
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE salary <=> 12000;
Query results
test
1. Query the name, department number and annual salary of the employee with employee number 176
Query code
SELECT first_name,last_name,department_id,salary*12*(1+IFNULL(commission_pct,0)) AS Annual salary FROM employees
Query results

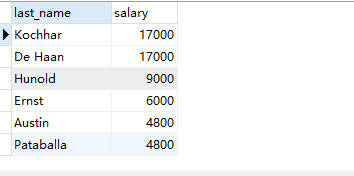
2. Query salary, last with no bonus and salary less than 18000_ name
Query code
SELECT last_name,salary FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NULL AND salary < 18000
Query results
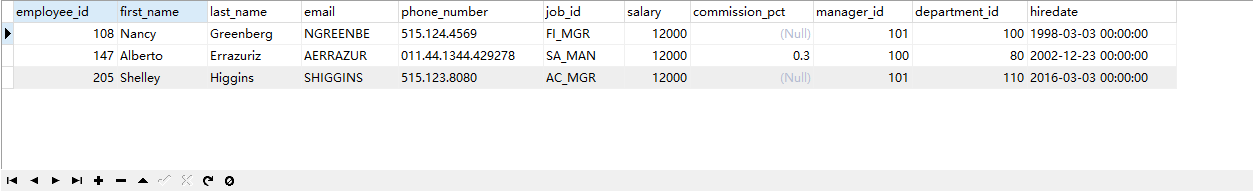
3. Query the employees table, job_ Employee information whose ID is not 'IT' or salary is 12000
Query code
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE job_id <> 'IT' OR salary = 12000;
Query results
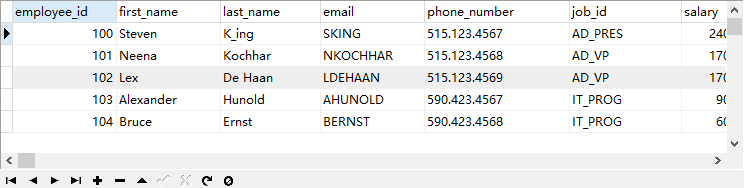
Classic interview questions
Question: select *from employees; And select *from employees where commission_pct like ‘%%’ and last_name like ‘%%’; Are the results the same? Please explain the reasons
Different. If the judged field has a null value