MySQL MHA
1, MHA concept
- MHA (MasterHigh Availability) is a set of excellent software for failover and master-slave replication in MySQL high availability environment.
- The emergence of MHA is to solve the problem of MySQL single point.
- During MySQL failover, MHA can automatically complete the failover operation within 0-30 seconds.
- MHA can ensure the consistency of data to the greatest extent in the process of failover, so as to achieve high availability in the real sense.
1. Composition of MHA
- MHA Node
The MHA Node runs on each MySQL server. - MHA Manager (management node)
MHA Manager can be deployed on an independent machine to manage multiple master slave clusters; It can also be deployed on a slave node.
The MHA Manager will periodically probe the master node in the cluster. When the master fails, it can automatically promote the slave of the latest data to the new master, and then point all other slave to the new master again. The entire failover process is completely transparent to the application.
2. Characteristics of MHA
- In the process of automatic failover, MHA tries to save binary logs from the down main server to ensure no data loss to the greatest extent
- Using semi synchronous replication can greatly reduce the risk of data loss. If only one slave has received the latest binary log, MHA can apply the latest binary log to all other slave servers, so it can ensure the data consistency of all nodes
- At present, MHA supports a master-slave architecture with at least three services, i.e. one master and two slaves
2, Build MySQL+MHA
| host | operating system | IP address | Installation package / software / tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| MHAmanager | CentOS7-3 | 192.168.172.50 | MHAnode component, MHAmanager component |
| master | CentOS7-3 | 192.168.172.10 | mysql-boost-5.7.20.tar.gz, MHAnode components |
| Slave1 | CentOS7-3 | 192.168.172.20 | mysql-boost-5.7.20.tar.gz, MHAnode components |
| Slave2 | CentOS7-3 | 192.168.172.30 | mysql-boost-5.7.20.tar.gz, MHAnode components |
Test three sets mysql Is the server service started netstat -natp | grep 3306
1. All servers, turn off the system firewall and security mechanism
systemctl stop firewalld systemctl disable firewalld setenforce 0
2. Modify the host names of master (192.168.172.10), Slave1 (192.168.172.20) and Slave2 (192.168.172.30)
hostnamectl set-hostname master su - hostnamectl set-hostname slave1 su - hostnamectl set-hostname slave2 su -
3. Modify the main configuration file / etc / my. Of the three MySQL servers cnf
master: master(192.168.172.10) vim /etc/my.cnf [mysqld] server-id = 1 log_bin = master-bin log-slave-updates = true systemctl restart mysqld ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql /usr/sbin/ ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog /usr/sbin/
slave: slave1(192.168.172.20),slave2(192.168.172.30) vim /etc/my.cnf server-id = 2 #Server id = 3, slave2 is 3, and the server IDs of the three servers cannot be the same log_bin = master-bin relay-log = relay-log-bin relay-log-index = slave-relay-bin.index systemctl restart mysqld ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql /usr/sbin/ ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog /usr/sbin/
4. Configure MySQL with one master and two slaves
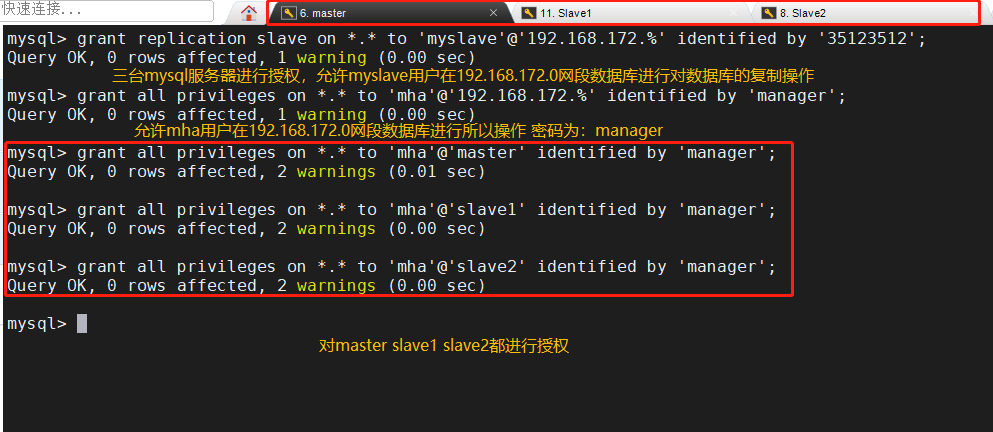
All MySQL servers are authorized to use mysql
grant replication slave on *.* to 'myslave'@'192.168.172.%' identified by '35123512'; grant all privileges on *.* to 'mha'@'192.168.172.%' identified by 'manager'; grant all privileges on *.* to 'mha'@'master' identified by 'manager'; grant all privileges on *.* to 'mha'@'slave1' identified by 'manager'; grant all privileges on *.* to 'mha'@'slave2' identified by 'manager';
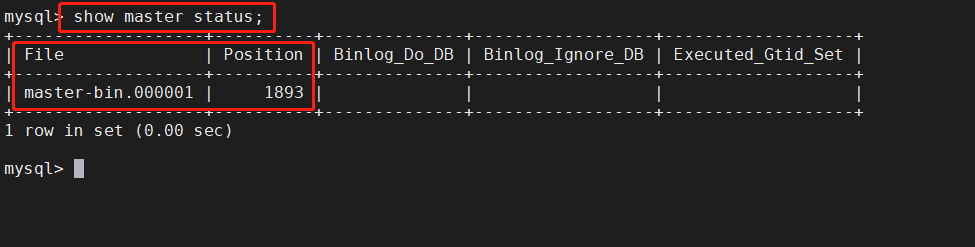
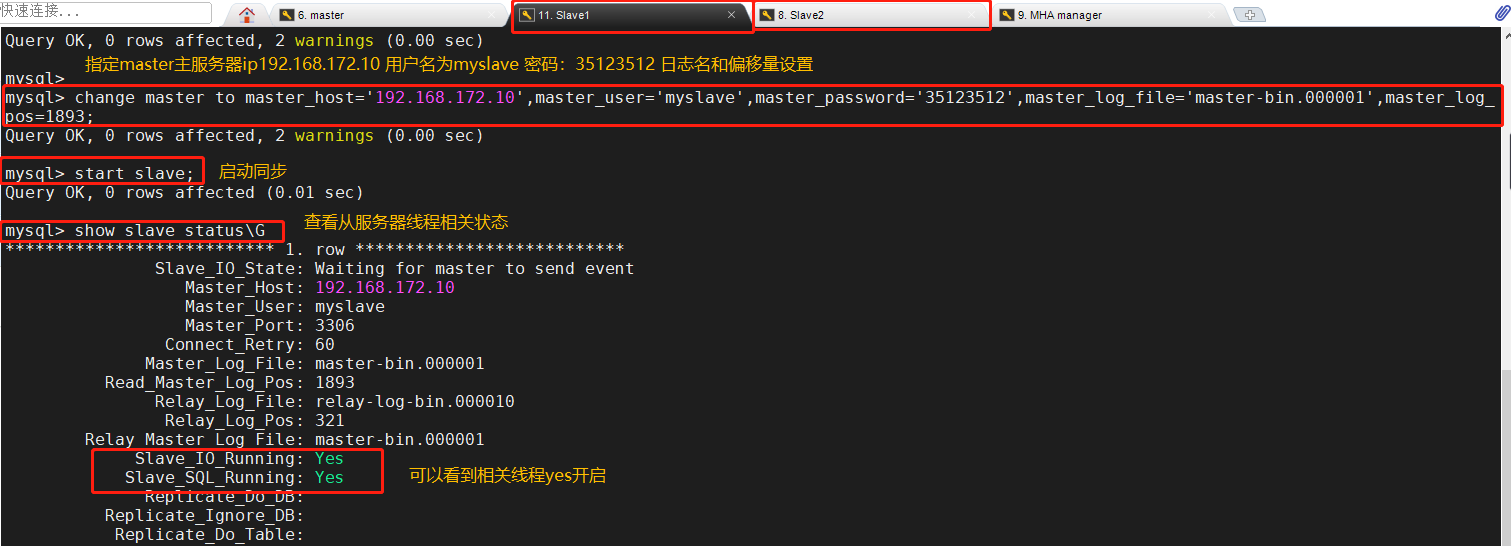
Perform synchronization operations at Slave1 and Slave2 nodes
stay Master Node view binaries and synchronization points show master status; stay Slave1,Slave2 The node performs synchronization operations change master to master_host='192.168.172.10',master_user='myslave',master_password='35123512',master_log_file='master-bin.000001',master_log_pos=1893; start slave; show slave status\G
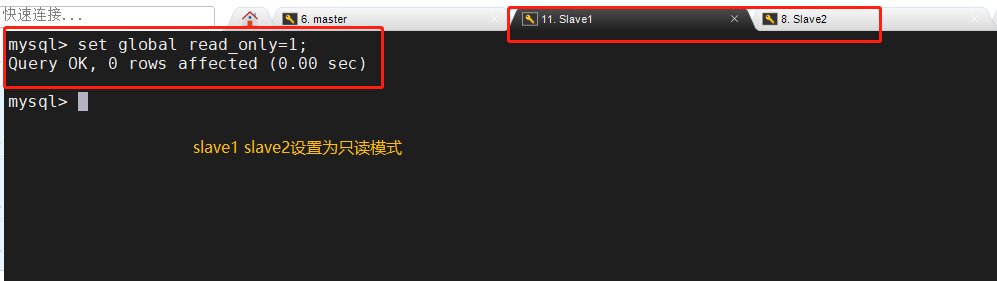
Slave1 and Slave2 nodes are set to read-only mode
Slave1,Slave2 The node is set to read-only mode set global read_only=1;
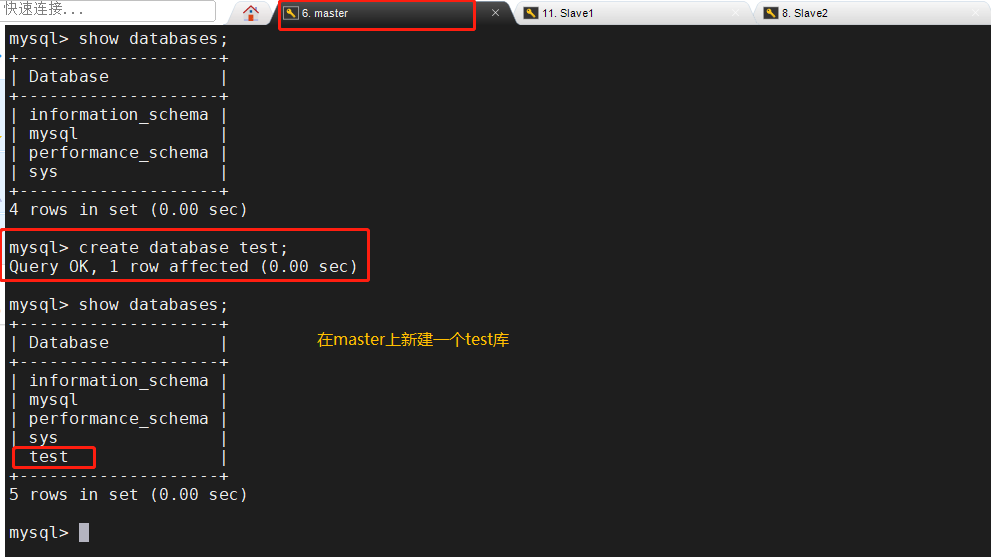
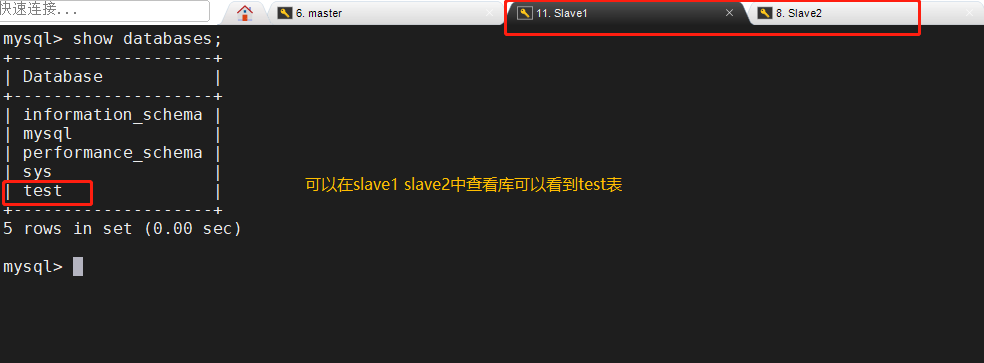
5. Master slave replication verification
6. Install MHA software
MHA dependent environments are installed on all servers
MHAmanager(192.168.172.50)
master(192.168.172.10)
slave1(192.168.172.20)
slave2(192.168.172.30)
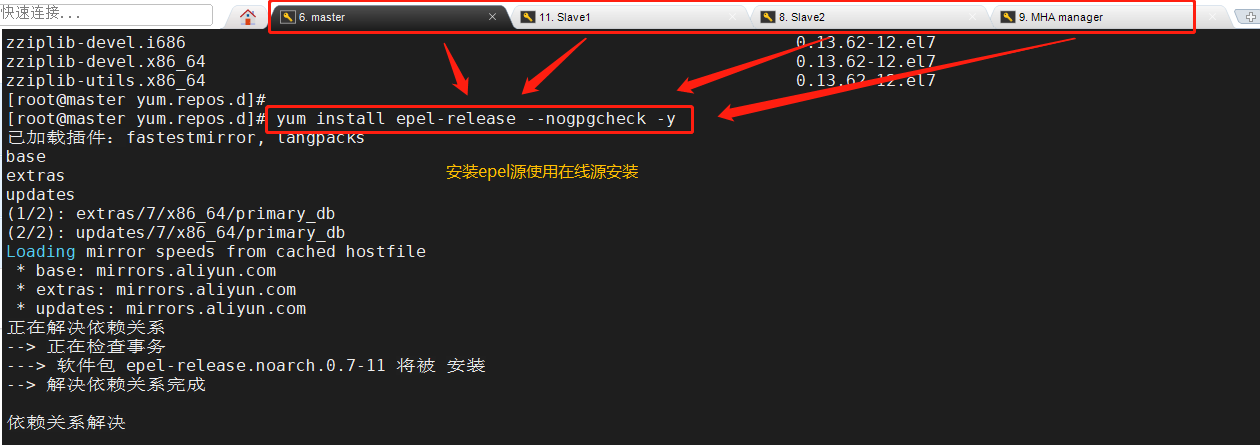
First install the epel source, which needs to be installed online
Then install the node component on all servers
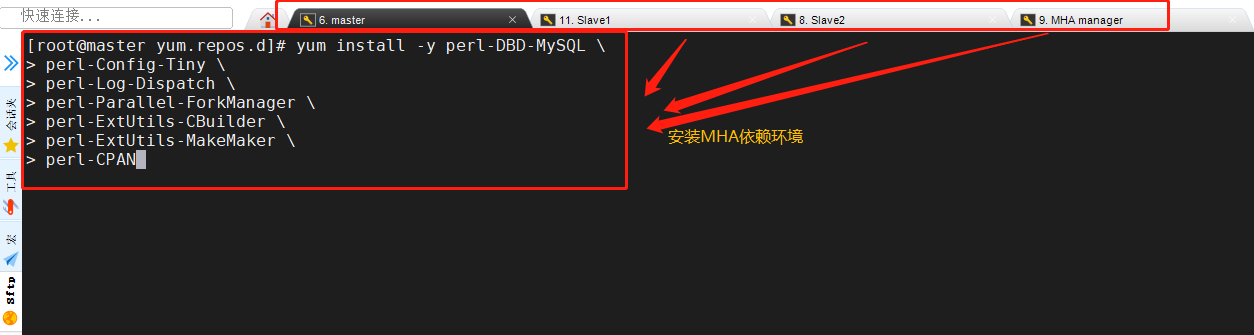
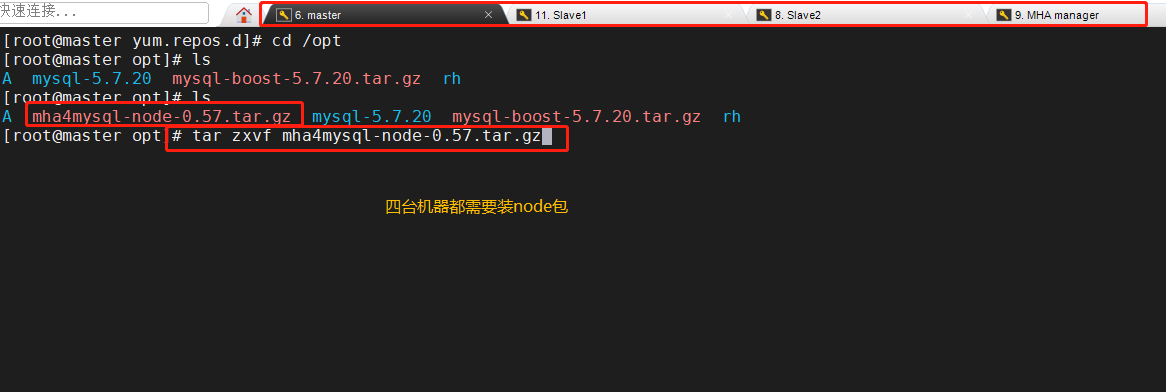
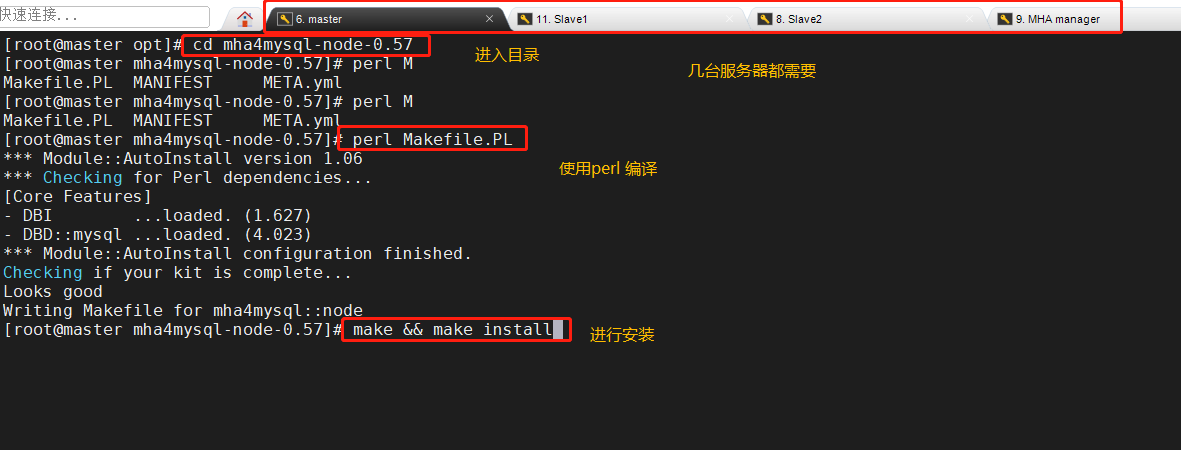
Here we use Alibaba source to download wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo yum list yum install epel-release --nogpgcheck -y yum install -y perl-DBD-MySQL \ perl-Config-Tiny \ perl-Log-Dispatch \ perl-Parallel-ForkManager \ perl-ExtUtils-CBuilder \ perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker \ perl-CPAN Package mha4mysql-node-0.57.tar.gz Put/opt Under the directory cd /opt tar zxvf mha4mysql-node-0.57.tar.gz cd mha4mysql-node-0.57 perl Makefile.PL make && make install
Install the manager component on the MHA manager node
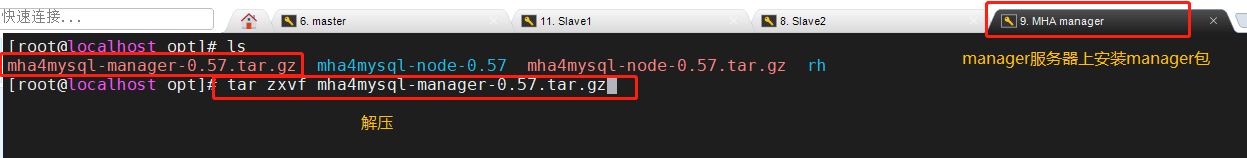
Package mha4mysql-manager-0.57.tar.gz Put/opt Under the directory cd /opt tar zxvf mha4mysql-manager-0.57.tar.gz cd mha4mysql-manager-0.57 perl Makefile.PL make && make install
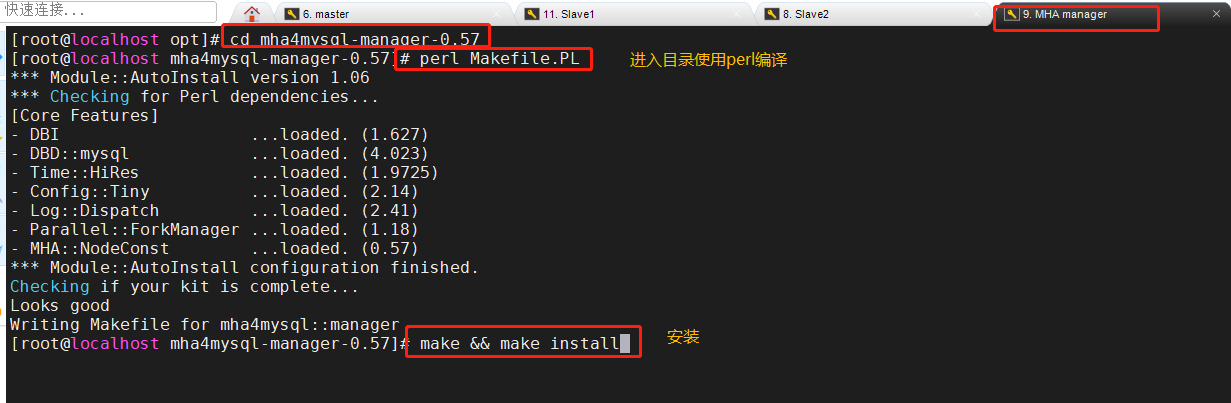
After the manager component is installed, several tools will be generated under / usr/local/bin, mainly including the following:
| assembly | effect |
|---|---|
| masterha_check_ssh | Check the SSH configuration of MHA |
| masterha_check_repl | Check MySQL replication status |
| masterha_manger | Script to start manager |
| masterha_check_status | Detect the current MHA operation status |
| masterha_master_monitor | Check whether the master is down |
| masterha_master_switch | Control failover (automatic or manual) |
| masterha_conf_host | Add or delete configured server information |
| masterha_stop | Close manager |
After installing node, several scripts will also be generated in / usr/local/bin directory, which need to be checked, mainly including the following
| script | effect |
|---|---|
| save_binary_logs | Save and copy binary logs of master |
| apply_diff_relay_logs | Identify the different relay log events and apply the different events to other slave s |
| filter_mysqlbinlog | Remove unnecessary ROLLBACK events (MHA no longer uses this tool) |
| purge_relay_logs | Clear relay log (does not block SQL thread) |
7. Configure password less authentication on all servers
Configure password free authentication to all database nodes on manager
ssh-keygen -t rsa #Press enter all the way ssh-copy-id 192.168.172.10 ssh-copy-id 192.168.172.20 ssh-copy-id 192.168.172.30
Configure password free authentication to slave1 and salve2 on the master
ssh-keygen -t rsa ssh-copy-id 192.168.172.20 ssh-copy-id 192.168.172.30
Configure password free authentication to master and salve2 on slave1
ssh-keygen -t rsa ssh-copy-id 192.168.172.10 ssh-copy-id 192.168.172.30
Configure password free authentication to master and salve1 on slave2
ssh-keygen -t rsa ssh-copy-id 192.168.172.10 ssh-copy-id 192.168.172.20
8. Configure MHA on the manager node
1. On the manager node, copy the relevant scripts to the / usr/local/bin directory
cp -rp /opt/mha4mysql-manager-0.57/samples/scripts /usr/local/bin #After copying, there will be four execution files ll /usr/local/bin/scripts/
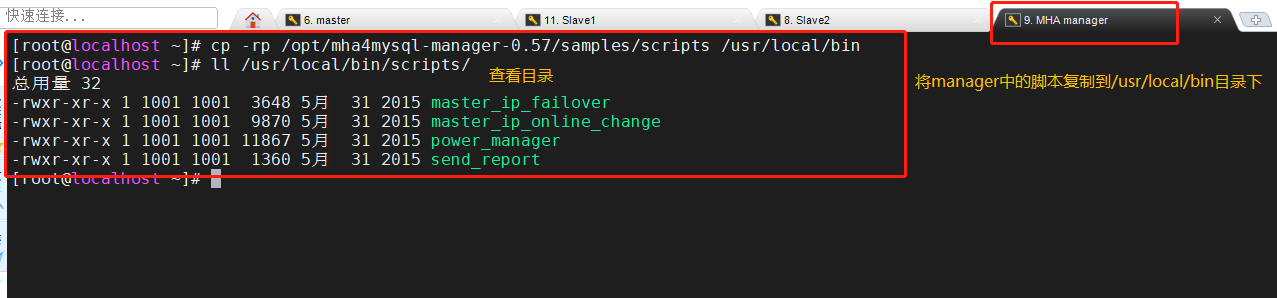
| file name | effect |
|---|---|
| master_ip_failover | Script of VIP management during automatic switching |
| master_ip_online_change | Management of vip during online switching |
| power_manager | Script to shut down the host after failure |
| send_report | Script for sending alarms after failover |
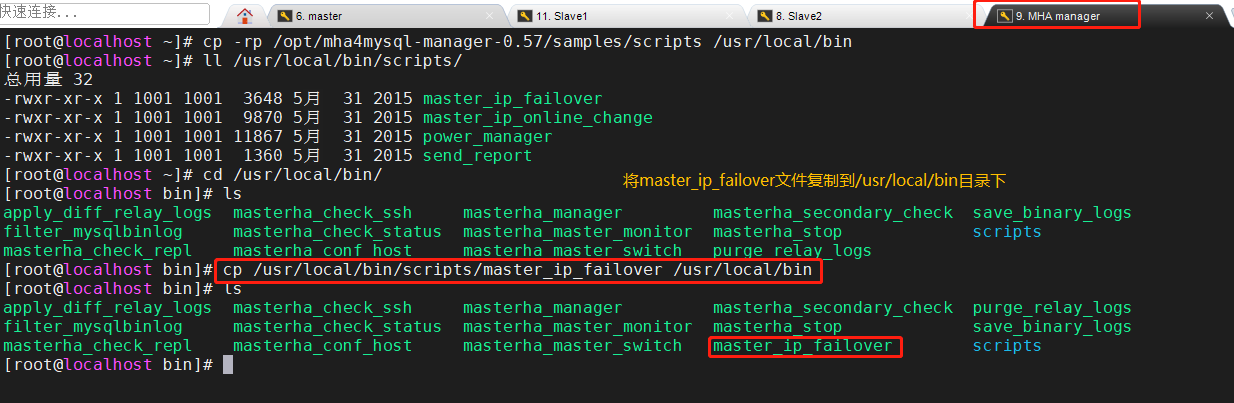
2. Copy the above master_ ip_ Failover (script for VIP management during automatic switching) to / usr/local/bin directory, where the script is used to manage VIP
cp /usr/local/bin/scripts/master_ip_failover /usr/local/bin
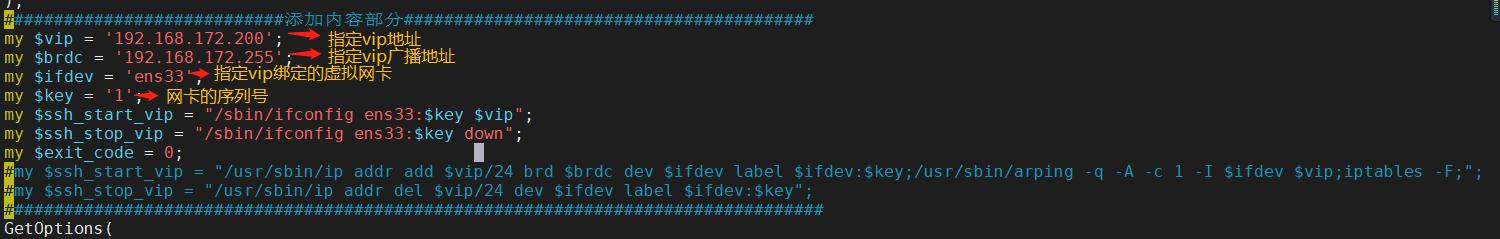
3. Modify master_ip_failover content (delete the original content, copy directly, and configure failover in the following parts)
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use strict;
use warnings FATAL => 'all';
use Getopt::Long;
my (
$command, $ssh_user, $orig_master_host, $orig_master_ip,
$orig_master_port, $new_master_host, $new_master_ip, $new_master_port
);
my $vip = '192.168.172.200';
my $brdc = '192.168.172.255';
my $ifdev = 'ens33';
my $key = '1';
my $ssh_start_vip = "/sbin/ifconfig ens33:$key $vip";
my $ssh_stop_vip = "/sbin/ifconfig ens33:$key down";
my $exit_code = 0;
#my $ssh_start_vip = "/usr/sbin/ip addr add $vip/24 brd $brdc dev $ifdev label $ifdev:$key;/usr/sbin/arping -q -A -c 1 -I $ifdev $vip;iptables -F;";
#my $ssh_stop_vip = "/usr/sbin/ip addr del $vip/24 dev $ifdev label $ifdev:$key";
GetOptions(
'command=s' => \$command,
'ssh_user=s' => \$ssh_user,
'orig_master_host=s' => \$orig_master_host,
'orig_master_ip=s' => \$orig_master_ip,
'orig_master_port=i' => \$orig_master_port,
'new_master_host=s' => \$new_master_host,
'new_master_ip=s' => \$new_master_ip,
'new_master_port=i' => \$new_master_port,
);
exit &main();
sub main {
print "\n\nIN SCRIPT TEST====$ssh_stop_vip==$ssh_start_vip===\n\n";
if ( $command eq "stop" || $command eq "stopssh" ) {
my $exit_code = 1;
eval {
print "Disabling the VIP on old master: $orig_master_host \n";
&stop_vip();
$exit_code = 0;
};
if ($@) {
warn "Got Error: $@\n";
exit $exit_code;
}
exit $exit_code;
}
elsif ( $command eq "start" ) {
my $exit_code = 10;
eval {
print "Enabling the VIP - $vip on the new master - $new_master_host \n";
&start_vip();
$exit_code = 0;
};
if ($@) {
warn $@;
exit $exit_code;
}
exit $exit_code;
}
elsif ( $command eq "status" ) {
print "Checking the Status of the script.. OK \n";
exit 0;
}
else {
&usage();
exit 1;
}
}
sub start_vip() {
`ssh $ssh_user\@$new_master_host \" $ssh_start_vip \"`;
}
## A simple system call that disable the VIP on the old_master
sub stop_vip() {
`ssh $ssh_user\@$orig_master_host \" $ssh_stop_vip \"`;
}
sub usage {
print
"Usage: master_ip_failover --command=start|stop|stopssh|status --orig_master_host=host --orig_master_ip=ip --orig_master_port=port --new_master_host=host --new_master_ip=ip --new_master_port=port\n";
}
4. Create MHA software directory and copy the configuration file, using app1 CNF configuration file is used to manage the mysql node server. The configuration file is generally placed in the / etc / directory
mkdir /etc/masterha cp /opt/mha4mysql-manager-0.57/samples/conf/app1.cnf /etc/masterha/
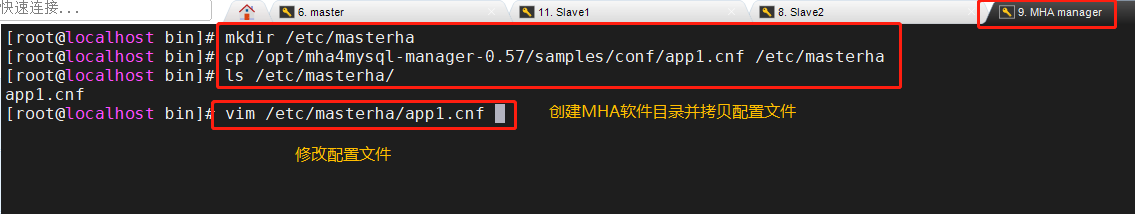
Delete the original content, directly copy and modify the IP address of the node server
[server default] manager_log=/var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log manager_workdir=/var/log/masterha/app1 master_binlog_dir=/usr/local/mysql/data master_ip_failover_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_failover master_ip_online_change_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_online_change password=manager user=mha ping_interval=1 remote_workdir=/tmp repl_password=35123512 repl_user=myslave secondary_check_script=/usr/local/bin/masterha_secondary_check -s 192.168.172.20 -s 192.168.172.30 shutdown_script="" ssh_user=root [server1] hostname=192.168.172.10 port=3306 [server2] candidate_master=1 check_repl_delay=0 hostname=192.168.172.20 port=3306 [server3] hostname=192.168.172.30 port=3306

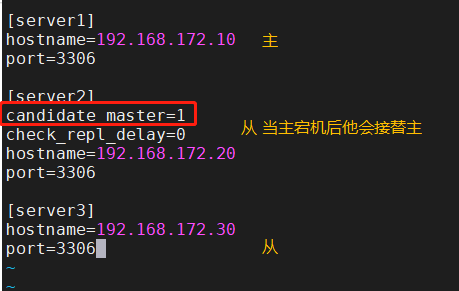
############################Profile resolution################# #manager working directory manager_log=/var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log #manager log manager_workdir=/var/log/masterha/app1 #The location where the master saves binlog. The path here should be the same as the binlog configured in the master master_binlog_dir=/usr/local/mysql/data #Switch scripts when setting automatic failover, that is, the last configured script master_ip_failover_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_failover #Set the switching script for manual switching master_ip_online_change_script=/usr/local/bin/master_ip_online_change #The password here is the password of the previously created monitoring user password=manager #Set monitoring user user=mha #Set the event interval for monitoring the main database and sending ping packets. The default is 3 seconds. When there is no response for three attempts, the system will automatically perform a sexual failover ping_interval=1 #Set the (temporary) save location of binlog in case of remote MySQL switching remote_workdir=/tmp #Set the password of the slave user repl_password=123456 #Set the account of the copying user repl_user=myslave #Set the script of the alarm sent after switching report_script=/usr/local/send_report #Set the script to check from the server secondary_check_script=/usr/local/bin/masterha_secondary_check -s 192.168.226.133 -s 192.168.226.134 #Set the script to close the failed host after the failure occurs shutdown_script="" #Set the login user name of ssh ssh_user=root [server2] #Set the candidate master. If this parameter is set, this library will be promoted to the master library after the master-slave switch candidate_master=1 #Replication check is supported. By default, if a slave lags behind the relay logs of the master by 100m, MHA The will not be selected slave As new master,If set to 0, this rule will be ignored check_repl_delay=0 hostname=192.168.226.131 port=3306
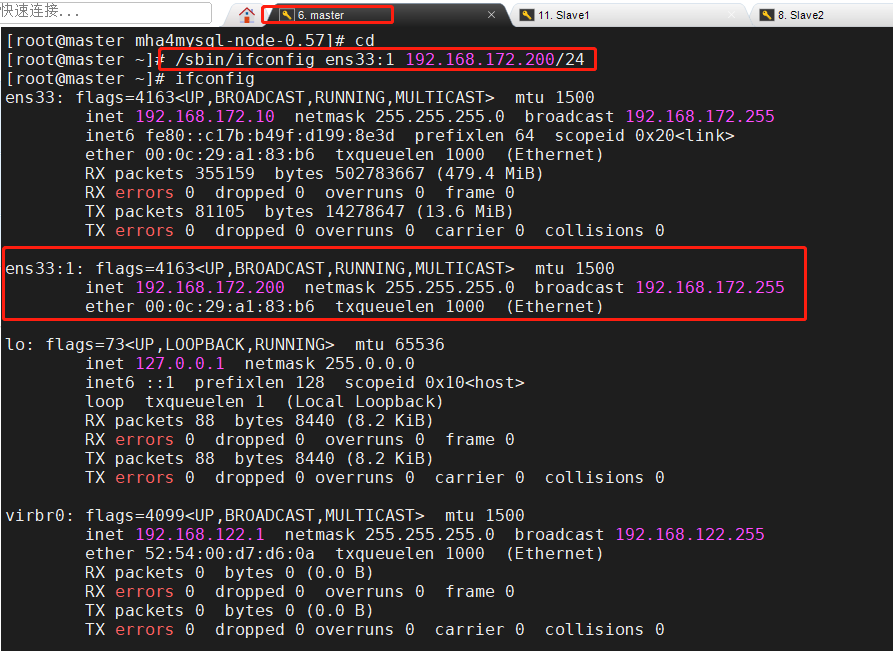
9. For the first configuration, you need to manually turn on the virtual IP on the master node
Master(192.168.172.10)
/sbin/ifconfig ens33:1 192.168.172.200/24
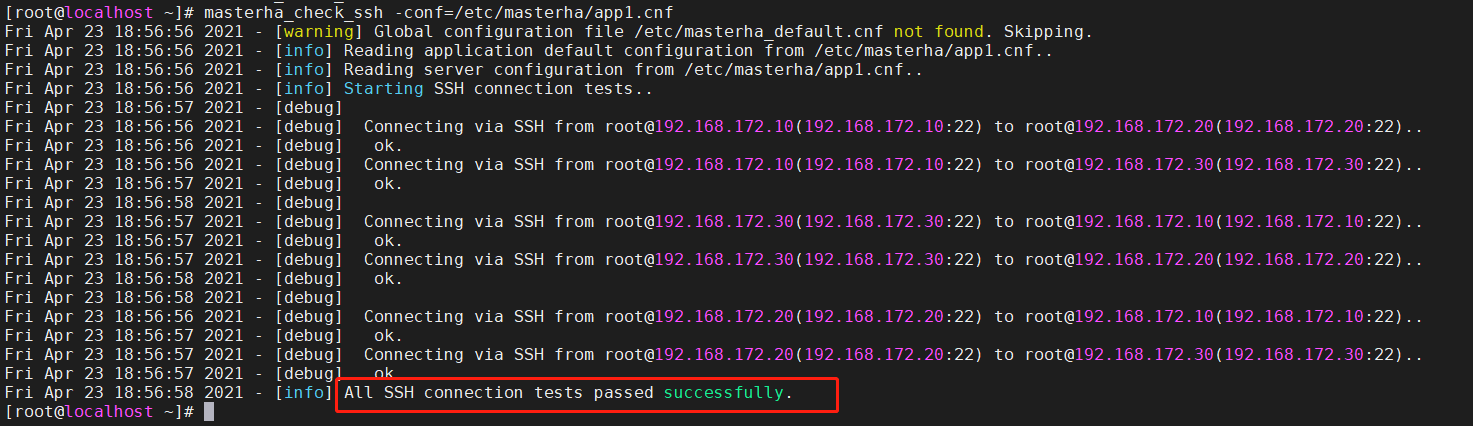
10. Test ssh password less authentication on the manager node
MHAmanager(192.168.172.50)
masterha_check_ssh -conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf #If it is normal, it will finally output successfully; #If it fails, you can go to the place where the server has no password authentication to see if there is a problem
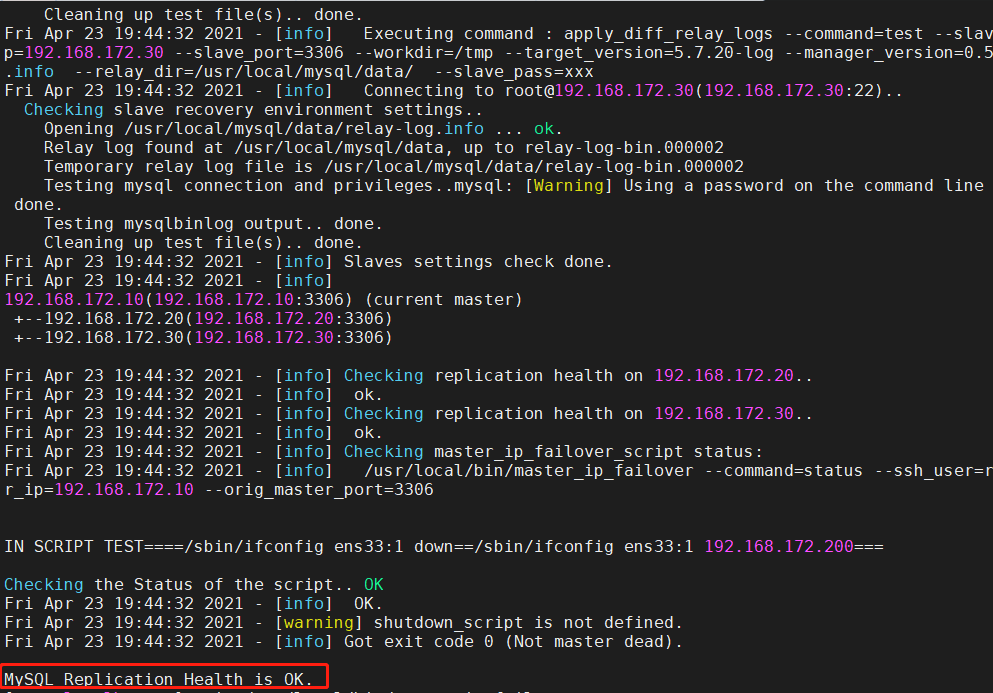
11. Test master-slave replication
masterha_check_repl -conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf #Finally, MySQL Replication Health is OK appears, indicating that it is normal; #MySQL Replication Health is NOT OK appears! , you can check whether there are fewer soft links on the mysql server -- > location of this article: 2,Modify three sets MySQL Master profile of the server/etc/my.cnf,And create a command soft link
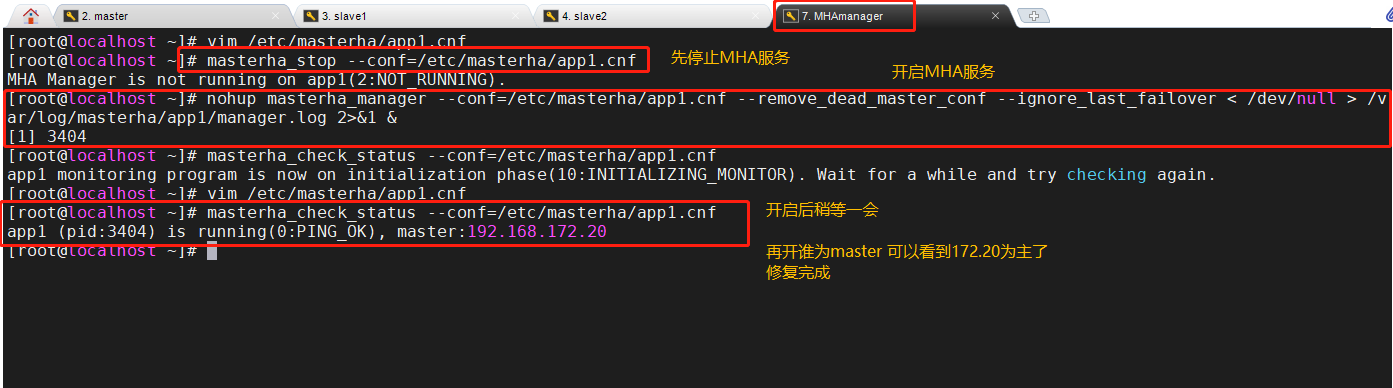
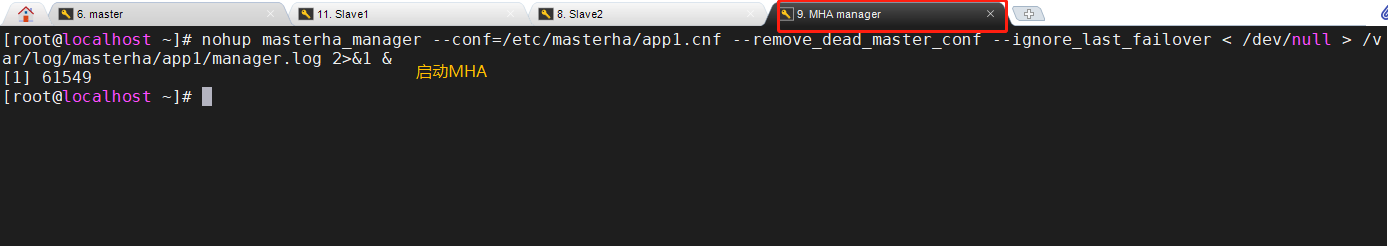
12. Start MHA on the manager node
nohup masterha_manager --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf --remove_dead_master_conf --ignore_last_failover < /dev/null > /var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log 2>&1 & nohup //option masterha_manager //open –conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf //Specify profile –remove_dead_master_conf //When the master server fails, the old master ip will be deleted from the master configuration file after the master-slave switch –ignore_last_failover //Ignore failover, ignore servers that are always down and unreliable
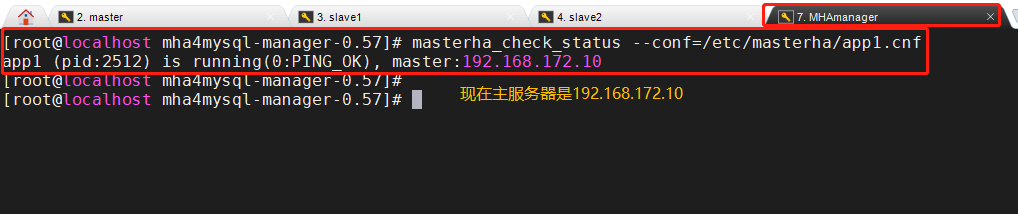
13. View relevant information
-
See who the current master node is
masterha_check_status --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf
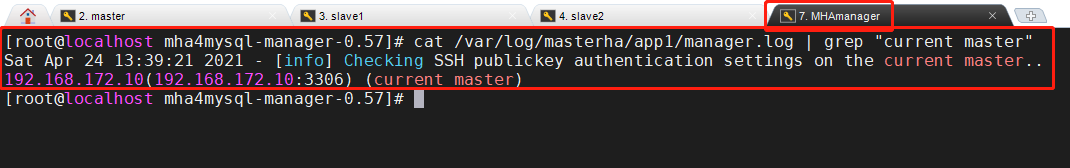
-
View current log information
cat /var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log | grep "current master"
-
Check whether the MySQL VIP address 192.168.172.200 exists. This VIP address will not disappear because the manager node stops MHA service
ifconfig
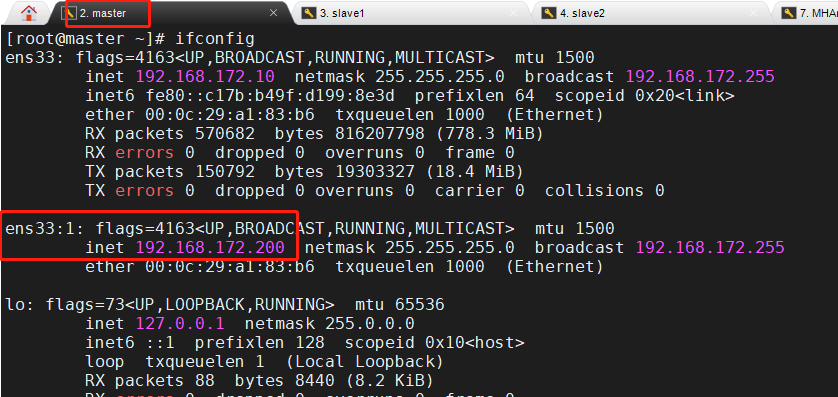
3, Fault simulation
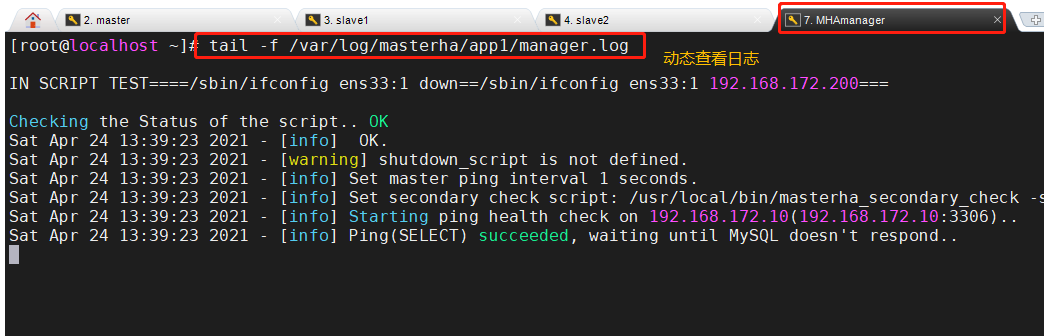
1. Monitor observation log records on the manager node
MHAmanager(192.168.172.50)
tail -f /var/log/masterha/app1/manager.log
2. Stop MySQL service on Master node Mysql1
mysql1(192.168.172.10)
systemctl stop mysqld or pkill -9 mysql
Insert picture description here
3. Check whether salve1 takes over VIP
slave1(192.168.172.20)
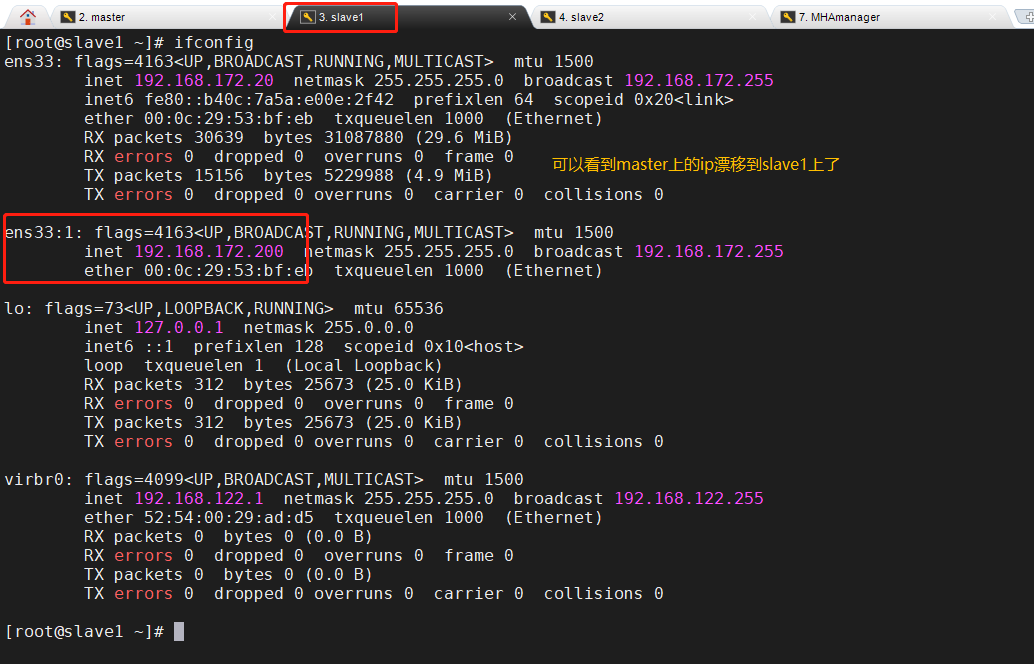
4. Monitor observation log records on the manager node
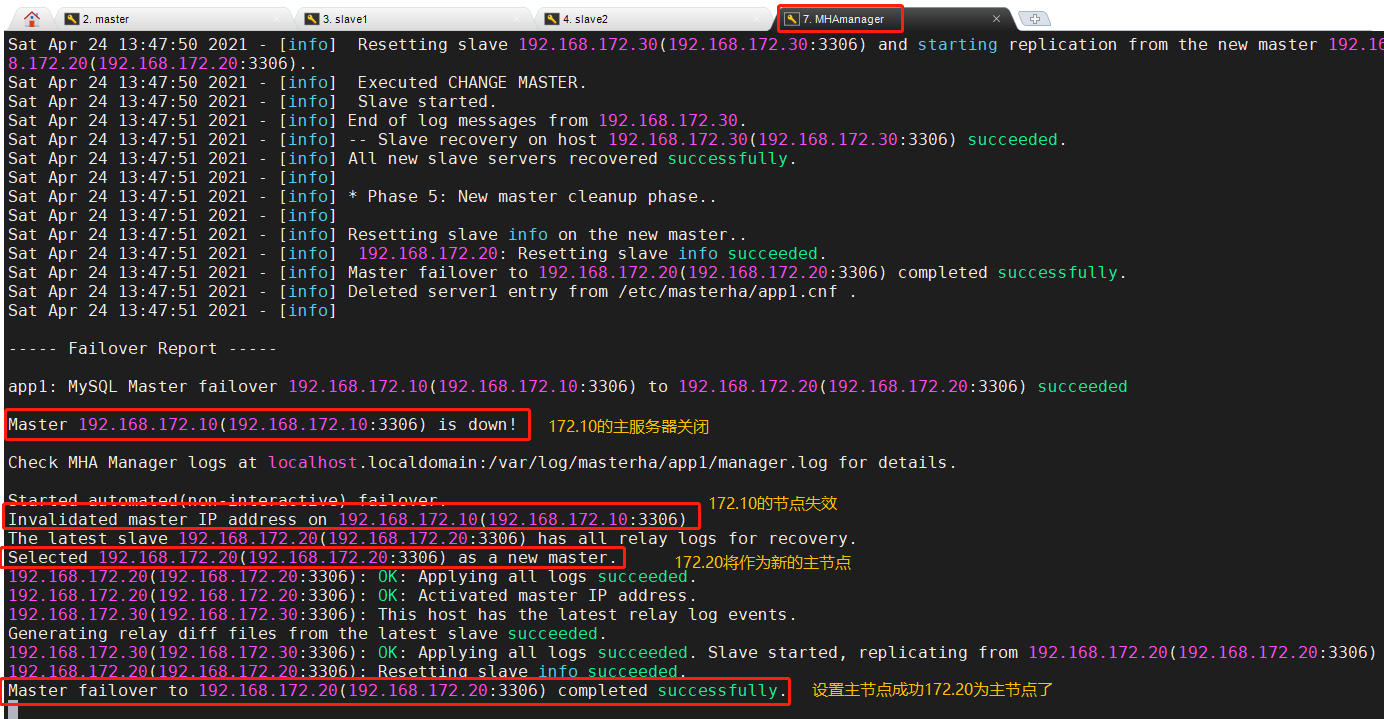
4, Troubleshooting steps
(1) Repair master
master(192.168.172.10) systemctl restart mysqld
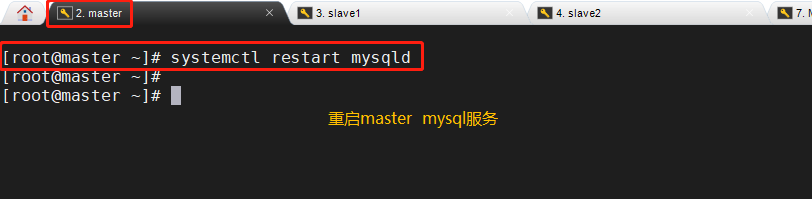
(2) Repair master-slave
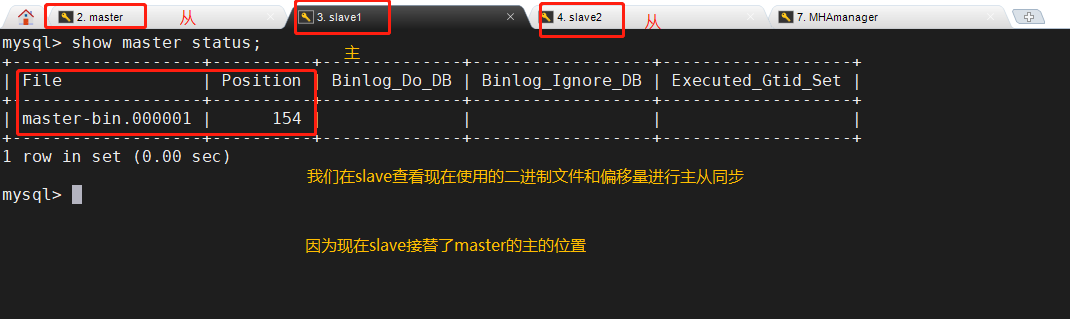

(3) On the manager node, modify the configuration file app1 cnf
vim /etc/masterha/app1.cnf ...... secondary_check_script=/usr/local/bin/masterha_secondary_check -s 192.168.172.10 -s 192.168.172.30 ...... [server1] hostname=192.168.172.20 port=3306 [server2] candidate_master=1 check_repl_delay=0 hostname=192.168.172.30 port=3306 [server3] hostname=192.168.172.10 port=3306
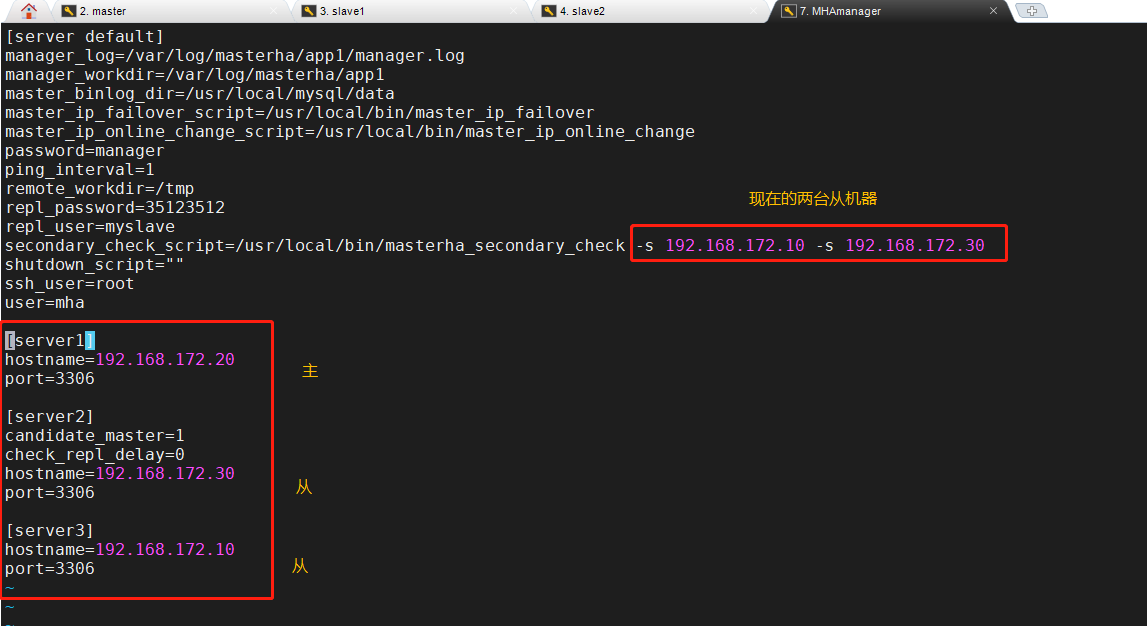
(4) Start MHA on the manager node