catalogue
In the previous initial experience of docker, I have tried to use it Port mapping access nginx , one network card can be configured with multiple IP addresses. Use ifconfig to configure IP addresses. Be sure to note that the IP addresses here cannot conflict. You can use ping ip. If the target IP of the same network segment cannot be pinged, it means it is available.
1. Configure IP
[root@localhost opt]# ifconfig ens33:1 192.168.0.101/24 up
[root@localhost opt]# ifconfig
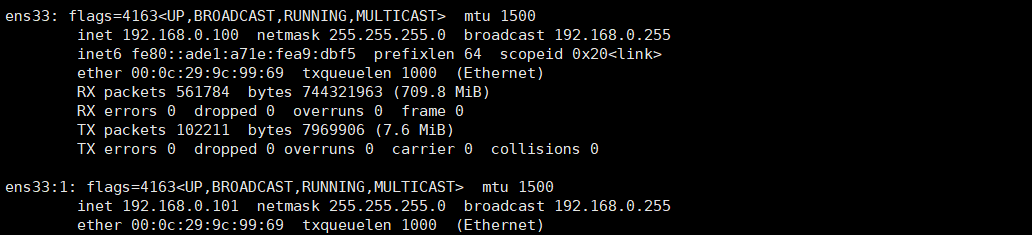
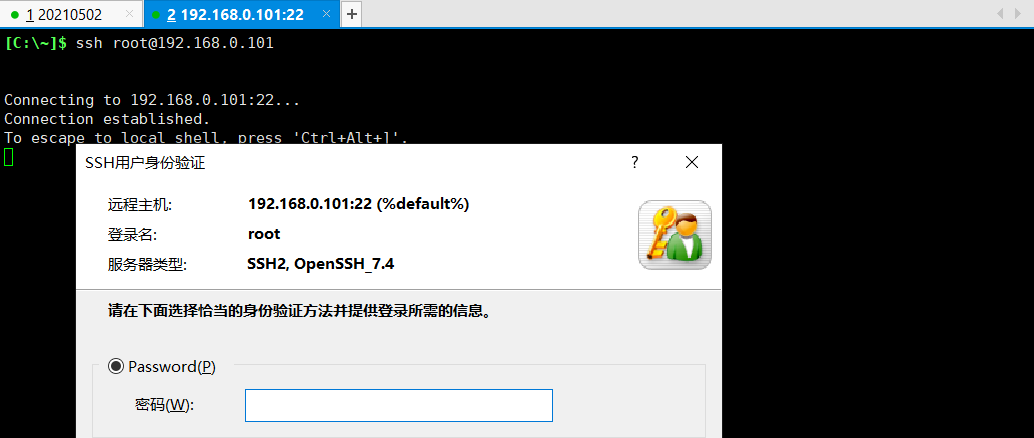
In this way, two ip addresses are configured. Can I log in?
ssh root@192.168.0.101
In this way, the host has two ip addresses. After using ifconfig, there are 192.168.0.100 and 192.168.0.101 ip addresses under ens33.
2. Start service
[root@localhost opt]# docker run -d -p 192.168.0.100:80:80 nginx:latest e2e1a5cbc8334d85acf1e8aa9da670dedbb96bb8fcc3ff7b338c5c63ab11eb91 [root@localhost opt]# docker run -d -p 192.168.0.101:80:80 nginx:latest 6ee5b735e75282d0f444ea54f7417bc3bfb3ff38cb0524e784f62a2f6d62a7ce
After startup, use the docker command to view
[root@localhost opt]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 6ee5b735e752 nginx:latest "/docker-entrypoint...." 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 192.168.0.101:80->80/tcp frosty_beaver e2e1a5cbc833 nginx:latest "/docker-entrypoint...." 4 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 192.168.0.100:80->80/tcp jovial_raman
[root@localhost opt]# netstat -lntup
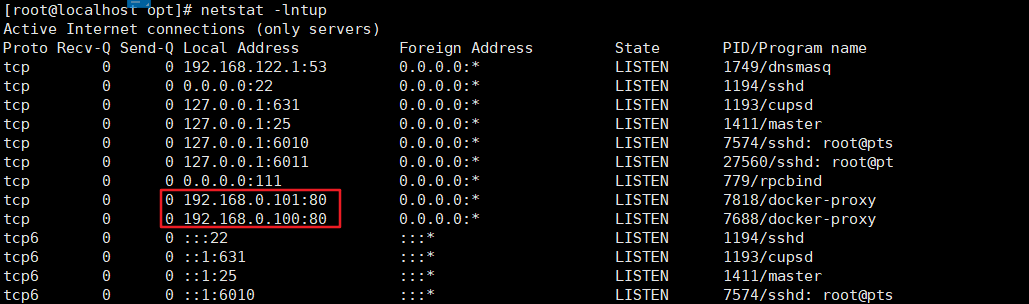
If the ip address is not written when mapping the port, the default ip address is used
[root@localhost opt]# docker run -d -p 81:80 nginx:latest
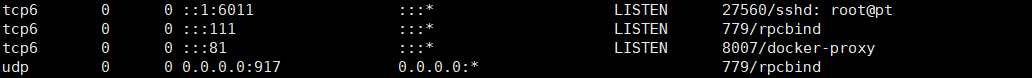
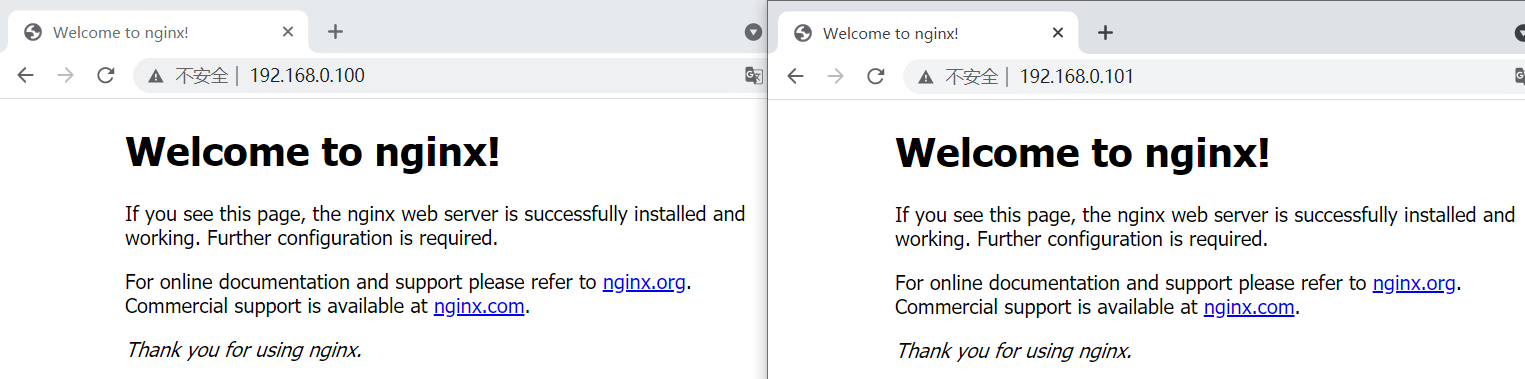
After that, it is equivalent to visiting one website when visiting 100 and another website when visiting 101
3. Service maintenance
[root@localhost opt]# docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES c2c9273e9484 nginx:latest "/docker-entrypoint...." 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 0.0.0.0:81->80/tcp, :::81->80/tcp mystifying_feistel 6ee5b735e752 nginx:latest "/docker-entrypoint...." 9 minutes ago Up 9 minutes 192.168.0.101:80->80/tcp frosty_beaver e2e1a5cbc833 nginx:latest "/docker-entrypoint...." 10 minutes ago Up 9 minutes 192.168.0.100:80->80/tcp jovial_raman
In this way, there are three containers. Enter one container and modify the home page information of the modifier
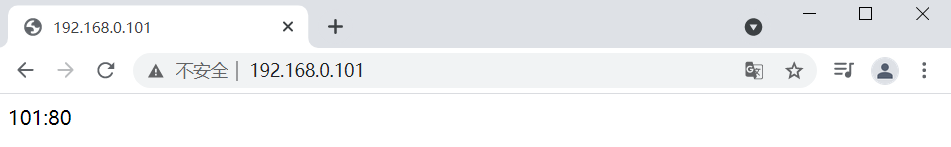
[root@localhost opt]# docker exec -it 6ee5b735e752 /bin/bash root@6ee5b735e752:/# echo '101:80'>/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
Visit 192.168.0.101 again
Of course, other commands can also be used for mapping
-p hostPort:containerPott -p ip:honstPort:containerPort Multiple containers want to use port 80 -p ip::containerPort(Random port) -p hostPort:containerPort:udp use udp agreement -p 192.168.0.104::53:udp 104 using host ip Address random port udp Protocol mapping to container udp Port 53 of the protocol -p 81:80 -p 443:443 Specify multiple port Random mapping-Random port docker run -P nginx:latest
The previous two have been introduced. Now let's see how to use random ports. First use the netstat command to check the current network information
[root@localhost opt]# netstat -lntup Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1749/dnsmasq tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1194/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1193/cupsd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1411/master tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7574/sshd: root@pts tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6011 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 27560/sshd: root@pt tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 779/rpcbind tcp 0 0 192.168.0.101:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7818/docker-proxy tcp 0 0 192.168.0.100:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7688/docker-proxy tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:81 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7999/docker-proxy tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1194/sshd tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 1193/cupsd tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1411/master tcp6 0 0 ::1:6010 :::* LISTEN 7574/sshd: root@pts tcp6 0 0 ::1:6011 :::* LISTEN 27560/sshd: root@pt tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 779/rpcbind tcp6 0 0 :::81 :::* LISTEN 8007/docker-proxy udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:917 0.0.0.0:* 779/rpcbind udp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* 1749/dnsmasq udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:67 0.0.0.0:* 1749/dnsmasq udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* 779/rpcbind udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:32973 0.0.0.0:* 772/avahi-daemon: r udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5353 0.0.0.0:* 772/avahi-daemon: r udp6 0 0 :::917 :::* 779/rpcbind udp6 0 0 :::111 :::* 779/rpcbind
Observe the above ip address and port information, and then use the following command to execute it twice in a row
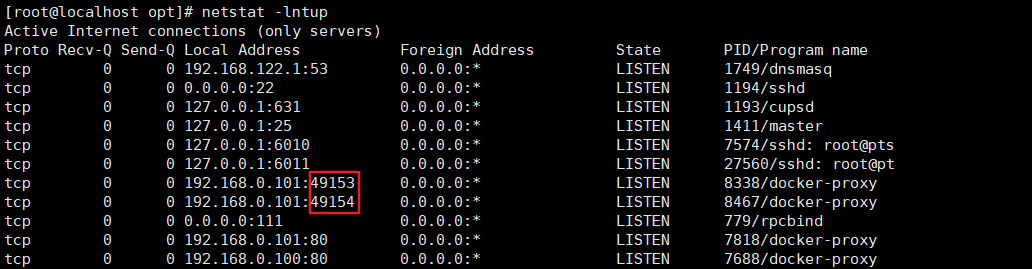
[root@localhost opt]# docker run -d -p 192.168.0.101::80 nginx:latest 3a885ede52674ad84570573ac9cb7f4182c809bfa9fd39b4c6ae4ff7a6026dc6 [root@localhost opt]# docker run -d -p 192.168.0.101::80 nginx:latest 738b4313c4f779212547a19a1a7ed231133e71d6ecd08b6f59faf90d0ccd304d
Using netstat again, you can find that there are two more ports, 49153 and 49154. Why is this port
This is determined by kernel parameters. Use sysctl to filter network information
[root@localhost opt]# [root@localhost opt]# sysctl -a|grep ipv4|grep rang net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 32768 60999 sysctl: reading key "net.ipv6.conf.all.stable_secret"
Ports range from 32768 to 60999. What is the application of this? For example, when users visit the web server, for example, when using nginx reverse proxy, we know that users can open multiple web pages.
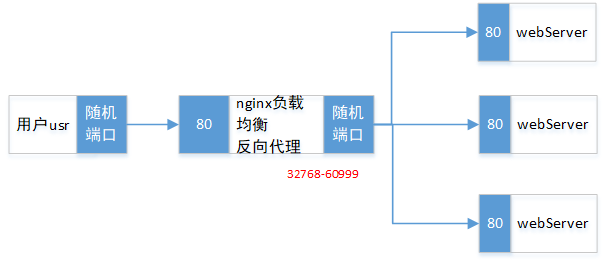
Therefore, if you don't use the tuning technology, you can only use three access requests. After tuning, for example, it can be adjusted to 10000-60999, and almost more than 50000 can't be broken through. Therefore, you can use multiple load balancing (for example, using four-tier load balancing, such as lvs) to connect to the web service cluster.