Network operation
Network support in Java:
- InetAddress: used to represent hardware resources on the network, i.e. IP address;
- URL: uniform resource locator;
- Sockets: use TCP protocol to realize network communication;
- Datagram: use UDP protocol to realize network communication.
InetAddress
There is no public constructor. You can only create instances through static methods.
InetAddress.getByName(String host); InetAddress.getByAddress(byte[] address);
public class NetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
// public static InetAddress getByName(String host)
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("LAPTOP-D9966H06");
//InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("223.3.108.211");
//InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.2.1");
// Get two things: host name and IP address
// public String getHostName()
String name = address.getHostName();
// public String getHostAddress()
String ip = address.getHostAddress();
System.out.println(name + "---" + ip);
}
}URL
Byte stream data can be read directly from the URL.
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com");
/* Byte stream */
InputStream is = url.openStream();
/* Character stream */
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is, "utf-8");
/* Provide caching function */
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}Sockets
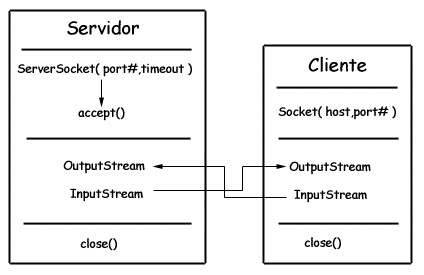
- ServerSocket: server-side class
- Socket: client class
- The server and client input and output through InputStream and OutputStream.
Datagram
- Datagram socket: communication class
- Datagram packet: packet class
UDP protocol
Communication rules
-
Encapsulate the data source and destination into data packets without establishing a connection;
-
The size of each datagram is limited to 64k;
-
Because there is no connection, it is an unreliable protocol;
-
No need to establish a connection, fast
Send data using UDP protocol
-
Create sender Socket object
-
Create data and package it
-
Call the sending method of the Socket object to send packets
-
Release resources
public class SendDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. Create the sending Socket object
DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket();
//2. Create data and package it
byte[] bys="hello".getBytes();
// length
int length = bys.length;
// IP address object
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("LAPTOP-D9966H06");
// port
int port = 10086;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, length, address, port);
//3. Call the sending method of Socket object to send data packet
ds.send(dp);
//4. Release resources
ds.close();
}
}UDP protocol receiving data
-
Create receiver Socket object
-
Create a packet (receive container)
-
Call the receiving method of the Socket object to receive data
-
Parse the packet and display it on the console
-
Release resources
public class ReceiveDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. Create a Socket object at the receiving end
DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(10086);
//2. Create a packet (receiving container)
byte[] bys=new byte[1024];
int length=bys.length;
DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bys,length);
//3. Call the receiving method of Socket object to receive data
//public void receive(DatagramPacket p)
ds.receive(dp);//Blocking type
//4. Parse the data package and display it on the console
InetAddress inetAddress=dp.getAddress();
String ip=inetAddress.getHostAddress();
// public byte[] getData(): get data buffer
// public int getLength(): get the actual length of the data
byte[] bys2 = dp.getData();
int len = dp.getLength();
String s = new String(bys2, 0, len);
System.out.println(ip + "The data transmitted is:" + s);
//5. Release resources
ds.close();
}
}Use UDP to transmit the data entered by keyboard
-
Receiving end:
public class ReceiveDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(12345); while (true){ byte[] bys=new byte[1024]; DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bys,bys.length); ds.receive(dp); //Blocking type String ip=dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); String s = new String(dp.getData(), 0, dp.getLength()); System.out.println(ip + "The data transmitted is:" + s); } //The receiving end should always be open to receive data without releasing resources //ds.close(); } } -
Sender:
public class SendDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(); //Encapsulate keyboard input data BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String line=null; while(true){ line=br.readLine(); if("-1".equals(line)){ break; } byte[] bys=line.getBytes(); DatagramPacket dp= new DatagramPacket(bys,bys.length,InetAddress.getByName("LAPTOP-D9966H06"),12345); ds.send(dp); } br.close(); //4. Release resources ds.close(); } }
TCP protocol
Communication rules
-
Establish a connection to form a channel for data transmission;
-
Large amount of data transmission in connection;
-
The connection is completed through three handshakes, which is a reliable protocol;
4. The connection must be established, and the efficiency will be slightly lower
TCP protocol sends data
-
Create the Socket object of the sender: if this step is successful, the connection has been established successfully.
-
Get output stream and write data
-
Release resources
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. Create the Socket object of the sender: if this step is successful, the connection has been established successfully.
Socket socket=new Socket("LAPTOP-D9966H06",8888);
//2. Obtain output stream and write data
OutputStream outputStream=socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("hello".getBytes());
//3. Release resources
socket.close();
}
}TCP protocol receiving data
-
Create the Socket object of the receiving end
-
Listen for client connections. Returns a corresponding Socket object
-
Get the input stream, read the data and display it on the console
-
Release resources
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. Create the Socket object of the receiving end
ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(8888);
//2. Listen for client connections. Returns a corresponding Socket object
Socket socket=serverSocket.accept();
//3. Get the input stream, read the data and display it on the console
InputStream inputStream=socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(bys);
// Blocking method
String str = new String(bys, 0, len);
String ip = socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip + "---" + str);
//4. Release resources
socket.close();
}
}- Note: in TCP communication, the server can also send data to the client
public class ServerDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. Create the Socket object of the receiving end
ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(8888);
//2. Listen for client connections. Returns a corresponding Socket object
Socket socket=serverSocket.accept();
//3. Get the input stream, read the data and display it on the console
InputStream inputStream=socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(bys);
String str = new String(bys, 0, len);
String ip = socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip + "---" + str);
//Send data to client
OutputStream outputStream=socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("Data received".getBytes());
//4. Release resources
socket.close();
}
}public class ClientDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. Create the Socket object of the sender: if this step is successful, the connection has been established successfully.
Socket socket=new Socket("LAPTOP-D9966H06",8888);
//2. Obtain output stream and write data
OutputStream outputStream=socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("hello".getBytes());
//Get feedback from the server
InputStream inputStream=socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bys=new byte[1024];
int len=inputStream.read(bys);
String reback=new String(bys,0,len);
System.out.println("reback:"+reback);
//3. Release resources
socket.close();
}
}Client keyboard input, server output to the console
-
Server:
public class ServerDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1. Create the Socket object of the receiving end ServerSocket serverSocket=new ServerSocket(8888); //2. Listen for client connections. Returns a corresponding Socket object Socket socket=serverSocket.accept(); //3. Get the input stream, read the data and display it on the console //The input stream is wrapped here InputStream inputStream=socket.getInputStream(); BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)); String line=null; while((line=br.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(line); } //4. Release resources socket.close(); } } -
client:
public class ClientDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1. Create the Socket object of the sender: if this step is successful, the connection has been established successfully. Socket socket=new Socket("LAPTOP-D9966H06",8888); //Keyboard input data BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); //2. Obtain output stream and write data //Wrap the output stream OutputStream outputStream=socket.getOutputStream(); BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream)); String line=null; while(true){ line=br.readLine(); if("-1".equals(line)){ break; } bw.write(line); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } //3. Release resources socket.close(); } }