1, IP address and port concept
1. IP address
In the network, each computer must have an IP address;
32 bits, 4 bytes, commonly expressed in dotted decimal format, for example: 192.168.1.100
127.0.0.1 is a fixed ip address, which represents the current computer and is equivalent to "this" in object-oriented
2. Port
When two computers are connected, there is always a server and a client.
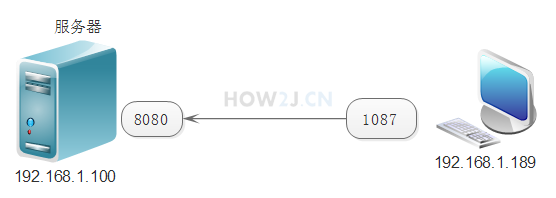
Communication between the server and the client takes place through the port. As shown in the figure:
The server with ip address 192.168.1.100 passes through port 8080
And the ip address is 192
1087 port communication of the client of. 168.1.189
3. Get native IP address
Get an InetAddress object through getLocalHost, which contains the domain name and IP address of the local machine. This is the domain name and IP address. Then get the corresponding address through * * getHostAddress() * * and this is only the IP address
package socket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class TestSocket {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
InetAddress host = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
String ip =host.getHostAddress();
System.out.println("Local machine ip Address:" + ip);
}
}4. ping command (the local IP address is 192.168.43.225)
Use ping to determine whether an address can be reached, that is, whether the IP address can be used
ping is not a java api, but a small tool in windows to determine the response time of an address
As shown in the figure
ping 192.168.2.106 can return the response time of this address. Time < 1ms indicates that it is very fast. This is generally the response time of LAN
ping 192.168.2.206 returns Request timed out, which means no response is returned after a long time. Basically, it is judged that this address is unavailable
2, Socket (socket) carries out communication between different programs
The server opens port 8888 and listens, waiting for the connection request of the client
The client knows the ip address and listening port number of the server and sends a request to the server
The port address of the client is allocated by the system and is usually greater than 1024
Once the connection is established, the server will get a new Socket object, which is responsible for communicating with the client.
be careful: In the process of development and debugging, if the Server code is modified, close the started Server, otherwise the new Server cannot be started because port 8888 is occupied
Establish contact and send and receive numbers, see the following code
//Server
package socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//The server opens port 8888
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
System.out.println("Listening on port number:8888");
Socket s = ss.accept();
//Open input stream
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
//Read data sent by client
int msg = is.read();
//Print out
System.out.println(msg);
is.close();
s.close();
ss.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();}}}
//client
package socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//Connect to the 8888 port of this computer
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
// Open output stream
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
// Send the number 110 to the server
os.write(110);
os.close();
s.close();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();}}}The sending / receiving string code is as follows
It is troublesome to send and receive strings directly using byte stream data stream Encapsulate the byte stream so that it is easy to send and receive strings
1. Encapsulate the output stream in DataOutputStream
Use writeUTF to send the string "legend!"
2. Encapsulate the input stream in DataInputStream
Use readUTF to read the string and print it
//Server
package socket;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
System.out.println("Listening on port number:8888");
Socket s = ss.accept();
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
//Encapsulate the input stream in the DataInputStream
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
//Read string using readUTF
String msg = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(msg);
dis.close();
s.close();
ss.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();}}}
//client
package socket;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
//Encapsulate the output stream in the DataOutputStream
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
//Send string using writeUTF
dos.writeUTF("Legendary!");
dos.close();
s.close();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();}}}
Using Scanner, the code is as follows
In the above steps, you need to modify the code every time you want to send different data
have access to Scanner Read the console input and send it to the server, so that different data can be sent each time.
The server does not change, just the client
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try{
//Connect to the 8888 port of this computer
Socket s=new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);
System.out.println(s);
//Open output stream
OutputStream os=s.getOutputStream();
//Encapsulate the output stream in the DataOutputStream
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(os);
//Send string using writeUTF
System.out.println("Please enter:");
Scanner ss=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=ss.next();
dos.writeUTF(str);
s.close();
}catch(UnknownHostException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}}
3, Multithreaded chat
If you use a single thread to develop Socket applications, you can either receive messages or send messages at the same time, but not at the same time.
In order to send and receive messages at the same time, multithreading is needed
Do an exercise and send and receive messages at the same time
In order to send and receive messages at the same time, the basic design idea is to send and receive messages in different threads
1. SendThread send message thread
2. Receivethread accept message thread
3. Once the server receives the connection, it starts sending and receiving two threads
4. Once the client has established a connection, start the sending and receiving threads
1: Send
package socket;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SendThread extends Thread{
private Socket s;
public SendThread(Socket s){
this.s=s;
}
public void run(){
try{
OutputStream cs=s.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos =new DataOutputStream(cs);
while(true){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter:");
String str=sc.next();
dos.writeUTF(str);
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}}
2, Receive
package socket;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
public class RecieveThread extends Thread{
private Socket s;
public RecieveThread(Socket s){
this.s=s;
}
public void run(){
try{
InputStream is=s.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(is);
while(true){
String msg=dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("Read write complete:"+msg);
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}}
3, Server
package socket;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(8888);
System.out.println("Listening port number: 8888");
Socket s=ss.accept();
//Start the send message thread
new SendThread(s).start();
//Start the accept message thread
new RecieveThread(s).start();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}}
4, Client
package socket;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
Socket s=new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);
// Start the send message thread
new SendThread(s).start();
// Start the accept message thread
new RecieveThread(s).start();
}catch(UnknownHostException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}}