Mad God video address: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1LJ411z7vY
1. General
Computer network refers to a computer system that connects multiple computers and their external devices with independent functions in different geographical locations through communication lines (linear and wireless), and realizes resource sharing and information transmission under the management and coordination of network operating system, network management software and network communication protocol.
Purpose of network programming
- Dissemination and exchange of information
- Data exchange and communication
What is needed to achieve this effect
- How to accurately locate a host on the network?
192.168. 1.100: port to locate a resource on this computer. - After finding the host, how to transmit data?
JavaWeb: Web programming B/S architecture
Network programming: TCP/IP C/S architecture
2. Elements of network communication
How to realize network communication?
- Address of communication parties: IP + port number (192.168.1.100:8080)
- Rules: protocols for network communication
TCP/IP reference model
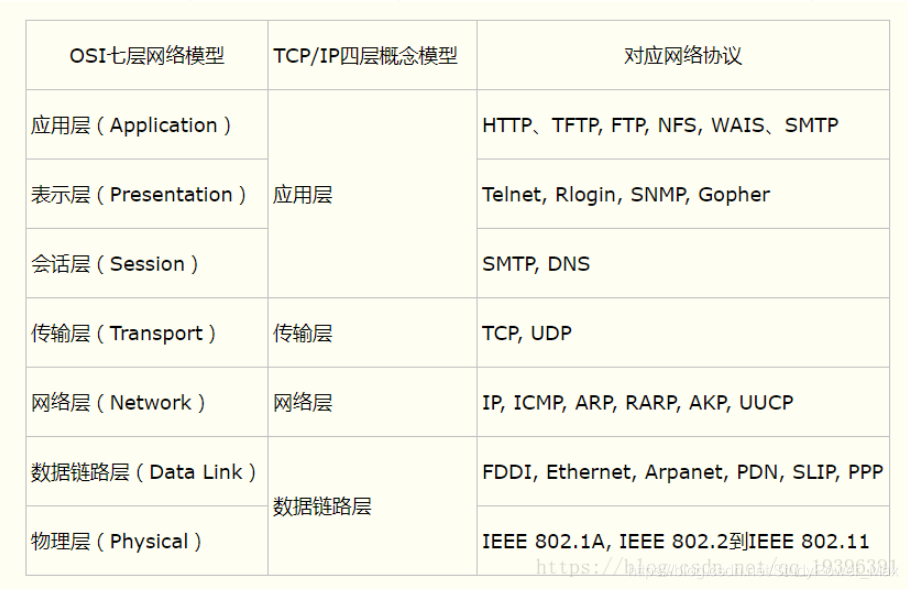
Summary:
- Two main problems in network programming
How to accurately locate one or more hosts on the network
How to communicate after finding the host - Elements in network programming
IP and port number
Network communication protocol - Everything in Java is an object
3. IP
ip address: InetAddress
- Uniquely locate a computer on a network
- 127.0. 0.1: local localhost
- Classification of ip addresses
- IPV4/IPv6
- IPV4 : 127.0. 0.1, composed of 4 bytes, 0-255, 4.2 billion, 3 billion, all in North America and 400 million in Asia. Exhausted in 2011
- IPV6: 128 bit. 8 unsigned integers!
- Public network (Internet) - private network (LAN)
- 192.168.xx.xx: for internal use of the organization
- IPV4/IPv6
- Domain name: memory ip problem
//Test ip
public class TestInetAddress {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//Query local address
InetAddress address1 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
System.out.println(address1); ///127.0.0.1
InetAddress address3 = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
System.out.println(address3); //localhost/127.0.0.1
InetAddress address4 = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println(address4); //Sunny/192.168.100.1
//Query URL ip address
InetAddress address2 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
System.out.println(address2); //www.baidu.com/36.152.44.95
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4. Port
A port represents the process of a program on a computer.
- Different processes have different port numbers to distinguish software
- Specified: 0-65535
- TCP/UDP: 65535 * 2. Port numbers cannot conflict under a single protocol
- Port classification:
- Public port: 0 ~ 1023
- HTTP : 80
- HTTPS : 443
- FTP : 21
- Telet : 23
- Program registration port: 1024-49151, assigned to users or programs
- Tomcat: 8080
- Mysql: 3306
- Oracle: 1521
- Dynamic, private: 49152-65535
- Public port: 0 ~ 1023
netstat -ano #View all ports netstat -ano | findstr "5900" #View the specified port tasklist | findstr "8696" #View processes on the specified port Ctrl + Shift + ESC # Open Task Manager
public class TestInetSocketAddress {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InetSocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080);
InetSocketAddress socketAddress1 = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080);
System.out.println(socketAddress); ///127.0.0.1:8080
System.out.println(socketAddress1); //localhost/127.0.0.1:8080
System.out.println(socketAddress.getAddress()); //ip address / 127.0 zero point one
System.out.println(socketAddress.getHostName()); //Host name 127.0 zero point one
System.out.println(socketAddress.getHostString()); //127.0.0.1
System.out.println(socketAddress.getPort());//Port 8080
}
}
5. Communication protocol
Agreement: agreement, just as we speak Mandarin now.
Network communication protocol: rate, transmission code rate, code structure, transmission control
TCP/IP protocol cluster: it is actually a group of protocols
Important:
- TCP: user transport protocol
- UDP: User Datagram Protocol
Famous agreement:
- TCP
- IP
Comparison between TCP and UDP:
TCP: call
- Connection: stable
- Three handshakes
At least three times are required to ensure stable connection A: What are you worried about? B: What do you think? A: Do it!
- Four waves
A: I'm disconnecting (I'm leaving) B: I know you're disconnecting (are you really leaving?) B: Are you really disconnected? Are you really leaving A: I'm really disconnected (I'm really leaving)
- Client, server
- The transmission is completed, the connection is released, and the efficiency is low
UDP: send SMS
- Not connected, unstable
- Client and server: there is no clear boundary
- Ready or not, it can be sent to you
- Missile
- DDOS: flood attack! (saturation attack)
6. TCP
client
- Connect to the server Socket
- send message
//client
public class TcpClientDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
// 1. Know the server address
InetAddress serverIp = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
//Port number
int port = 9999;
// 2. Create a Socket connection
socket = new Socket(serverIp,port);
// 3. Send message IO stream
os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("Hello, welcome to study java".getBytes());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (socket != null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
The server
- Establish service port ServerSocket
- Wait for the user's connection accept
- Accept user messages
//The server
public class TcpServerDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket accept = null;
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
try {
// 1. I have to have an address
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
// 2. Wait for the client to connect
accept = serverSocket.accept();
// 3. Read the message from the client
is = accept.getInputStream();
//Pipe flow
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=is.read(buffer)) != -1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//close resource
if (baos != null){
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (accept != null){
try {
accept.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (serverSocket != null){
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
File upload via TCP
//The server
public class TcpServerDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. Create service
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9000);
//2. Listen for client connections
Socket accept = serverSocket.accept(); //Blocking listening, waiting for the client to connect
//3. Get input stream
InputStream is = accept.getInputStream();
//4. File output
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("receive.png"));//The pipeline flow of the file is used to receive the file
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(buff)) != -1){
fos.write(buff,0,len);
}
//Notify the client that I have received it
OutputStream os = accept.getOutputStream();
os.write("I'm finished. You can disconnect".getBytes());
fos.close();
is.close();
accept.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
//client
public class TcpClientDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1. Establish connection
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"), 9000);
//2. Create an output stream
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
//3. Read file
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("1.png"));
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
int len;
//4. Write out the document
while ((len = is.read(buff)) != -1) {
os.write(buff, 0, len);
}
//Notify the server that I'm finished
socket.shutdownOutput();//I have transmitted the meaning
//Make sure that the server has received it before you can disconnect
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();//A pipe stream that receives characters and bytes
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buff2 = new byte[1024];
int len2;
while ((len2 = inputStream.read(buff2)) != -1) {
baos.write(buff2, 0, len2);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
//5. Release resources
baos.close();
inputStream.close();
is.close();
os.close();
socket.close();
}
}
7. UDP
Send text messages without connecting. You need to know the other party's IP address.
- send message
Sender
//No connection to the server is required
public class UdpClientDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1. Create a Socket
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();
//2. Build a package
String msg = "Hello, server";
//3. To whom
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
int port = 9090;
//Data, starting length of data, to whom
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(msg.getBytes(), 0, msg.getBytes().length, address, port);
//4. Send packet
socket.send(packet);
//5. Close the flow
socket.close();
}
}
receiving end
//Or do you want to wait for the client to connect
public class UdpServerDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//Open port
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(9090);
//Receive packet
byte[] buff =new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buff, 0, buff.length);
socket.receive(packet);//Blocking reception
System.out.println(packet.getAddress());
System.out.println(new String(packet.getData(),0,packet.getData().length));
//Close connection
socket.close();
}
}
- UDP consultation
Loop send message
send out:
public class UdpSenderDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(8888);
//Prepare data, read from console, system in
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (true) { //Cyclic input
String data = reader.readLine();
byte[] bytes = data.getBytes();
DatagramPacket dgp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, 0, bytes.length, new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 6666));
socket.send(dgp);
if (data.equals("bye")){
break;
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
receive
public class UdpReceiveDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(6666);
while (true) { //Cyclic reception
//Ready to receive package
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bytes,0,bytes.length);
socket.receive(packet); //Blocking receiving package
//Disconnect
byte[] data = packet.getData();
String receiceData = new String(data, 0, data.length);
System.out.println(receiceData);
if (receiceData.equals("bye")){
break;
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
- Online consultation
Both can be senders and receivers
send out:
public class TalkSend implements Runnable {
DatagramSocket socket = null;
BufferedReader reader = null;
private int fromPort;
private String toIp;
private int toPort;
public TalkSend(int fromPort, String toIp, int toPort) {
this.fromPort = fromPort;
this.toIp = toIp;
this.toPort = toPort;
try {
socket = new DatagramSocket(fromPort);
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
} catch (SocketException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) { //Cyclic input
String data = null;
try {
data = reader.readLine();
byte[] bytes = data.getBytes();
DatagramPacket dgp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, 0, bytes.length, new InetSocketAddress(this.toIp, this.toPort));
socket.send(dgp);
if (data.equals("bye")){
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
receive:
public class TalkReceive implements Runnable {
DatagramSocket socket = null;
private int port;
private String msgFrom;
public TalkReceive(int port, String msgFrom) {
this.port = port;
this.msgFrom = msgFrom;
try {
//Open connection
socket = new DatagramSocket(port);
} catch (SocketException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) { //Cyclic reception
try {
//Ready to receive package
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bytes,0,bytes.length);
socket.receive(packet); //Blocking receiving package
//Disconnect
byte[] data = packet.getData();
String receiceData = new String(data, 0, data.length);
System.out.println(msgFrom + ":" + receiceData);
if (receiceData.equals("bye")){
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
student:
public class TalkStudent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Open two threads
new Thread(new TalkSend(7777,"localhost",9999)).start();
new Thread(new TalkReceive(8888,"teacher")).start();
}
}
teacher:
public class TalkTeacher {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Open two threads
new Thread(new TalkSend(5555,"localhost",8888)).start();
new Thread(new TalkReceive(9999,"student")).start();
}
}
8. URL
Uniform resource locator: to locate a resource on the Internet.
https://www.baidu.com/
Protocol: / / ip address: port / project name / resource
public class TestUrlDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException {
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8080/hello.java/index.jsp?username=zs&password=123");
System.out.println(url.getProtocol()); //Protocol http
System.out.println(url.getHost()); //Host ip localhost
System.out.println(url.getPort()); //Port 8080
System.out.println(url.getPath()); //Full path / Hello java/index. jsp
System.out.println(url.getFile()); //File / Hello java/index. jsp? username=zs&password=123
System.out.println(url.getQuery()); //Parameter username = ZS & password = 123
}
}
Download Network Resources
public class TestUrlDown {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Download address
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8080/urlTest/test.txt");
//Connect to this resource http
HttpURLConnection urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
InputStream is = urlConnection.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test1.text");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=is.read(bytes)) != -1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len); //Write this data
}
fos.close();
is.close();
urlConnection.disconnect(); //Disconnect
}
}