catalog
Article catalog
Socket API under Linux
Create Socket
int socket(int af, int type, int protocol);
- AF: AF (Address Family), IP address type, commonly used as AF_INET and AF_INET6, which can also be prefixed with PF (Protocol Family), that is, PF_INET and PF_INET6.
- type: data transmission mode, commonly used as SOCK_STREAM) mode (i.e. TCP) and no connection (sock)_ Dgram).
- Protocol: transport protocol, commonly used is IPPROTO_TCP and IPPTOTO_UDP, which represents TCP transport protocol and UDP transport protocol respectively.
To create a TCP socket:
int tcp_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
To create a UDP socket:
int udp_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP);
Bind Socket
int bind(int sock, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);
- sock: Socket file descriptor.
- addr: pointer to the sockaddr structure variable.
- addrlen: the size of the addr variable, which can be calculated by sizeof().
Bind the created socket ServerSock to the local IP and port:
int ServerSock = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP); struct sockaddr_in ServerSockAddr; memset(&ServerSockAddr, 0, sizeof(ServerSockAddr)); ServerSockAddr.sin_family = PF_INET; ServerSockAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1"); ServerSockAddr.sin_port = htons(1314); bind(ServerSock, (SOCKADDR*)&ServerSockAddr, sizeof(SOCKADDR));
Among them, struct SOCKADDR_ The structure variable of type in is used to save the IP information of IPv4. If IPv6, there is a corresponding structure:
struct sockaddr_in6 { sa_family_t sin6_family; // Address type, value is AF_INET6 in_port_t sin6_port; // 16 bit port number uint32_t sin6_flowinfo; // IPv6 stream information struct in6_addr sin6_addr; // Specific IPv6 address uint32_t sin6_scope_id; // Interface scope ID };
Request Socket connection
int connect(int sock, struct sockaddr *serv_addr, socklen_t addrlen);
Example:
int ClientSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP); connect(ClientSock, (SOCKADDR*)&ServerSockAddr, sizeof(SOCKADDR));
Monitor Socket
int listen(int sock, int backlog);
- sock: the Socket that needs to enter the listening state.
- backlog: the maximum length of the request queue.
Accept request
int accept(int sock, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);
- sock: server socket.
- addr: sockaddr_in structure variable.
- addrlen: the length of addr, which can be obtained from sizeof().
- Return value: a new socket to communicate with the client.
Example:
/* Listen to client requests, accept() returns a new socket, which is used for sending and receiving */ int ClientSock = accept(ServerSock, (SOCKADDR*)&ClientAddr, &len);
Close connection
int close(int fd);
- fd: file descriptor to close.
Sending and receiving of data
- read()/write()
- recv()/send()
- recvmsg()/sendmsg()
- recvfrom()/sendto()
- readv()/writev()
Send send function
ssize_t send(int sockfd, const void *buf, size_t len, int flags);
- sockfd: socket to send data.
- buf: the buffer address to hold the sent data.
- len: the number of bytes of data to send.
- flags: the option to send data. It is always 0.
recv receive function
ssize_t recv(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len, int flags);
- sockfd: socket to receive data.
- buf: buffer address to hold received data.
- len: the number of bytes of data to receive.
- flags: the option to receive data. It is always 0.
sendto send function
ssize_t sendto(int sock, void *buf, size_t nbytes, int flags, struct sockaddr *to, socklen_t addrlen);
- sock: socket used to transmit UDP data;
- buf: buffer address to save data to be transmitted;
- nbytes: length of data with transmission (in bytes);
- flags: optional parameter, if no 0 can be passed;
- to: the address of the sockaddr structure variable containing the target address information;
- addrlen: the length of the address value structure variable passed to the parameter to.
recvfrom receive function
ssize_t recvfrom(int sock, void *buf, size_t nbytes, int flags, struct sockadr *from, socklen_t *addrlen);
- sock: socket used to receive UDP data;
- buf: buffer address to save received data;
- nbytes: the maximum number of bytes that can be received (cannot exceed the size of buf buffer);
- flags: optional parameter, if no 0 can be passed;
- from: the address of the sockaddr structure variable containing the address information of the sender;
- addrlen: saves the variable address value of the structure variable length of the parameter from.
TCP Socket example
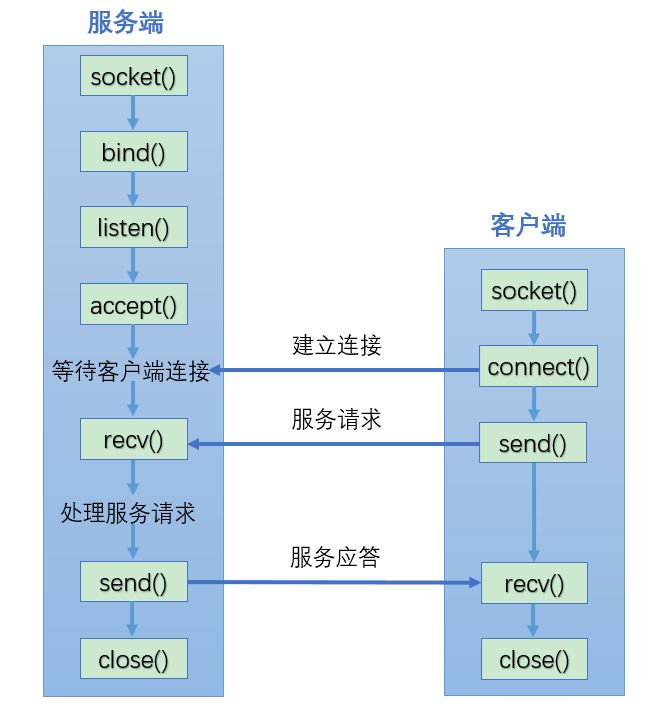
- Server
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <errno.h> #define BUF_LEN 100 /* Size of buffer. */ /* Print exception information. */ #define ERR_MSG(errnum) do { \ errnum = errno; \ fprintf(stderr, "ERROR num: %d\n", errnum); \ perror("PERROR message"); \ fprintf(stderr, "STRERROR message: %s\n", strerror(errnum)); \ } while (0) extern int errno; int main(void) { int server_fd = 0; int client_fd = 0; char buf[BUF_LEN] = {0}; int addr_len = 0; int recv_len = 0; int optval = 1; struct sockaddr client_addr; memset(&client_addr, 0, sizeof(struct sockaddr)); struct sockaddr_in server_addr; memset(&server_addr, 0, sizeof(struct sockaddr)); /* Create a TCP server Socket file descriptor. */ if (-1 == (server_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP))) { printf("socket ERROR.\n"); ERR_MSG(errno); exit(1); } server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); // INADDR_ANY, i.e. 0.0.0.0, means listening to all IP addresses of the machine. It is not recommended in production environment. server_addr.sin_port = htons(6666); /* Setting the address and port number can be reused, avoiding the problem of possible port conflicts, which is not recommended in the production environment.*/ if (setsockopt(server_fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &optval, sizeof(optval)) < 0) { printf("setsockopt ERROR.\n"); ERR_MSG(errno); exit(1); } if (-1 == (bind(server_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&server_addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr)))) { printf("bind ERROR.\n"); ERR_MSG(errno); exit(1); } if (-1 == (listen(server_fd, 10))) { printf("listen ERROR.\n"); ERR_MSG(errno); exit(1); } addr_len = sizeof(struct sockaddr); while (1) { /* Listen to a client's connection request and return the Socket file descriptor of the client. This Socket is used for sending and receiving the client. */ if (-1 == (client_fd = (accept(server_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &addr_len)))) { printf("accept ERROR.\n"); ERR_MSG(errno); exit(1); } if ((recv_len = recv(client_fd, buf, BUF_LEN, 0)) < 0) { printf("recv ERROR.\n"); ERR_MSG(errno); exit(1); } printf("Client sent data %s\n", buf); send(client_fd, buf, recv_len, 0); /* Close the socket. */ close(client_fd); memset(buf, 0, BUF_LEN); } return 0; }
- client
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <errno.h> #define BUF_LEN 100 /* Size of buffer. */ /* Print exception information. */ #define ERR_MSG(errnum) do { \ errnum = errno; \ fprintf(stderr, "ERROR num: %d\n", errnum); \ perror("PERROR message"); \ fprintf(stderr, "STRERROR message: %s\n", strerror(errnum)); \ } while (0) extern int errno; int main(void) { int client_fd; char buf[BUF_LEN] = {0}; struct sockaddr_in server_addr; memset(&server_addr, 0, sizeof(struct sockaddr)); /* Connect to the specified server. */ server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1"); server_addr.sin_port = htons(6666); while (1) { if (-1 == (client_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP))) { printf("socket ERROR.\n"); ERR_MSG(errno); exit(1); } /* Sends a connection request to the specified server. */ if (-1 == (connect(client_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&server_addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr)))) { printf("connect ERROR.\n"); ERR_MSG(errno); exit(1); } printf("Send to client >"); gets(buf); send(client_fd, buf, BUF_LEN, 0); memset(buf, 0, BUF_LEN); recv(client_fd, buf, BUF_LEN, 0); printf("Receive from server: %s\n", buf); memset(buf, 0, BUF_LEN); close(client_fd); } return 0; }
compile:
gcc tcp_server.c -o tcp_server gcc tcp_client.c -o tcp_client
function:
- Start TCP Server first:
# ./tcp_server
- Check whether the listening Socket is bound successfully:
$ netstat -lpntu | grep 6666 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:6666 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 28675/./tcp_server
- Start TCP Client
# ./tcp_client
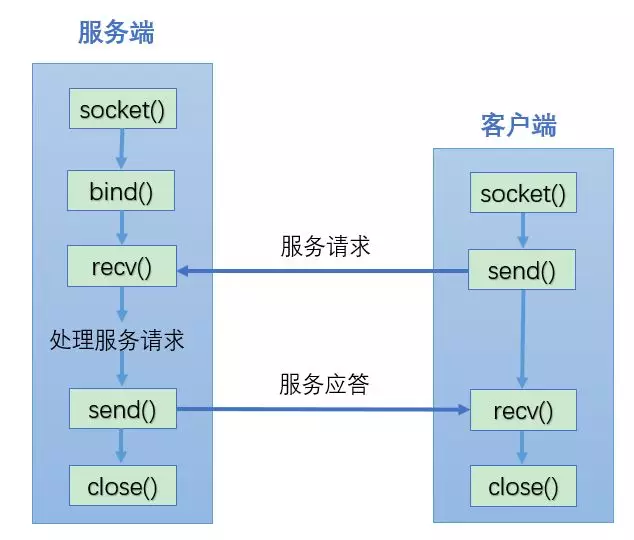
UDP communication process
- Server
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #define BUF_LEN 100 int main(void) { int ServerFd; char Buf[BUF_LEN] = {0}; struct sockaddr ClientAddr; struct sockaddr_in ServerSockAddr; int addr_size = 0; int optval = 1; /* Create UDP server Socket */ if ( -1 == (ServerFd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP))) { printf("socket error!\n"); exit(1); } /* Set server information */ memset(&ServerSockAddr, 0, sizeof(ServerSockAddr)); // Clear the ServerSockAddr of the structure ServerSockAddr.sin_family = AF_INET; // Use IPv4 address ServerSockAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); // Get IP address automatically ServerSockAddr.sin_port = htons(1314); // port // Set address and port number for reuse if (setsockopt(ServerFd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &optval, sizeof(optval)) < 0) { printf("setsockopt error!\n"); exit(1); } /* Bind operation, add the above socket property to the reusable address before binding */ if (-1 == bind(ServerFd, (struct sockaddr*)&ServerSockAddr, sizeof(ServerSockAddr))) { printf("bind error!\n"); exit(1); } addr_size = sizeof(ClientAddr); while (1) { /* Accept client's return data */ int str_len = recvfrom(ServerFd, Buf, BUF_LEN, 0, &ClientAddr, &addr_size); printf("The data sent by the client is:%s\n", Buf); /* Send data to client */ sendto(ServerFd, Buf, str_len, 0, &ClientAddr, addr_size); /* Clear buffer */ memset(Buf, 0, BUF_LEN); } close(ServerFd); return 0; }
- client
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #define BUF_LEN 100 int main(void) { int ClientFd; char Buf[BUF_LEN] = {0}; struct sockaddr ServerAddr; int addr_size = 0; struct sockaddr_in ServerSockAddr; /* Create client socket */ if (-1 == (ClientFd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP))) { printf("socket error!\n"); exit(1); } /* Request to server */ memset(&ServerSockAddr, 0, sizeof(ServerSockAddr)); ServerSockAddr.sin_family = PF_INET; ServerSockAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1"); ServerSockAddr.sin_port = htons(1314); addr_size = sizeof(ServerAddr); while (1) { printf("Please enter a string and send it to the server:"); gets(Buf); /* Send data to the server */ sendto(ClientFd, Buf, strlen(Buf), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&ServerSockAddr, sizeof(ServerSockAddr)); /* Accept the return data of the server */ recvfrom(ClientFd, Buf, BUF_LEN, 0, &ServerAddr, &addr_size); printf("The data sent by the server is:%s\n", Buf); memset(Buf, 0, BUF_LEN); // Reset buffer } close(ClientFd); // Close socket return 0; }
function:
$ netstat -lpntu | grep 1314 udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:1314 0.0.0.0:* 29729/./udp_server