Nginx from installation to high availability!
1, Nginx installation
1. Go to the official website http://nginx.org/ Download the corresponding nginx package. It is recommended to use a stable version
2. Upload nginx to linux system
3. Installation dependent environment
(1) Install gcc environment
yum install gcc-c++
(2) Installs the PCRE library for parsing regular expressions
yum install -y pcre pcre-devel
(3)zlib compression and decompression dependencies
yum install -y zlib zlib-devel
(4)SSL secure encrypted socket protocol layer is used for HTTP secure transmission, that is, https
yum install -y openssl openssl-devel
4. Decompression, you need to note that after decompression, you get the source code. The source code needs to be compiled before installation
tar -zxvf nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz
5. Before compiling, create the nginx temporary directory. If it is not created, an error will be reported during the process of starting nginx
mkdir /var/temp/nginx -p
6. In the nginx directory, enter the following command for configuration in order to create a makefile file
./configure \ --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \ --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid \ --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock \ --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \ --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \ --with-http_gzip_static_module \ --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/client \ --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/proxy \ --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/fastcgi \ --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/uwsgi \ --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/scgi
Note: represents a line break in the command line to improve readability. Configure the command:
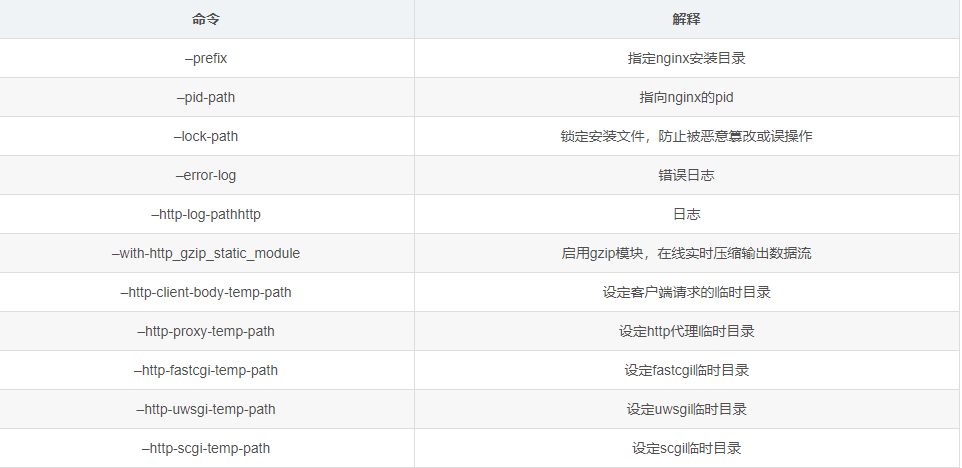
7. make compile & install
makemake install
8. Enter sbin directory and start nginx
Start: nginx stop it:./nginx -s stop Reload:./nginx -s reload
2, Configure reverse proxy
1. Configure upstream
upstream [proxyName] { server 192.168.1.173:8080; server 192.168.1.174:8080; server 192.168.1.175:8080;}
2. Configure server
server { listem 80; server_name www.tomcats.com; location / { proxy_pass http://tomcats; }}
3, Configure load balancing
nginx uses rotation training for load balancing by default
1. Use weighted polling
upstream [proxyName] { server 192.168.1.173:8080 weight=1; server 192.168.1.174:8080 weight=5; server 192.168.1.175:8080 weight=2;}
2. hash load balancing
upstream [proxyName] { ip_hash server 192.168.1.173:8080; server 192.168.1.174:8080; server 192.168.1.175:8080;}
In fact, the hash algorithm only calculates 192.168.1 for hashing
Use IP_ Notes to hash:
- The background server cannot be removed directly. It can only be marked down
3. url hash load balancing
upstream [proxyName] { hash $request_url; server 192.168.1.173:8080; server 192.168.1.174:8080; server 192.168.1.175:8080;}
4. Minimum connection load balancing
upstream [proxyName] { least_conn; server 192.168.1.173:8080; server 192.168.1.174:8080; server 192.168.1.175:8080;}
4, upstream instruction parameters
-
max_conns: limit the maximum number of simultaneous connections. Before 1.11.5, it can only be used in the commercial version
-
slow_start: the unit is second. The weight rises from 1 to the specified value within the specified time. It is not applicable to hash load balancing and random load balancing. If there is only one server in upstream, this parameter is invalid (only in commercial version)
-
down: disable access
-
backup: the standby machine can only be accessed when other servers cannot access it. It is not applicable to hash load balancing and random load balancing
-
max_ Failures: indicates several failures. It indicates that the server has been down, and the default value of upstream service is 1
-
fail_timeout: indicates the failed retry time. The default value is 10
1,keepalived
upstream [proxyName] { server 192.168.1.173:8080 weight=1; server 192.168.1.174:8080 weight=5; server 192.168.1.175:8080 weight=2; keepalive 32; #Number of connections maintained}server { listem 80; server_name www.tomcats.com; location / { proxy_pass http://tomcats; proxy_http_version 1.1; # Connected protocol version proxy_set_header Connection ""; Clear connection request header}
2. Control browser cache
server { listem 80; server_name www.tomcats.com; location / { proxy_pass http://tomcats; expires 10s; # The browser cache lasts for 10 seconds #expires @22h30m # expires at 10:30 pm #expires -1h # the cache expires one hour ago #expires epoch # do not set the cache #expires off # the cache is closed, and the browser controls the cache #expires max # maximum expiration time}}
3. Reverse proxy cache
upstream [proxyName] { server 192.168.1.173:8080 weight=1; server 192.168.1.174:8080 weight=5; server 192.168.1.175:8080 weight=2;}#proxy_cache_path Sets the location of the directory where the cache is saved#keys_zone Set the amount of space in and occupied by the share#mas_size Set maximum cache space#inactive Cache expiration time. If you miss this time, it will be cleaned up automatically#use_temp_path Close zero hour directory proxy_cache_path /usr/local/nginx/upsteam_cache keys_zone=mycache:5m max_size=1g inactive=8h use_temp_path=off;server { listem 80; server_name www.tomcats.com; #Enable and use cache proxy_cache mycache; #Cache expiration time proxy for 200 and 304 response codes_ cache_ valid 200 304 8h; location / { proxy_pass http://tomcats ; }}
5, Configure ssl certificate to provide https access
1. Install the SSL module
To configure https in nginx, you must install the SSL module, that is, http_ssl_module.
Enter the unzipped directory of nginx: / home/software/nginx-1.16.1
Add ssl modules (the original modules need to be retained)
./configure \--prefix=/usr/local/nginx \--pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid \--lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock \--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \--with-http_gzip_static_module \--http-client-body-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/client \--http-proxy-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/proxy \--http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/fastcgi \--http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/uwsgi \--http-scgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/scgi \--with-http_ssl_module
Compilation and installation
makemake install
2. Configure HTTPS
ssl certificate * crt and private key * Copy the key to the / usr/local/nginx/conf directory.
Add server listening 443 port:
server { listen 443; server_name www.imoocdsp.com; # open ssl ssl on; # to configure ssl certificate ssl_certificate 1_www.imoocdsp.com_bundle.crt; # Configure certificate key ssl_certificate_key 2_www.imoocdsp.com.key; # ssl conversation cache ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl Session timeout ssl_session_timeout 5m; # Configure the encryption suite and write it in accordance with the openssl standard SSL_ protocols TLSv1 TLSv1. 1 TLSv1. 2; ssl_ ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:HIGH:! aNULL:! MD5:! RC4:! DHE; ssl_ prefer_ server_ ciphers on; location / { proxy_pass http://tomcats/ ; index index. html index. htm; }}
6, Configure ha nginx
1. Install keepalived
(1) Download
https://www.keepalived.org/download.html
(2) Decompress
tar -zxvf keepalived-2.0.18.tar.gz
(3) Use the configure command to configure the installation directory and the location of the core configuration file:
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/keepalived --sysconf=/etc
-
prefix: keepalived installation location sysconf: keepalived core configuration file location, fixed location. If it is changed to another location, keepalived cannot be started, and an error will be reported in / var/log/messages
-
sysconf: keepalived: the location of the core configuration file is fixed. If it is changed to another location, keepalived cannot be started, and an error will be reported in / var/log/messages
Warning messages may appear during configuration, as follows:
*** WARNING - this build will not support IPVS with IPv6. Please install libnl/libnl-3 dev libraries to support IPv6 with IPVS.# Installing libnl/libnl-3 depends on Yum - y install libnl libnl devel
(4) Install keepalived
make && make install
(5) The configuration file is in / etc / kept / kept conf
(6) If you forget to install the configured directory, you can find it through the following command:
whereis keepalived
(7) Start keepalived
Enter sbin directory
./keepalived
2. Configuring a keepalived host
(1) Via the command VIM keepalived Conf open configuration file
global_defs { # route id: Current installation keepalived Node host identifier to ensure global uniqueness router_id keep_171 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { # Indicates that the status is MASTER Host or standby BACKUP state MASTER # Network card bound to this instance interface ens33 # Ensure that the primary and standby nodes are consistent virtual_router_id 51 # Weight, master The weight is generally higher than backup,If there are more than one, it is election. Whoever has a high weight will be elected priority 100 # Synchronization check interval between active and standby, in seconds advert_int 2 # Authentication authority password to prevent illegal nodes from entering authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } # The virtual ip can have multiple (vip) virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.1.161 }}
Attachment: command to view network card information
ip addr
(2) Start keepalived
(3) View process
ps -ef|grep keepalived
(4) View VIP (virtual ip)
Under the network card ens33, there is an additional 192.168.1.161, which is the virtual ip
3. Register keepalived as a system service
(1) Copy profile
-
Set the keepalived directory to etc / init D / kept copied to / etc / init D / down
-
Copy etc/sysconfig / kept in the kept directory to / etc/sysconfig /
(2) Refresh systemctl
systemctl daemon-reload
(3) Start, stop and restart kept
#start-up systemctl start keepalived.service#stop it systemctl stop keepalived.service#Restart systemctl restart kept service
4. Realize dual active standby high availability
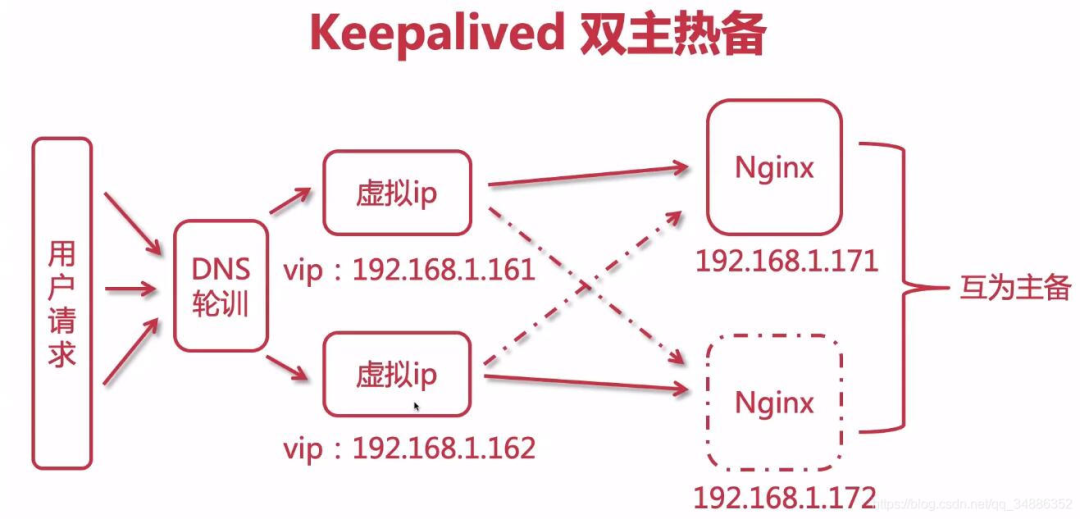
(1) Modify standby configuration
global_defs { router_id keep_172 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { # Standby set to BACKUP state BACKUP interface ens33 virtual_router_id 51 # Weight below MASTER priority 80 advert_int 2 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { # Note: both active and standby VIPs are the same and bound to the same vip 192.168.1.161}}
(2) Start Keepalived
(3) You can access the host by accessing the vip. When the host fails, accessing the vip will access the standby machine
5. keepalived configure nginx automatic restart
(1) Script
Create a script check under / etc / kept /_ nginx_ alive_ or_ not
#!/bin/bash A=`ps -C nginx --no-header |wc -l` # judge nginx Is it down? If so, try restarting if [ $A -eq 0 ];then /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx # Check nginx again after a while. If it fails to start successfully, stop keepalived and start the standby machine sleep 3 if [` PS - C nginx -- no header | WC - L ` - EQ 0]; then killall keepalived fi fi
(2) Add run permissions
chmod +x /etc/keepalived/check_nginx_alive_or_not.sh
(3) Configure keepalived listening nginx script
vrrp_script check_nginx_alive { script "/etc/keepalived/check_nginx_alive_or_not.sh" interval 2 # Run the previous line of script every two seconds weight 10 # If the script fails to run, the upgrade weight is + 10}
(4) In VRRP_ New monitoring script in instance
track_script { check_nginx_alive # Tracking nginx scripts}
(5) Restart Keepalived to make the configuration file effective
systemctl restart keepalived
6. Kept dual active hot standby
(1) Configure DNS polling
Configure two ip addresses under the same domain name to Baidu itself
(2) Configure first host
global_defs { router_id keep_171 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state MASTER i nterface ens33 virtual_router_id 51 priority 100 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.1.161 } } vrrp_instance VI_2 { state BACKUP interface ens33 virtual_router_id 52 priority 80 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.1.162 }}
(3) Configure second host
global_defs { router_id keep_172 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state BACKUP interface ens33 virtual_router_id 51 priority 80 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.1.161 }} vrrp_instance VI_2 { state MASTER interface ens33 virtual_router_id 52 priority 100 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.1.162 }}
(4) Restart two Keepalived
systemctl restart keepalived
7, LVS (Linux Virtual Server) to achieve high availability load balancing
1. Why use LVS+Nginx
-
lvs is based on four layers load balancing , the work efficiency is higher than the seven layer load of Nginx. Using LVS to build Nginx cluster can improve the performance
-
Four layer load balancing can not process information, and can only be forwarded through ip + ports, so 70% of the load is required for data processing
-
When Nginx receives a request back and forth, LVS can only accept no response
2. Three modes of LVS
(1)NAT mode
-
The client sends the request to LVS, and LVS will select a server to respond to the request. The server will return the result to LVS, and LVS will return it to the client.
-
In NAT mode, the gateway of the server must point to LVS, otherwise the message cannot be delivered to the client
-
NAT technology rewrites the address of the requested message and the response message through LVS. Therefore, when the website traffic is relatively large, the load balancing scheduler has a relatively large bottleneck, which generally requires up to 10-20 nodes
-
NAT mode supports IP address and port conversion. That is, the port requested by the user and the port of the real server can be inconsistent
(2)TUN mode
-
The client sends the request to LVS. LVS will select a server to respond to the request, establish a tunnel between the client and the server, and the server will directly return the response when returning the result, not through LVS.
-
In TUN mode, VIP IP addresses must be bound to all servers, and all servers must have network cards.
-
TUN mode is difficult for tunnel operation and maintenance, and will directly expose the server address
-
The server sends the response packet directly to the user. Therefore, a large amount of data flow of the load balancer is reduced. The load balancer is no longer the bottleneck of the system and can handle a huge amount of requests. In this way, a load balancer can distribute to many servers. And running on the public network can be distributed in different regions
(3)DR mode
-
The client sends the request to LVS, and LVS will select a server to respond to the request. When returning the result, it will be returned through a unified route, not through LVS.
-
Like the TUN mode, LVS only distributes requests, and the response packets are returned to the client through a separate route. Compared with TUN, this method does not need a tunnel structure and is compatible with most operating systems. At the same time, the unified route can hide the real physical server. DR mode is more efficient, but the configuration is more complex
-
All server nodes and LVS can only be in one LAN.
3. Build LVS-DR mode
Close the network configuration manager on the server first to avoid network interface conflict
systemctl stop NetworkManagersystemctl disable NetworkManager
(1) Create sub interface (create virtual ip of LVS)
Enter the network card configuration directory / etc / sysconfig / network scripts /, and find the network card configuration file. Take ifcfg-ens33 as an example, copy and create sub interfaces
cp ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-ens33:1
Modify the sub interface configuration as follows
- 192.168.1.150 in the configuration is vip, which is the ip address provided for Internet users to access
DEVICE="ens33:1"ONBOOT="yes"IPADDR=192.168.1.150NETMASK=255.255.255.0BOOTPROTO=static
- service network restart
service network restart
After the restart is successful, check the ip addr. You will find that there is one more ip, that is, virtual ip (vip)
Note: Alibaba cloud does not support the configuration of network cards. You need to purchase corresponding load balancing services. Tencent cloud supports the configuration of network cards, but you need to purchase network card support. One network card supports 10 virtual ip configurations
(2) Install ipvsadm
Today's centos are integrated with LVS, so ipvs comes with it. We only need to install ipvsadm (ipvsadm is a tool for managing clusters. Through ipvs, you can manage clusters, view clusters, etc.)
yum install ipvsadm
(3) Configure the virtual ip of the server (RS)
Enter the network card configuration directory / etc / sysconfig / network scripts /, find ifcfg lo, copy and create sub interfaces
cp ifcfg-lo ifcfg-lo:1
Modify the sub interface configuration as follows
DEVICE="lo:1"IPADDR=192.168.1.150NETMASK=255.255.255.255NETWORK=127.0.0.0BROADCAST=127.255.255.255ONBOOT="yes"NAME=loopback
After restarting the network service successfully, check ip addr. You will find that there is an additional ip, that is, virtual ip (vip)
(4) Configure arp for server (RS)
Description of ARP response level and notification behavior parameters
arp-ignore: ARP Response level (processing request) 0: as long as the machine is configured ip,You can respond to the request 1: Only when the target address of the request reaches the corresponding network interface will the request be responded to arp-announce: ARP Notification behavior (return response) 0: any network interface on this machine will announce to the outside, and all network cards can receive the announcement 1: Try to avoid the announcement between this network card and mismatched targets. 2: only announce on this network card
Open sysctl conf:
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
Configure the arp response level and notification behavior of all network cards, default network cards and virtual network cards, corresponding to: all, default, lo
# configration for lvs net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1 net.ipv4.conf.default.arp_ignore = 1 net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1 net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2 net.ipv4.conf.default.arp_announce = 2 net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2
Refresh profile
sysctl -p
A gateway is added to receive data messages. When a request arrives at the local machine, it will be handed over to lo for processing
route add -host 192.168.1.150 dev lo:1
Add gateway to boot
echo "route add -host 192.168.1.150 dev lo:1" >> /etc/rc.local
(4) Configuring cluster rules using ipvsadm
Create an LVS node and the cluster scheduler accessed by the user
ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.1.150:80 -s rr -p 5
-
-A: Add cluster
-
-t: tcp protocol ip address: set cluster access
-
ip: that is, the virtual ip of LVS
-
-s: Set the load balancing algorithm,
-
rr: indicates polling
-
-p: Set the connection persistence time. Within the specified time, the requests of the same user will access the same server
Create multiple RS real servers
ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.1.150:80 -r 192.168.1.171:80 -g ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.1.150:80 -r 192.168.1.172:80 -g
-
-a: Add real server
-
-t: tcp protocol
-
-r: ip address of real server
-
-g: Set DR mode
Save to the rule base, otherwise the restart will be invalid
ipvsadm -S
Check cluster
#View cluster list ipvsadm -Ln#View cluster status ipvsadm -Ln --stats
Some other commands
# restart ipvsadm,Reconfiguration is required after restart service ipvsadm restart # View persistent connections ipvsadm -Ln --persistent-conn # View connection request expiration time and request source ip And objectives ip ipvsadm -Lnc # set up tcp tcpfin udp Expiration time of (generally remain default) ipvsadm --set 1 1 1 # View expiration time ipvsadm -Ln --timeout
(5) Access virtual ip and complete LVS construction
Load balancing algorithm for LVS
(1) Static algorithm
Static: distribute user requests according to the free fixed algorithm of LVS itself.
-
Round Robin (abbreviated as' rr '): the polling algorithm assumes that all servers have the same ability to process requests, and the scheduler will distribute all requests equally to each real server. (same as polling of Nginx)
-
Weighted round robin (abbreviated as' wrr '): install the weight proportion to allocate user requests. The higher the weight, the more requests are assigned to processing. (same as the weight of Nginx)
-
Source Hash (abbreviated 'sh'): the request of the same user IP will be processed by the same RS. (same as ip_hash of Nginx)
-
Destination Hash (short for 'dh'): request different RS according to different URLs. (same as the url_hash of Nginx)
(2) Dynamic algorithm
Dynamic: user requests will be allocated according to different traffic or server pressure, which is calculated dynamically.
-
Least Connections (abbreviated as' lc '): allocate new connection requests to the server with the smallest number of connections at present.
-
Weighted least connections (wlc): the processing performance of the server is represented by a numerical value. The greater the weight, the more requests will be processed. There may be performance differences between real servers. wlc dynamically obtains the load status of different servers and distributes requests to servers with good performance and relatively idle.
-
Shortest Expected Delay (abbreviated as' sed '): a special wlc algorithm. For example, suppose there are three ABC servers with weights of 1, 2 and 3 respectively. If the wlc algorithm is used, when a new request comes in, it may be distributed to any one of the ABC. After using sed algorithm, the following operations will be performed:
-
A: (1+1)/1=2
-
B: (1+2)/2=3/2
-
C: (1+3)/3=4/3
In the end, the request will be sent to the server with the smallest calculation result. Least queue scheduling (abbreviated 'nq'): never use a queue. If the number of connections to a Real Server is equal to 0, the request will be allocated directly. There is no need to wait in the queue (sed operation).
8, Build a protected + LVS + nginx high availability cluster load balancing
If LVS+nginx is configured on the original server, you need to clear the configuration in ipvsadm
ipvsadm -C
If a Keepalived+Nginx dual master cluster is configured, the original configuration in Keepalived should also be removed and configured as described later
(1) Configuring Master LVS with keepalived
Install on LVS machines keepalived , refer to the above for the installation process
(1) Modify the configuration of keepalived
global_defs { router_id keep_151 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state MASTER interface ens33 virtual_router_id 41 priority 100 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.1.150 }} #Configure cluster access ip+Ports, ports and nginx bring into correspondence with virtual_server 192.168.1.150 80{ #Time of health check, in seconds delay_loop 6 #Configure the load balancing algorithm and the default polling lb_algo rr #set up LVS Mode of NAT|TUN|DR lb-kind DR #Set the duration of session persistence persistence_timeout 5 #agreement protocol TCP #Configure a real server for load balancing, that is nginx Node specific ip address real_server 192.168.1.171 80{ #Polling weight matching weight 1 #Set health check TCP_CHECK { #Check port 80 connect_port 80 #Timeout connect_timeout 2 #retry count nb_get_retry 2 #Retry interval_ before_ retry 3 } } real_server 192.168.1.171 80{ weight 1 TCP_CHECK { connect_port 80 connect_timeout 2 nb_get_retry 2 delay_before_retry 3 } }}
(2) Start / restart keepalived
systemctl restart keepalived
(2) Configuring Backup LVS with keepalived
Configured on standby machine
global_defs { router_id keep_152 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state BACKUP interface ens33 virtual_router_id 41 priority 50 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.1.150 }} #Configure cluster access ip+Ports, ports and nginx bring into correspondence with virtual_server 192.168.1.150 80{ #Time of health check, in seconds delay_loop 6 #Configure the load balancing algorithm and the default polling lb_algo rr #set up LVS Mode of NAT|TUN|DR lb-kind DR #Set the duration of session persistence persistence_timeout 5 #agreement protocol TCP #Configure a real server for load balancing, that is nginx Node specific ip address real_server 192.168.1.171 80{ #Polling weight matching weight 1 #Set health check TCP_CHECK { #Check port 80 connect_port 80 #Timeout connect_timeout 2 #retry count nb_get_retry 2 #Retry interval_ before_ retry 3 } } real_server 192.168.1.171 80{ weight 1 TCP_CHECK { connect_port 80 connect_timeout 2 nb_get_retry 2 delay_before_retry 3 } }}