1. Load balancing: configuring real columns
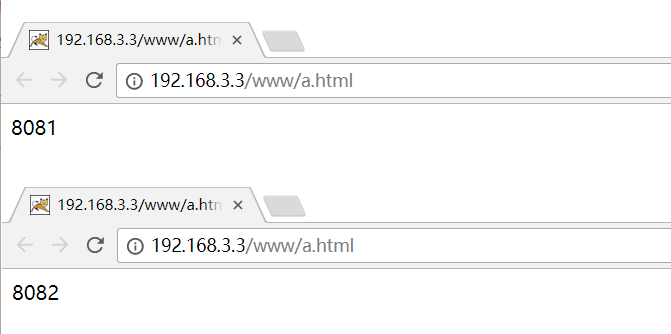
implementation effect: enter the address in the browser address bar http://192.168.xxx.xxx/www/a.html , load balancing effect, average to ports 8081 and 8082
preparation:
1. Prepare two tomcat servers, one 8081 and one 8082
[root@localhost ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 802047bd7530 nginx "/docker-entrypoin..." 17 hours ago Up 27 minutes 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp mynginx afb277b2006e mytomcat "catalina.sh run" 21 hours ago Up 16 minutes 0.0.0.0:8081->8080/tcp mytomcat1 ba962911646b mytomcat "catalina.sh run" 21 hours ago Up 11 minutes 0.0.0.0:8082->8080/tcp mytomcat2
2. Create folders and test pages
since you will find it from the ROOT file under webapps, you can create it in the ROOT directory
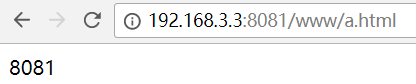
Access path: http://192.168.3.3:8081/www/a.html
[root@localhost ~]# docker exec -it afb277b2006e bash root@ba962911646b:/usr/local/tomcat# cd webapps/ROOT/www/ root@ba962911646b:/usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT/www# ls a.html
8081 port display interface
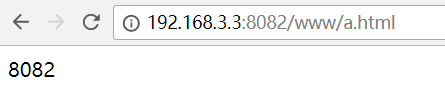
access path: http://192.168.3.3:8082/www/a.html
[root@localhost ~]# docker exec -it ba962911646b bash root@ba962911646b:/usr/local/tomcat# cd webapps/ROOT/www/ root@ba962911646b:/usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT/www# ls a.html
8082 port display interface
3. Configure in nginx
3.1 the document is in root@802047bd7530 : / # CD nginx under etc / nginx / conf
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
#Add myserver for load balancing
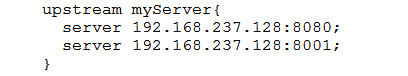
upstream myserver {
server 192.168.3.3:8081;
server 192.168.3.3:8082;
}
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}
3.2 the document is in root@802047bd7530:/# cd etc/nginx/conf.d/ conf
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
#Change localhost to ip address
server_name 192.168.3.3;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# proxy_pass http://192.168.3.3:8080;
#Load the configured myserver to achieve load balancing
proxy_pass http://myserver;
index index.html index.htm;
}
# location ~ /yee/ {
# proxy_pass http://192.168.3.3:8081;
# }
# location ~ /yew/ {
# proxy_pass http://192.168.3.3:8082;
# }
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
nginx. The listening port defaults to 80. Access test: http://192.168.3.3/www/a.html
2. Equilibrium strategy
2.1 round robin (default)
each request is allocated to different application servers one by one in chronological order. If the application server goes down, it can be automatically eliminated.
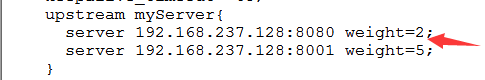
2.2 weight
specify the polling probability by configuring the weight. The weight is directly proportional to the access ratio, which is used in the case of uneven performance of the application server. Default: weight=1
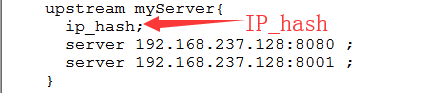
2.3 ip_ Hash algorithm
each request is allocated according to the hash result of the access ip. In this way, each visitor accesses an application server regularly, which can solve the problem of session sharing
2.4 least_conn minimum connection
forward the request to the back-end server with fewer connections. Polling algorithm is to forward requests to each back end evenly to make their load roughly the same; However, some requests take a long time, resulting in a high load on the back end. In this case, least_conn this way can achieve better load balancing effect
upstream dynamic_zuoyu {
least_conn; #Forward the request to the back-end server with fewer connections
server localhost:8080 weight=2; #tomcat 7.0
server localhost:8001; #tomcat 8.0
server localhost:8082 backup; #tomcat 8.5
server localhost:8083 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=20s; #tomcat 9.0
}
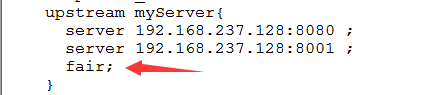
2.5 Fair (third party)
requests are allocated according to the response time of the back-end server, and those with short response time are allocated first
2.6 url_hash (third party)
allocate the request according to the hash result of the access url, so that each url is directed to the same back-end server, which is more effective when the back-end server is cache

| fail_timeout | max_ Use with failures |
|---|---|
| max_fails | Set in fail_ The maximum number of failures within the time set by the timeout parameter. If all requests to the server fail within this time, the server is considered to be down |
| fail_time | The length of time that the server will be considered down. The default is 10s |
| backup | Mark the server as an alternate server. When the primary server stops, requests are sent to it |
| down | Mark the server down permanently |