catalogue
1, Installing and configuring mysql module
1. Steps to operate mysql in a project
2. Install and configure mysql module
(3) Test whether the mysql module works normally
2, Using MySQL module to operate MySQL database
1, Installing and configuring mysql module
1. Steps to operate mysql in a project
- Install the third-party module (mysql) that operates the mysql database
- Connect to MySQL database through MySQL module
- Execute SQL statements through mysql module
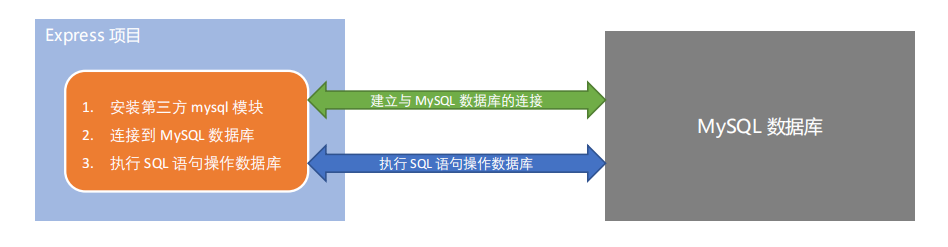
2. Install and configure mysql module
(1) Install mysql module
The mysql module is hosted on npm
Third party module
. It provides in node JS project
connect
and
operation
MySQL database capabilities.
To use it in the project, you need to run the following command to install mysql as the dependent package of the project:
npm install mysql
(2) Configure mysql module
Before using the MySQL module to operate the MySQL database,
The mysql module must be configured first
, the main configuration steps are as follows:
(1) Import mysql module
(2) create database connection pool
(2) create database connection pool
mysql.createPool({
connectionLimit: the maximum number of connections. The default value is 0,
multipleStatements: whether multiple sql statements are allowed to be executed. The default value is false
host: database server address,
Database: database name,
User: user name,
Password: password
connectionLimit: the maximum number of connections. The default value is 0,
multipleStatements: whether multiple sql statements are allowed to be executed. The default value is false
host: database server address,
Database: database name,
User: user name,
Password: password
})
(3) Get database connection object
pool.getConnection(function(err,conn){})
Code demonstration:
// 1. Import mysql module
const mysql = require('mysql');
//2. Establish link relationship with mysql database
const db = mysql.createPool({
host: '127.0.0.1', //IP address of the database
user: 'root', // Account to log in to the database
password: '123456',
database:'dbtest' // Specify which database to operate on
})(3) Test whether the mysql module works normally
Call dB The query() function specifies the SQL statement to be executed and gets the execution result through the callback function
// Test whether the mysql module works normally
db.query('select 1', (err, results) => {
// An error was reported during mysql operation
if (err) return console.log(err.message);
// The SQL statement can be executed successfully
console.log(results);
}) [note]: as long as the results of [rowdatepacket {'1': 1}] can be printed, it proves that the database can be connected normally
2, Using MySQL module to operate MySQL database
1. Query data
Query all data in the employees table:
// Query all data in the table
const sqlStr = 'select * from employees';
db.query(sqlStr, (err, results) => {
// If the query is successful
if (err) return console.log(err.message);
//If the query is successful
console.log(results);
}) 2. Insert data
Add data to the employees table
// insert data
const user = { name: 'Huashaobei', gender: 'male' }
// Define the SQL statement to be executed? Represents a placeholder
const sqlStr = 'insert into employees(name,gender) values(?,?)';
//Execute SQL statement
db.query(sqlStr, [user.name, user.gender], (err, results) => {
if (err) return console.error(err);
// If the execution is successful, judge whether the number of affected rows is equal to 1
//Note: if the insert into statement is executed, results is an object,
//You can judge whether the data is inserted successfully by the affectRows property
if (results.affectedRows === 1) {
console.log('Insert successful');
}
}) Convenient way to insert data:
When adding data to the employees table, if
Each attribute of the data object and the fields of the data table
One to one correspondence
, you can
To quickly insert data:
// Convenient way to insert data
const user = { name: 'Some fantasy', gender: 'male', birthday: '1999-04-02', address: 'Qingdao' };
// //SQL statement to be executed
const sqlStr = 'insert into employees set ?';
// //Execute statement
db.query(sqlStr, user, (err, results) => {
if (err) return console.log(err.message);
if (results.affectedRows===1) {
console.log('Insert successful');
}
}) 3. Update data
When updating the employees table data, if
Each attribute of the data object
and
Data table fields
One to one correspondence
, you can
Method to quickly update table data
// Convenient way to update data
const user = { id: 5, name: 'Huashaobei', birthday: '1996-09-08', phone: '145875xxxxx' };
//Define SQL statement
const sqlStr = 'update employees set ? where id=?'
//Execute statement
db.query(sqlStr, [user, user.id], (err, results) => {
if (err) return console.log(err.message);
if (results.affectedRows) {
console.log('Data update succeeded');
}
}) 4. Delete data
When deleting data, it is recommended to delete the corresponding data according to the unique id. Examples are as follows:
//Delete user with id 5
//Define SQL statement
const sqlStr = 'update employees set ? where id=?'
//Execute statement
db.query(sqlStr, 5, (err, results) => {
if (err) return console.log(err.message);
if (results.affectedRows==1) {
console.log('Data deleted successfully');
}
})