1, Introduction to Nodejs
1. Getting to know NodeJS
NodeJS is a javascript running environment based on Chrome V8 engine.
2. Module
There are many built-in API modules in NodeJS: fs, path, http, js built-in object, querystring, etc; Cannot operate without DOM and BOM.
3. Learn what NodeJS can do?
1. web application development can be done based on the express framework of Node
2. It can build cross platform desktop applications based on the Electron framework
3. Can be based on the restify framework. Interface development can be implemented
4. You can operate and process the database
2, Install NodeJS
Search the Internet for the Chinese version of NodeJS, download the v16.13.0 document, and then install it according to the prompts; After downloading, you can enter node -v on the cmd command line. If you use it in the code, use ctrl + ` backquotes to enter the terminal, and then enter node xx.js.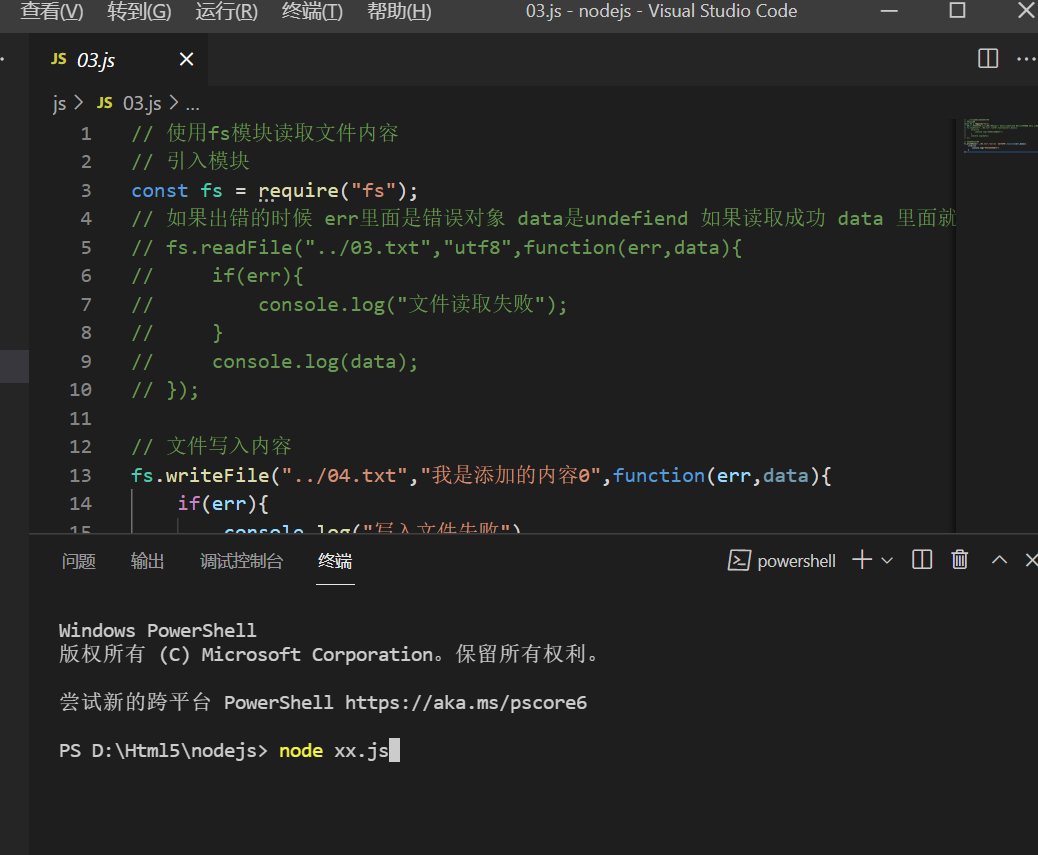
3, fs file system module
1. readFile read file
fs module is a module for operating files provided by NodeJS.
Syntax of reading file: fs.readFile(path[,options],callback)
Code example:
// Read file contents using fs module
// Introduction module
const fs = require("fs");
// If an error occurs, the error object is in err and the data is undefiend. If the reading is successful, the data is in data
// 03.txt is created by yourself. Enter the content in it
fs.readFile("../03.txt","utf8",function(err,data){
if(err){
console.log("File read failed");
}
console.log(data);
});2. writeFile write file
Syntax: fs.writeFile(file,data[,options],callback)
Code example:
// Introduction module
const fs = require("fs");
// File write content
// 04.txt you can create a new file or not. The code will create a new file after running
fs.writeFile("../04.txt","I am adding 0",function(err,data){
if(err){
console.log("fail to write to file")
}
})3,_ dirname automatically gets the directory where the file is located
// Introduction module
const fs = require("fs");
// File write content
// 04.txt you can create a new file or not. The code will create a new file after running
fs.writeFile(_dirname + "../04.txt","I am adding 0",function(err,data){
if(err){
console.log("fail to write to file")
}
})
// _ dirname dynamically obtains the directory and automatically obtains the address where the file is located4, path module
The path module is a module officially provided by NodeJS that deals with paths
1,path.join()
The path.join() method can splice multiple path fragments into a complete path
Syntax: path.join([...path])
const path = require("path");
let str = "D:\Html5\nodejs\js";
let filename = "../html/00.html";
console.log(path.join(str,filename))2,path.basename
The path.basename() method can resolve the file name in the provided path string
Syntax: path.basename(path[,ext])
const path = require("path");
const str = "code/test/01.txt";
console.log(path.basename(str)); //01.txt get the full file name
console.log(path.basename(str, ".txt")); //01 get file name after excluding suffix
3,path.extname
Gets the suffix of the file
Syntax: path.extname(path)
const path = require("path");
const str = "code/test/01.txt";
console.log(path.extname(str)); //. txt get the suffix of the file
5, Http module
Use steps:
- Introduce http module
- Create web server request
- Listen for client requests
- Start the server
Template:
const http = require("http");
const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request", (req, res) => {
console.log("The server has been requested");
});
server.listen(80, () => {
console.log("server is listen:127.0.0.1");
});1,req Test get request
req is the request object captured from the client to the server. The attributes are:
- req.url can get the address requested by the client
- req.method can obtain the method of client request
Code example:
// The http module in nodejs is connected to the local server
const http = require("http");// Introduction module
const server = http.createServer();// Create local service example
// Listen for requests sent by clients
server.on("request",(req,res)=>{
// Req refers to the request method req.mthod and the request address req.url sent by the request object acquisition front end
// res is the content returned to the client by the response object
// console.log(req.url);
// console.log(req.method);
console.log(req.url);// Get request address
console.log(req.method);// Get request method
res.end("hello world");
});
server.listen("80",()=>{
console.log("The local service has started https://127.0.0.1 ");
})2. post request
To test the post request, you need to borrow a software postman; This can be found on the Internet. It is an interface testing tool. It can simulate all kinds of HTTP requests initiated by users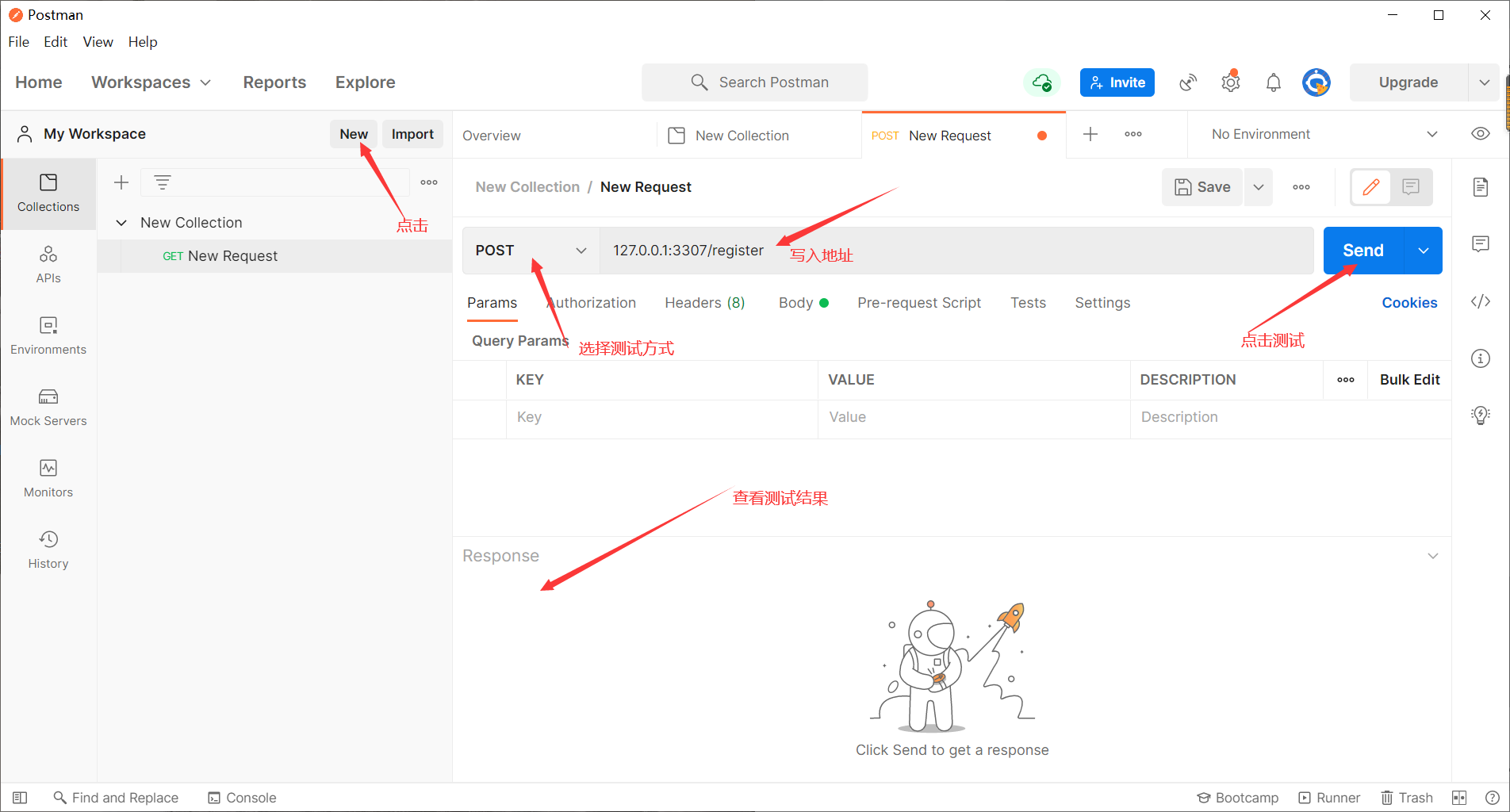
3,res Response content Response garbled code
If the code changes, you can exit with ctrl+c, and then start the service.
Code example:
// The http module in nodejs is connected to the local server
const http = require("http");// Introduction module
const server = http.createServer();// Create local service example
// Listen for requests sent by clients
server.on("request",(req,res)=>{
// Set response header
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=utf-8");// Solve the problem of response garbled code
res.end("China chane")
});
server.listen("80",()=>{
console.log("The local server has started https://127.0.0.1 ");
})4. Different addresses respond to different contents
Code example:
// The http module in nodejs is connected to the local server
const http = require("http");// Introduction module
const server = http.createServer();// Create local service example
// Listen for requests sent by clients
server.on("request",(req,res)=>{
// Req refers to the request method req.mthod and the request address req.url sent by the request object acquisition front end
// res is the content returned to the client by the response object
// console.log(req.url);
// console.log(req.method);
// console.log(req.url);
// console.log(req.method);
// res.end("hello world");
// Resolve response garbled code
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=utf-8");
// // index.html home page / detail.html detail page 404 page
if(req.url == "/"||req.url=="/index.html"){
res.end("Home page content");
}else if(req.url=="/detail.html"){
res.end("Detail page");
}else{
res.end("404 page")
}
});
server.listen("80",()=>{
console.log("The local service has started https://127.0.0.1 ");
})6, Package management tools
Package is what we call module or software; The download method is also to enter the terminal through ctrl + ` backquote and enter the command in the terminal. Download command
The npm install package name is the latest version installed by default
npm install package name @ version number can install the specified version 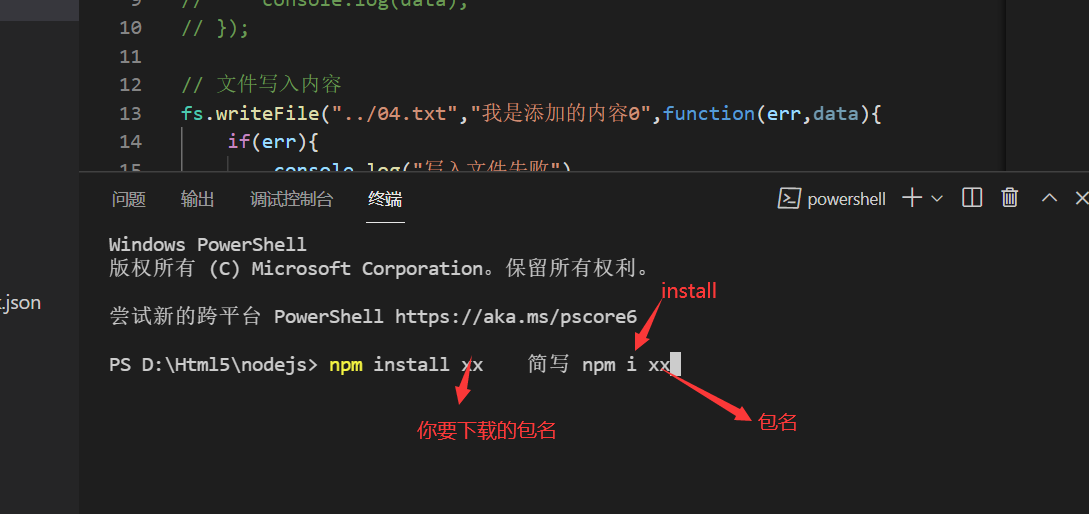
7, express
express is a Node js web application development framework.
1. Basic use
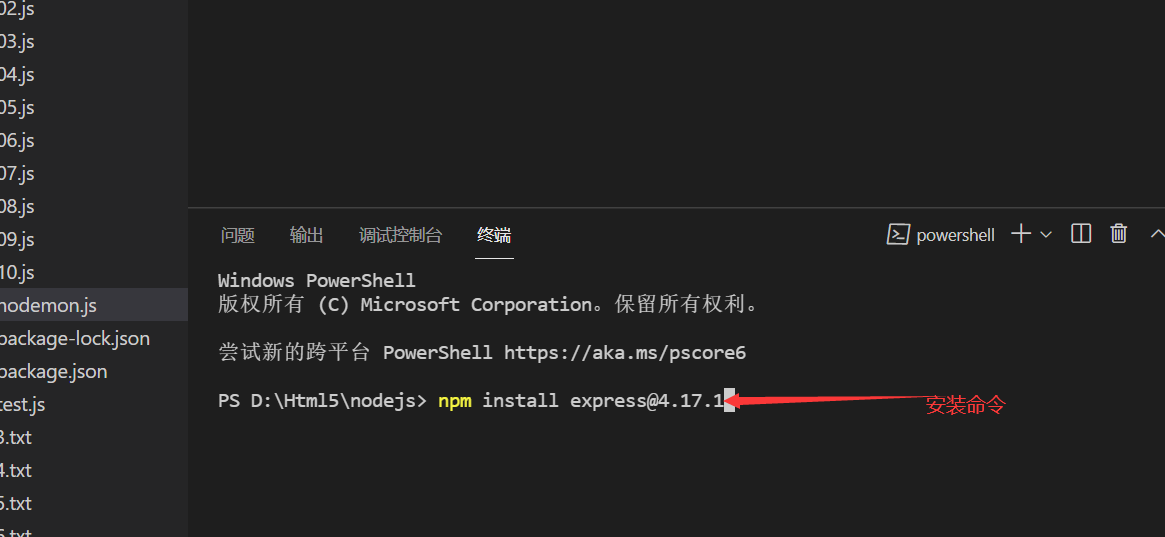
Code template:
// Building web services with express framework
const express = require("express");//1. Introduction framework
const app = express();//2. Create service instance
//app.use(express.static("./test"));
// Start service
app.listen("80",() => {
console.log("The server has started 127.0.0.1");
});2. get and post requests for express
Code example:
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
// Send get request / product enter 127.0.0.1 in the address bar
app.get("/product",(req,res)=>{
res.send("get Request for data information");
});
// Send a post request / product/add. Enter 127.0.0.1 in the address field
app.post("/product/add",(req,res)=>{
res.send("post Request for add function")
});
// Start service
app.listen("80",()=>{
console.log("The service has started 127.0.0.1")
});Test through postman and enter the corresponding address command in the address bar.
3. Get request parameters Get request get parameters
req.query can get the parameters requested by the client
app.get("/user", (req, res) => {
let msg = req.query;
res.send({ code: 200, msg: msg, status: 1 });
});Dynamic parameters:
// Send get request
app.get("/user/:id/:name", (req, res) => {
let msg = req.params;
res.send({ code: 200, msg: msg, status: 1 });
});