Object oriented programming of Java core
essence
Organize code in the form of class and encapsulate data in the form of object
Review method calls
static
Static method
static is loaded with the class
//demo01
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
student.say();//Direct call
}
}
//student
public class student {
public static void say(){
System.out.println("The student spoke");
}
}
Non static method
Class does not exist until it is instantiated
// Instantiate this class new
// Object type object name = object value;
student stu=new student();
stu.say();
contrast
public static void a(){
b();//Cannot call because b is not instantiated and does not exist at this time
}
public void b(){
System.out.println("call b method");
}
Reference pass parameter
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
person per=new person();//Instantiation class
System.out.println(per.name);
change(per);//The object here is still a value passed parameter
System.out.println(per.name);
}
public static void change(person per){
per.name="Qin River";
}
}
class person{
String name;
int age;
}
Method overloading
Method overloading: multiple methods have the same name but different formal parameter lists
object
Creation of classes and objects
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
person per=new person();//Instantiation class
System.out.println(per.name);
change(per);//The object here is still a value passed parameter
System.out.println(per.name);
}
public static void change(person per){
per.name="Qin River";
}
}
class person{
String name;
int age;
}
constructor
Even if a class doesn't write anything, there will be a method
effect:
1. Using the new keyword is essentially a call to the constructor
2. The value used to initialize the object
be careful:
1. A parameterless construct is defined. If you want to use a parameterless construct, you must define a parameterless construct
Shortcut key generation constructor:
Alt+insert
Create object memory analysis
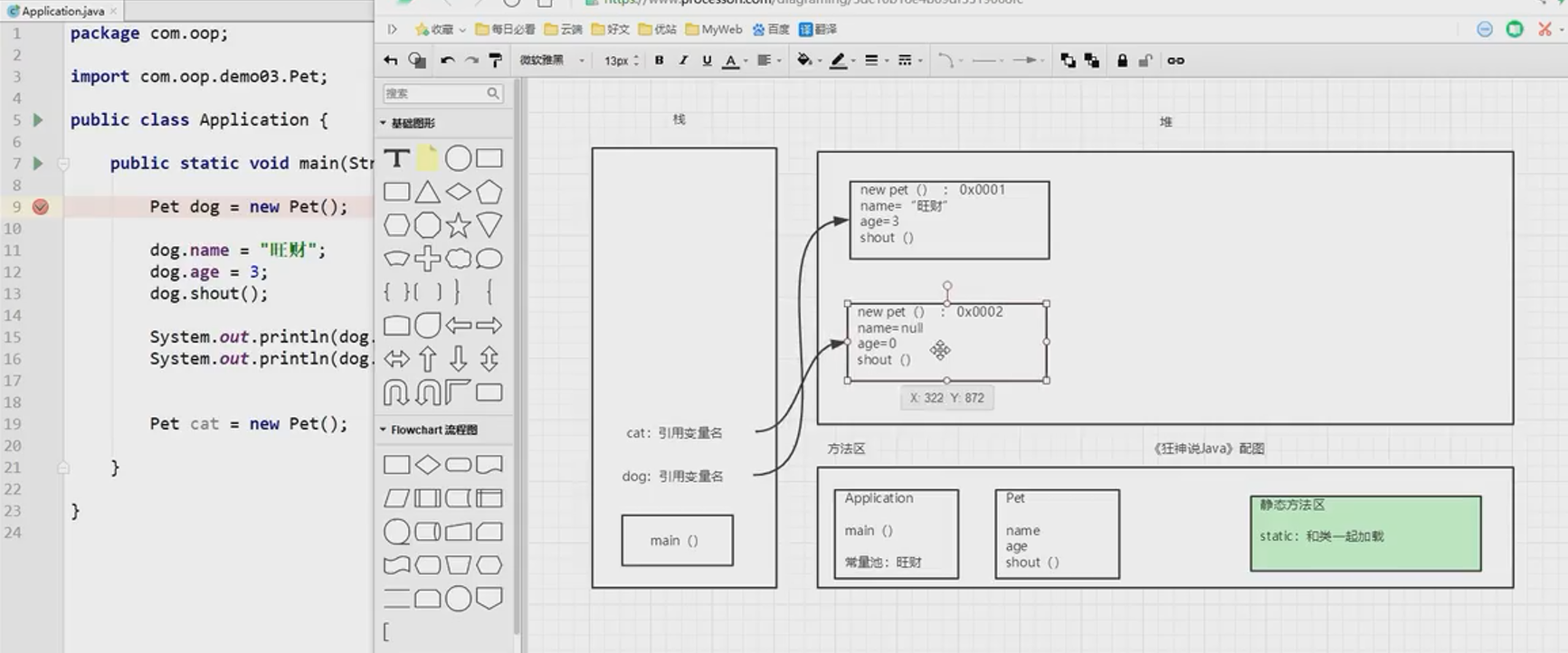
Three characteristics
encapsulation
"High cohesion, low coupling"
Private: private
private String name; private int id; private String sex;
Get get data
public String getName() {
return name;
}
set assigns a value to the data
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
Shortcut key: Alt+insert
inherit
1. Essence: the abstraction of a certain batch of classes for better modeling
2. Classes in Java only have single inheritance, not multiple inheritance;
3. Inheritance is the relationship between classes
4. Subclasses inherit the parent class with extensions. Subclasses can call methods and properties in the parent class
public class student extends Person{}
5. All classes in Java will inherit object indirectly or directly
public class student extends Object{}
6. The private property of the parent class cannot be inherited
Super
1. super calls the constructor of the parent class, which must be placed first in the constructor;
2. super must only appear in the methods or constructors of subclasses;
3. super and this cannot be used at the same time;
4. If there is only parameter construction in the parent class, the child class cannot call the parameterless construction of the parent class. At this time, super(); Cannot be called, but super(123); The parent class can be called to construct with parameters;
The difference between this and super
1. Different representative objects:
this object is the caller
super: represents the parent object application
2. Premise:
this: it can be used without inheritance
super: only used under inheritance conditions
3. Construction method:
this(); This kind of structure
super(); Parent class construction
Method rewrite
The subclass overrides the method of the parent class. All overrides are method overrides and have nothing to do with attributes
1. Same method name
2. The parameter list must be the same
3. Modifier: the scope can be expanded public > protected > Default > private
4. Throwing a field can be abbreviated, but it cannot be expanded
Shortcut key: Alt+insert: override;
polymorphic
Dynamic compilation
public class duoTai {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person s1=new Student();//The reference of the parent class points to the child class
Student s2=new Student();
s1.run();//son performed a method override
s2.run();//son
// s1.eat(); It cannot be executed because the method that the instance object can implement is related to the object type on the left, but not to the object type on the right
((Student)s1).eat();//Can be executed after cast
s2.eat();
}
}
public class Person {
public void run(){
System.out.println("father");
}
}
public class Student extends Person{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("son");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat");
}
}
matters needing attention:
1. Polymorphism is the polymorphism of methods, and there is no polymorphism of attributes
2. Existence conditions: inheritance relationship; Method needs to be overridden, and the parent class reference points to the child class override
3. static, final, private, etc. cannot be rewritten
Type conversion (instanceof)
High to low: forced conversion
Low to high: precision may be lost without forced conversion
Some methods may be lost when a subclass turns into a parent class
((Student)s1).eat();//Parent class, rotor class, cast
static keyword
public class person {
{//2 can be used for assignment
System.out.println("Anonymous code block");
}
static {//1 execute only once
System.out.println("Static code block");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {//3
person per1=new person();
System.out.println("============");
person per2=new person();
}
}
Static import package
import static java.lang.Math.random; System.out.println(random());//call
abstract class
1. new is not an abstract class, but can only be implemented with subclasses. It is the existence of constraints
2. Ordinary methods can be written in abstract classes
3. Abstraction can be used to improve development efficiency
4. Abstract classes are abstract
Interface
The essence of interface is contract
1. Constraints
2. Define some methods for different people to realize
3. The interface cannot be instantiated and has no construction method
4.implements can implement multiple interfaces
5. The method in the interface must be rewritten
Steps:
1. interface creation
2. Define methods on the interface
public interface UserServer {
int age=100;
void add(String name);
void delete(String name);
void update(String name);
void query(String name);
}
2. Use the implements interface in the class and override the method
public class UserServerImpl implements UserServer,TimeServer{
@Override
public void add(String name) {
}
@Override
public void delete(String name) {
}
@Override
public void update(String name) {
}
@Override
public void query(String name) {
}
}
Inner class
Internal classes can access private properties
public static void main(String[] args) {
outer app=new outer();
outer.inner Inner=app.new inner();
Inner.inner();
}
public class outer {
private int a=100;//Private property
public void outer(){
System.out.println("This is an external class method");
}
public class inner{
public void inner(){
System.out.println("This is an inner class method");
System.out.println(a);//Access private properties
}
}
}
args) {
outer app=new outer();
outer.inner Inner=app.new inner();
Inner.inner();
}
public class outer {
private int a=100;//Private property
public void outer(){
System.out.println("This is an external class method");
}
public class inner{
public void inner(){
System.out.println("This is an inner class method");
System.out.println(a);//Access private properties
}
}
}