Multi table query, sub query, common function
1, Multi table query
Multi table query: connect multiple tables through key fields with the same meaning in different tables to query the field information in different tables.
Correspondence
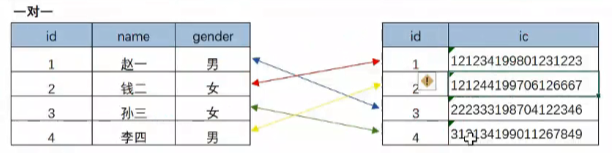
One to one: for example, the personnel information table and the personnel identity card corresponding table below, one employee will have only one ID number.
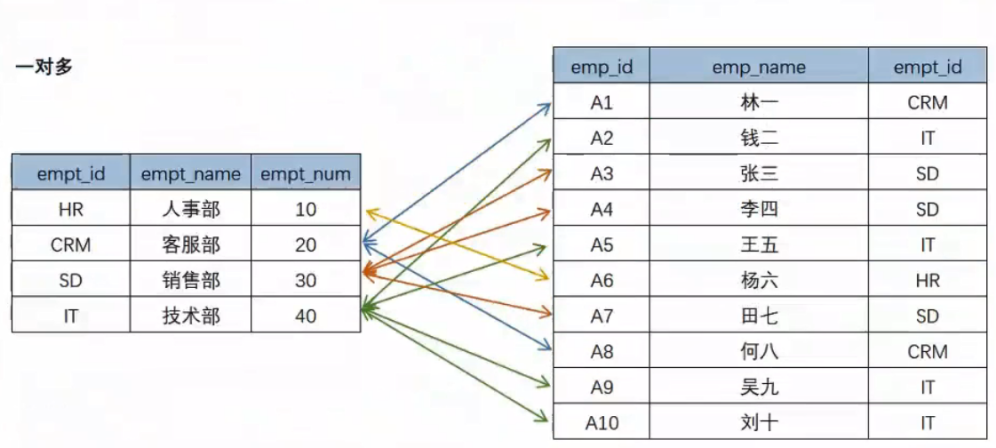
One to many: for example, in the Department information table and department personnel table in the following figure, there may be multiple employees in a department;
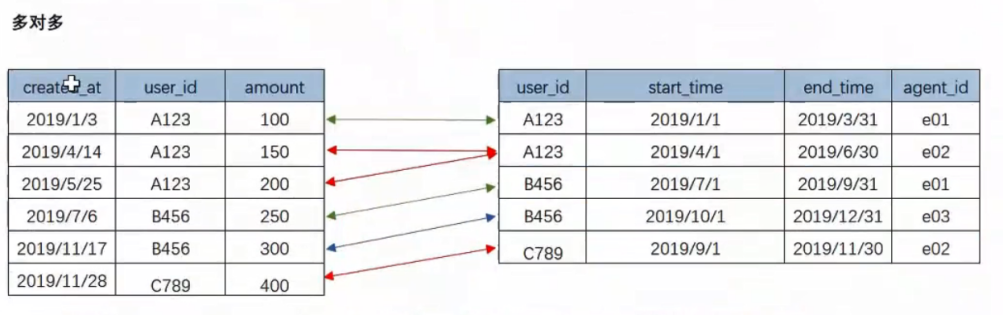
Many to many: the many to many situation is more complex. It is recommended to split the table, so as to save storage space and avoid data redundancy;
Connection mode
Inner connection and outer connection (left outer connection and right outer connection).
The result of multi table connection is determined by three attributes
- Directionality: in the external connection, the table written in the front is the left table, and the table written in the back is the right table;
- Master attachment relationship: all data ranges should be listed in the master table. If there is no matching item between the attached table and the master table, it is marked as null, and there is no master attached table in internal connection;
- Correspondence: tables with duplicate values in key fields are multiple tables, and tables without duplicate values are one table;
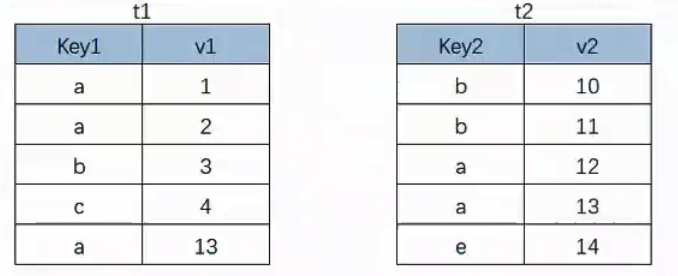
For example, table t1 and table t2 in the above figure:
If left outer connection: t1 is the main table and t2 is the attached table;
If the right outer connection: t2 is the main table and t1 is the attached table;
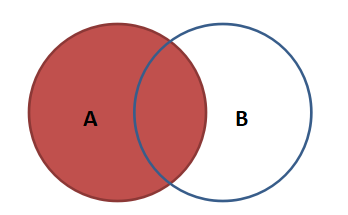
Left connection:
In addition to the rows that meet the connection conditions, the result also includes all rows of the left table.
select field 1[,...] from table 1 left join table 2 on table 1 Key = Table 2 key;
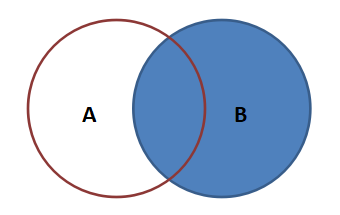
Right connection:
In addition to the rows that meet the connection conditions, the result also includes all the rows on the right.
select field 1[,...] from table 1 right join table 2 on table 1 Key = Table 2 key;
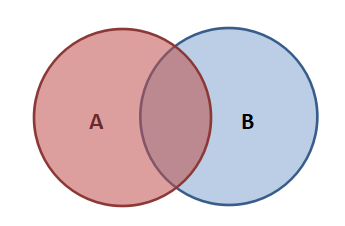
Internal connection:
Merge the two tables according to the connection conditions and return the rows that meet the conditions.
There is no master-slave relationship and no direction.
select field 1[,...] from table 1 [inner] join table 2 on table 1 Key = Table 2 key;
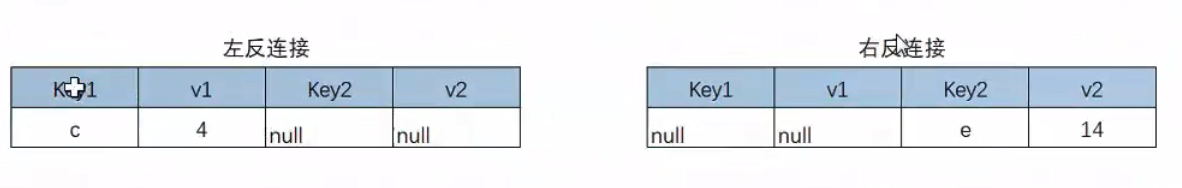
In addition, among other tools, there are full connection, left reverse connection and right reverse connection (Power BI).
-- Inner connection select * from t1 inner join t2 on t1.key1 = t2.key2; -- Left connection select * from t1 left join t2 on t1.key1 = t2.key2; -- Right connection select * from t1 right join t2 on t1.key1 = t2.key2;
Vertical consolidation (joint query):
Merge the query results of multiple select statements into one result set, that is, append / add records.
It refers to the vertical consolidation of data sets, from which the data sets are merged to the master data set.
 be careful:
be careful:
Two tables must have the same number of fields;
The order of fields in two tables must be the same;
The data types of the fields of the two tables must be the same;
Field names can be different. Select the field name in the main dataset (the first table).
Union de duplication: select field 1 [, field 2,...] from table name union select field 1 [, field 2,...] from table name;
Union all: select field 1 [, field 2,...] from table name union all select field 1 [, field 2,...] from table name;
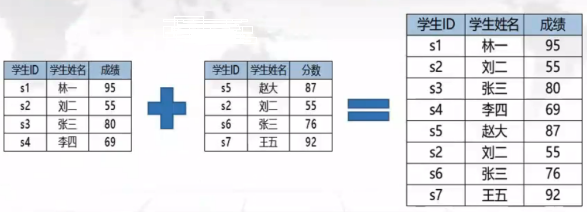
-- Merge query select * from t1 union all select * from t2; -- union duplicate removal select * from t1 union select * from t2;
[test questions]
Table a userid
Table b userid
The query appears in table a, not in the userid of table b.
Idea: left reverse connection and right reverse connection
select * from table_a left join table_b on table_a.userid = table_b.userid where table_b.userid is null;
order table: userid, endtime
Find the latest end time of each userid
select userid,max(endtime) from order group by uderid;
order table: userid, endtime
user table: userid, tel
Find the tel of the userid whose end time is in March
select order.userid, user.tel from user right join order on user.userid = order.userid where month(endtime) = 3; select order.userid, user.tel from user right join order on user.userid = order.userid where endtime between '2021-03-01' and '2021-03-31';
Query the employee name and the corresponding leader name in a table
-- Self connection: by setting alias, the same table is regarded as two tables select t1.ename Employee name,t2.ename Leader name from emp t1 left join emp t2 on t1.mgr = t2.empno;
Query the information of employees whose entry date is earlier than their direct leaders: empno, ename, dName (department table)
select t1.empno Employee number,t1.ename Employee name,t3.dname Department name from emp t1 left join emp t2 on t1.mgr = t2.empno inner join dept t3 on t1.deptno = t3.deptno where t1.hiredate < t2.hiredate;
2, Subquery
Subquery: contains one or more complete select statements in a select statement.
Where the subquery appears
Appear in the where clause: take the results returned by the sub query as the conditions of the main query;
Appear in the from clause: take the results returned by the sub query as a table of the main query;
Classification of subqueries
- Scalar subquery: the returned result is a data (single row and single column);
- Row sub query: the returned result is one row (single row and multiple columns);
- Column subquery: the returned result is one column (multiple rows and single column);
- Table sub query: the returned result is a temporary table (multiple rows and columns);
Operator of subquery:
- [NOT] IN: in [not in]
- ANY: ANY one of them
- ALL: ALL (each)
--Subquery: scalar subquery
-- Query the information of employees whose basic salary is higher than the average salary of the company(where Aggregate functions cannot be used directly in clauses) select * from emp where sal > (select avg(sal) from emp); -- Query the employee information of the same leader as "Zhang Xiaoming": empno,ename,job,mgr select empno,ename,job,mgr from emp where mgr = (select mgr from emp where ename = 'Zhang Xiaoming') and ename <> 'Zhang Xiaoming';
--Subquery: row subquery
-- Query the employee information of the same department and position as "Xu Feilong": empno,ename,job,deptno select empno,ename,job,deptno from emp where (deptno,job) = (select deptno,job from emp where ename = 'Xu Feilong') and ename <> 'Xu Feilong';
--Subquery: column subquery
-- Query salary grade of ordinary employees: empno,ename,sal,grade select empno Employee number,ename Employee name,sal base pay,grade Wage scale from emp left join salgrade on sal between losal and hisal where empno not in (select distinct mgr from emp where mgr is not null); -- Query all employee information of the Department with no less than 3 employees: empno,ename,deptno -- Idea: first find out the department number of more than or equal to 3 people select empno,ename,deptno from emp where deptno in (select deptno from emp group by deptno having count(*) >= 3); -- Query the employee information of any employee whose basic salary is higher than 51 departments select * from emp where sal > any (select sal from emp where deptno = 51) and deptno <> 51; select * from emp where sal > (select min(sal) from emp where deptno = 51) and deptno <> 51; -- Query the employee information of all employees in departments whose basic salary is higher than 51 select * from emp where sal > all (select sal from emp where deptno = 51) and deptno <> 51;
--Subquery: from subquery
-- Query the highest paid employees in each department: empno,ename,sal,deptno -- Table subqueries must have aliases set select empno,ename,sal,emp.deptno from emp left join (select deptno,max(sal) as Maximum wage from emp group by deptno) as t on emp.deptno = t.deptno where sal = Maximum wage;
3, Functions
--String function
select concat('My','Name','Is','Jack'); #MyNameIsJack
select concat('My','Name','Is',null); #null
select instr('ABCDE','C'); #3
select left('ABCDE',4); #ABCD
select right('ABCDE',4); #BCDE
select mid('ABCDEFG', 3, 4); #CDEF
select mid('ABCDEFG', 3); #CDEFG
select substring('ABCDEFG', 3, 4); #CDEF
select substring('ABCDEFG', 3); #CDEFG
select ltrim(' ABC'); #ABC
select rtrim('ABC '); #ABC
select trim(' ABC '); #ABC
select replace('ABCdeF','de','DE'); #ABCDEF
select repeat('Shit',3); #ShitShitShit
select reverse('ABCDE'); #EDCBA
select upper('abcde'); #ABCDE
select lower('ABCDE'); #abcde
-- The first letter of the name in the employee table is capitalized and the other letters are lowercase
select concat(upper(left(ename,1)),lower(mid(ename,2))) from emp;Mathematical function
For example:
abs() absolute value
Floor (rounded down) – floor
Ceiling – ceiling
round(), the second parameter is the number of decimal places reserved
rand() returns a random decimal number between 0 and 1
select rand(1); The input random seeds are the same, and the results are the same.
Date time function
date() returns the date of the specified date time expression or converts a text string format date to a standard date format
select date('20200101'); #2020-01-01
select date('2020-01-01 11:11:11'); #2020-01-01
select week('2022-01-01'); #0
select month('2020-01-01 11:11:11'); #1
select quarter('2020-12-01 11:11:11'); #4
select year('2020-12-01 11:11:11'); #2020
select year('20-12-01'); #2020
select date_add('2022-01-01',interval 1 day); #2022-01-02
select date_add('2022-01-01',interval 1 year); #2023-01-01
select adddate('2022-01-01',interval 1 month); #2022-02-01
select date_sub('2022-01-01',interval 1 day); #2021-12-31
select date_sub('2022-01-01',interval 1 year); #2021-01-01
select subdate('2022-01-01',interval 1 month); #2021-12-01
select date_format('2022-01-06 15:05:20','%Y-%m-%d'); #2022-01-06
select date_format('2022-01-06 15:05:20','%Y-%m'); #2022-01
select date_format('2022-01-06 15:05:20','%m'); #01
select curdate(); #Nonparametric function, current computer system date
select curtime(); #Nonparametric function, current computer system time
select now(); #Nonparametric function, date and time of current computer system
select datediff('20220106','20211228'); #9 days between dates
-- Calculate the length of service of each employee in the employee table
use test;
select ename full name,hiredate Entry date,round(datediff(curdate(),hiredate)/365) working years
from emp;
select unix_timestamp(); #How many seconds has passed since the current date started from 1970-01-01 00:00:00
select unix_timestamp('2022-01-06'); #1641398400
select from_unixtime(1641473220); #2022-01-06 20:47:00
-- Query the probation end date of each employee (probation period is three months): ename,hiredate,Trial deadline
select ename,hiredate,adddate(hiredate,interval 3 month) Trial deadline
from emp;Group merge function_ concat()
Merge text strings and use them in combination with group by to return a string result.
Usually, after group by, we can only aggregate numeric types, not string data.
Ignore empty null
-- Query which employees are in each department select deptno,group_concat(ename) from emp group by deptno; -- Query which employees are in each department(duplicate removal) select deptno,group_concat(distinct ename) from emp group by deptno; -- Query which employees are in each department(sort) select deptno,group_concat(distinct ename order by sal desc) from emp group by deptno; -- Query which employees are in each department(Specify separator/) select deptno,group_concat(distinct ename order by sal desc separator '/') from emp group by deptno;
Logic function
ifnull()
-- Calculate the actual salary of each employee: basic salary + Commission -- Idea: no commission null 0 is required instead select ename,sal,ifnull(comm,0)+sal net salary from emp;
if()
-- Judge the salary level of each employee select ename,sal,if(sal>=15000,'high',if(sal<=9000,'low','in')) Wage scale from emp;
case when end
-- Judge the salary level of each employee select ename,sal,case when sal>=15000 then'high' when sal<=9000 then'low' else 'in' end Wage scale from emp;
Windowing function
Only MySQL 8.0 is supported.
Windowing function is a special function executed on a set of records that meet certain conditions.
Static window sliding window
The essence is aggregation operation, but it is flexible to use. It is executed on each record line and returns the calculation results.
Syntax:
Windowing function name ([< field name >]) over ([partition by < grouping field >] [order by < sorting field > [desc]] [< subdivision Window >])
For the range assignment of sliding windows, the between frame is usually used_ start and frame_end syntax to represent the line range, frame_ Start and frame_end can support the following keywords to determine different dynamic line records:
- The current row boundary is the current row, which is generally used together with other range keywords;
- unbounded preceding boundary is the first row in the partition;
- unbounded following boundary is the last row in the partition;
- expr preceding boundary is the value of the current row minus expr;
- The expr following boundary is the value of the current row plus expr;
For example, the following are legal scope:
The rows between 1 preceding and 1 following window ranges from the current line, the previous line, and the next line;
The range of rows unbounded preceding window is from the current row to the last row of the partition;
rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following the window range refers to all rows in the current partition, which is equivalent to not writing;
Ordinal function
- row_number(): displays the serial number in the partition without repetition or interruption;
- dense_rank(): displays the repeated and uninterrupted serial numbers in the partition;
- rank(): displays the serial number of repeated breaks in the partition;
-- Windowing function: aggregate function -- Average salary of all employees select avg(sal) avg_sal from emp; #Get a value select *,avg(sal) over() avg_sal from emp; #Get a column of values (each record row) -- Query the average salary of each department select deptno,avg(sal) avg_sal from emp group by deptno; select *,avg(sal) over(partition by deptno) avg_sal from emp; #The data of the same department will be divided into one region -- Each department calculates the cumulative salary according to the employment date select *,sum(sal) over(partition by deptno order by hiredate asc) sum_sal from emp; -- Calculate the average salary of the previous line and the next line of the current line of each department according to the employment date -- For example: group by department, arrange in ascending order by employment date, scan the first record and calculate its previous line+Current row+Average salary of the latter line select *,avg(sal) over(partition by deptno order by hiredate rows between 1 preceding and 1 following) avg_sal from emp; -- Windowing function: sequence number function -- All employees are ranked according to their employment date select *,row_number() over(order by hiredate) as 'ranking' from emp; #Sort by employment date in one area -- Employees in each department are ranked according to their basic salary select *,row_number() over(partition by deptno order by sal desc) as 'row_number ranking' from emp; select *,dense_rank() over(partition by deptno order by sal desc) as 'dense_rank ranking' from emp; select *,rank() over(partition by deptno order by sal desc) as 'rank ranking' from emp;
[exercise]
It is calculated that users with each investment greater than 500000 yuan in 2017
select user_id from cmn_investment_request where year(created_at)=2017 group by user_id having min(invest_amount)>500000;
Calculate the users who only invested in CFH and AX products in 2017
select user_id,group_concat(distinct invest_item order by invest_item desc) from cmn_investment_request where year(created_at)=2017 group by user_id having group_concat(distinct invest_item order by invest_item desc)='CFH,AX';
Calculate the investment amount attributable to 10002 salesman
select sum(invest_amount) from dim_agent left join cmn_investment_request on cmn_investment_request.user_id=dim_agent.user_id and created_at between start_date and end_date where agent_id='10002';
