Project introduction
Core functions
- Title Management: (title information: Title Stem + test case)
- Title list page: displays the title list
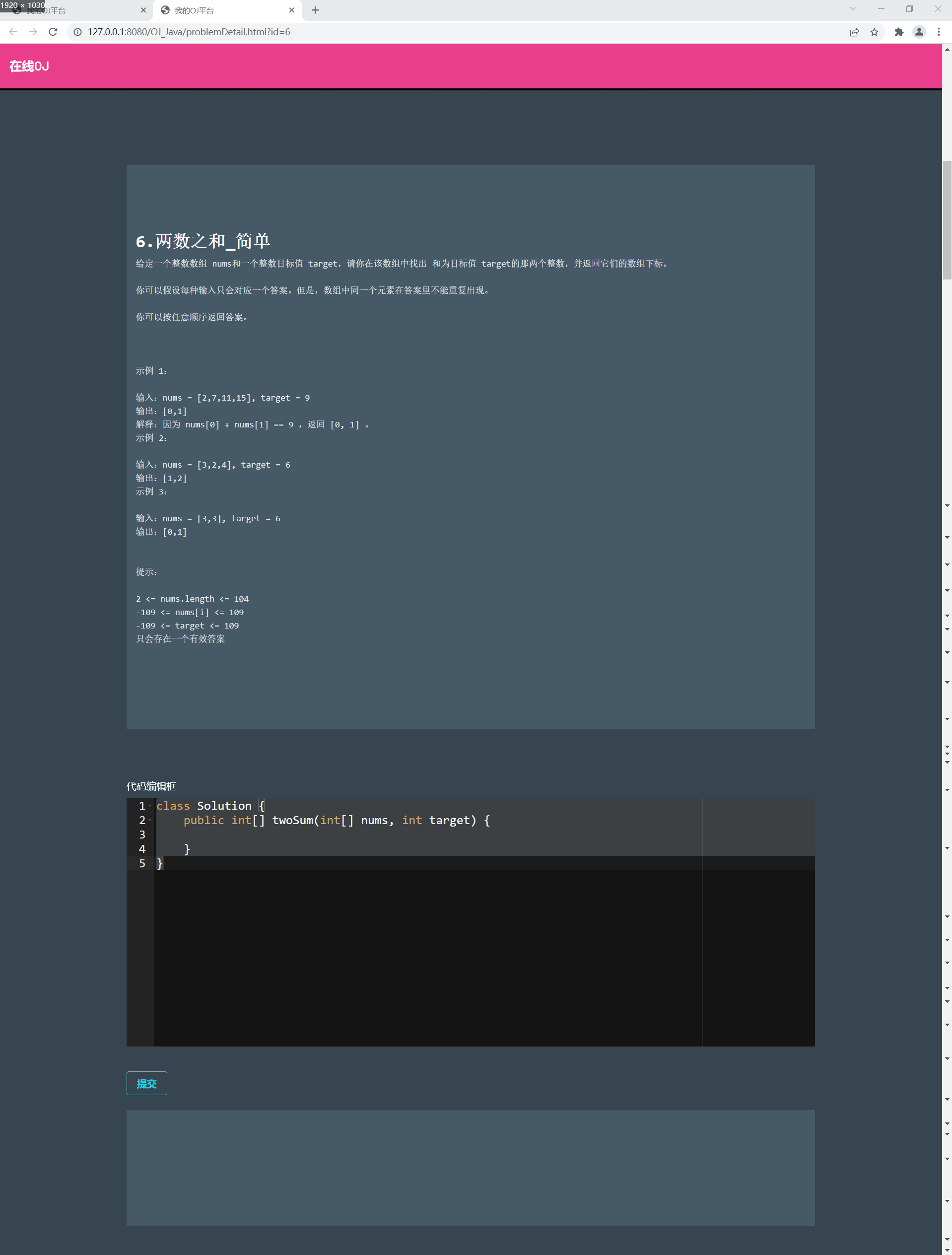
- Title details page: displays the title details + code edit box
- Submit the running Title: click the button, the web page will give the source code to the server, the server will execute the code, and return whether it passes and the test case.
- View operation results: show whether the last submission passed, error test cases, and historical submission records
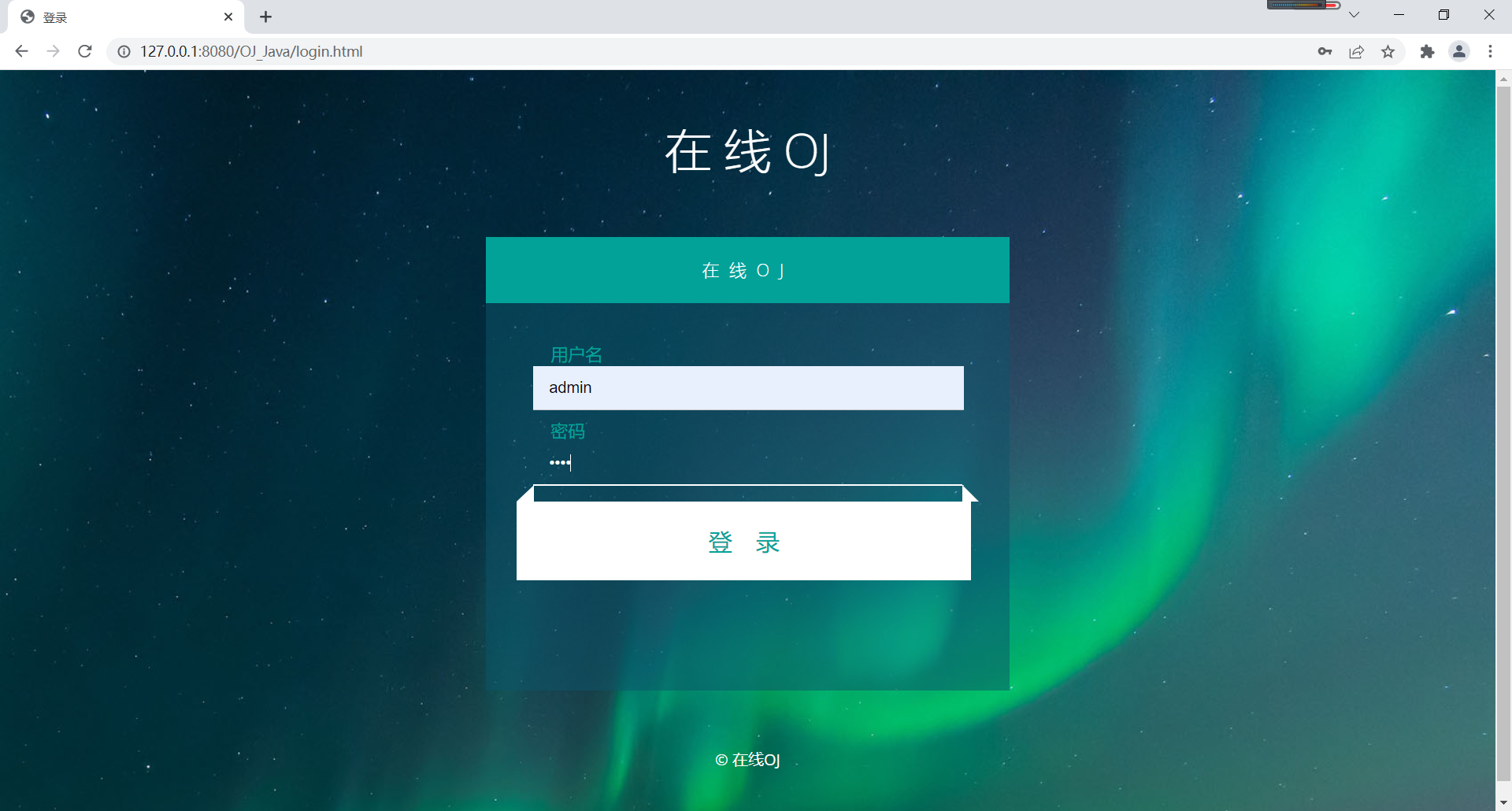
- Login page: login through user name and password
Realization effect
Login page
Title list page

Title details page
Compiler module design
Realize calling the program through the command line
Create compile package, CommandUtil class
1. Master the concepts of standard input, standard output and standard error
- Standard input: read data from the standard input device (usually the keyboard). When the user enters the data, press Enter to Enter the data, which becomes available. The read() method returns one byte of data at a time
- Standard output: display
- Standard error: the display displays an error message
2 realize the manual redirection process to redirect the standard output and standard errors
3. The exec execution process is asynchronous. Use the waitFor method to block and wait for the end of command execution
public class CommandUtil {
public static int run(String cmd,String stdoutFile,String stderrFile) {
try {
//1. Get the Runtime instance through the Runtime class and execute the exec method
Process process=Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
//2. Obtain the standard output and write it to the specified file
if(stdoutFile != null) {
InputStream stdoutFrom = process.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream stdoutTo = new FileOutputStream(stdoutFile);
while (true) {
int ch=stdoutFrom.read();
if(ch == -1) {
break;
}
stdoutTo.write(ch);
}
stdoutFrom.close();
stdoutTo.close();
}
//3. Get the standard error and write it to the specified file
if (stderrFile != null) {
InputStream stderrFrom = process.getErrorStream();
FileOutputStream stderrTo = new FileOutputStream(stderrFile);
while (true) {
int ch = stderrFrom.read();
if(ch == -1) {
break;
}
stderrTo.write(ch);
}
stderrFrom.close();
stderrTo.close();
}
//4. Wait for the subprocess to finish, get the status code of the subprocess and return
int exitCode=process.waitFor();
return exitCode;
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
}
}
Validate CommandUtil class
public static void main(String[] args) {
CommandUtil.run("javac","stdout.txt","stderr.txt");
}
Implementation of compilation and running process
Under the compile package, create the following classes:
Create Question class
Question class, representing the input code
public class Question {
private String code;
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
}
Create Answer class
The Answer class represents the output content. The Answer class contains error code, error prompt, standard output obtained by running the program, and standard error obtained by running the program.
public class Answer {
//Error code: the conventional error is 0, which means that the compilation and operation are ok, 1 means that the compilation and operation are wrong, and 2 means that the operation is wrong
private int error;
//Error prompt message if error is 1, compilation error message will be put in reason, operation exception will be put in reason, and exception error message will be put in reason
private String reason;
//Standard output from running the program
private String stdout;
//Standard error from running the program
private String stderr;
public int getError() {
return error;
}
public void setError(int error) {
this.error = error;
}
public String getReason() {
return reason;
}
public void setReason(String reason) {
this.reason = reason;
}
public String getStdout() {
return stdout;
}
public void setStdout(String stdout) {
this.stdout = stdout;
}
public String getStderr() {
return stderr;
}
public void setStderr(String stderr) {
this.stderr = stderr;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Answer{" +
"error=" + error +
", reason='" + reason + '\'' +
", stdout='" + stdout + '\'' +
", stderr='" + stderr + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Create Task class
Task class. Each compilation run is called a task.
public class Task {
public Answer compileAndRun(Question question) {
//1. Create a directory to store temporary files
//2. Create a temporary file according to Question
//3. Construct and execute the compilation command
//4. Build and execute the run command
//5. Package the running results into the final Answer object
}
}
Contract temporary file name
In order to effectively "communicate between processes", we first use a set of constants to restrict the name of temporary files.
//Directory of temporary files
private static final String WORK_DIR="./tmp/";
//Contract code class name
private static final String CLASS="Solution";
//Specifies the name of the code file to compile
private static final String CODE=WORK_DIR+"Solution.java";
//Agree on the file name for storing compilation error information
private static final String COMPILE_ERROR=WORK_DIR+"compileError.txt";
//Specifies the file name for storing the standard output of the runtime
private static final String STDOUT=WORK_DIR+"stdout.txt";
//Agree on the file name for storing runtime standard errors
private static final String STDERR=WORK_DIR+"stderr.txt";
Create FileUtil class
Create common package and FileUtil class to read and write files
In order to facilitate the subsequent file operation, simple encapsulation is carried out first
Create common package and FileUtil class
public class FileUtil {
//Be responsible for reading out the file content corresponding to filePath and putting it into the return value
public static String readFile(String filePath) {
StringBuilder result=new StringBuilder();
try(FileReader fileReader=new FileReader(filePath)) {
while (true) {
int ch= fileReader.read();
if(ch==-1) {
break;
}
result.append((char)ch);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result.toString();
}
//Be responsible for writing content into the file corresponding to filePath
public static void writeFile(String filePath,String content) {
try(FileWriter fileWriter=new FileWriter(filePath)) {
fileWriter.write(content);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Implement task Compileandrun method
Use the compileAndRun method to encapsulate the compilation command and get the compilation result
complieAndRun direction implementation steps
- Create a directory for temporary files.
- Write the contents of the question to the specified solution Java file.
- Create a child process and call the javac command to compile.
- Create a child process, call the java command and execute it.
- The parent process obtains the compilation execution result and packages it into an Answer object.
public class Task {
//Parameter: java source code to compile and run
//Return value: indicates the result of compilation and operation: compilation error / operation error / correct operation
public Answer compileAndRun(Question question) {
Answer answer=new Answer();
//0. Create a directory for temporary files
File workDir=new File(WORK_DIR);
if(!workDir.exists()) {
//Create multi-level directory
workDir.mkdirs();
}
//1. Write the code in question into a solution Java file
FileUtil.writeFile(CODE,question.getCode());
//2. Create a sub process and call javac for compilation
//Construct compile command first
String compileCmd=String.format("javac -encoding utf8 %s -d %s",CODE,WORK_DIR);
//For the javac process, the standard output does not pay attention to the standard error. Once the compilation error occurs, the content will be fed back through the standard error
CommandUtil.run(compileCmd,null,COMPILE_ERROR);
//If the compilation fails, the error message will be put into COMPILE_ERROR in this file, there is no error, and the file is empty
String compileError=FileUtil.readFile(COMPILE_ERROR);
if(!compileError.equals("")) {
//If the compilation error is directly returned to Answer convention 1, it means that the compilation error occurs
System.out.println("Compilation error");
answer.setError(1);
answer.setReason(compileError);
return answer;
}
//3. Create a sub process, call java commands and execute them
String runCom = String.format("java -classpath %s %s",WORK_DIR,CLASS);
CommandUtil.run(runCom,STDOUT,STDERR);
String runError=FileUtil.readFile(STDERR);
if(!runError.equals("")) {
System.out.println("Run error");
answer.setError(2);
answer.setReason(runError);
return answer;
}
//4. The parent process obtains the results of the compilation execution just now and packages them into an Answer object
answer.setError(0);
answer.setStdout(FileUtil.readFile(STDOUT));
return answer;
}
}
Validate Task class
public static void main(String[] args) {
Task task=new Task();
Question question=new Question();
question.setCode("public class Solution {\n" +
" public static void main(String[] args) {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"hello world\");\n" +
" }\n" +
" \n" +
"}");
Answer answer=task.compileAndRun(question);
System.out.println(answer);
}
Topic management module design
Database design
create database if not exists oj_databases;
use oj_databases;
drop table if exists oj_table;
create table oj_table(
id int primary key auto_increment,
title varchar(50),
level varchar(20),
description varchar(4096),
templateCode varchar(4096),
testCode varchar(4096)
);
drop table if exists user;
create table user(
userId int primary key auto_increment,
username varchar(128),
password varchar(128)
);
Title indicates the title of the topic, level indicates the difficulty, description indicates the description of the topic, templateCode indicates the code template, and testCode indicates the test case code
Create DBUtil class
Create DBUtil class under common package
Complete the database connection operation
public class DBUtil {
private static final String url="jdbc:mysql:///oj_databases?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false";
private static final String USERNAME="root";
private static final String PASSWORD="1234";
private static volatile DataSource dataSource=null;
//Implement getDataSource and thread safe singleton mode
public static DataSource getDataSource() {
if(dataSource==null) {
synchronized (DBUtil.class) {
if(dataSource==null) {
dataSource=new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL(url);
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser(USERNAME);
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword(PASSWORD);
}
}
}
return dataSource;
}
//Implement getConnection
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return getDataSource().getConnection();
}
//Implement close
public static void close(Connection connection, PreparedStatement statement, ResultSet resultSet){
if(resultSet!=null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(statement!=null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection!=null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Realize topic storage and user storage
Create dao package. The following classes are created under dao package
Create Problem class
The Problem class represents a Problem.
public class Problem {
private int id;
private String title;
private String level;
private String description;
private String templateCode;
private String testCode;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getLevel() {
return level;
}
public void setLevel(String level) {
this.level = level;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public String getTemplateCode() {
return templateCode;
}
public void setTemplateCode(String templateCode) {
this.templateCode = templateCode;
}
public String getTestCode() {
return testCode;
}
public void setTestCode(String testCode) {
this.testCode = testCode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Problem{" +
"id=" + id +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", level='" + level + '\'' +
", description='" + description + '\'' +
", templateCode='" + templateCode + '\'' +
", testCode='" + testCode + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Create ProblemDao class
The topic manager class is responsible for interacting with the database
public class ProblemDAO {
// New topic
public void insert(Problem problem) {
// TODO
}
// Delete title
public void delete(int id) {
// TODO
}
// Query all topics
public List<Problem> selectAll() {
}
// Query the details of the specified topic
public Problem selectOne(int problemId) {
}
}
Implement insert
public void insert(Problem problem) {
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
try {
connection=DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="insert into oj_table values(null,?,?,?,?,?)";
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,problem.getTitle());
statement.setString(2,problem.getLevel());
statement.setString(3,problem.getDescription());
statement.setString(4,problem.getTemplateCode());
statement.setString(5,problem.getTestCode());
int ret=statement.executeUpdate();
if(ret!=1) {
System.out.println("Failed to add title");
} else {
System.out.println("Successfully added topic");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
Implement delete
public void delete(int id) {
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
try {
connection=DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="delete from oj_table where id=?";
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,id);
int ret=statement.executeUpdate();
if(ret!=1) {
System.out.println("Failed to delete title");
} else {
System.out.println("Delete Title succeeded");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
Implement selectAll
public List<Problem> selectAll() {
List<Problem> list=new ArrayList<>();
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
connection=DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="select * from oj_table";
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet=statement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
Problem problem=new Problem();
problem.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
problem.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
problem.setLevel(resultSet.getString("level"));
list.add(problem);
}
return list;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
return null;
}
Implement selectOne
public Problem selectOne(int id) {
Problem problem=new Problem();
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
connection=DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="select * from oj_table where id=?";
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,id);
resultSet=statement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet.next()) {
problem.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
problem.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
problem.setLevel(resultSet.getString("level"));
problem.setDescription(resultSet.getString("description"));
problem.setTemplateCode(resultSet.getString("templateCode"));
return problem;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
return null;
}
Verify insert
private static void testInsert() {
ProblemDao problemDAO=new ProblemDao();
Problem problem=new Problem();
problem.setTitle("Sum of two numbers");
problem.setLevel("simple");
problem.setDescription("Given an array of integers nums And an integer target value target,Please find and as the target value in the array target And return their array subscripts.\n" +
"\n" +
"You can assume that each input will correspond to only one answer. However, the same element in the array cannot appear repeatedly in the answer.\n" +
"\n" +
"You can return answers in any order.\n" +
"\n" +
"\n" +
"\n" +
"Example 1:\n" +
"\n" +
"Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9\n" +
"Output:[0,1]\n" +
"Explanation: because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,return [0, 1] . \n" +
"Example 2:\n" +
"\n" +
"Input: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6\n" +
"Output:[1,2]\n" +
"Example 3:\n" +
"\n" +
"Input: nums = [3,3], target = 6\n" +
"Output:[0,1]\n" +
"\n" +
"\n" +
"Tips:\n" +
"\n" +
"2 <= nums.length <= 104\n" +
"-109 <= nums[i] <= 109\n" +
"-109 <= target <= 109\n" +
"There will only be one valid answer\n" +
"\n" );
problem.setTemplateCode("class Solution {\n" +
" public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {\n" +
"\n" +
" }\n" +
"}");
problem.setTestCode("public static void main(String[] args) {\n" +
" Solution solution=new Solution();\n" +
" //testcase1\n" +
" int[] nums={2,7,11,15};\n" +
" int target=9;\n" +
" int[] result=solution.twoSum(nums,target);\n" +
" if(result.length==2 &&result[0]==0&&result[1]==1) {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase1 Ok\");\n" +
" } else {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase1 failed\");\n" +
" }\n" +
" //testcase2\n" +
" int[] nums2={3,2,4};\n" +
" int target2=6;\n" +
" int[] result2=solution.twoSum(nums2,target2);\n" +
" if(result.length==2 &&result2[0]==1&&result2[1]==2) {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase2 Ok\");\n" +
" } else {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase2 failed\");\n" +
" }\n" +
" }");
problemDAO.insert(problem);
}
Verify delete
public static void testDelete() {
ProblemDao problemDao=new ProblemDao();
problemDao.delete(5);
}
Validate selectAll
public static void testSelectAll() {
ProblemDao problemDao=new ProblemDao();
List<Problem> problems=problemDao.selectAll();
System.out.println(problems);
}
Validate selectOne
public static void testSelectOne() {
ProblemDao problemDao=new ProblemDao();
Problem problem=problemDao.selectOne(7);
System.out.println(problem);
}
Create User class
User Id, a user name, a password
public class User {
private int userId;
private String username;
private String password;
public int getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(int userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"userId=" + userId +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Create UserDao class
The user manager class is responsible for interacting with the database
public class UserDao {
//New user
public void insert(User user) {
}
//delete user
public void delete(int userId) {
}
//Query users by user name
public User select(String username) {
}
//Query users by user id
public User selectId(int userId) {
}
}
Implement insert
public void insert(User user) {
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
try {
connection= DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="insert into user values(null,?,?)";
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,user.getUsername());
statement.setString(2,user.getPassword());
int ret=statement.executeUpdate();
if(ret!=1) {
System.out.println("Failed to add user");
} else {
System.out.println("Successfully added user");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
Implement delete
public void delete(int userId) {
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
try {
connection=DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="delete from user where userId=?";
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,userId);
int ret=statement.executeUpdate();
if(ret!=1) {
System.out.println("Failed to delete user");
} else {
System.out.println("User deleted successfully");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
Implement select
public User select(String username) {
User user=new User();
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
connection=DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="select * from user where username=?";
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,username);
resultSet=statement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet.next()) {
user.setUserId(resultSet.getInt("userId"));
user.setUsername(resultSet.getString("username"));
user.setPassword(resultSet.getString("password"));
return user;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
return null;
}
Implement selectId
public User selectId(int userId) {
User user=new User();
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
connection=DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="select * from user where userId=?";
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,userId);
resultSet=statement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet.next()) {
user.setUserId(resultSet.getInt("userId"));
user.setUsername(resultSet.getString("username"));
user.setPassword(resultSet.getString("password"));
return user;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
return null;
}
Verify insert
private static void testInsert() {
UserDao userDao=new UserDao();
User user=new User();
user.setUsername("zhangsan");
user.setPassword("1234");
userDao.insert(user);
}
Verify delete
private static void testDelete(int id) {
UserDao userDao=new UserDao();
userDao.delete(id);
}
Validate select
private static void testSelect(String name) {
UserDao userDao=new UserDao();
User user=userDao.select(name);
System.out.println(user);
}
Validate selectId
private static void testSelectId(int Id) {
UserDao userDao=new UserDao();
User user=userDao.selectId(Id);
System.out.println(user);
}
Server API
Create an API package. The following classes are in the API package
Implement the ProblemServlet class
Determine whether to obtain the topic list page or the topic detail page according to whether the req contains id. obtain the topic detail page with id and obtain the topic list page without id
@WebServlet("/problem")
public class ProblemServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper=new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setStatus(200);
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf8");
ProblemDao problemDao=new ProblemDao();
String idString=req.getParameter("id");
if(idString==null||idString.equals("")) {
//Get title list page
List<Problem> list=problemDao.selectAll();
String respString=objectMapper.writeValueAsString(list);
resp.getWriter().write(respString);
} else {
//Get title details page
Problem problem=problemDao.selectOne(Integer.parseInt(idString));
String respString=objectMapper.writeValueAsString(problem);
resp.getWriter().write(respString);
}
}
}
Implement CompileServlet
It contains two internal classes, corresponding to compilation request and compilation response respectively
@WebServlet("/compile")
public class CompileServlet extends HttpServlet {
static class CompileRequest {
public int id;
public String code;
}
static class CompileResponse {
public int error;
public String reason;
public String stdout;
}
private ObjectMapper objectMapper=new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1. Read the request and parse it in json format
//2. Find the details of the corresponding topic according to the id in the request
//3. Splice the user submitted code and test cases
//4. Create the Task class and compile the running code
}
}
Implement doPost method
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
CompileRequest compileRequest=null;
CompileResponse compileResponse=new CompileResponse();
try {
resp.setStatus(200);
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf8");
//1. Read the request and parse it in json format
String body=readBody(req);
compileRequest=objectMapper.readValue(body,CompileRequest.class);
//2. Find the details of the corresponding topic according to the id in the request
ProblemDao problemDao=new ProblemDao();
Problem problem=problemDao.selectOne(compileRequest.id);
if(problem==null) {
//The corresponding topic id cannot be found
throw new ProblemNotFoundExec();
}
//User submitted code
String requestCode=compileRequest.code;
//test case
String testCode=problem.getTestCode();
//3. Splice the user submitted code and test cases
String finalCode=mergeCode(requestCode,testCode);
if(finalCode==null) {
throw new CodeInValidException();
}
//4. Create the Task class and compile the running code
Task task=new Task();
Question question=new Question();
question.setCode(finalCode);
Answer answer=task.compileAndRun(question);
compileResponse.error=answer.getError();
compileResponse.reason=answer.getReason();
compileResponse.stdout=answer.getStdout();
} catch (ProblemNotFoundExec problemNotFoundExec) {
compileResponse.error=3;
compileResponse.reason="subject id non-existent id="+compileRequest.id;
} catch (CodeInValidException e) {
compileResponse.error=3;
compileResponse.reason="The submitted code is unqualified";
} finally {
String respString=objectMapper.writeValueAsString(compileResponse);
resp.getWriter().write(respString);
}
}
Implement the read body method to read out all the bodies in the request
private static String readBody(HttpServletRequest req) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
int len=req.getContentLength();
byte[] bytes=new byte[len];
try(InputStream inputStream=req.getInputStream()) {
inputStream.read(bytes);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new String(bytes,"utf8");
}
The mergeCode method is implemented to splice the code submitted by the user and the test case
private String mergeCode(String requestCode, String testCode) {
int index=requestCode.lastIndexOf("}");
if(index==-1) {
return null;
}
String subStr=requestCode.substring(0,index);
return subStr+testCode+"\n}";
}
Implement LoginServlet
Front - end and back - end interaction through the from form
@WebServlet("/login")
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("test/html,charset=utf8");
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf8");
String username=req.getParameter("username");
String password=req.getParameter("password");
if(username==null||password==null||username.equals("")||password.equals("")) {
String html="<h3>Login failed! Wrong user name or password<h3>";
resp.getWriter().write(html);
return;
}
UserDao userDao=new UserDao();
User user=userDao.select(username);
if(user==null) {
String html="<h3>Login failed! Wrong user name or password<h3>";
resp.getWriter().write(html);
return;
}
if(!user.getPassword().equals(password)) {
String html="<h3>Login failed! Wrong user name or password<h3>";
resp.getWriter().write(html);
return;
}
HttpSession session=req.getSession(true);
session.setAttribute("username",username);
resp.sendRedirect("index.html");
}
}