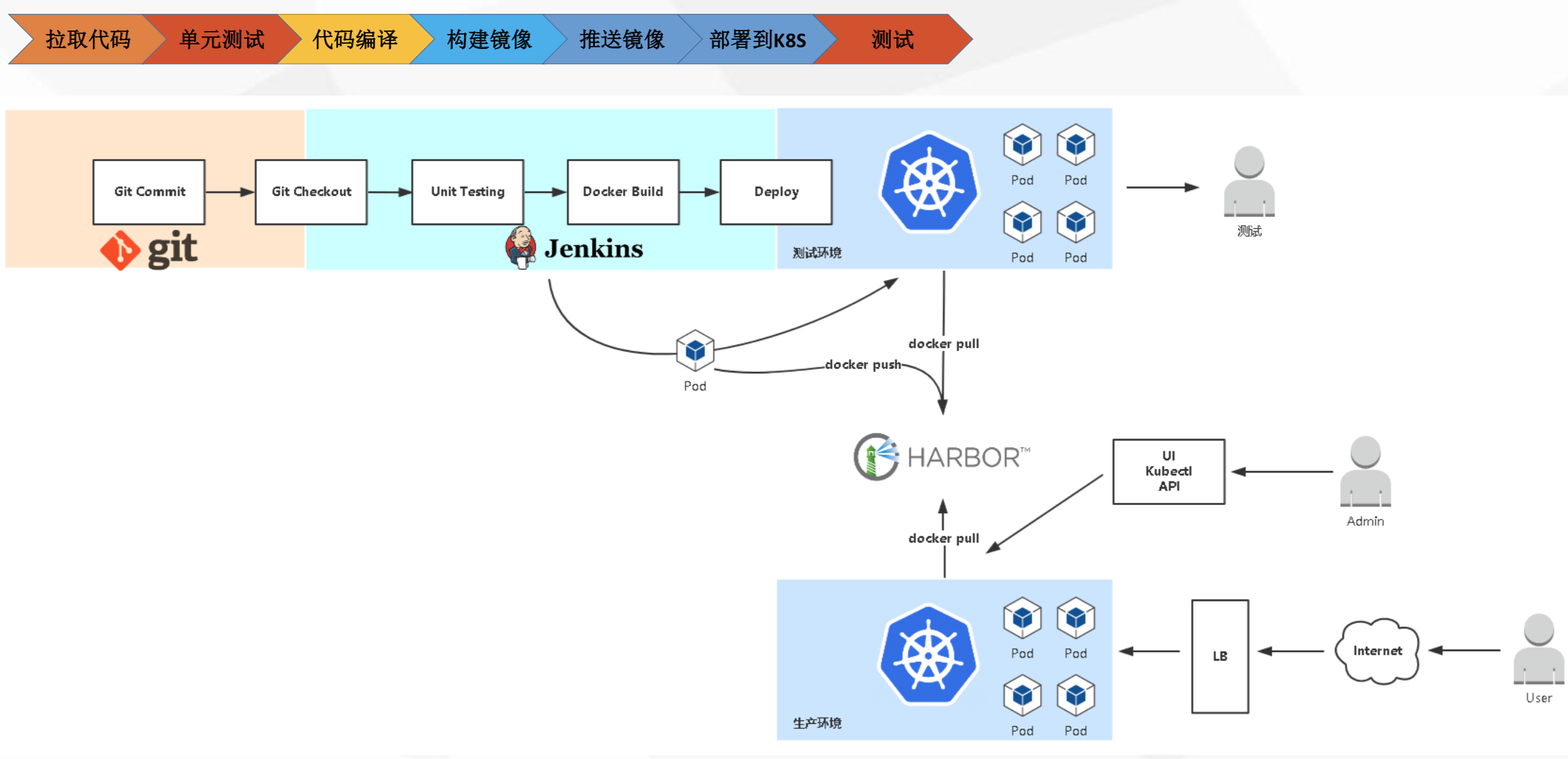
CICD continuous integration based on kubernetes platform
1. Continuous integration of Jenkins based on k8s cluster
The process of Jenkins updating the traditional LNMT project is very simple. Jenkins only needs to be deployed on the physical server to realize the continuous update iteration of the project version
If the project is deployed in the k8s cluster and Jenkins is still deployed on the physical machine, the project update process will become cumbersome. The general process is as follows: firstly, Jenkins compiles the project into a war package, and then runs the war on a physical machine. If the operation is successful, another Jenkins task will be called, The main function of Jenkins task is to copy the war package and ROOT directory into the initial image. After the image is built, push the image to the harbor platform, and then the operation and maintenance department takes the image version and puts it in k8s to upgrade.
If Jenkins is only deployed on a physical machine, the whole CI/CD platform will not be able to update and iterate after a Jenkins hangs up, which is a very serious consequence. If Jenkins is deployed on the k8s platform, with the help of the k8s pod self-healing function, Jenkins hangs up almost never.
After Jenkins is deployed in the k8s environment, by establishing RBAC authorization mechanism, Jenkins can realize one click Update iteration to the k8s environment without the cumbersome steps of using the physical machine environment
Update process after Jenkins and kubernetes integration:
1) Jenkins pulls the development submitted code from gitlab
2) Jenkins calls maven to compile the project
3) Jenkins calls docker to build the written dockerfile into an image
4) Push the image to the harbor warehouse
5) Jenkins calls k8s to deploy the image in the k8s environment
2. Deploy Jenkins in k8s cluster
Deployment idea:
1. Because Jenkins wants to update items to various namespaces, it needs to do RBAC authorization, prepare a ServiceAccount, and directly bind the ServiceAccount to the cluster admin cluster role, so that Jenkins has operation permissions on items under all namespaces.
2. The Jenkins deployment adopts the statefullset controller and cooperates with StorageClass to dynamically persist Jenkins data.
3. Prepare svc resources and expose ports 8080 / 50000 of Jenkins.
2.1. Write Jenkins namespace file
[root@k8s-master1 jenkins]# cat jenkins-namespace.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: jenkins
2.2. Prepare Jenkins rbac authorization document
Create a serviceaccount account Jenkins, and directly bind the sa account to the cluster admin cluster role
[root@k8s-master1 jenkins]# cat jenkins-rbac.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: jenkins namespace: jenkins --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: jenkins-crb roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-admin subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: jenkins namespace: jenkins
2.3. Write Jenkins statefullset resource file
Jenkins also generates data, so stateful services are deployed with stateful set, and storage systems are dynamically created with StorageClass
[root@k8s-master1 jenkins]# cat jenkins-statefulset.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: jenkins-master
namespace: jenkins
spec:
replicas: 1
serviceName: jenkins
selector:
matchLabels:
app: jenkins-master
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: jenkins-master
spec:
serviceAccount: jenkins
initContainers:
- name: jenkins-chown
image: harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/busybox:1.30
command: ["sh","-c","chown -R 1000:1000 /var/jenkins_home"]
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeMounts:
- name: jenkins-data
mountPath: /var/jenkins_home
containers:
- name: jenkins-master
image: harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/jenkinsci-blueocean:1.24.6
env:
- name: JAVA_OPTS
value: "-Xms4096m -Xmx5120m -Duser.timezone=Asia/Shanghai -Dhudson.model.DirectoryBrowserSupport.CSP="
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 8080
- name: slave
containerPort: 50000
volumeMounts:
- name: jenkins-data
mountPath: /var/jenkins_home
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: jenkins-data
spec:
storageClassName: jenkins-storageclass
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
2.4. Write Jenkins StorageClass resource file
[root@k8s-master1 jenkins]# cat jenkins-storageclass.yaml apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: StorageClass metadata: name: jenkins-storageclass provisioner: nfs-storage-01 reclaimPolicy: Retain
2.5. Write Jenkins svc resource file
[root@k8s-master1 jenkins]# cat jenkins-svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: jenkins-master
name: jenkins-svc
namespace: jenkins
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
nodePort: 38080
- name: slave
port: 50000
targetPort: 50000
nodePort: 50000
selector:
app: jenkins-master
type: NodePort
2.6. Prepare Jenkins images and push them to harbor
[root@k8s-master1 jenkins]# docker pull jenkinsci/blueocean:1.24.6 [root@k8s-master1 jenkins]# docker tag jenkinsci/blueocean:1.24.6 harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/jenkinsci-blueocean:1.24.6 [root@k8s-master1 jenkins]# docker push harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/jenkinsci-blueocean:1.24.6
2.7. Create all resources and view their status
1.Create all resources [root@k8s-master1 jenkins]# kubectl apply -f ./ namespace/jenkins created serviceaccount/jenkins created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/jenkins-crb created statefulset.apps/jenkins-master created storageclass.storage.k8s.io/jenkins-storageclass created service/jenkins-svc created 2.View resource status [root@k8s-master1 jenkins]# kubectl get pod,statefulset,svc,storageclass,sa -n jenkins NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/jenkins-master-0 1/1 Running 0 31m NAME READY AGE statefulset.apps/jenkins-master 1/1 31m NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/jenkins-svc NodePort 10.101.2.5 <none> 8080:38080/TCP,50000:50000/TCP 31m NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE storageclass.storage.k8s.io/jenkins-storageclass nfs-storage-01 Retain Immediate false 31m NAME SECRETS AGE serviceaccount/jenkins 1 31m 3.see pvc,Created dynamically [root@k8s-master1 jenkins]# kubectl get pvc -n jenkins NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE jenkins-data-jenkins-master-0 Bound pvc-3f49831b-7faa-456e-9a2f-65b6085933de 10Gi RWX jenkins-storageclass 32m
2.8. Jenkins installation page
Access any ip+38080 port of the cluster node
Visit the following page to see that Jenkins is still starting. When the log is output to the following figure, refresh Jenkins to enter the system, copy the password in the log and unlock Jenkins
[the external chain picture transfer fails, and the source station may have an anti-theft chain mechanism. It is recommended to save the picture and upload it directly (img-Gq67dowz-1629451468833)(.\k8s+jenkins realize continuous integration - note picture storage \ 1621415881187.png)]
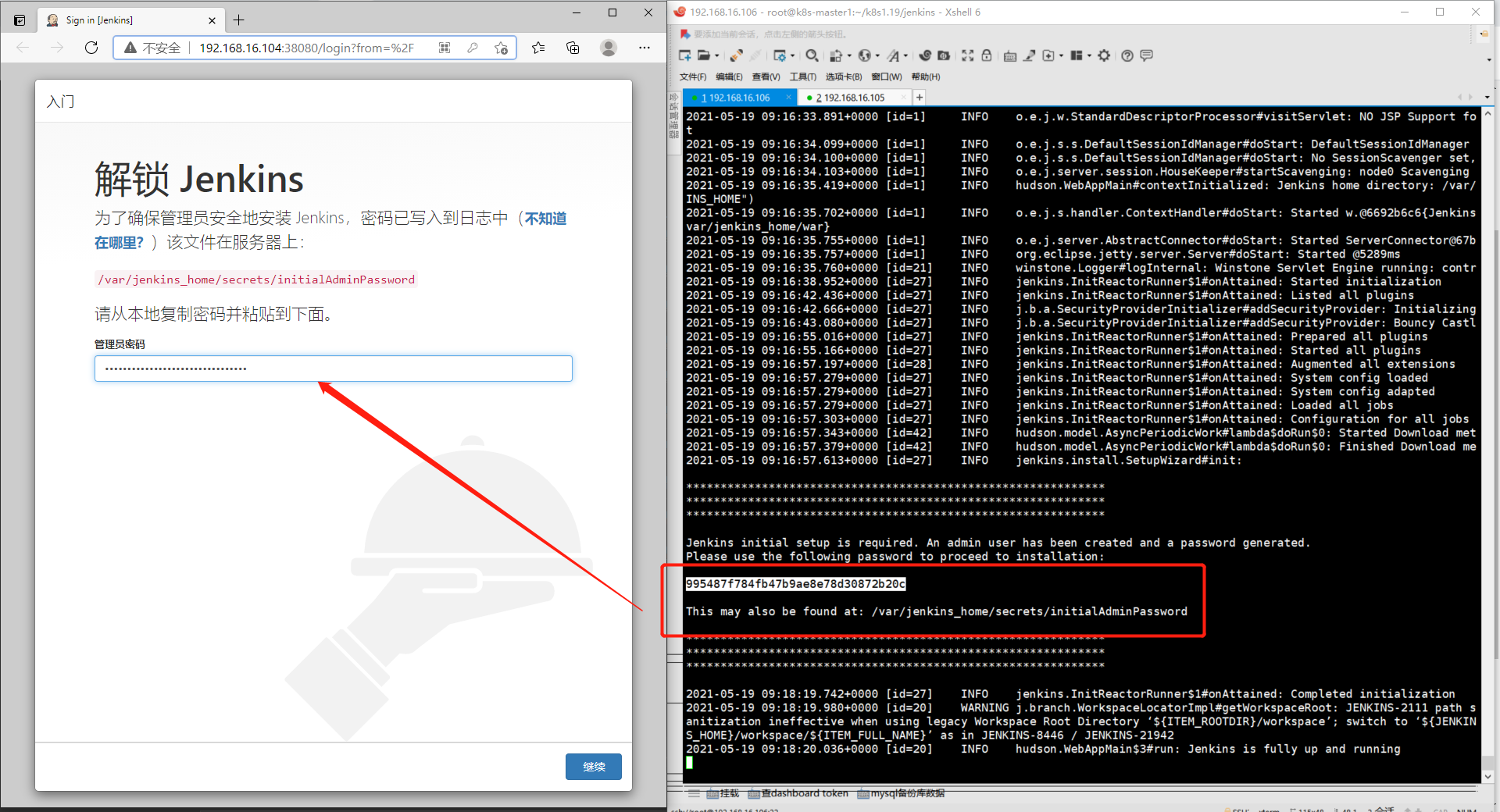
1) Unlock Jenkins
You can copy the password in the log or view / var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword this file
2) Select the plug-in to install
Check all plug-ins to avoid software dependency in the later stage
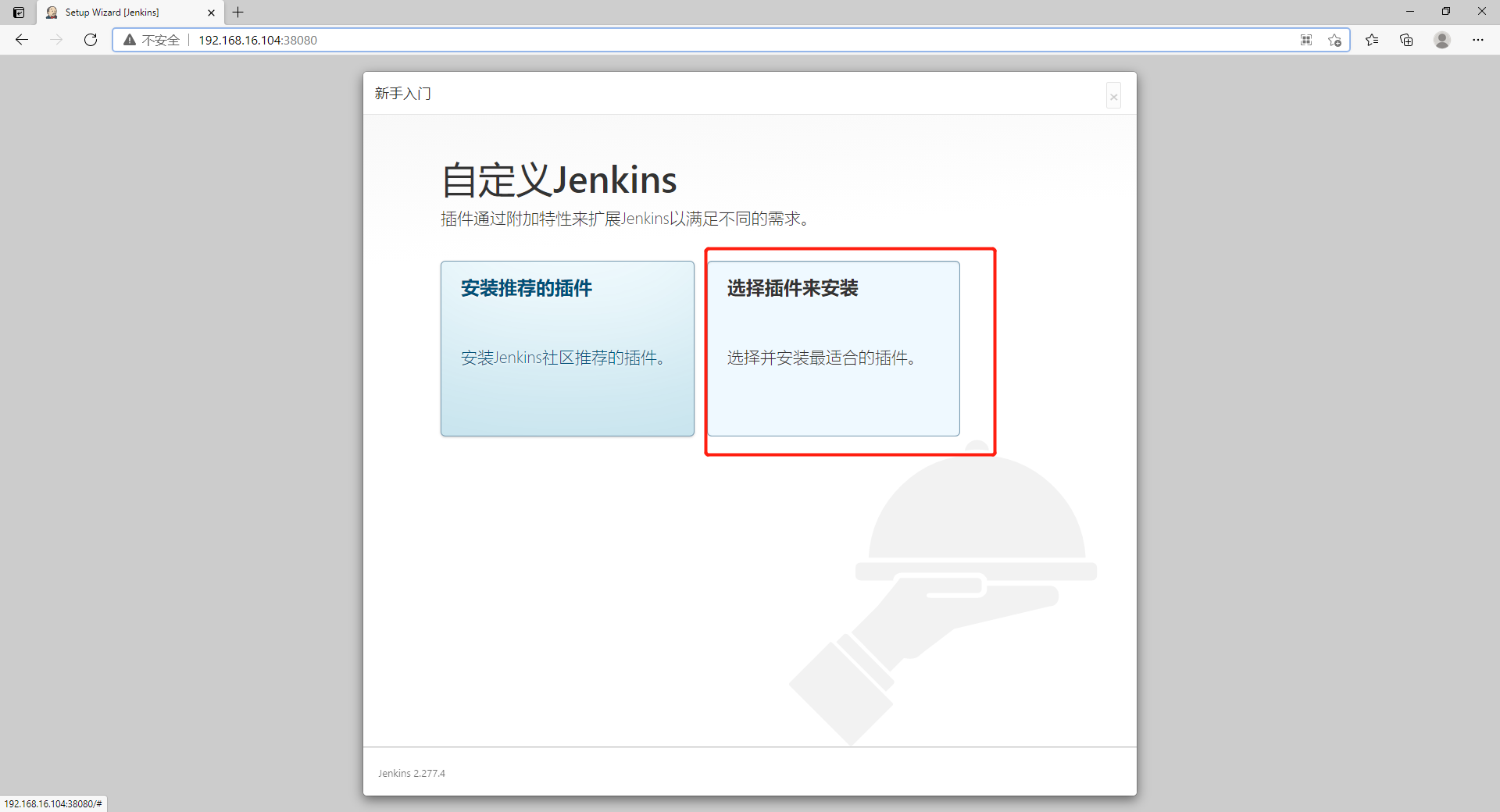
Click all to check all

3) Wait until the plug-in is installed
4) Create Jenkins account
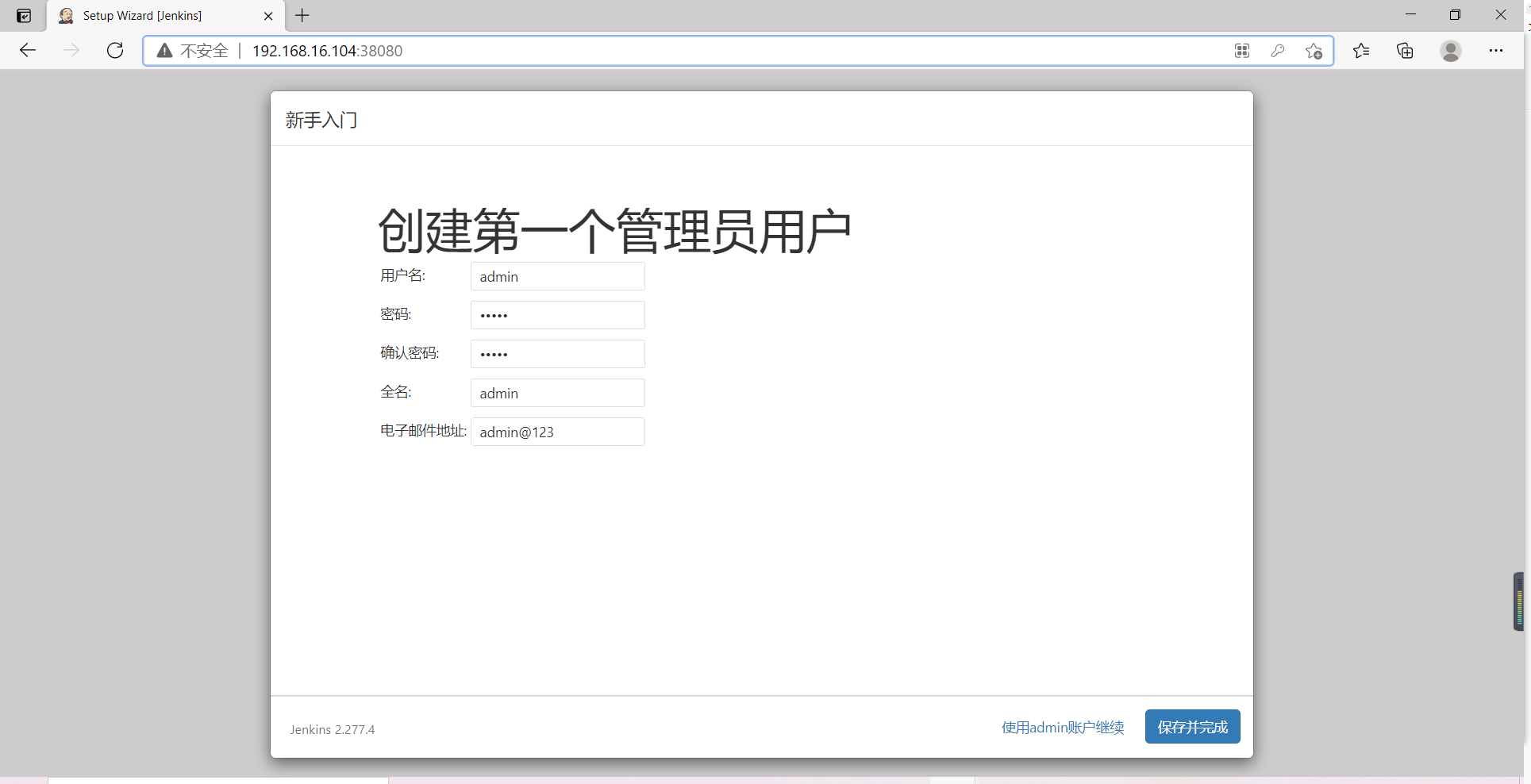
5) Set instance address

6) Restart Jenkins
2.9. Login Jenkins
Account admin password admin
3. Deploy gitlab using docker
Here is just an extension of how to deploy gitlab with docker. It is recommended to deploy gitlab with k8s in 4
3.1. Deploy gitlab
[root@k8s-master2 ~]# docker run -d --hostname 192.168.16.105 -p 8443:443 -p 8080:80 -p 8022:22 --name gitlab --restart always -v /data2/k8s/gitlab-data/config/:/etc/gitlab -v /data2/k8s/gitlab-data/logs/:/var/log/gitlab -v /data2/k8s/gitlab-data/data/:/var/opt/gitlab gitlab/gitlab-ce:13.11.4-ce.0 [root@k8s-master2 ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 33d868fe0369 gitlab/gitlab-ce:13.11.4-ce.0 "/assets/wrapper" 14 minutes ago Up 4 minutes (healthy) 0.0.0.0:8022->22/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8080->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8443->443/tcp gitlab
When the following page appears, gitlab startup is complete
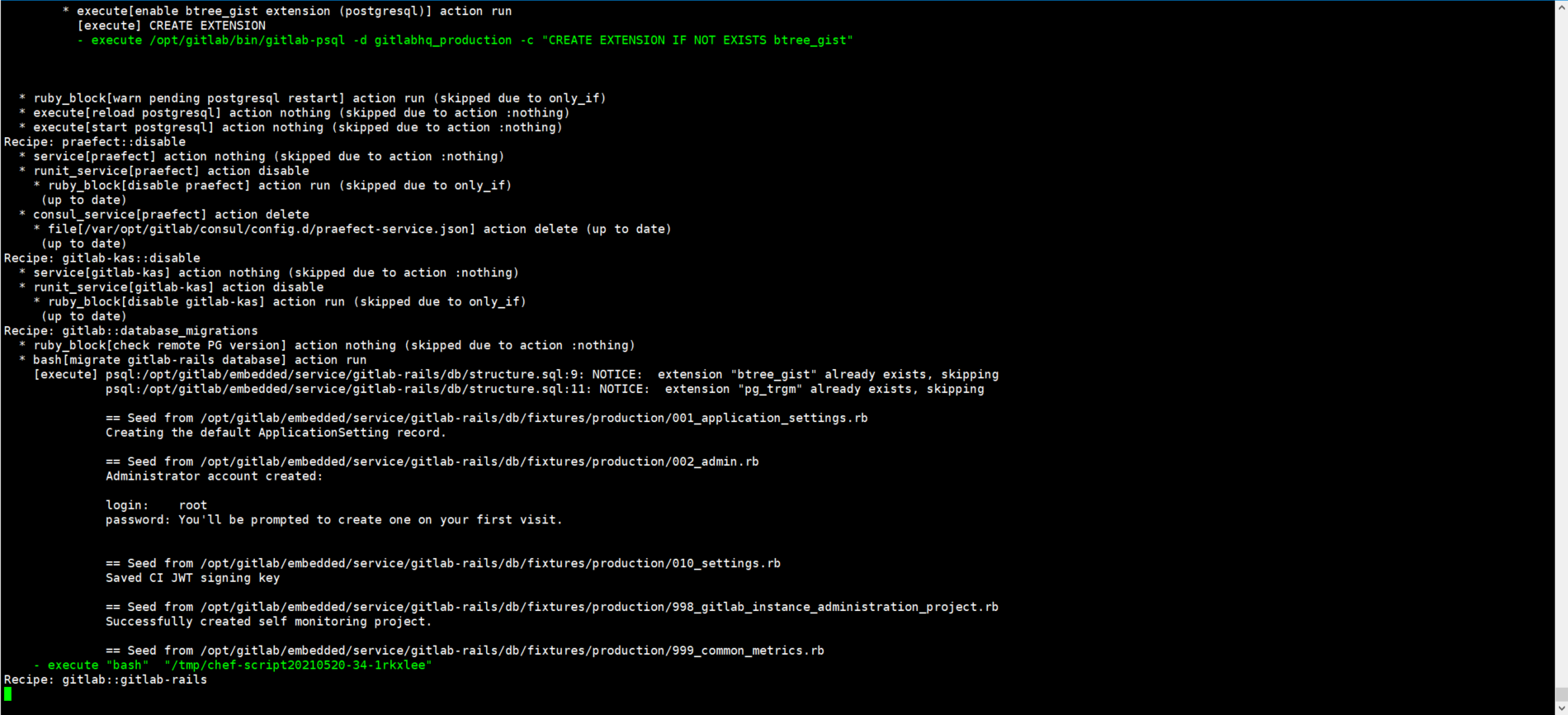
3.2. Access gitlab
visit http://192.168.16.105:8080/
The root password needs to be set for the first login
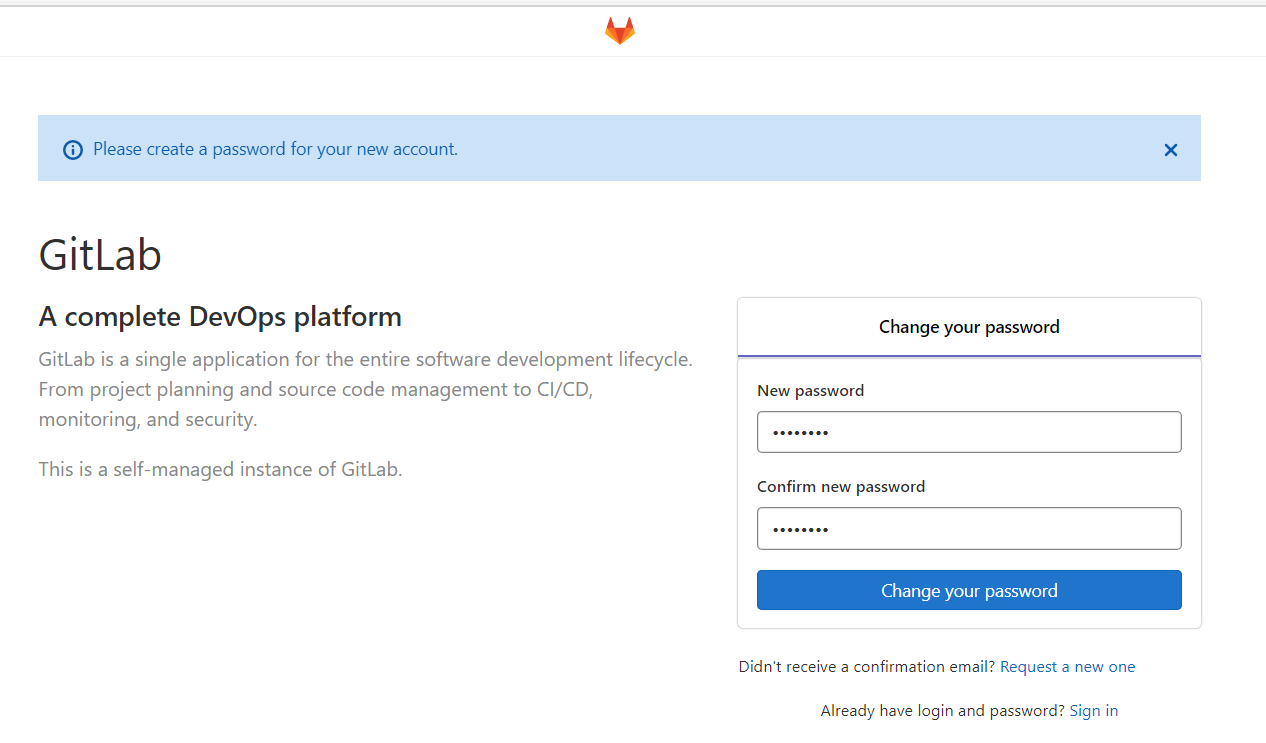
After setting the password, you can log in to the system

4. Deploy gitlab in k8s cluster
Deployment Analysis:
- Gitlab is deployed by the statefullset controller, and the gitlab configuration file and gitlab data file are persistently stored through StorageClass
- Because the gitlab image integrates many components, and the user groups used by each component in the gitlab data directory are different, you need to modify the corresponding user for each component, otherwise you have no permission to start relevant components. First, run the gitlab image with docker to query the different users corresponding to different components in the gitlab data directory, Then weight it in the initialization container
- Modify the configuration file of gitlab to determine the url for external access
- Port 80 of gitlab is exposed through svc resources
4.1. Push gitlab image to harbor warehouse
[root@k8s-master1 ~]# docker tag gitlab/gitlab-ce:13.11.4-ce.0 harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/gitlab-ce:13.11.4-ce.0 [root@k8s-master1 ~]# docker push harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/gitlab-ce:13.11.4-ce.0
4.2. Use docker to run gitlab to query the user's id number
Each component of gitlab is managed by different users. We don't know the uid and gid of each user, so we need to start the query with docker first
Remember the user uid and gid of these components, which will be used later when defining the initialization container in the statful resource
1.use docker function gitlab container [root@k8s-master1 ~]# docker run -d harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/gitlab-ce:13.11.4-ce.0 2.Enter container [root@k8s-master1 ~]# docker exec -it 33d868fe0369 bash 3.see gitlab The user of each component in the data path root@192:/# ll /var/opt/gitlab/ total 20 drwxr-xr-x 20 root root 4096 May 20 09:12 ./ drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 20 May 14 15:17 ../ drwxr-xr-x 2 git git 6 May 20 09:01 .bundle/ -rw-r--r-- 1 git git 363 May 20 09:01 .gitconfig drwx--->---> 2 git git 29 May 20 09:01 .ssh/ drwxr-x---> 3 gitlab-prometheus root 42 May 20 09:11 alertmanager/ drwx--->---> 2 git root 6 May 20 09:01 backups/ -rw--->--->- 1 root root 38 May 20 09:06 bootstrapped drwx--->---> 3 git git 26 May 20 09:01 git-data/ drwx--->---> 3 git root 123 May 20 09:11 gitaly/ drwxr-xr-x 3 git root 20 May 20 09:01 gitlab-ci/ drwxr-xr-x 2 git root 53 May 20 09:11 gitlab-exporter/ drwxr-xr-x 9 git root 160 May 20 09:11 gitlab-rails/ drwx--->---> 2 git root 24 May 20 09:10 gitlab-shell/ drwxr-x---> 3 git gitlab-www 55 May 20 09:11 gitlab-workhorse/ drwx--->---> 4 gitlab-prometheus root 83 May 20 09:12 grafana/ drwx--->---> 3 root root 71 May 21 02:21 logrotate/ drwxr-x---> 9 root gitlab-www 163 May 20 09:05 nginx/ drwx--->---> 2 gitlab-psql root 26 May 20 09:11 postgres-exporter/ drwxr-xr-x 3 gitlab-psql root 81 May 20 09:11 postgresql/ drwxr-x---> 4 gitlab-prometheus root 53 May 20 09:11 prometheus/ -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 226 May 20 09:12 public_attributes.json drwxr-x---> 2 gitlab-redis git 60 May 21 02:29 redis/ -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 40 May 20 09:01 trusted-certs-directory-hash 4.Just look postgresql,reids,gitlab-data,prometheus Directory users can, mainly these four #You can see that gitlab data users are git, postgresql users are gitlab PSQL, and redis users are gitlab redis root@192:/# id git uid=998(git) gid=998(git) groups=998(git) root@192:/# root@192:/# id gitlab-psql uid=996(gitlab-psql) gid=996(gitlab-psql) groups=996(gitlab-psql) root@192:/# root@192:/# id gitlab-redis uid=997(gitlab-redis) gid=997(gitlab-redis) groups=997(gitlab-redis) root@192:/# root@192:/# id gitlab-prometheus uid=992(gitlab-prometheus) gid=992(gitlab-prometheus) groups=992(gitlab-prometheus)
4.3. Write gitlab StorageClass resource file
[root@k8s-master1 gitlab]# vim gitlab-storageclass.yaml apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: StorageClass metadata: name: gitlab-storageclass provisioner: nfs-storage-01 reclaimPolicy: Retain
4.4. Write gitlab statefullset resource file
The StorageClass pvc template defines two, one for storing gitlab data and the other for storing gitlab configuration files
Assign the user uid and gid just found to each component directory through the initialization container
[root@k8s-master1 gitlab]# vim gitlab-statefulset.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: gitlab
namespace: jenkins
spec:
replicas: 1
serviceName: gitlab
selector:
matchLabels:
app: gitlab
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: gitlab
spec:
initContainers: #Define the initialization container and assign each component path to the corresponding user permissions
- name: gitlab-data-git
image: harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/busybox:1.30
command: ["sh","-c","chown -R 998:998 /var/opt/gitlab"] #git users authorize the entire gitlab data directory
securityContext: #Enable privileged mode
privileged: true
volumeMounts: #Mount the data persistent pvc
- name: gitlab-data
mountPath: /var/opt/gitlab
- name: gitlab-data-psql
image: harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/busybox:1.30
command: ["sh","-c","chown -R 996:996 /var/opt/gitlab/postgresql*"] #Gitlab PSQL authorization postgresql directory
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeMounts:
- name: gitlab-data
mountPath: /var/opt/gitlab
- name: gitlab-data-redis
image: harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/busybox:1.30
command: ["sh","-c","chown -R 997:997 /var/opt/gitlab/redis"] #Gitlab redis authorized redis directory
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeMounts:
- name: gitlab-data
mountPath: /var/opt/gitlab
- name: gitlab-data-prome #Gitlab prometheus user authorization prometheus directory
image: harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/busybox:1.30
command: ["sh","-c","chown -R 992:992 /var/opt/gitlab/alertmanager /var/opt/gitlab/grafana /var/opt/gitlab/prometheus"]
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeMounts:
- name: gitlab-data
mountPath: /var/opt/gitlab
- name: gitlab-config-chown #The initialization container is mainly used to authorize the configuration directory, which is optional, because the user of this directory is root, and the storage path created by nfs is also the owner of root by default
image: harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/busybox:1.30
command: ["sh","-c","chown -R 998:998 /etc/gitlab"] #Authorized to gitlab users
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeMounts:
- name: gitlab-config
mountPath: /etc/gitlab
containers: #Define master container
- name: gitlab
image: harbor.jiangxl.com/jenkins/gitlab-ce:13.11.4-ce.0
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
volumeMounts: #The path to mount the persistent data volume to the container
- name: gitlab-data
mountPath: /var/opt/gitlab
- name: gitlab-config
mountPath: /etc/gitlab
volumeClaimTemplates: #Define pvc template
- metadata: #Metadata is in the form of an array, so multiple can be defined. A metadata is a pvc template
name: gitlab-data #pvc name
spec:
storageClassName: gitlab-storageclass #StorageClass name used
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany #The access mode is multi host read-write
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
- metadata:
name: gitlab-config
spec:
storageClassName: gitlab-storageclass
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
4.5. Write gitlab service resource file
[root@k8s-master1 gitlab]# vim gitlab-svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: gitlab
name: gitlab-svc
namespace: jenkins
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 30080
selector:
app: gitlab
type: NodePort
4.6. Create all resources and view status
1.Create all resources [root@k8s-master1 gitlab]# kubectl apply -f ./ statefulset.apps/gitlab created storageclass.storage.k8s.io/gitlab-storageclass created service/gitlab-svc created 2.View the status of resources [root@k8s-master1 gitlab]# kubectl get all -n jenkins NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/gitlab-0 1/1 Running 0 4m21s pod/jenkins-master-0 1/1 Running 0 18h NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/gitlab-svc NodePort 10.101.97.95 <none> 80:30080/TCP 57m service/jenkins-svc NodePort 10.99.113.179 <none> 8080:38080/TCP,50000:50000/TCP 23h NAME READY AGE statefulset.apps/gitlab 1/1 57m statefulset.apps/jenkins-master 1/1 23h 3.see pvc Status of the resource [root@k8s-master1 gitlab]# kubectl get pvc -n jenkins NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE gitlab-config-gitlab-0 Bound pvc-91e63538-e07d-4196-82e8-4195b29d9352 1Gi RWX gitlab-storageclass 64m gitlab-data-gitlab-0 Bound pvc-2a300c8d-49e6-4035-99f1-81c3e190fe3e 10Gi RWX gitlab-storageclass 57m jenkins-data-jenkins-master-0 Bound pvc-9efb572b-d566-418d-bb6e-b225b43de4a5 10Gi RWX jenkins-storageclass 23h
4.7. Modify gitlab configuration
After the gitlab service is started, the configuration file and data directory will be stored on pvc. We need to modify the gitlab configuration file to specify the access address
Main: only write the address here and do not add the port. If a port other than 80 is added, the 80 of gitlab in the container will be changed to the port you specify, and the svc will fail to expose gitlab
This step can also be omitted, because for k8s, it is mapped through the ip of any node in the cluster
[root@k8s-master2 ~]# vim /data2/k8s/storageclass/jenkins-gitlab-config-gitlab-0-pvc-91e63538-e07d-4196-82e8-4195b29d9352/gitlab.rb external_url 'http://192.168.16.106'
After modification, redeploy gitlab
[root@k8s-master1 gitlab]# kubectl replace -f gitlab-statefulset.yaml statefulset.apps/gitlab replaced
4.8. Access gitlab
Access http: / / any node of the cluster ip:30080 port
Gitlab starts slowly. Enter the container to check the status of gitlab. You can access it after run ning

1) Set user password
At least 8 bits. admin123 is set here
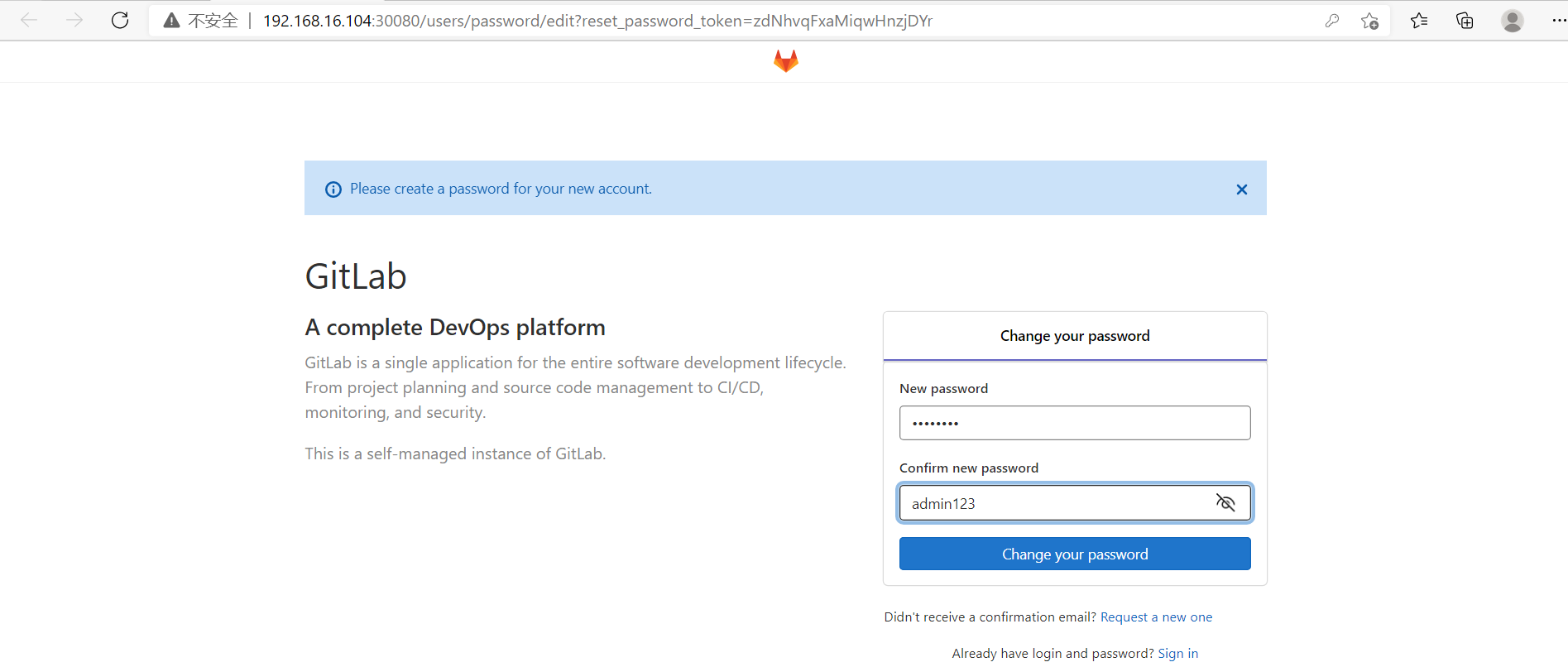
2) Enter gitlab

3) Set language to Chinese

5. Submit the program code to gitlab
5.1. Create a new project
1) Click new item
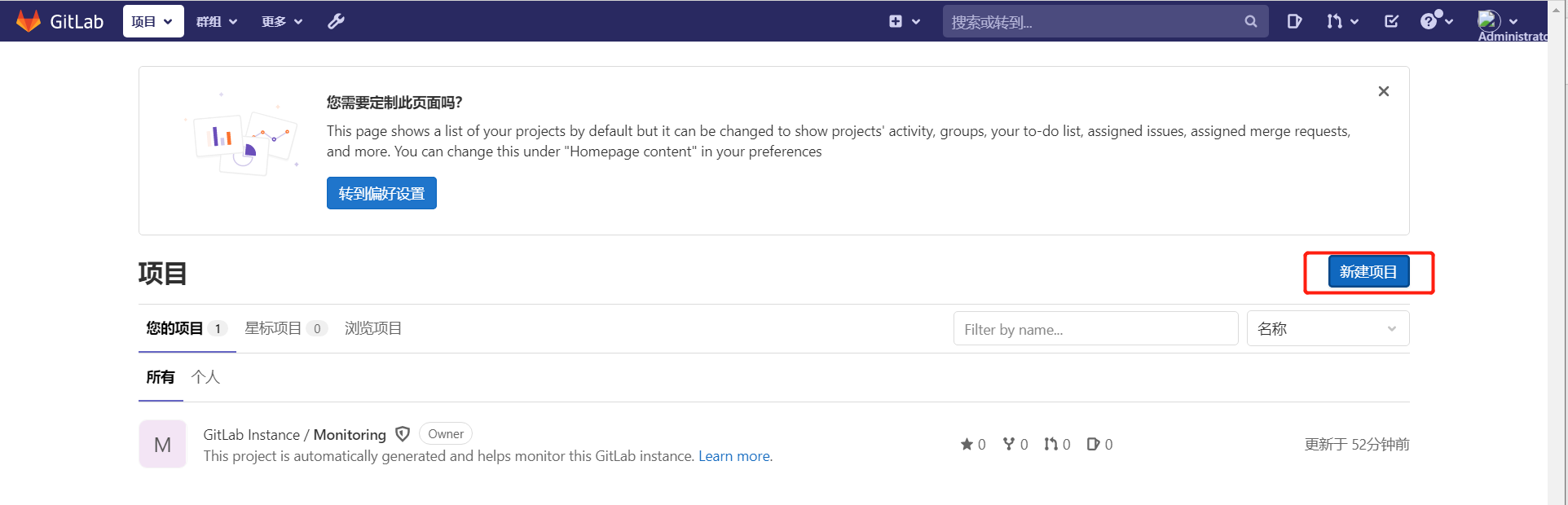
2) Create a blank item

3) Fill in project information
The visibility level is set to public
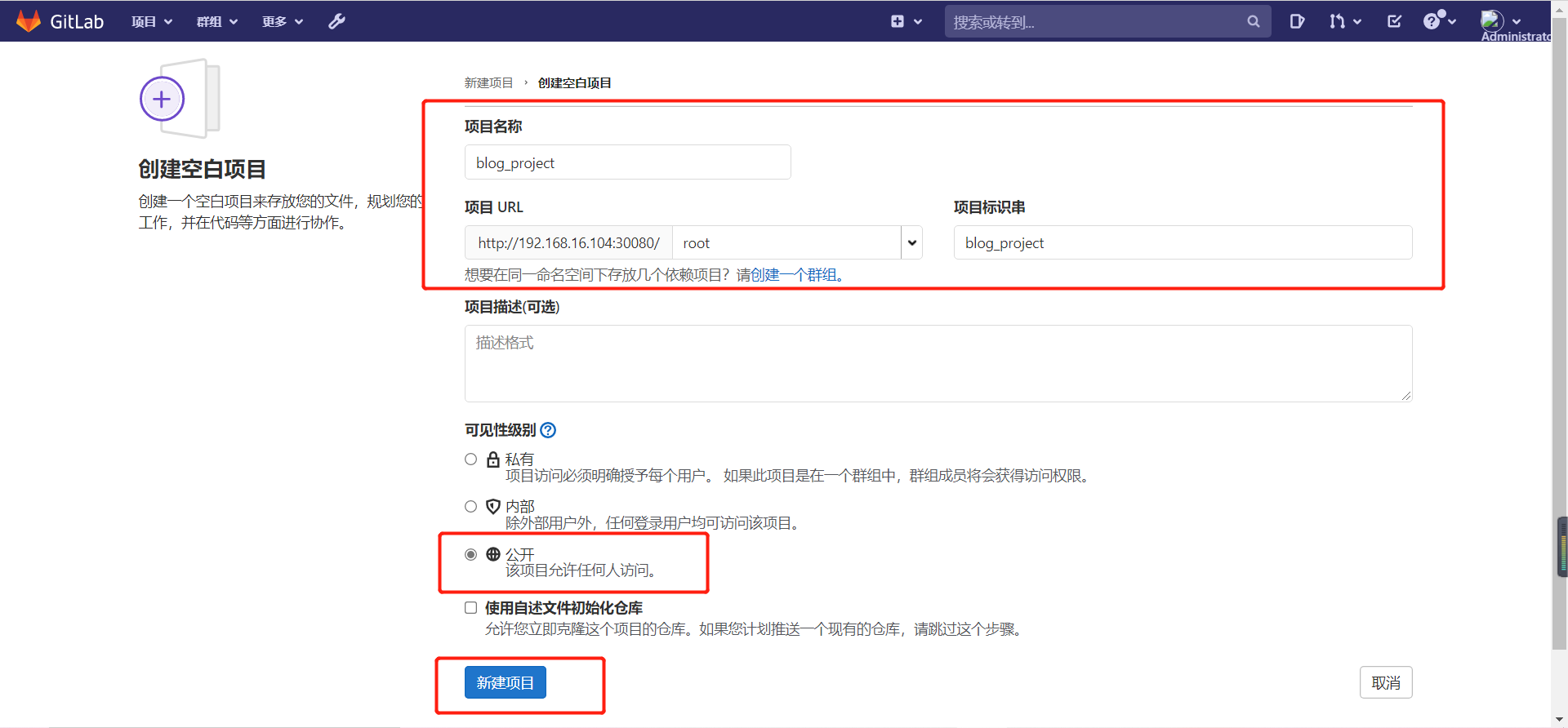
4) Creation complete

5.2. Submit the program code to gitlab
[root@k8s-master1 python-demo]# git init Initialize empty Git Version library at /root/gitlab_project/python-demo/.git/ [root@k8s-master1 python-demo]# git remote add origin http://192.168.16.106:30080/root/blog_project.git [root@k8s-master1 python-demo]# git add . [root@k8s-master1 python-demo]# git commit -m "Initial commit" [root@k8s-master1 python-demo]# git push -u origin master Username for 'http://192.168.16.106:30080': root # enter one user name Password for 'http://root@192.168.16.106:30080': # Input password Counting objects: 48, done. Delta compression using up to 4 threads. Compressing objects: 100% (44/44), done. Writing objects: 100% (48/48), 978.49 KiB | 0 bytes/s, done. Total 48 (delta 4), reused 0 (delta 0) To http://192.168.16.106:30080/root/blog_project.git * [new branch] master -> master branch master Set to track from origin Remote branch of master.
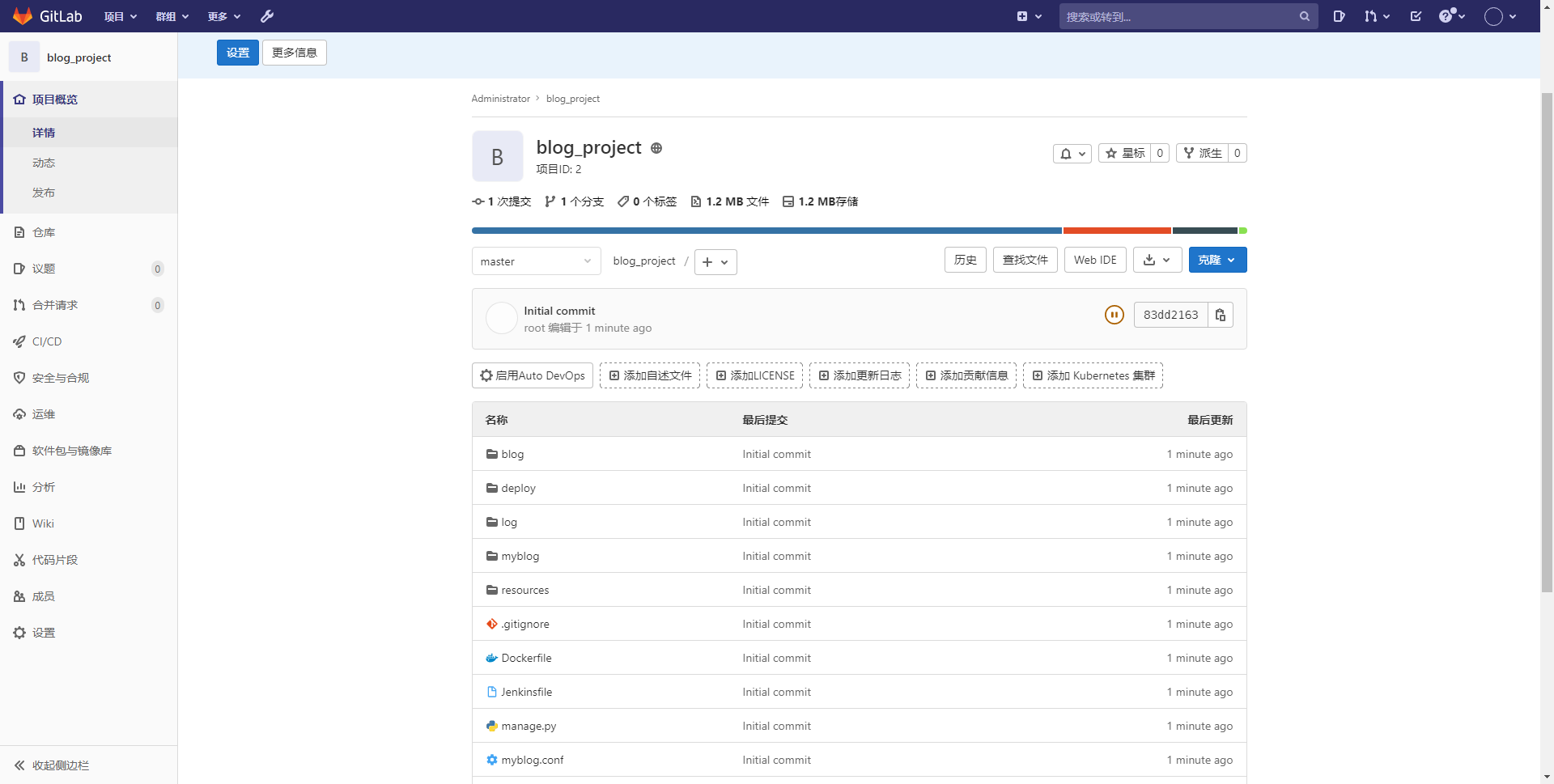
6.Jenkins integrated gitlab
gitlab address must be configured in jenkins, otherwise pipeline cannot find git lab address
6.1. Installing the gitlab plug-in on Jenkins
Modify Jenkins default source to Tsinghua source
1.Modify source cd /data2/k8s/storageclassjenkins-jenkins-data-jenkins-master-0-pvc-9efb572b-d566-418d-bb6e-b225b43de4a5/updates sed -i 's/http:\/\/updates.jenkins- ci.org\/download/https:\/\/mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn\/jenkins/g' default.json sed -i 's/http:\/\/www.google.com/https:\/\/www.baidu.com/g' default.json 2.restart Jenkins [root@k8s-master1 ~]# kubectl replace -f /root/k8s1.19/jenkins/jenkins-statefulset.yaml statefulset.apps/jenkins-master replaced
System management - > plug-in management - > optional plug-ins - > search gitlab - > install

6.2. Generate token on gitlab
edit profile - > access token - > fill in the token name - > check the permission range
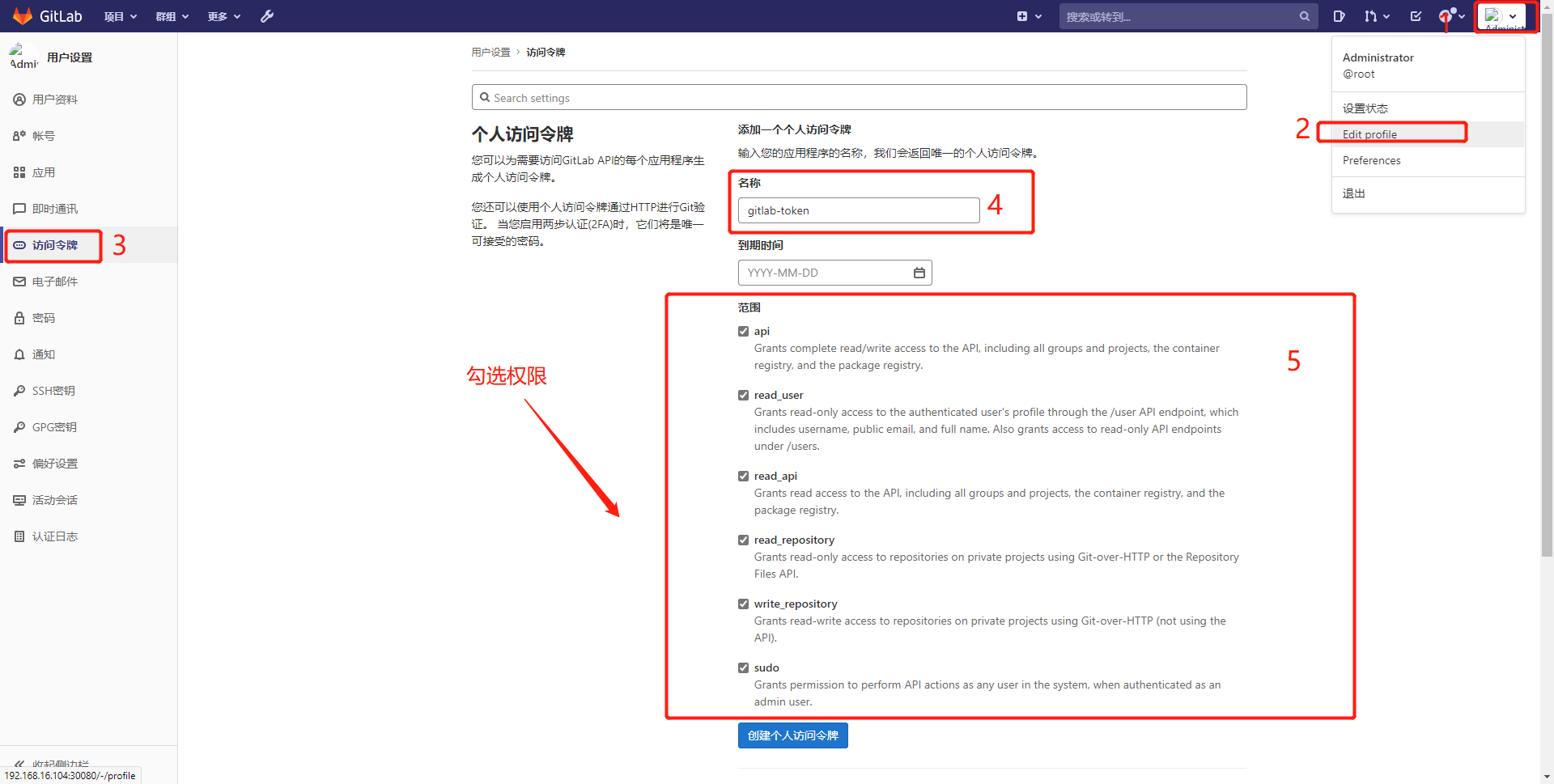
The token is displayed only once and kept properly: F4N8_LrfC7BdNWXXyJA2
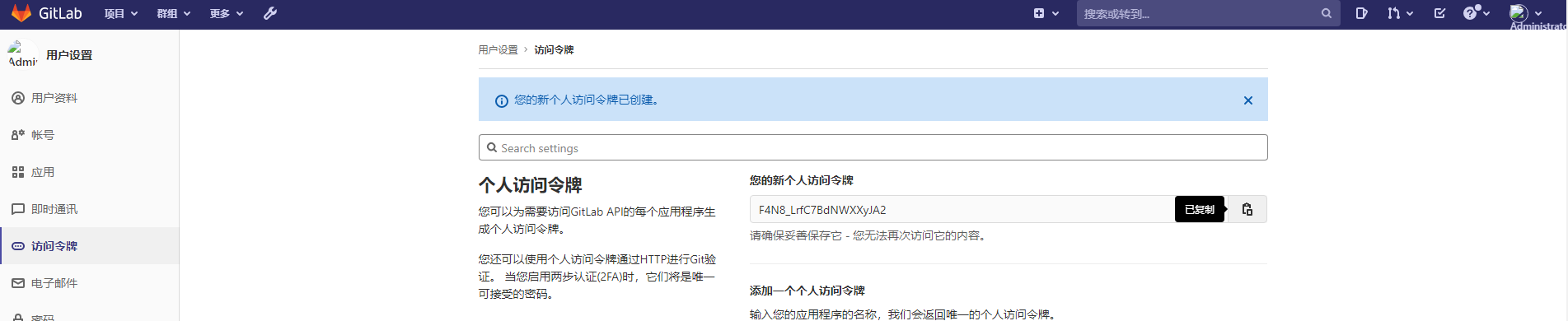
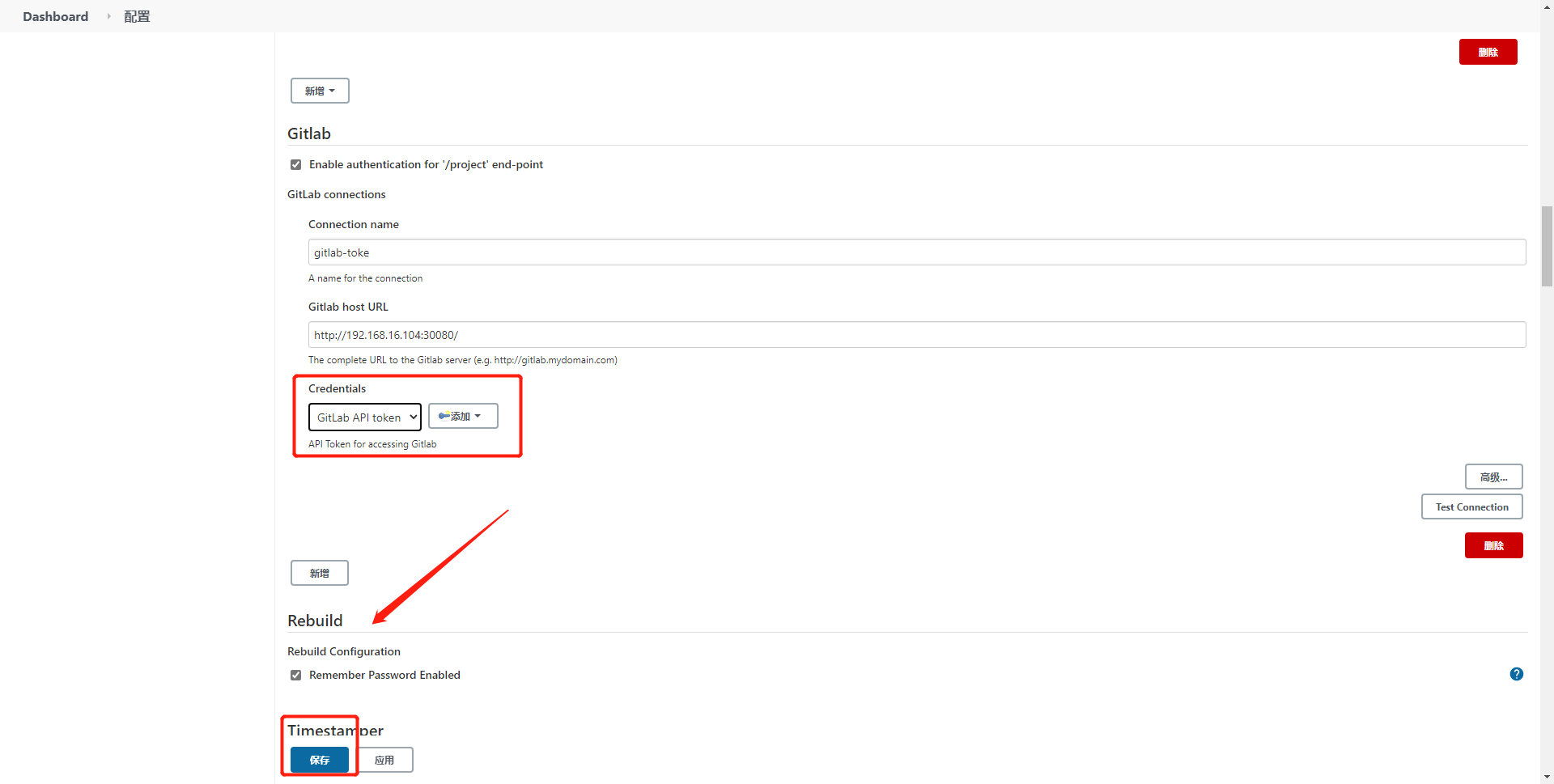
6.3. Add gitlab api token in Jenkins
System management - > find gitlab - > configure it
Connection name: gitlab-token
Gitlab host URL: http://192.168.16.104:30080/

After filling in the basic information, click add gitlab token. You can only select gitlab api token as the type and paste it in

After adding the token, select the token just added from the drop-down list. It will no longer turn red, indicating that the connection to gitlab is successful
7.Jenkins distributed master slave mode
Jenkins distributed means that there are multiple slave nodes. When there are many projects to be built, the performance of the master will be affected. The slave will bear the workload of the master and create projects on the slave. The difference between the slave node and the master node is that the slave does not need to install Jenkins
slave nodes can be deployed in many ways. We use
7.1. Add Jenkins node
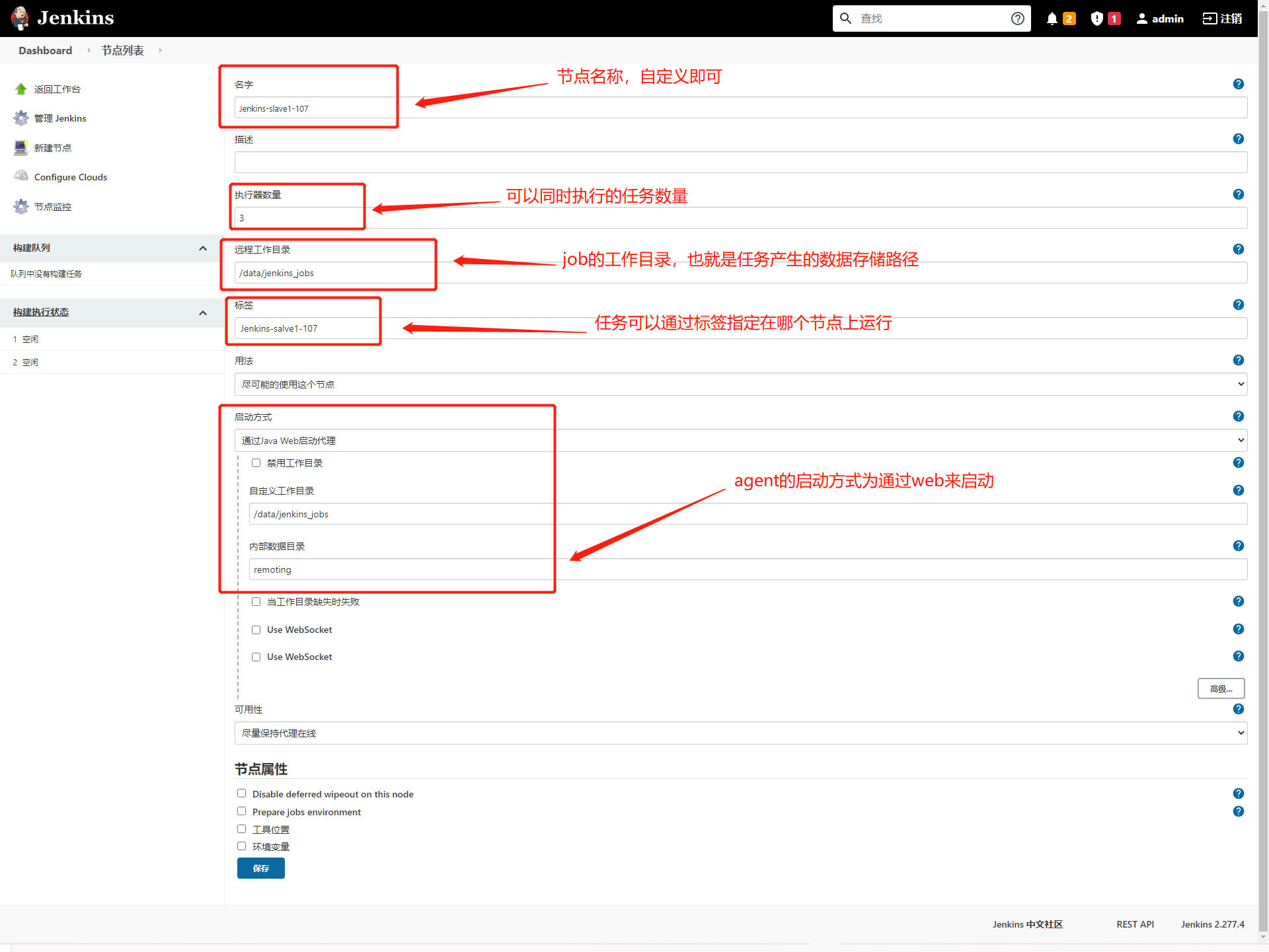
1) System management - > node management - > new node - > fill in node name - > fixed node - > OK

2) Add node details
Name: Jenkins-slave1-107
Number of actuators: 3
Remote working directory: / data/jenkins_jobs
Label: Jenkins-slave1-107 # is used to make Jenkins run a task on a node
Usage: use this node as much as possible
Start method: start the agent through java web
Custom working directory: / data/jenkins_jobs
3) After adding the node, it is found that the node is red, which indicates that the agent has not been started, and Jenkins does not know who the node is
Click the node and you will see how to start the agent. Right click to copy the agent Get the link address of jar, download the jar package on the corresponding server, and then start to successfully add the node
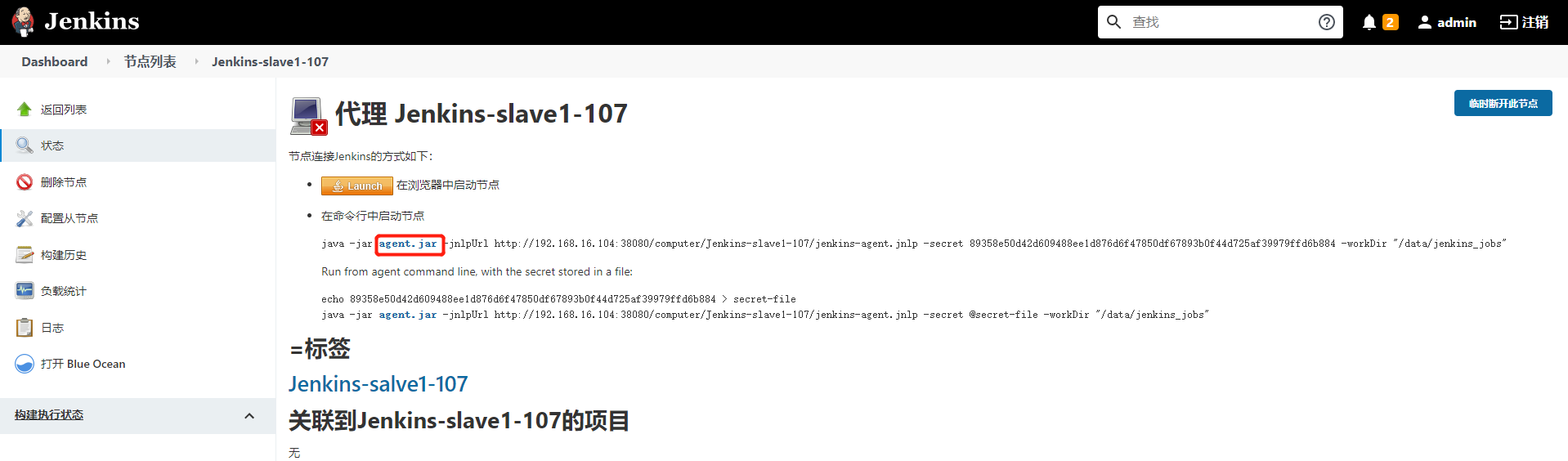
1.Create node working directory [root@k8s-node2 ~]# mkdir /data/jenkins_jobs [root@k8s-node2 ~]# cd /data/jenkins_jobs 2.download agent program [root@k8s-node2 /data/jenkins_jobs]# wget http://192.168.16.104:38080/jnlpJars/agent.jar 3.start-up agent [root@k8s-node2 /data/jenkins_jobs]# nohup java -jar agent.jar -jnlpUrl http://192.168.16.104:38080/computer/Jenkins-slave1-107/jenkins-agent.jnlp -secret efbde6c51590ca2c9097e6866de9f2d18520bfc05440a1872135e78b47283721 -workDir "/data/jenkins_jobs" & Command interpretation: java -jar agent.jar \ #Start the jar package -jnlpUrl http://192.168.16.104:38080/computer/Jenkins-slave1-107/jenkins-agent.jnlp \ # This path is the path of the node after we create a new node on Jenkins. If it is not specified, Jenkins does not know which server this node corresponds to -secret efbde6c51590ca2c9097e6866de9f2d18520bfc05440a1872135e78b47283721 \ #authentication -workDir "/data/jenkins_obs" & #working directory
After the agent is started, observe the node on the Jenkins page and find that it is already available
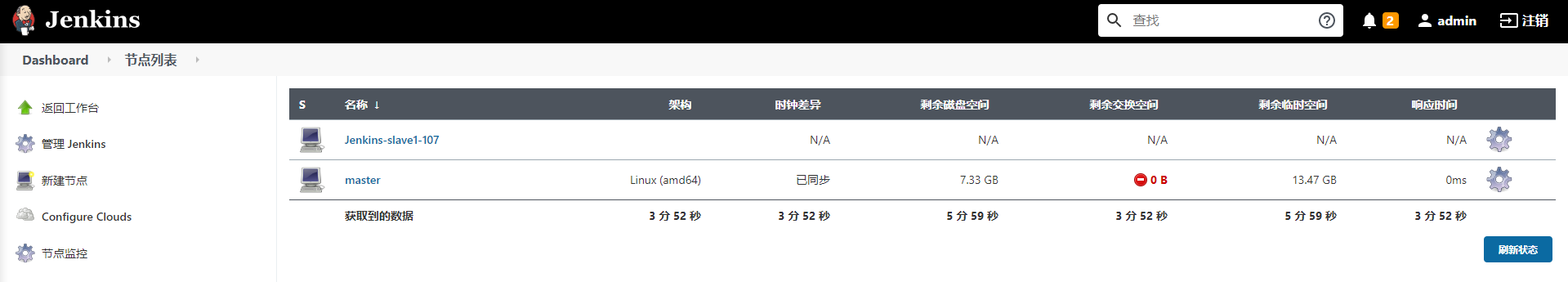
7.2. Create a new task to run on the slave1 node
1) Configure task - > General - > restrict the running node of the project - > fill in the label set by the node

2) Run the task to observe which node it is running on
Select the master branch to start building

The task has been run on the jenkins-slave 1-107 node
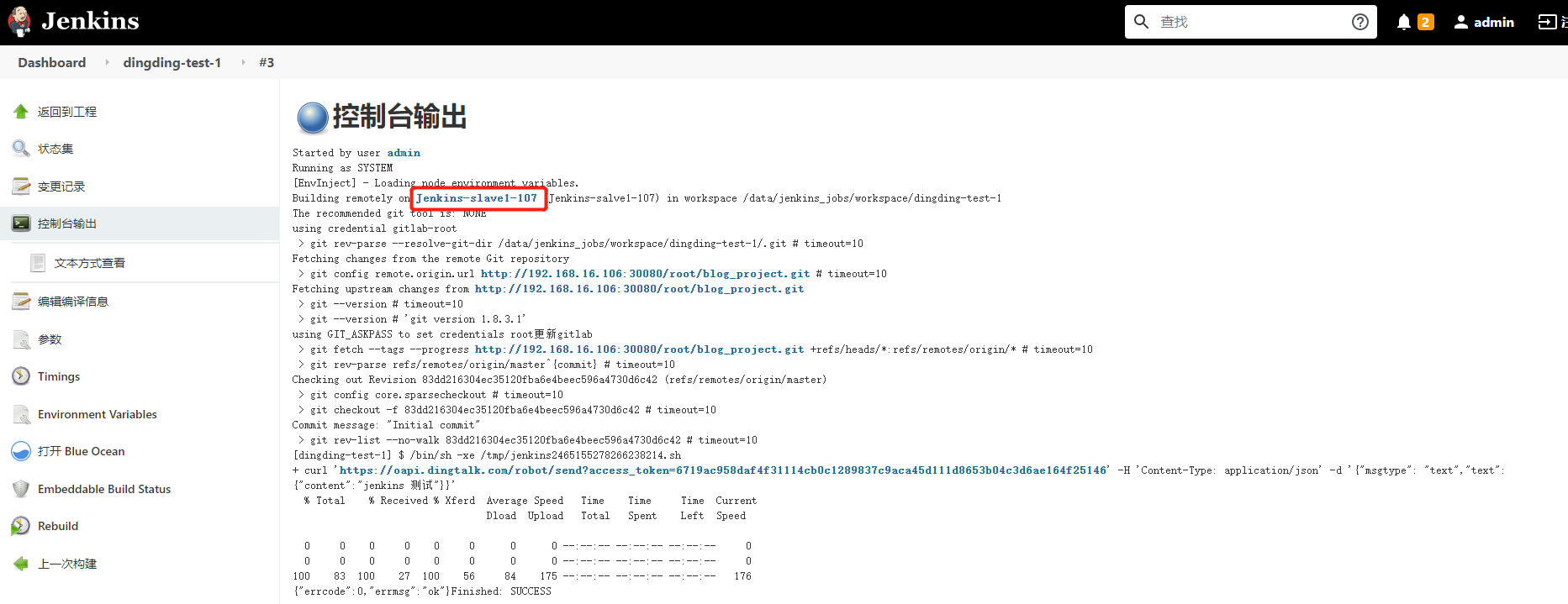
The nail has received the information and has generated data in the node working directory
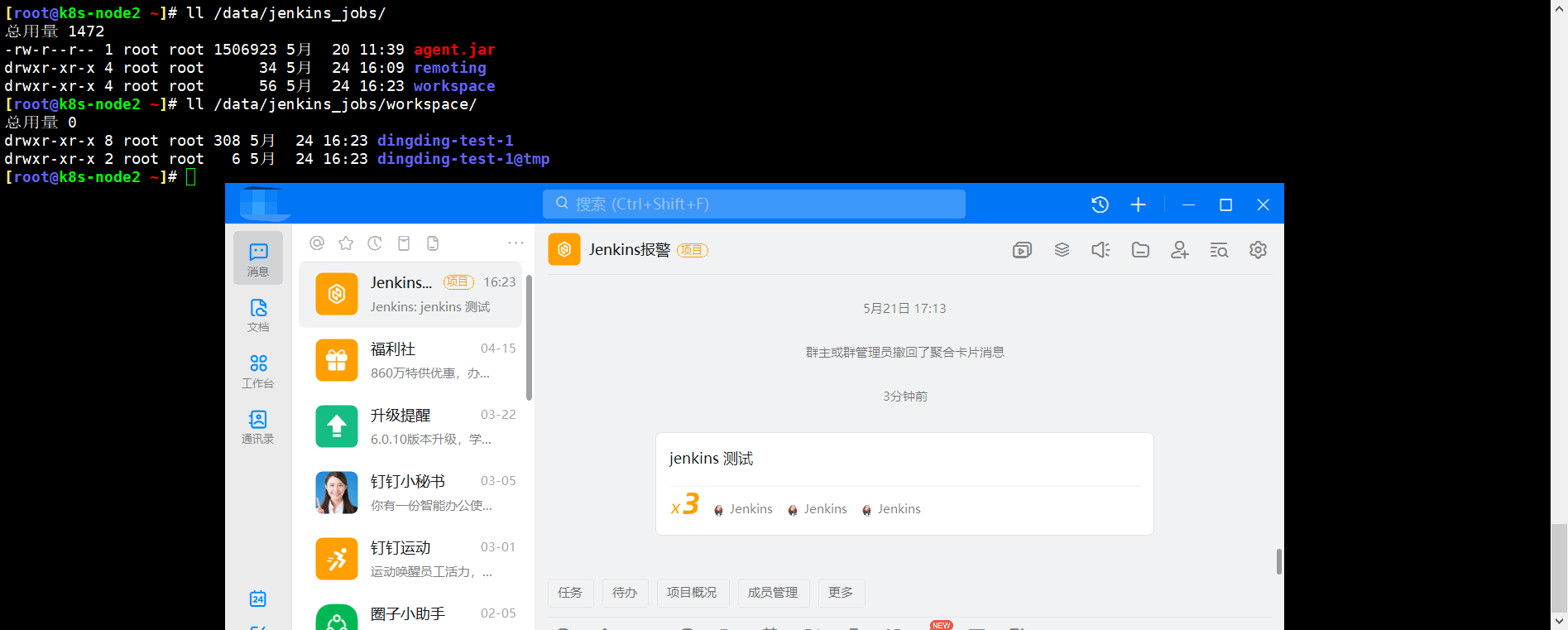
7.3. Execution tasks associated with observation nodes
At this stage, the CI/CD platform has been deployed. We can create a new process and update the program to the kubernetes platform
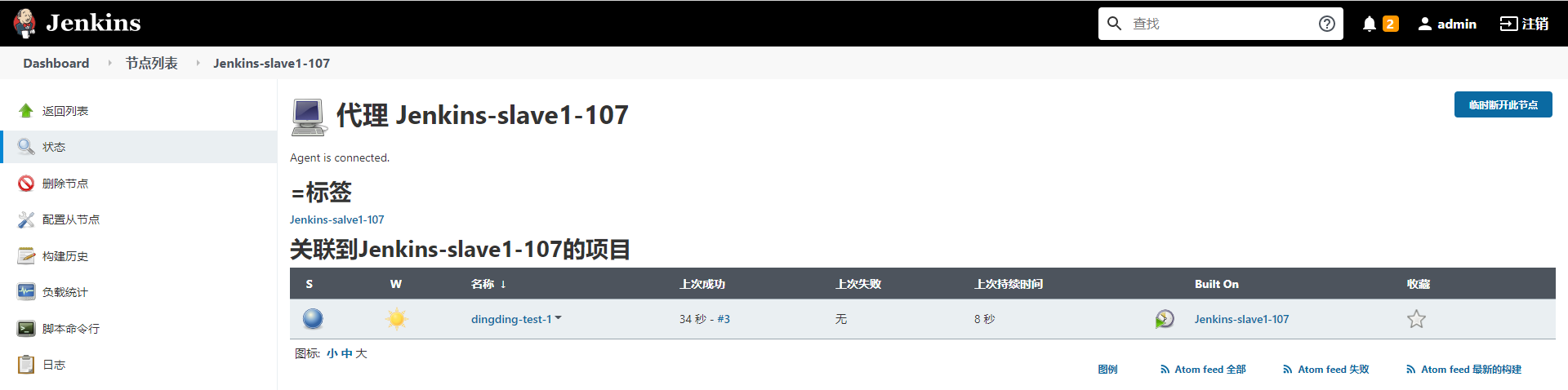
8. Update the know system project to the kubernetes environment using the pipeline pipeline
There are two ways to update k8s
1. Upload the resource yaml file to the code warehouse. After the project is mirrored, we can replace the latest version of the image into the deployment resource by replacing the string of the image specified by the deployment resource. Finally, execute kubectl apply/ Update complete
2. Execute the kubectl command to update the image of the deployment resource
Since our construction tasks are run through agent s, which are deployed on the k8s node and inherit the docker and kubectl commands, there is no need to worry about the failure of the kubectl command
8.1. Realization idea
1. First, deploy the know system in k8s to realize the accessible state
2. Copy the yaml file of the deployment know system to the code directory, and change the image corresponding to the container image in the deployment resource to a string, so that when the pipeline is updated, the latest image version can be replaced into the deployment resource by replacing the string, and finally push the code and deployment file to gitlab
3. Optimize pipeline script and add k8s deployment steps
4. Update the code and use the pipeline to update the project to k8s
8.2. Deploy the know system in k8s
1) Prepare project yaml files
1.prepare deployment resources
[root@k8s-master1 know-system]# cat nginx-depoly.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: know-system
namespace: know-system
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: know-system
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: know-system
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: harbor.jiangxl.com/project/nginx-project:v1-code
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: nginx-data
mountPath: /data/code
- name: nginx-config
mountPath: /data/nginx/conf/conf.d/
volumes:
- name: nginx-config
configMap:
name: nginx-configmap
- name : nginx-data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc-know
readOnly: false
2.prepare configmap resources
[root@k8s-master1 know-system]# cat nginx-configmap.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-configmap
namespace: know-system
data:
know.jiangxl.com.conf: |
server {
listen 80;
server_name know.jiangxl.com;
location / {
root /data/code/know_system;
index index.html;
}
}
3.prepare svc resources
[root@k8s-master1 know-system]# cat nginx-svc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
namespace: know-system
spec:
selector:
app: know-system
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
2) Create all resources
[root@k8s-master1 know-system]# kubectl apply -f ./ configmap/nginx-configmap unchanged deployment.apps/know-system configured service/nginx-service configured
3) View project home page
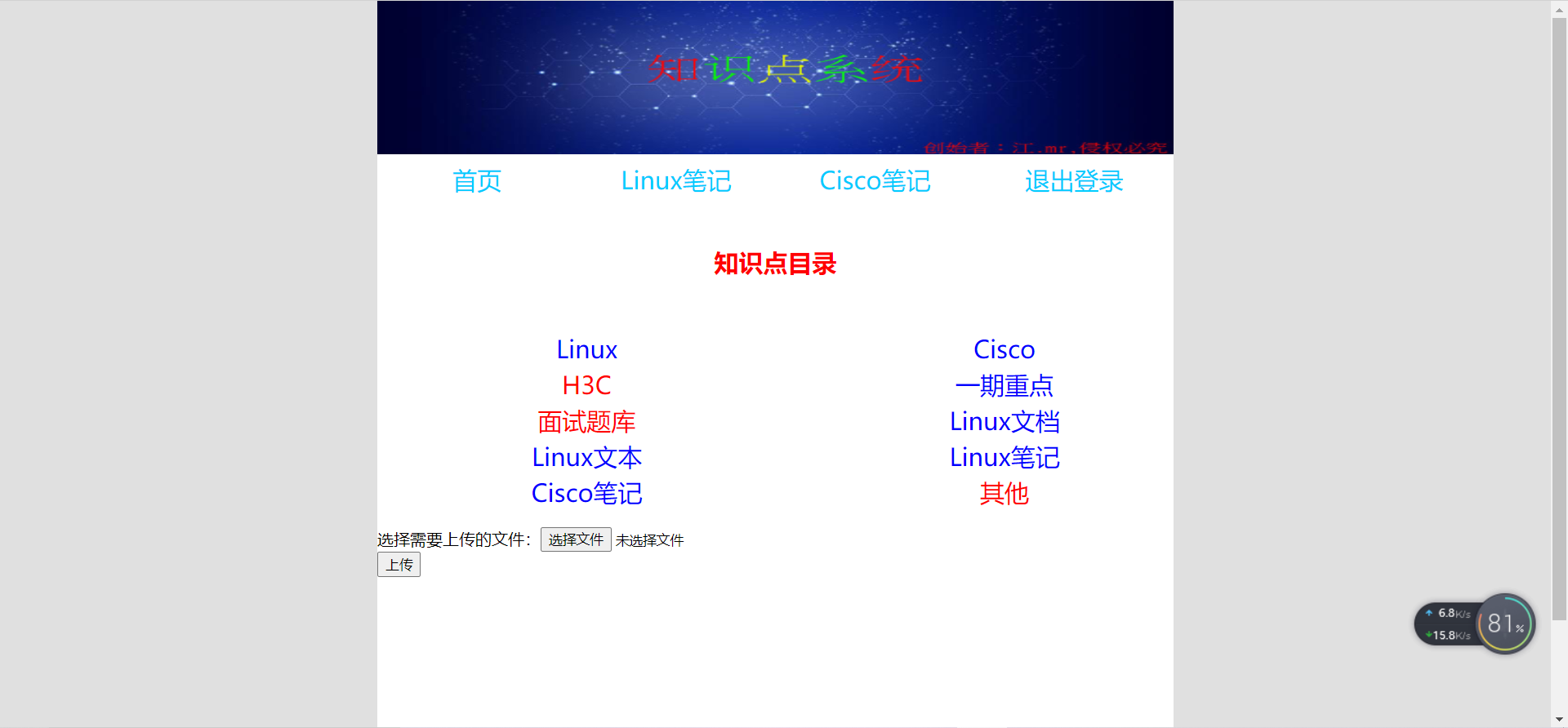
8.3. Submit the k8s resource file to gitlab
1.Copy the deployment file to the code directory
[root@k8s-master1 know_system]# mkdir deploy
[root@k8s-master1 know_system]# cp /root/k8s1.19/know-system/* deploy/
2.modify deployment In resources image
#Change the image corresponding to the image into a string. When updating the pipeline, you can replace the latest image into the deployment resource by replacing this string
[root@k8s-master1 know_system]# vim deploy/nginx-depoly.yaml
image: {{updateimage}}
2.Submit to gitlab
[root@k8s-master1 know_system]# git add .
[root@k8s-master1 know_system]# git commit -m "deploy"
[root@k8s-master1 know_system]# git push origin master
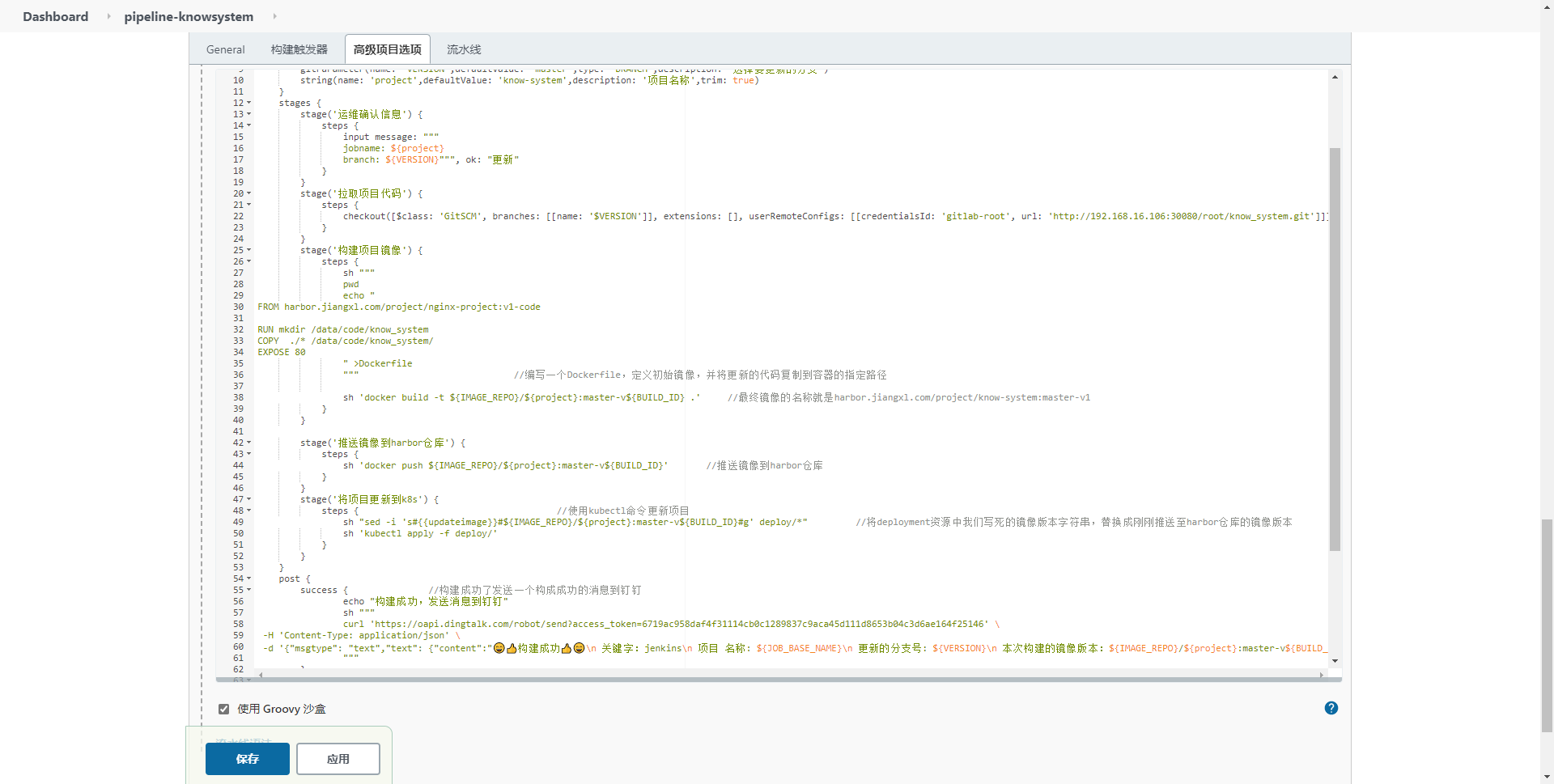
8.4. Write Jenkins pipeline to update the project to k8s
The current pipeline script mainly updates the project pod created with yaml file
pipeline {
agent { label 'Jenkins-slave1-107' } //Make the pipeline always run on the Jenkins-slave1-107 Jenkins agent node, because the server where this node is located can run the docker and kubelet commands of the k8s cluster
environment { //Environment is mainly used to define environment variables. Some commonly used values can be made into environment variables
IMAGE_REPO="harbor.jiangxl.com/project"
}
parameters { //Define parametric build process
gitParameter(name: 'VERSION',defaultValue: 'master',type: 'BRANCH',description: 'Select the branch to update') //Define a gitparamters parameterized build process for selecting updated code
string(name: 'project',defaultValue: 'know-system',description: 'entry name',trim: true) //Define a blank string to declare the project name
}
stages { //Define pipeline execution phase
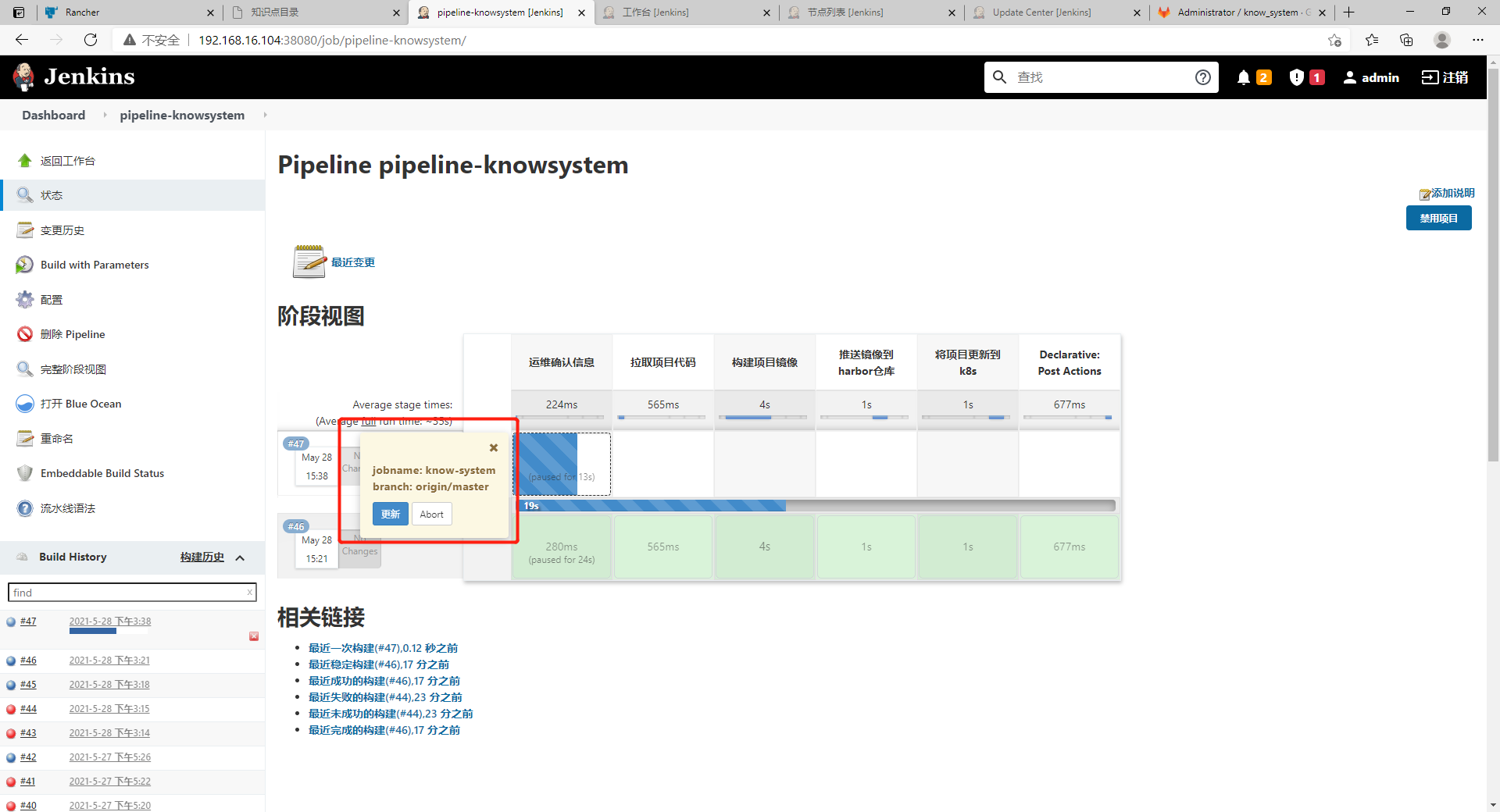
stage('Operation and maintenance confirmation information') { //In phase 1, an interactive is used to let the operation confirm the update information. If there is an error, you can directly exit the update to avoid the update error
steps {
input message: """
jobname: ${project}
branch: ${VERSION}""", ok: "to update" //Interactively output an updated item and branch number
}
}
stage('Pull item code') { //Phase 2 is used to pull the corresponding project code on git
steps {
checkout([$class: 'GitSCM', branches: [[name: '$VERSION']], extensions: [], userRemoteConfigs: [[credentialsId: 'gitlab-root', url: 'http://192.168.16.106:30080/root/know_system.git']]])
}
}
stage('Build project image') { //Phase 3 It is used to update the project code to the initial docker image. The main step is to produce a dockerfile, copy the code to the image, and finally build the image according to the dockerfile
steps {
sh """
pwd
echo "
FROM harbor.jiangxl.com/project/nginx-project:v1-code
RUN mkdir /data/code/know_system
COPY ./* /data/code/know_system/
EXPOSE 80
" >Dockerfile
""" //Write a Dockerfile, define the initial image, and copy the updated code to the specified path of the container
sh 'docker build -t ${IMAGE_REPO}/${project}:master-v${BUILD_ID} .' //The name of the final image is harbor jiangxl. com/project/know-system:master-v1
}
}
stage('Push mirror to harbor Warehouse') { //In phase 4, the constructed image is pushed to the harbor warehouse to k8s pull the update program
steps {
sh 'docker push ${IMAGE_REPO}/${project}:master-v${BUILD_ID}' //Push image to harbor warehouse
}
}
stage('Update project to k8s') { //Phase 5 is mainly to update k8s the container used by the project, replace the newly built image with the project pod, and then update the pod
steps { //Update the project using the kubectl command
sh "sed -i 's#{{updateimage}}#${IMAGE_REPO}/${project}:master-v${BUILD_ID}#g' deploy/*" // Replace the image version string we wrote in the deployment resource with the image version just pushed to the harbor warehouse
sh 'kubectl apply -f deploy/' //When the image version is replaced, the project update can be completed by updating the yaml file of the resource
}
}
}
post {
success { //The build successfully sends a message constituting success to the nail
echo "Build succeeded, send message to nail"
sh """
curl 'https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=6719ac958daf4f31114cb0c1289837c9aca45d111d8653b04c3d6ae164f25146' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"msgtype": "text","text": {"content":"😄👍Build successful👍😄\n keyword: jenkins\n Project name: ${JOB_BASE_NAME}\n Updated branch number: ${VERSION}\n Image version of this build: ${IMAGE_REPO}/${project}:master-v${BUILD_ID}\n Build address: ${RUN_DISPLAY_URL} "}}'
"""
}
failure { //The build failed. Send a success message to the nail
echo "Build failed, send message to pin"
sh """
curl 'https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=6719ac958daf4f31114cb0c1289837c9aca45d111d8653b04c3d6ae164f25146' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"msgtype": "text","text": {"content":"😖❌Build failed❌😖\n keyword: jenkins\n Project name: ${JOB_BASE_NAME}\n Updated branch number: ${VERSION}\n Image version of this build: ${IMAGE_REPO}/${project}:master-v${BUILD_ID}\n Build address: ${RUN_DISPLAY_URL} "}}'
"""
}
always { //Perform this step regardless of success or failure
echo "End of construction process"
}
}
}
8.5. Paste pipeline into pipeline task
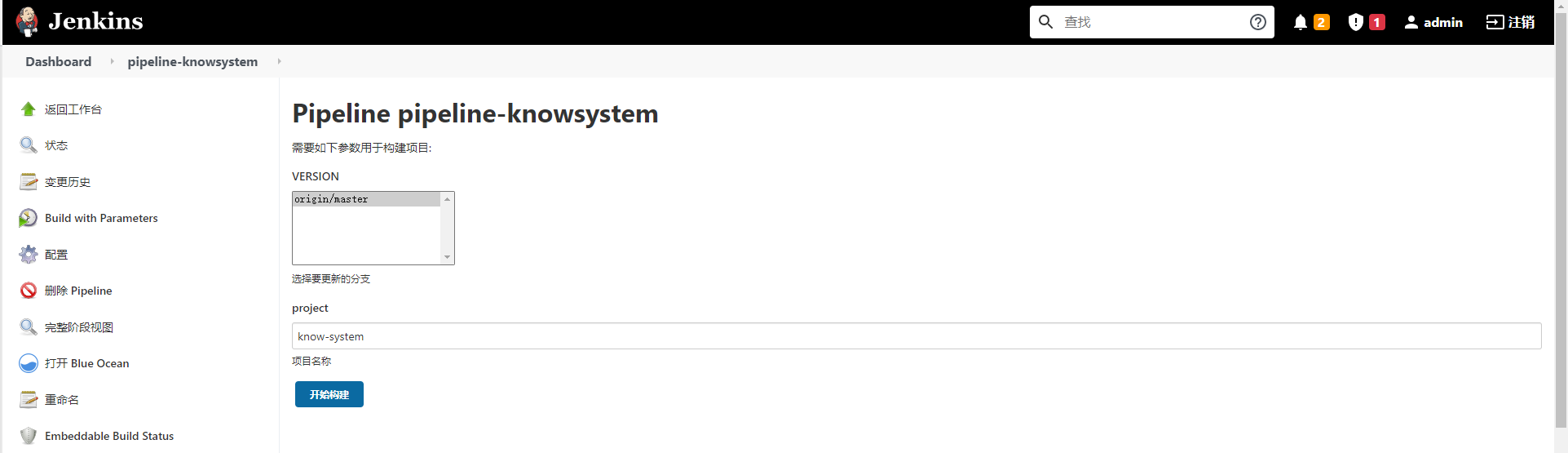
8.6. Build master branch to complete project update
1) Select update information
2) Operation and maintenance confirmation information
3) pipeline task updated successfully
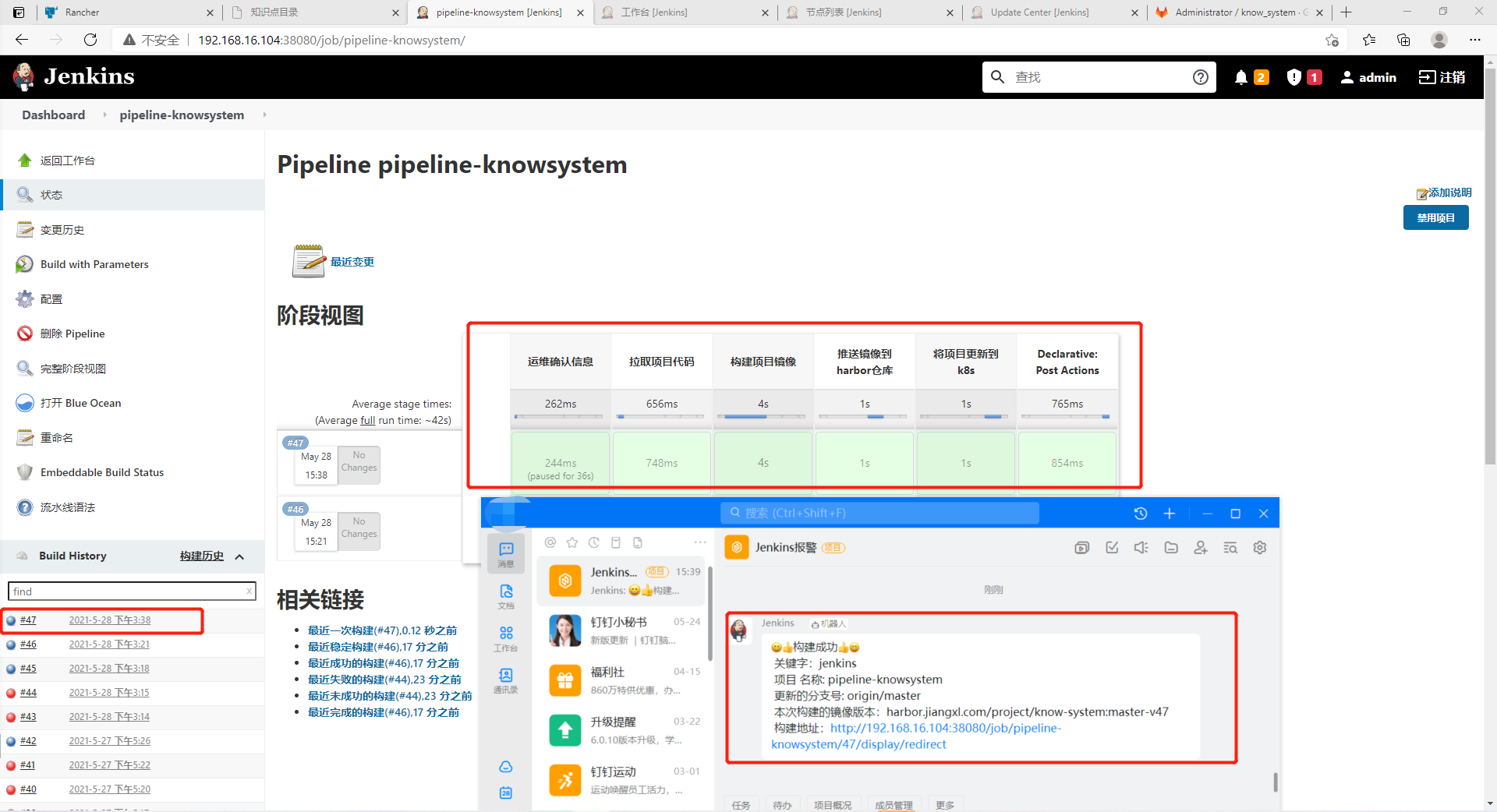
4) View the updated image version in blue ocean
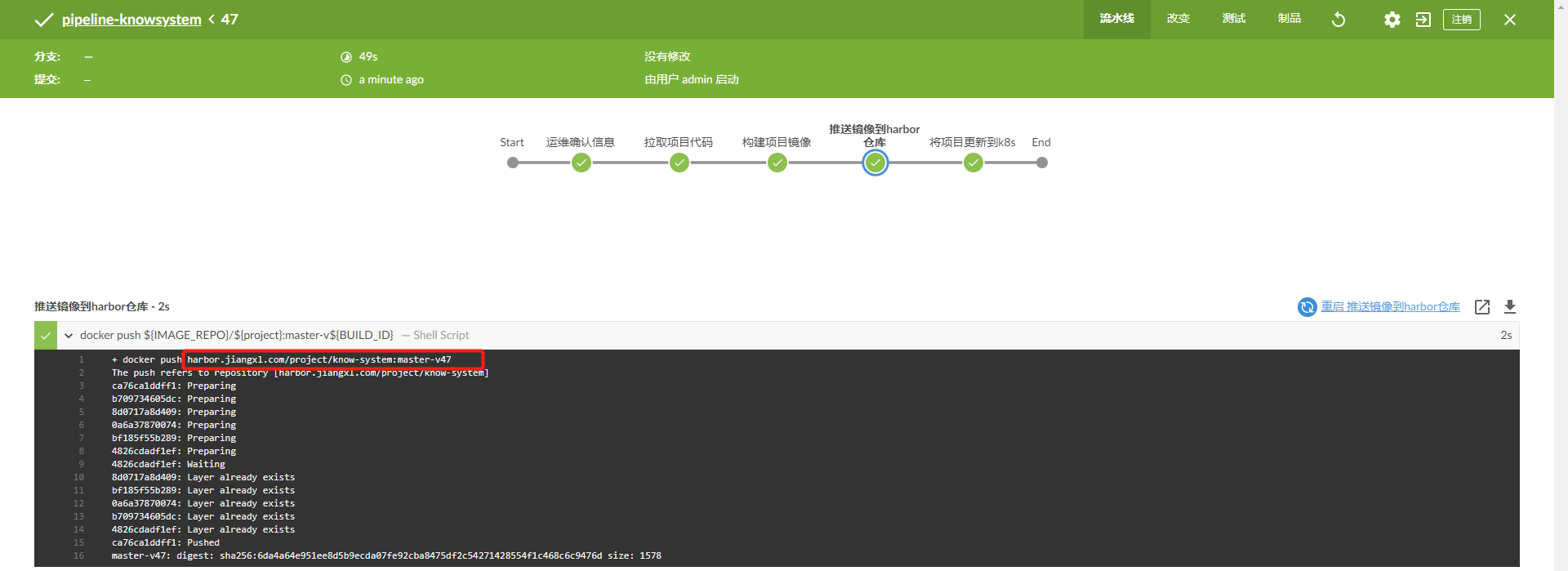
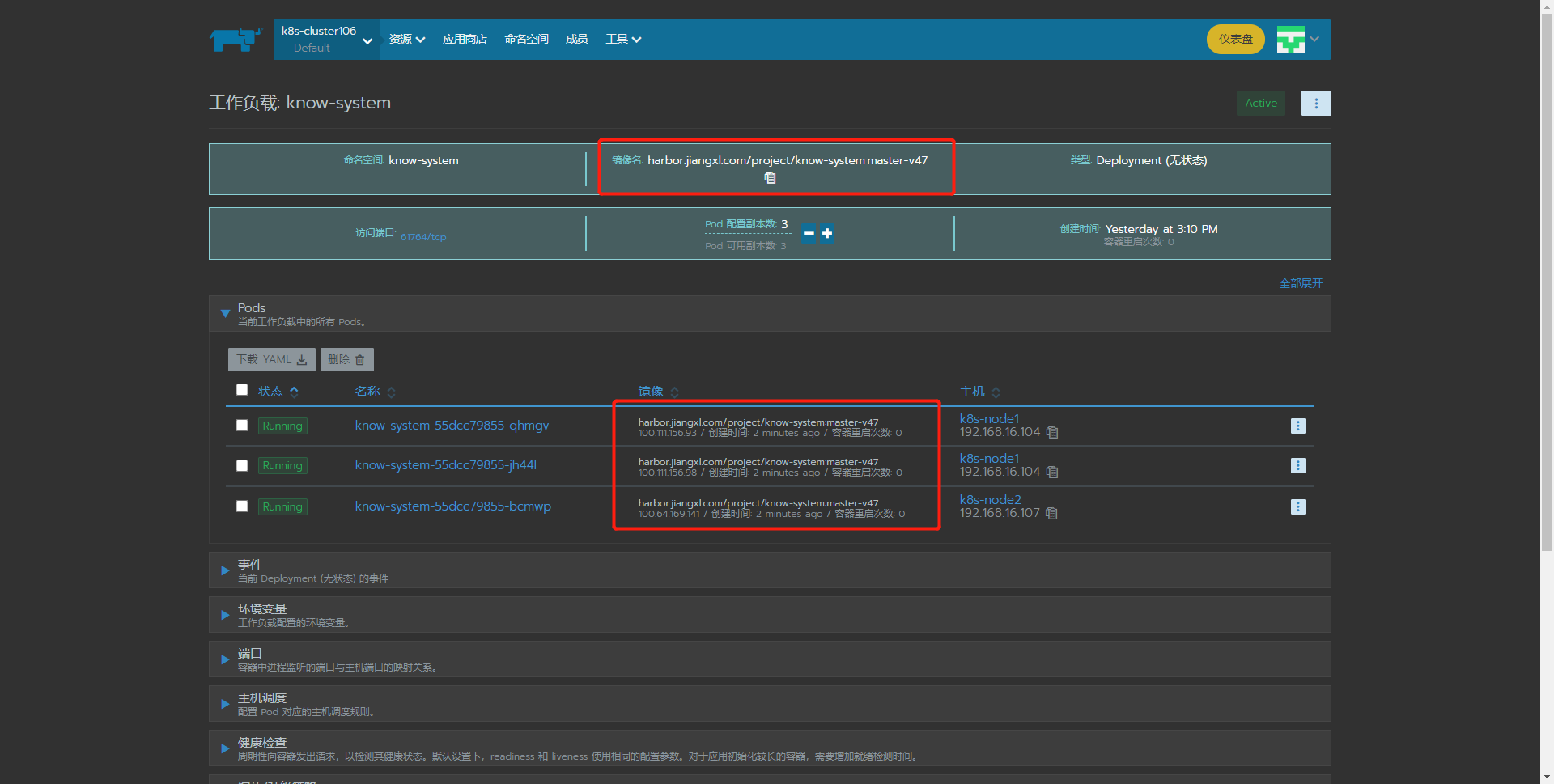
5) Observe whether the project is updated to the latest mirror version on rancher
The update process completed successfully!