First, read the image and gray it.
cv::Mat srcImg = cv::imread("group.jpg");
if (srcImg.empty())
{
cout << "error";
return -1;
}
cv::namedWindow("SRC", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow("SRC", srcImg);
cv::Mat srcGray;
cv::cvtColor(srcImg, srcGray, cv::COLOR_RGB2GRAY);
cv::namedWindow("GRAY", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow("GRAY", srcGray);

The gray image is binarized.
cv::Mat thesImg;
cv::threshold(srcGray, thesImg, 60, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow("THRESHOLD", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow("THRESHOLD", thesImg);
Morphological filtering is applied to binary image, which first opens and then closes to remove noise. In order to facilitate subsequent display, the results are reversed.
cv::Mat element(5, 5, CV_8U, cv::Scalar(1));
cv::Mat opened;
cv::morphologyEx(thesImg, opened, cv::MORPH_OPEN, element);
cv::Mat closed;
cv::morphologyEx(opened, closed, cv::MORPH_CLOSE, element);
cv::Mat morphInv = 255 - closed;
cv::namedWindow("MORPH", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow("MORPH", morphInv);
OpenCV provides a function to extract contours of contiguous regions in an image. Its prototype function is
void cv::findContours(InputOutputArray image,
OutputArrayOfArrays contours,
OutputArray hierarchy,
int mode,
int method,
Point offset = Point()
) Where the value of mode is in the enumeration type cv::RetrievalModes in

The method value is taken in the enumeration type cv::ContourApproximationModes in

std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>> contours;
cv::findContours(morphInv, contours, cv::RETR_EXTERNAL, cv::CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
cv::Mat result(opened.size(), CV_8U, cv::Scalar(255));
cv::drawContours(result, contours, -1, 0, 2);
cv::namedWindow("CONTOURS", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow("CONTOURS", result);

If the size of the object of interest is known beforehand, the continuous regions identified can be analyzed independently, and some regions can be deleted.
int cmin = 50;
int cmax = 500;
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>>::iterator it = contours.begin();
while (it != contours.end())
{
if (it->size() < cmin || it->size() > cmax)
{
it = contours.erase(it);
}
else
{
++it;
}
}
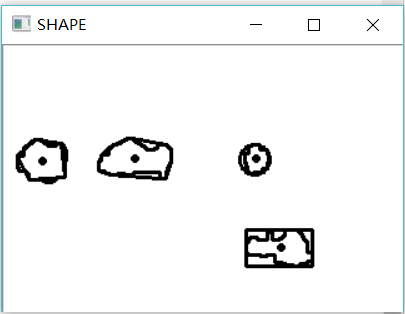
There are many functions for shape description in OpenCV.
cv::Rect r0 = cv::boundingRect(contours[0]);//Boundary box
cv::rectangle(result, r0, 0, 2);//Draw a rectangle
float radius;
cv::Point2f center;
cv::minEnclosingCircle(contours[1], center, radius);//Covering circle
cv::circle(result, center, static_cast<int>(radius), cv::Scalar(0), 2);//Circle drawing
std::vector<cv::Point> poly;
cv::approxPolyDP(contours[2], poly, 5, true);//Polygonal approximation
cv::polylines(result, poly, true, 0, 2);//Polygon
std::vector<cv::Point> hull;
cv::convexHull(contours[3], hull);//convex hull
cv::polylines(result, hull, true, 0, 2);
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>>::iterator itc = contours.begin();
while (itc != contours.end())
{
cv::Moments mom = cv::moments(cv::Mat(*itc++));//Contour moment
cv::circle(result, cv::Point(mom.m10 / mom.m00, mom.m01 / mom.m00), 2, cv::Scalar(0), 2);//Draw the center of gravity
}
cv::namedWindow("SHAPE", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow("SHAPE", result);