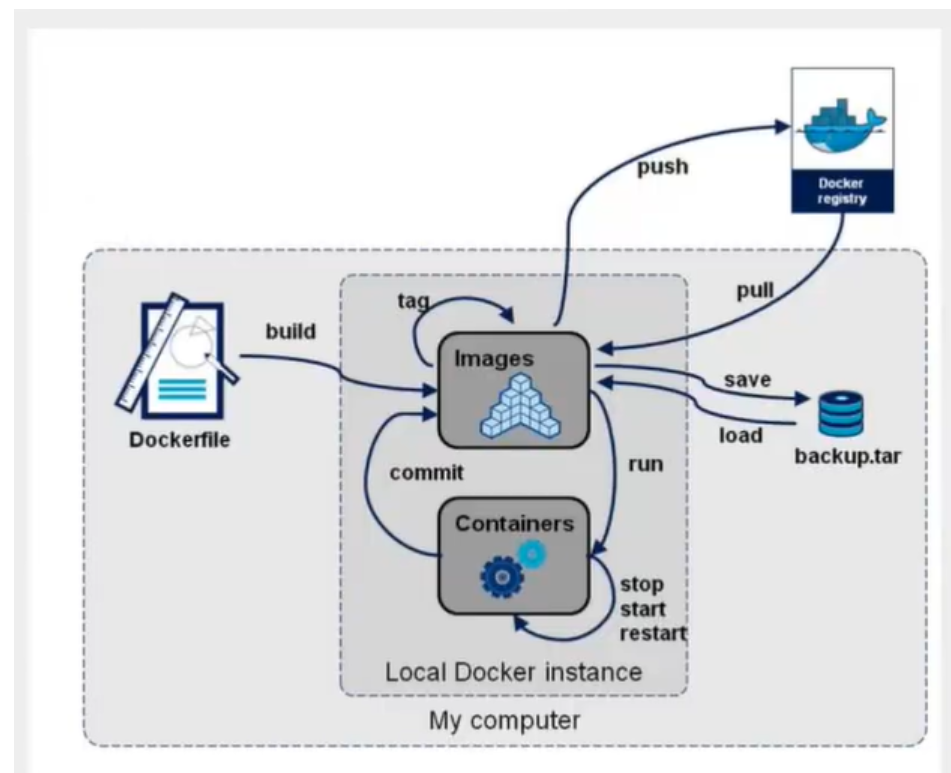
1.Docker introduction
The appearance of Docker is simply to solve the inconsistency between the running environment and software configuration, and package the running environment required by the software by using Docker image. Containers are created through Docker build and run, which are deployed and run on the corresponding host hardware machine.
Docker is a lightweight container technology. Unlike virtual machines, containers do not need to be bound with a complete set of operating systems, but only need the resources and settings required for software work. Therefore, the system becomes efficient and can ensure that the software deployed in any environment can run consistently.
1.1. Containerization Technology
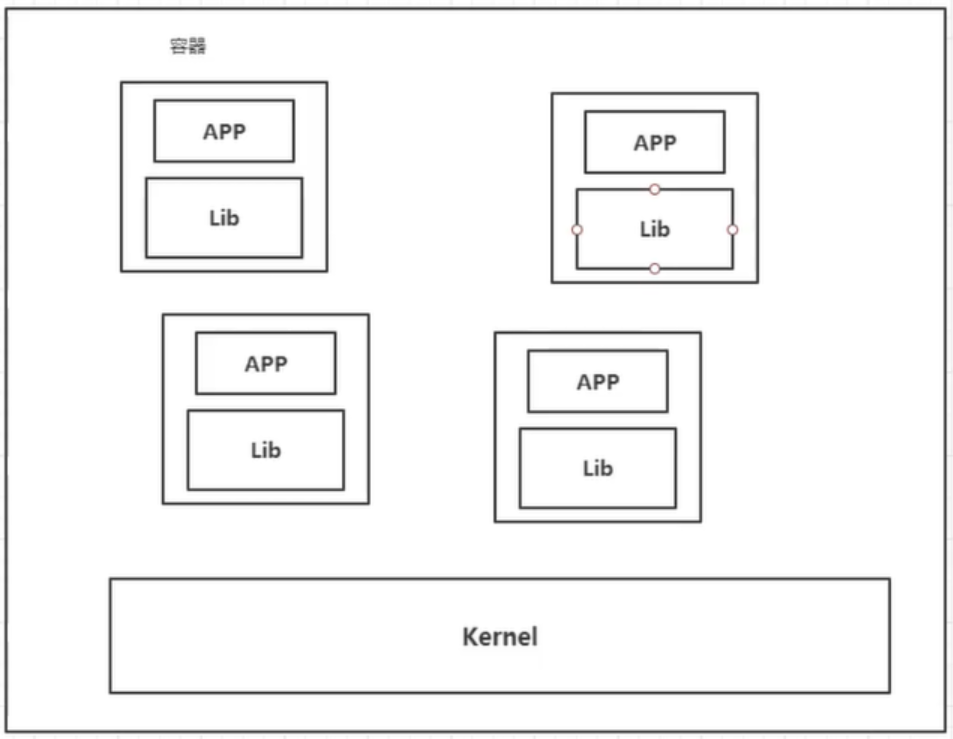
Containerization technology is not a complete operating system for simulation.
Compare Docker and virtual machine technologies:
-
The traditional virtual machine virtualizes a piece of hardware, runs a complete operating system, and then installs and runs software on this system.
-
The applications in the container run directly in the kernel of the host, and the container does not have its own kernel. There is no virtual hardware, so it's light
-
Each container is isolated from each other. Each container has its own file system and does not affect each other.
1.2. Basic composition
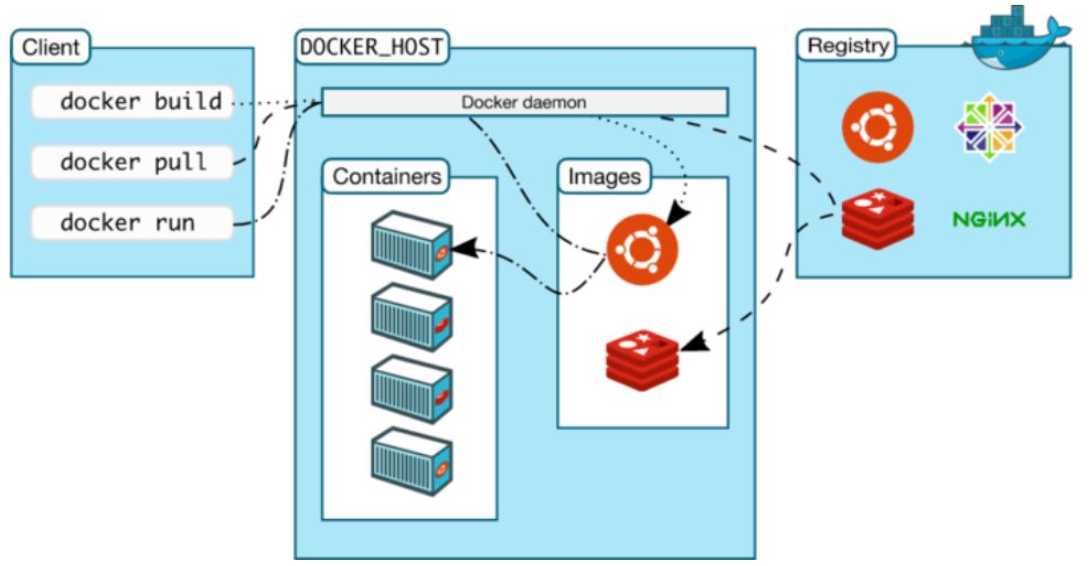
As can be seen from the above figure, docker mainly depends on docker client, docker host (main body: including container and docker image running in container)
docker hub (similar to github, which is a docker image repository).
image:
The docker image is like a template, which can be used to create container services. The Tomcat image -- > run -- > tomcat01 container (provides the server). Through this image, multiple containers can be created (the final service or project is running in the container).
container:
Docker uses container technology to run one or a group of applications independently and create them through image.
Start, stop, delete, basic commands.
At present, this container can be understood as a simple linux system.
repository:
The warehouse is where the images are stored.
Warehouses are divided into public warehouses and private warehouses. (Docker Hub is foreign by default, and Alibaba cloud has container services -- image acceleration needs to be configured)
2. Play Docker
After understanding the concept of docker, we can try to play docker and learn about its installation, deployment and common commands on linux
2.1.Docker installation
- Environmental preparation
CentOS7
Docker official website address: https://www.docker.com/get-started
Docker Hub address: https://hub.docker.com , which is equivalent to github and Docker image warehouse. You can upload and download images.
- Environment view
#The system kernel is above 3.10 [root@yifcloud ~]# uname -r 3.10.0-1127.19.1.el7.x86_64
#System version [root@yifcloud ~]# cat /etc/os-release NAME="CentOS Linux" VERSION="7 (Core)" ID="centos" ID_LIKE="rhel fedora" VERSION_ID="7" PRETTY_NAME="CentOS Linux 7 (Core)" ANSI_COLOR="0;31" CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:centos:centos:7" HOME_URL="https://www.centos.org/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.centos.org/" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT="CentOS-7" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT_VERSION="7" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT="centos" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT_VERSION="7"
- install
Check the official docker documentation: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/centos/
#1.Uninstall old version sudo yum remove docker \ docker-client \ docker-client-latest \ docker-common \ docker-latest \ docker-latest-logrotate \ docker-logrotate \ docker-engine #2.Install required packages sudo yum install -y yum-utils #3.Set the warehouse of the image sudo yum-config-manager \ --add-repo \ https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo #The default is from abroad, which is very slow #It is recommended to use the image address of domestic Alibaba cloud sudo yum-config-manager \ --add-repo \ http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo #Update the yum package index before installing docker yum makecache fast #4.install docker # docker-ce Community Edition docker-ee Enterprise Edition sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io #5.start-up docker sudo systemctl start docker #6.use docker version Test whether the installation is successful docker version
#7.hello-world docker run hello-world
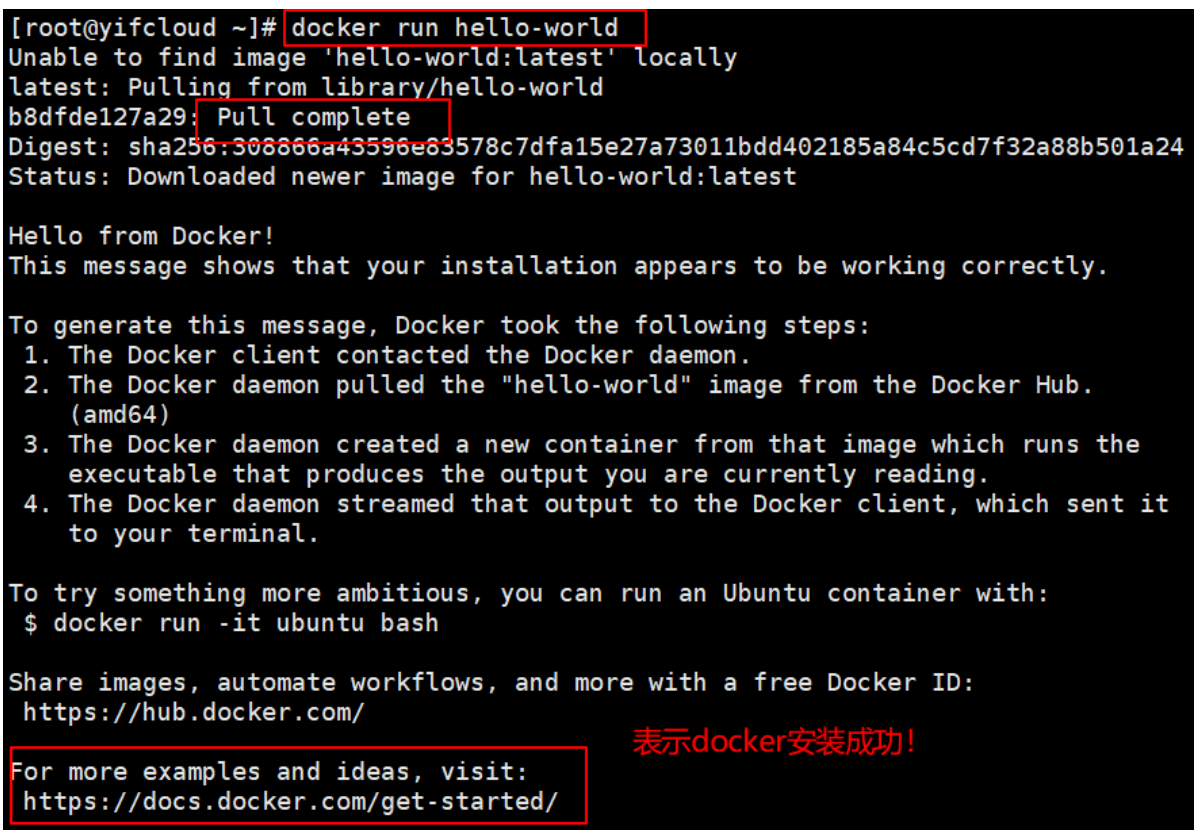
#8.Check out this download hello-world image [root@yifcloud ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest d1165f221234 4 weeks ago 13.3kB
2.2. Uninstall docker
#1.Stop operation docker container systemctl stop docker #2.Unload dependency sudo yum -y remove docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io #2.Delete resource # /var/lib/docker docker Default working path for sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerd
2.3. Configure image acceleration
- Tencent cloud image source acceleration
After installing Docker software, you can directly pull the image through the docker pull command. If you do not configure the image acceleration source, directly pull the image in DockerHub, and the download speed is usually slow. Therefore, we recommend that you use Tencent cloud Docker image source to speed up image download. The detailed operation steps of different operating systems are slightly different. Please use the corresponding operation steps for configuration.
Examples for Linux operating system:
1. Execute the following command to open / etc / docker / daemon JSON configuration file.
vim /etc/docker/daemon.json
2. Press i to switch to editing mode, add the following contents and save them.
{ "registry-mirrors": [ "https://mirror.ccs.tencentyun.com" ] }
3. Execute the following command and restart Docker. The example command takes CentOS 7 as an example.
sudo systemctl restart docker
- Alibaba cloud image acceleration
1. Log in to alicloud, access the container and middleware, and the container image service ACR;

2. Find the official image acceleration service:
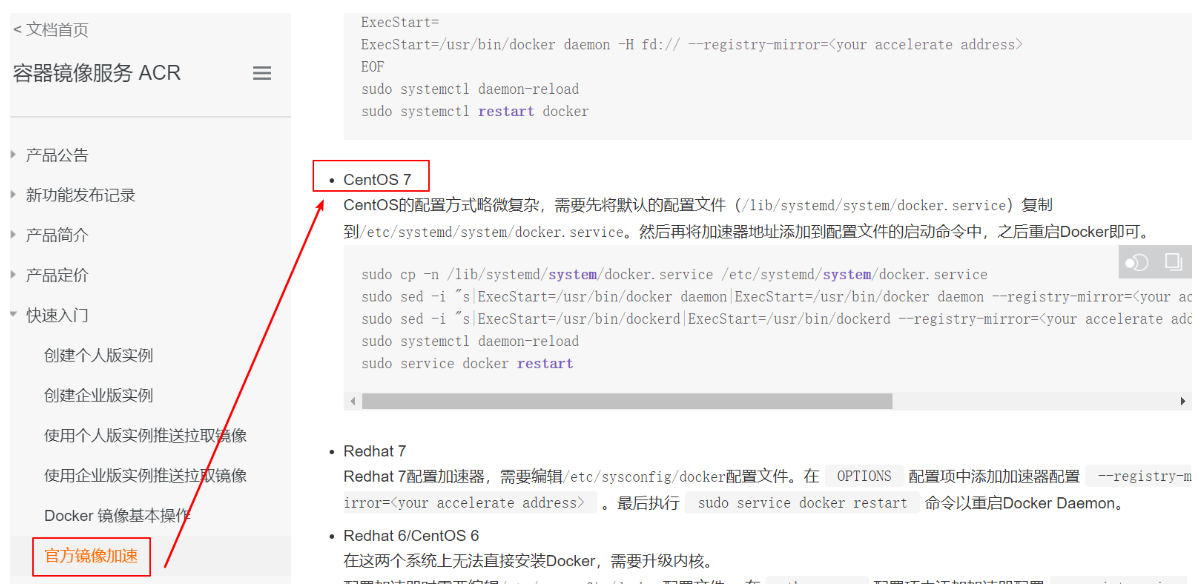
3. Configuration use
sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF' { "registry-mirrors": ["https://qiyb9988.mirror.aliyuncs.com"] } EOF sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl restart docker
2.4.docker run run process
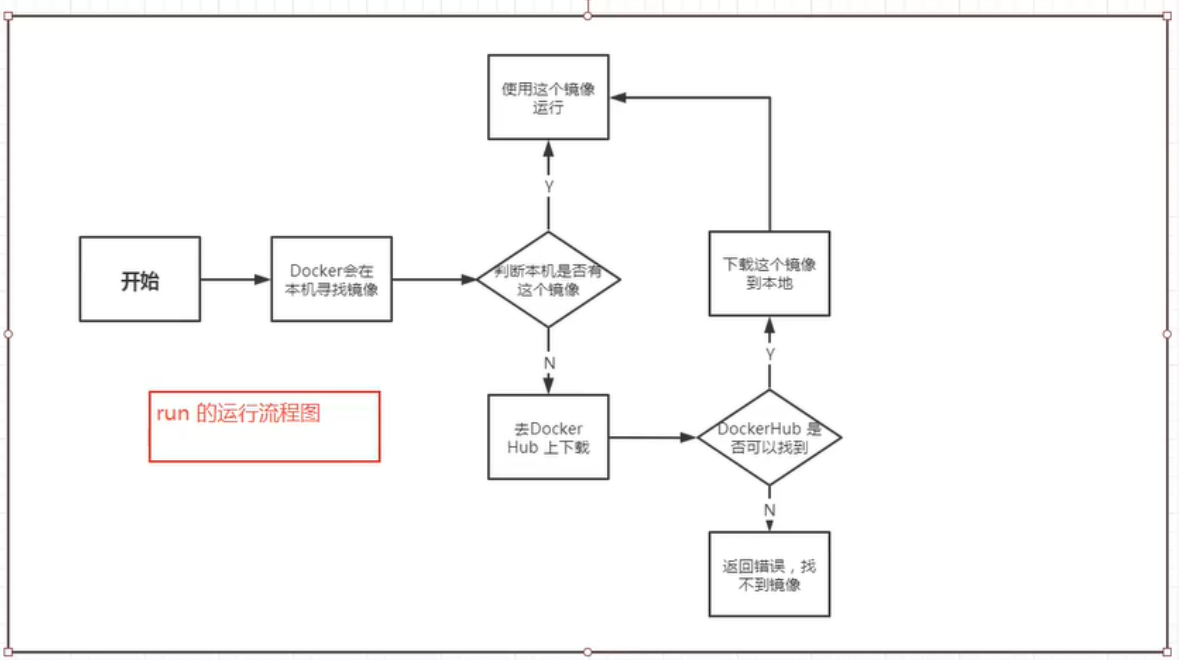
- Underlying principle
How does docker work?
Docker is a client server system. The daemon of docker runs on the host. Access from the client through Socket!
DockerServer will execute this command after receiving the docker client instruction!
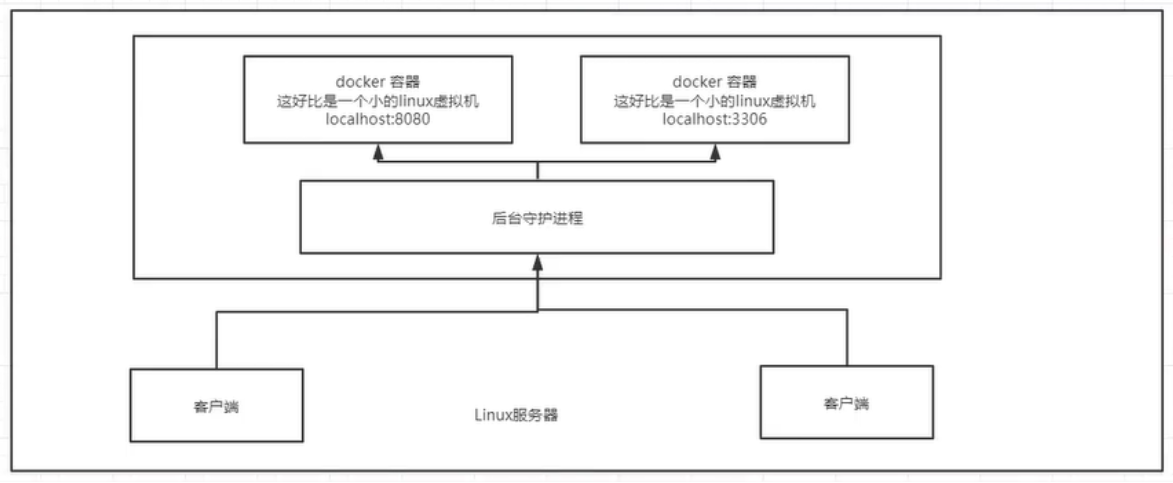
Why is Docker faster than VM?
1.Docker has fewer abstraction layers than virtual machines. (virtual machine level is missing);
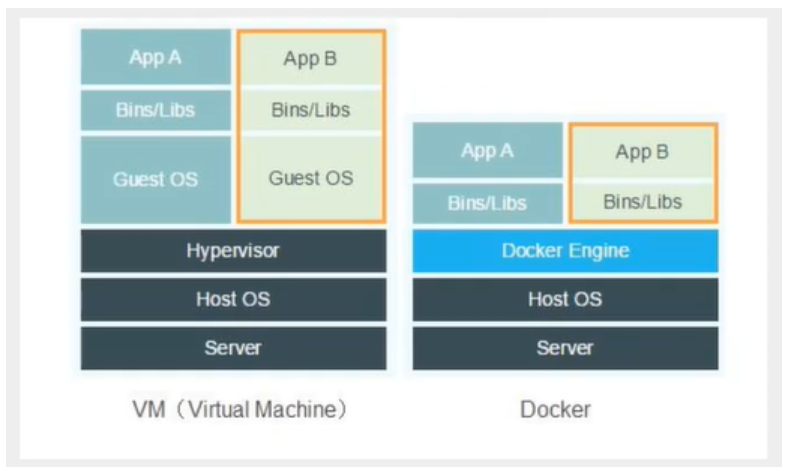
2.Docker uses the kernel of the host, and the VM needs the Guest OS.
Therefore, when creating a new container, docker does not need to reload an operating system kernel like a virtual machine to avoid boot operation.
The virtual machine loads the Guest OS at the minute level, while docker uses the host operating system, omitting this complex process, which is at the second level.
| Docker container | LXC | VM | |
| Virtualization type | OS virtualization | OS virtualization | Hardware virtualization |
| performance | =Physical machine performance | =Physical machine performance | 5% - 20% loss |
| Isolation | NS isolation | NS isolation | strong |
| QoS | Cgroup weak | Cgroup weak | strong |
| Security | in | difference | strong |
| GuestOS | Only Linux is supported | Only Linux is supported | whole |
3. Common docker commands
3.1. Help command
docker version #Display the version information of docker docker info #Displays the system information of docker, including the number of images and containers docker command --help #Help command
Command review: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/cli/
3.2. Mirror command
-
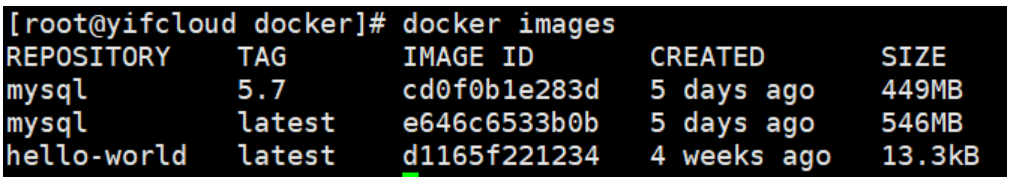
docker images: view images on all local hosts
[root@yifcloud docker]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest d1165f221234 4 weeks ago 13.3kB # explain REPOSITORY Mirrored warehouse source TAG Mirrored label IMAGE ID mirrored ID CREATED Creation time of image SIZE Mirror size # Optional Options: -a, --all #List all mirrors -q, --quiet #Only the id of the image is displayed
-
docker search: search for images
[root@yifcloud docker]# docker search mysql NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED mysql MySQL is a widely used, open-source relation... 10706 [OK] mariadb MariaDB Server is a high performing open sou... 4026 [OK] # Optional, filter by collection --filter=STARS=3000 #The images searched are those with STARS greater than 3000
Corresponding dockerhub website: https://hub.docker.com/search
-
docker pull: Download Image
# Download Image docker pull image name [: tag] [root@yifcloud docker]# docker pull mysql Using default tag: latest #If you do not write tag, the default version is latest latest: Pulling from library/mysql 75646c2fb410: Pull complete # Layered download, the core of docker imgae, federated file system 878f3d947b10: Pull complete 1a2dd2f75b04: Pull complete 8faaceef2b94: Pull complete b77c8c445ec2: Pull complete 074029aeaa5f: Pull complete 5a1122545c6c: Pull complete 6c95ccd00139: Pull complete 60a719448fdb: Pull complete f31898a387a3: Pull complete bcf402a978dc: Pull complete cf0bc7da512e: Pull complete Digest: sha256:c35eb76bbccfd0138c8c68ccb9b4cffe42c488a27f64ddc31a2b5f65aa93fce6 # autograph Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:latest docker.io/library/mysql:latest # Real address # The following two commands are equivalent docker pull mysql docker pull docker.io/library/mysql:latest #Specified version download [root@yifcloud docker]# docker pull mysql:5.7 #Using the tag command 5.7: Pulling from library/mysql 75646c2fb410: Already exists 878f3d947b10: Already exists 1a2dd2f75b04: Already exists 8faaceef2b94: Already exists b77c8c445ec2: Already exists 074029aeaa5f: Already exists 5a1122545c6c: Already exists 0539e5d96e0a: Pull complete 5bf3befab801: Pull complete a8ba39ab191f: Pull complete d472d441f7e9: Pull complete Digest: sha256:dce7f54b744d09e95525ff8c767c5ba1c6a5a54d04c208fa55e3052ded713453 Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:5.7 docker.io/library/mysql:5.7
-
Image: RMI docker delete
[root@yifcloud docker]# docker rmi -f container id #Deletes the specified container [root@yifcloud docker]# docker rmi -f container id container id container id #Delete multiple containers [root@yifcloud docker]# docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq) #Delete all mirrors
3.3. Container command
Note: only when we have an image can we create a container. For linux, download a centos image to test and learn
docker pull centos
- Create a new container and start
docker run [Optional parameters] image # Parameter description --name="Name" Container name tomcat01 tomcat02,Used to distinguish containers -d Run in background mode -it Run in interactive mode and enter the container to view the content -p Specify the port of the container -p 8080:8080 -p ip:Host port:Container port -p Host port:Container port (common) -p Container port -P Randomly assigned port # Test, start and enter the container [root@yifcloud /]# docker run -it centos /bin/bash #Check the centos of the container class, the basic version, and many commands are imperfect [root@4419343d4c5a /]# ls bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var #Return the host from the container [root@4419343d4c5a /]# exit exit
-
List all running containers
# docker ps command #Lists the currently running containers -a #Lists the currently running containers+Bring out containers that have been run in history -n=? #Display recently created containers, - n=1 Indicates that only one item is listed -q #Displays only the number of the container [root@yifcloud /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES [root@yifcloud /]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 4419343d4c5a centos "/bin/bash" 5 minutes ago Exited (0) 2 minutes ago intelligent_davinci 12e76cfae025 d1165f221234 "/hello" 13 hours ago Exited (0) 13 hours ago frosty_pike [root@yifcloud /]# docker ps -n=1 CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 4419343d4c5a centos "/bin/bash" 8 minutes ago Exited (0) 6 minutes ago intelligent_davinci
-
Exit container
exit #Container stop and exit ctrl+P+Q #The container does not stop exiting [root@3393124f1c1f /]# [root@yifcloud /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 3393124f1c1f centos "/bin/bash" 28 seconds ago Up 27 seconds magical_williamson
-
Delete container
docker rm container id #Delete the specified container. You cannot delete the running container. If you want to force the deletion, use rm-f docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq) #Delete all containers docker ps -a -q|xargs docker rm #Delete all containers
-
Start and stop container operation
docker start container id #Start container docker restart container id #Restart container docker stop container id #Stop the currently running container docker kill container id #Force stop of current container
3.4. Other common commands
-
Background startup container
#Command docker run-d Image name [root@yifcloud /]# docker run -d centos b70f8ad27e215087e543f535941f0f4ef31fb6b932815d3d99e18da84d90ff4e #Problem docker ps,find centos Stopped [root@yifcloud /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES #In the common pit, if the docker container runs in the background, there must be a foreground process. If docker finds that there is no application, it will automatically stop #After the nignx container starts, if it finds that it does not provide services, it will stop immediately, that is, there is no program
-
View log information
docker logs #View container log #Show log -tf #Show log --tail number #Number of log entries to display [root@yifcloud /]# docker logs -tf --tail 10 3393124f1c1f
-
View process information in the container
#Command docker top container id [root@yifcloud /]# docker top 93138a2af466 UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 6006 5985 0 16:23 pts/0 00:00:00 /bin/bash
-
View image metadata
#command docker inspect container id #test [root@yifcloud /]# docker inspect 93138a2af466 [ { "Id": "93138a2af466c5d30364b4cdba77700aaef5c6a50d5dafc01a8d2a2965083fbb", "Created": "2021-04-06T08:23:53.545067675Z", "Path": "/bin/bash", "Args": [], "State": { "Status": "running", "Running": true, "Paused": false, "Restarting": false, "OOMKilled": false, "Dead": false, "Pid": 6006, "ExitCode": 0, "Error": "", "StartedAt": "2021-04-06T08:23:53.917131264Z", "FinishedAt": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z" }, "Image": "sha256:300e315adb2f96afe5f0b2780b87f28ae95231fe3bdd1e16b9ba606307728f55", "ResolvConfPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/93138a2af466c5d30364b4cdba77700aaef5c6a50d5dafc01a8d2a2965083fbb/resolv.conf", "HostnamePath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/93138a2af466c5d30364b4cdba77700aaef5c6a50d5dafc01a8d2a2965083fbb/hostname", "HostsPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/93138a2af466c5d30364b4cdba77700aaef5c6a50d5dafc01a8d2a2965083fbb/hosts", "LogPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/93138a2af466c5d30364b4cdba77700aaef5c6a50d5dafc01a8d2a2965083fbb/93138a2af466c5d30364b4cdba77700aaef5c6a50d5dafc01a8d2a2965083fbb-json.log", "Name": "/determined_tharp", "RestartCount": 0, "Driver": "overlay2", "Platform": "linux", "MountLabel": "", "ProcessLabel": "", "AppArmorProfile": "", "ExecIDs": null, "HostConfig": { "Binds": null, "ContainerIDFile": "", "LogConfig": { "Type": "json-file", "Config": {} }, "NetworkMode": "default", "PortBindings": {}, "RestartPolicy": { "Name": "no", "MaximumRetryCount": 0 }, "AutoRemove": false, "VolumeDriver": "", "VolumesFrom": null, "CapAdd": null, "CapDrop": null, "CgroupnsMode": "host", "Dns": [], "DnsOptions": [], "DnsSearch": [], "ExtraHosts": null, "GroupAdd": null, "IpcMode": "private", "Cgroup": "", "Links": null, "OomScoreAdj": 0, "PidMode": "", "Privileged": false, "PublishAllPorts": false, "ReadonlyRootfs": false, "SecurityOpt": null, "UTSMode": "", "UsernsMode": "", "ShmSize": 67108864, "Runtime": "runc", "ConsoleSize": [ 0, 0 ], "Isolation": "", "CpuShares": 0, "Memory": 0, "NanoCpus": 0, "CgroupParent": "", "BlkioWeight": 0, "BlkioWeightDevice": [], "BlkioDeviceReadBps": null, "BlkioDeviceWriteBps": null, "BlkioDeviceReadIOps": null, "BlkioDeviceWriteIOps": null, "CpuPeriod": 0, "CpuQuota": 0, "CpuRealtimePeriod": 0, "CpuRealtimeRuntime": 0, "CpusetCpus": "", "CpusetMems": "", "Devices": [], "DeviceCgroupRules": null, "DeviceRequests": null, "KernelMemory": 0, "KernelMemoryTCP": 0, "MemoryReservation": 0, "MemorySwap": 0, "MemorySwappiness": null, "OomKillDisable": false, "PidsLimit": null, "Ulimits": null, "CpuCount": 0, "CpuPercent": 0, "IOMaximumIOps": 0, "IOMaximumBandwidth": 0, "MaskedPaths": [ "/proc/asound", "/proc/acpi", "/proc/kcore", "/proc/keys", "/proc/latency_stats", "/proc/timer_list", "/proc/timer_stats", "/proc/sched_debug", "/proc/scsi", "/sys/firmware" ], "ReadonlyPaths": [ "/proc/bus", "/proc/fs", "/proc/irq", "/proc/sys", "/proc/sysrq-trigger" ] }, "GraphDriver": { "Data": { "LowerDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a49b7e336b7c3892f3f933d162798dab2d89600a9819e1318e1dc5f7f1b27080-init/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/61a4f0d180efc1642f2dc0cec97a3b5333a231256fadd22723eeef4e95b79308/diff", "MergedDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a49b7e336b7c3892f3f933d162798dab2d89600a9819e1318e1dc5f7f1b27080/merged", "UpperDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a49b7e336b7c3892f3f933d162798dab2d89600a9819e1318e1dc5f7f1b27080/diff", "WorkDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a49b7e336b7c3892f3f933d162798dab2d89600a9819e1318e1dc5f7f1b27080/work" }, "Name": "overlay2" }, "Mounts": [], "Config": { "Hostname": "93138a2af466", "Domainname": "", "User": "", "AttachStdin": true, "AttachStdout": true, "AttachStderr": true, "Tty": true, "OpenStdin": true, "StdinOnce": true, "Env": [ "PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin" ], "Cmd": [ "/bin/bash" ], "Image": "centos", "Volumes": null, "WorkingDir": "", "Entrypoint": null, "OnBuild": null, "Labels": { "org.label-schema.build-date": "20201204", "org.label-schema.license": "GPLv2", "org.label-schema.name": "CentOS Base Image", "org.label-schema.schema-version": "1.0", "org.label-schema.vendor": "CentOS" } }, "NetworkSettings": { "Bridge": "", "SandboxID": "63102349b23ecd6e2010847962056df4132651b106ed28de8528e50d6a961c9c", "HairpinMode": false, "LinkLocalIPv6Address": "", "LinkLocalIPv6PrefixLen": 0, "Ports": {}, "SandboxKey": "/var/run/docker/netns/63102349b23e", "SecondaryIPAddresses": null, "SecondaryIPv6Addresses": null, "EndpointID": "eeed2d848ba97279f514e161744414dc8dff922d395c6a8b0ae7bad5fbb88f7e", "Gateway": "172.17.0.1", "GlobalIPv6Address": "", "GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0, "IPAddress": "172.17.0.2", "IPPrefixLen": 16, "IPv6Gateway": "", "MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:02", "Networks": { "bridge": { "IPAMConfig": null, "Links": null, "Aliases": null, "NetworkID": "511233d65ba29e0a71d9f1c712fb4de3aad881771488f988034d0eeb1559d3ae", "EndpointID": "eeed2d848ba97279f514e161744414dc8dff922d395c6a8b0ae7bad5fbb88f7e", "Gateway": "172.17.0.1", "IPAddress": "172.17.0.2", "IPPrefixLen": 16, "IPv6Gateway": "", "GlobalIPv6Address": "", "GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0, "MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:02", "DriverOpts": null } } } } ]
-
Enter the currently running container
# We usually use the background mode to run the container. We need to enter the container and modify some configurations # command docker exec -it container id bashShell #test [root@yifcloud /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 93138a2af466 centos "/bin/bash" 23 minutes ago Up 23 minutes determined_tharp [root@yifcloud /]# docker exec -it 93138a2af466 /bin/bash [root@93138a2af466 /]# ls bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var [root@93138a2af466 /]# ps -ef UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 1 0 0 08:23 pts/0 00:00:00 /bin/bash root 15 0 0 08:48 pts/1 00:00:00 /bin/bash root 30 15 0 08:48 pts/1 00:00:00 ps -ef # Mode 2 docker attach container id # test [root@yifcloud /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 93138a2af466 centos "/bin/bash" 28 minutes ago Up 28 minutes determined_tharp [root@yifcloud /]# docker attach 93138a2af466 # docker exec #After entering the container, open a new terminal, which can be operated inside (commonly used) # docker attach #Entering the terminal where the container is executing will not start a new process
-
Copy files from container to host
docker cp container id:Host path for in container destination #Copy the files in the docker container to the destination host path [root@yifcloud /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES [root@yifcloud /]# docker run -it centos /bin/bash [root@b53c599f8830 /]# [root@yifcloud /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES b53c599f8830 centos "/bin/bash" 16 seconds ago Up 15 seconds goofy_elion [root@yifcloud /]# cd home/ #View files in the current directory [root@yifcloud home]# ls fengye test [root@yifcloud home]# touch fengye.java [root@yifcloud home]# ls fengye fengye.java test [root@yifcloud home]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES b53c599f8830 centos "/bin/bash" 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes goofy_elion #Enter the docker container [root@yifcloud home]# docker attach b53c599f8830 [root@b53c599f8830 /]# cd home/ #Create a new file in the container [root@b53c599f8830 home]# touch test.java [root@b53c599f8830 home]# ls test.java [root@b53c599f8830 home]# exit exit [root@yifcloud home]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES #Copy this file to the host [root@yifcloud home]# docker cp b53c599f8830:/home/test.java /home [root@yifcloud home]# ls fengye fengye.java test test.java # Note: copying here is a manual process, which we will use later -v Volume technology can realize data synchronization between host and container
4. Quick query of docker command
Here, the common commands of docker are listed in the order of letters a-z for quick check later:
attach Attach to a running container #The attach connection under the current shell specifies the running image build Build an image from a Dockerfile #Customized image through Dockerfile commit create a new image from a container changes #Commit the current container as a new image cp Copy files/folders from the containers filesystem to the host path #Copy the specified file or directory from the container to the host create create a new container #Create a new container, the same as run, but do not start the container diff Inspect changes on a container's filesystem #View docker container changes events Get real time events from the server #Get container real-time events from docker service exec Run a command in an existing container #Run the command on an existing container export Stream the contents of a container as a tar archive #Export the contents of the container as a tar archive [corresponding to import] history Show the history of an image #Show a mirror formation history images List images #Lists the current image of the system import Create a new filesystem image from the contents of a tarball #Create a new file system image from the contents of the tar package [corresponding to export] info Display system-wide information #Display system related information inspect Return low-level information on a container #View container details kill kill a running container #kill appoint docker container load Load an image from a tar archive #Load an image from a tar package [corresponding to save] login Register or Login to the docker registry server #Register or log in to a docker source server logout Log out from a Docker registry server #Exit from the current Docker registry logs Fetch the logs of a container #Output current container log information port Lookup the public-facing port which is NAT-ed to PRIVATE_PORT #View the internal source port of the container corresponding to the mapped port pause Pause all processes within a container #Pause container ps List containers #List containers pull Pull an image or a repository from the docker registry server #Pull the specified image or library image from the docker image source server push Push an image or a repository to the docker regitsry server #Push the specified image or library image to the docker source server restart Restart a running container #Restart the running container rm Remove one or more containers #Remove one or more containers rmi Remove one or more images #Remove one or more images [no container can be deleted without using the image, otherwise the relevant container needs to be deleted before continuing or deleting-f Force deletion] run Run a command in a new container #Create a new container and run a command save Save an image to a tar archive #Save an image as a tar package [corresponding to load] search Search for an image on the Docker Hub #Search for images in docker hub start Start a running containers #Start container stop Stop a running containers #Stop container tag Tag an image into a repository #Label the image in the source top Lookup the running processes of a container #View the process information running in the container unpause Unpause a paused container #Unsuspend container version Show the docker version information #View docker version number wait Block until a container stops, then print its exit code #Intercept the exit status value when the container stops
5.Commit DIY image
docker commit #Submit the container as a new copy #The principle of the command is similar to that of git docker commit -m="Description information submitted" -a="author" container id Target image name:[TAG]
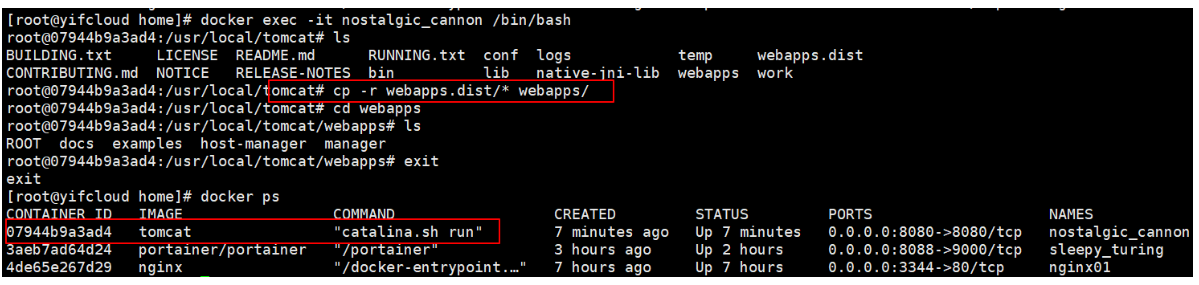
Here, you have created a webapps directory that you can start by copying. Now you can upload your own tomcat image.
Actual test:
[root@yifcloud home]# docker commit -m="tomcatplus" -a="fengye" 07944b9a3ad4 tomcat02:1.0 sha256:6ce798d173775d606beb3d0dec6d05b7a08ddb8b24790d3efcd319ce0e77bd92 [root@yifcloud home]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE tomcat02 1.0 6ce798d17377 20 seconds ago 672MB tomcat 9.0 bcd554d24cc5 5 days ago 667MB tomcat latest bcd554d24cc5 5 days ago 667MB nginx latest 7ce4f91ef623 6 days ago 133MB portainer/portainer latest 580c0e4e98b0 2 weeks ago 79.1MB centos latest 300e315adb2f 3 months ago 209MB
You can see that the docker image tomcat02 already exists in the container.
Therefore, if you want to save the state of the current container, you can commit through commit to obtain an image, just like a snapshot of the VM we studied before.
6. Container data volume
6.1. Data volume concept
docker packages the application and environment into an image. If the data is stored in the container, the data will be lost if we delete the container. At this time, we need to make the data persistent
Put Mysql in the container, delete the database and run away. Requirement: Mysql data needs to be stored locally
There can be a data sharing technology between containers. The data generated in the Docker container is synchronized to the local.
This is volume technology. Directory mount, mount the directory in our container to Linux!
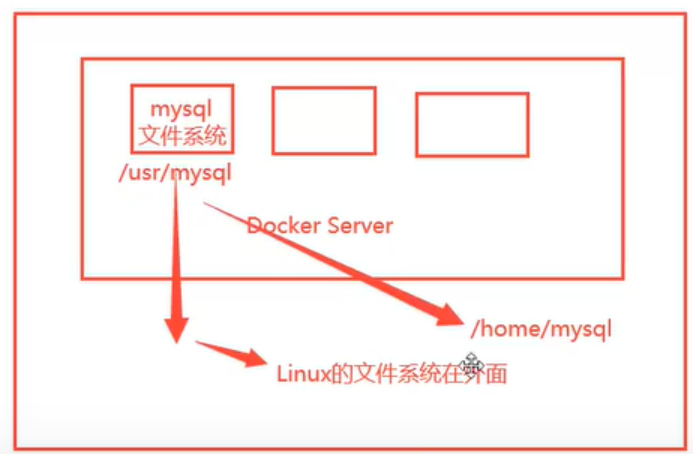
In a word: container persistence and synchronization! Data can also be shared between containers.
6.2. Using data volumes
- Method 1: directly use the command to mount - v

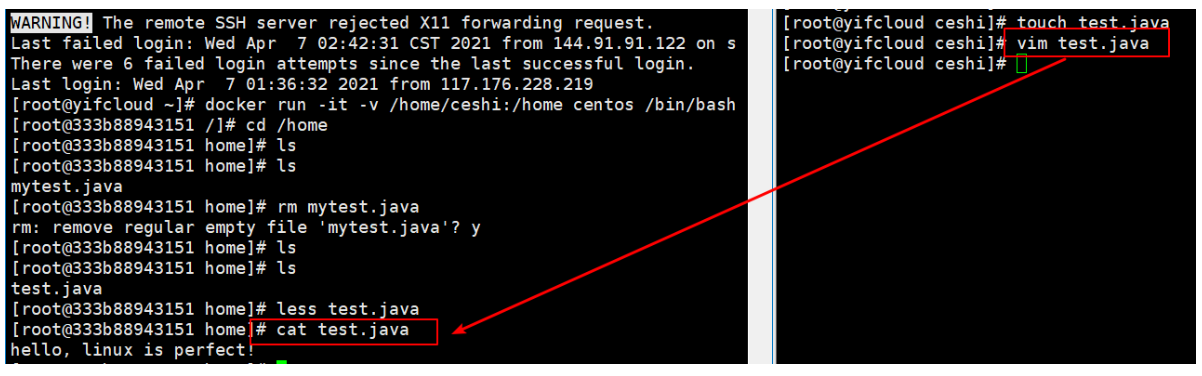
#Where / home is the docker container address/ home/ceshi yes linux Address in host [root@yifcloud ~]# docker run -it -v /home/ceshi:/home centos /bin/bash #We can view the mount through docker inspect container id
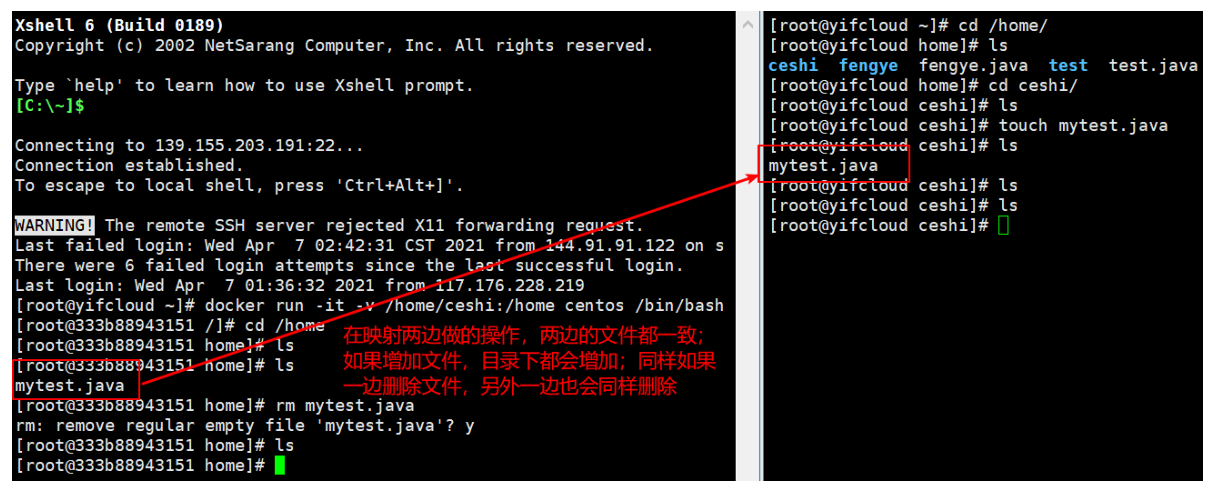
Test again!
1. Stop the container;
2. Modify the file on the host computer;
3. Start the container;
4. The data in the container is still synchronized!
6.3. Named and anonymous mount
#Anonymous mount -v Path in container! docker run -d -P --name nginx01 -v /ect/nginx nginx #View all volume s [root@yifcloud /]# docker volume ls DRIVER VOLUME NAME local 05672ea78a0ea26e67072bc8af4a95bfbfe52e2b9b19586999e97be7c5bc6973 local f8e2e398e59f01321393bead423d8c69c67a38c82c101f8575fc71b703af41a2 #It is found here that this is anonymous mount. We are-v Only the path inside the container is written, not the path outside the container! #Named mount [root@yifcloud /]# docker run -d -P --name nginx02 -v juming-nginx:/etc/nginx nginx 6232abbe4046e654254f62a407e54af96eaa01ea7185eb70d1a3147e290aac70 [root@yifcloud /]# docker volume ls DRIVER VOLUME NAME local 05672ea78a0ea26e67072bc8af4a95bfbfe52e2b9b19586999e97be7c5bc6973 local f8e2e398e59f01321393bead423d8c69c67a38c82c101f8575fc71b703af41a2 local juming-nginx #adopt -v Volume name:Path in container #Take a look at this volume
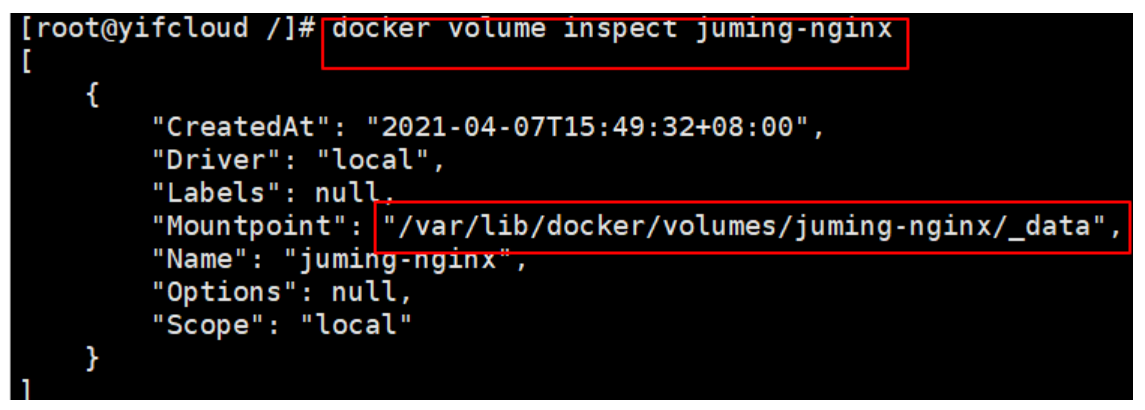
All volumes in the docker container are in '/ var / lib / docker / volumes / XXXX' without a specified directory/_ Under 'data'.
We can easily find one of our volumes through named mount. In most cases, it is recommended to use 'named mount'.
# How to determine whether it is a named mount or an anonymous mount, or a specified path mount -v Path in container # Anonymous mount -v Volume name:Path in container # Named mount -v /Host path: path within container #Specified path mount
expand:
#Pass-v Path in container: ro rw Change read and write permissions ro readonly #read-only rw readwrite #Readable and writable #Once the container permission is set, the container will limit the content we mount! docker run -d -P --name nginx02 -v juming-nginx:/etc/nginx:ro nginx docker run -d -P --name nginx02 -v juming-nginx:/etc/nginx:rw nginx #As long as ro sees ro, it means that this path can only be operated by the host, and it cannot be operated inside the container!
7.Dockerfile
Dockerfile is the build file used to build the docker image. Command script.
Through this script, you can generate an image. The image is layer by layer. The script commands one by one, and each command is a layer.
Construction steps:
1. Write a dockerfile file
2. Build docker build into an image
3.docker run run image
4.docker push publishing images (DockerHub, Alibaba cloud image warehouse)
7.1.Dockerfile construction process
1. Each reserved keyword (instruction) must be capitalized
2. Instructions are executed in order from top to bottom
3. # indicates a comment
4. Each instruction will create and submit a new image layer
Dockerfile is development oriented. In order to publish projects and make images in the future, you need to write dockerfile.
DockerFile: build a file that defines all the steps and source code.
DockerImages: images generated through DockerFile construction, and products finally released and run.
Docker container: a container is an image that runs to provide services.
7.2.Dockerfile instruction
FROM #Basic image, everything starts from here MAINTAINER #Who wrote the image? General format: name+mailbox RUN #Commands to run during image construction ADD #Step, tomcat image, this tomcat compressed package, add content WORKDIR #Mirrored working directory VOLUME #Mounted directory EXPOSE #Specify exposed port configuration CMD #Specify the command to run when the container starts. Only the last one will take effect and can be replaced ENTRYPOINT #Specify the commands to be run when the container is started, and you can append commands ONBUILD #When constructing an inherited DockerFile, the ONBUILD instruction will be run to trigger the instruction COPY #Similar to ADD, copy our files to the image ENV #Setting environment variables during construction

For example, you can use dockerfile to create your own centos:
#1.to write dockerfile Documents [root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# cat mydockerfile-centos FROM centos MAINTAINER fengye<2416675247@qq.com> ENV MYPATH /usr/local WORKDIR $MYPATH RUN yum -y install vim RUN yum -y install net-tools EXPOSE 80 CMD echo $MYPATH CMD echo "----end----" CMD /bin/bash #2.Build an image from this file #Command: docker build -f dockerfile File path -t Image name:[tag] #3.test run
You can view the creation process of the image through the command docker history:
[root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE fengye/centos 1.0 d3a3ab46c15e 4 hours ago 209MB centos latest 300e315adb2f 4 months ago 209MB [root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker history 300e315adb2f IMAGE CREATED CREATED BY SIZE COMMENT 300e315adb2f 4 months ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) CMD ["/bin/bash"] 0B <missing> 4 months ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) LABEL org.label-schema.sc... 0B <missing> 4 months ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) ADD file:bd7a2aed6ede423b7... 209MB
- Difference between CMD and ENTRYPOINT
CMD #Specify the command to run when the container starts. Only the last one will take effect and can be replaced
ENTRYPOINT #Specify the commands to be run when the container is started, and you can append commands
Test cmd
[root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# vim dockerfile-cmd-test [root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker build -f dockerfile-cmd-test -t cmdtest . Sending build context to Docker daemon 3.072kB Step 1/2 : FROM centos ---> 300e315adb2f Step 2/2 : CMD ["ls", "-a"] ---> Running in f68f9538a93b Removing intermediate container f68f9538a93b ---> ca751f13b6b6 Successfully built ca751f13b6b6 Successfully tagged cmdtest:latest [root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker run ca751f13b6b6 . .. .dockerenv bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var #If you want to append a command, you can only use all the commands [root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker run ca751f13b6b6 -l docker: Error response from daemon: OCI runtime create failed: container_linux.go:367: starting container process caused: exec: "-l": executable file not found in $PATH: unknown. [root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker run ca751f13b6b6 ls -al total 56 drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 May 3 06:05 . drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 May 3 06:05 .. -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 0 May 3 06:05 .dockerenv lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Nov 3 15:22 bin -> usr/bin drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 340 May 3 06:05 dev drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 May 3 06:05 etc drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 15:22 home lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Nov 3 15:22 lib -> usr/lib lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Nov 3 15:22 lib64 -> usr/lib64 drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 lost+found drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 15:22 media drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 15:22 mnt drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 15:22 opt dr-xr-xr-x 111 root root 0 May 3 06:05 proc dr-xr-x--- 2 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 root drwxr-xr-x 11 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 run lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 8 Nov 3 15:22 sbin -> usr/sbin drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 15:22 srv dr-xr-xr-x 13 root root 0 Apr 28 06:51 sys drwxrwxrwt 7 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 tmp drwxr-xr-x 12 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 usr drwxr-xr-x 20 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 var
Test ENTRYPOINT:
[root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker build -f dockerfile-entrypoint-test -t entrypointtest . Sending build context to Docker daemon 4.096kB Step 1/2 : FROM centos ---> 300e315adb2f Step 2/2 : ENTRYPOINT ["ls", "-a"] ---> Running in 2f373923b6ab Removing intermediate container 2f373923b6ab ---> 89dd49fd6ba2 Successfully built 89dd49fd6ba2 Successfully tagged entrypointtest:latest [root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker run 89dd49fd6ba2 . .. .dockerenv bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var #Our append command can be appended directly after run [root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker run 89dd49fd6ba2 -l total 56 drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 May 3 06:30 . drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 May 3 06:30 .. -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 0 May 3 06:30 .dockerenv lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Nov 3 15:22 bin -> usr/bin drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 340 May 3 06:30 dev drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 May 3 06:30 etc drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 15:22 home lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Nov 3 15:22 lib -> usr/lib lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Nov 3 15:22 lib64 -> usr/lib64 drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 lost+found drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 15:22 media drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 15:22 mnt drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 15:22 opt dr-xr-xr-x 111 root root 0 May 3 06:30 proc dr-xr-x--- 2 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 root drwxr-xr-x 11 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 run lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 8 Nov 3 15:22 sbin -> usr/sbin drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 15:22 srv dr-xr-xr-x 13 root root 0 Apr 28 06:51 sys drwxrwxrwt 7 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 tmp drwxr-xr-x 12 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 usr drwxr-xr-x 20 root root 4096 Dec 4 17:37 var
7.3. Publish image
- DockerHub
1. Address https://hub.docker.com/ , register your account;
2. Confirm that this account can be logged in;
3. Submit your own image on our server
[root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker login --help Usage: docker login [OPTIONS] [SERVER] Log in to a Docker registry. If no server is specified, the default is defined by the daemon. Options: -p, --password string Password --password-stdin Take the password from stdin -u, --username string Username [root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker login -u fengye -p 123456
4. After logging in, you can submit the image, which is a one-step docker push
#push your own image to the server [root@aliyunCloud docker-test-volume]# docker push fengye/diytomcat:1.0 #Docker pushes the image published by itself with the version number as much as possible docker tag f8559daf1fc2 fengye/tomcat:1.0 docker push fengye/tomcat:1.0
When submitting, it is also submitted according to the image level!
- Publish to alicloud image library
1. Log in to alicloud
2. Find the container image service
3. Create namespace
4. Create container image
Detailed reference: https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/60997.html?spm=a2c4g.11186623.6.597.17e372c0s9AmRb , Alibaba cloud builds warehouse and image
Flow chart summarizing dokerfile execution process: