1: Cartesian product problem
1. Cartesian product: all records in multiple tables will match each other once. For example, if there are m records in Table 1 and n records in Table 2, Cartesian product will produce m*n records, such as select * from table 1 and table 2
2. In order to avoid Cartesian product, you can add effective connection conditions in WHERE, such as: select * from table 1, table 2, WHERE table 1 Id = Table 2 id
2: Oracle connectivity
1. Internal connection:
Meaning: merge rows of more than two tables with the same column. The result set does not contain rows that do not match one table with another
Internal connection diagram:
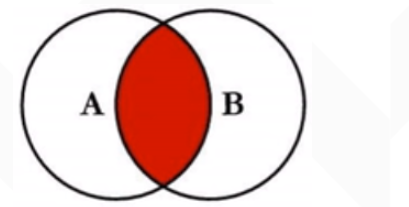
(1) Equivalent connection
Method 1: use = associated table field
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column, table2.column
FROM table1, table2
WHERE table1.column1 = table2.column2;
- Write join condition in WHERE clause
- When there are the same columns in the table, prefix the column name with the table name
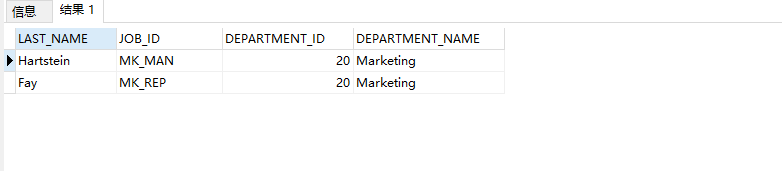
Example 1: two table connection: query the ID of the company employee, last_ name,depatment_ id, department_ name
SELECT e.EMPLOYEE_ID,e.LAST_NAME,e.DEPARTMENT_ID,d.DEPARTMENT_NAME FROM EMPLOYEES e ,DEPARTMENTS d WHERE e.DEPARTMENT_ID=d.DEPARTMENT_ID
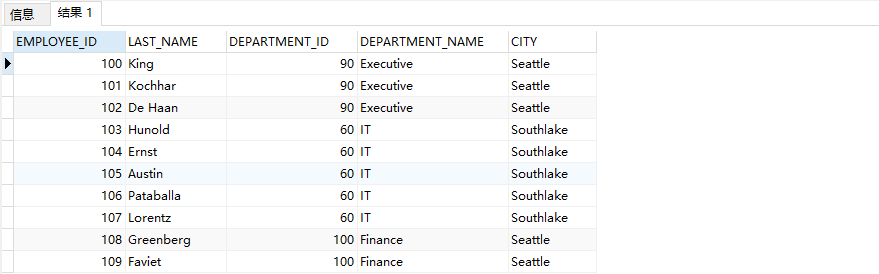
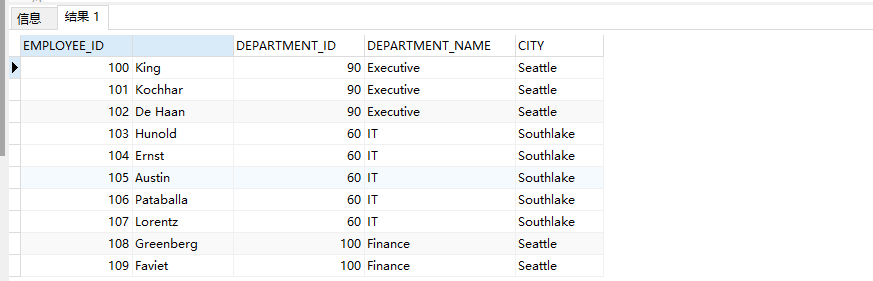
Example 2: three table connection: query the last of the company's employees_ name, department_ name, city
SELECT e.EMPLOYEE_ID,e.LAST_NAME,d.DEPARTMENT_ID,d.DEPARTMENT_NAME,l.CITY FROM EMPLOYEES e ,DEPARTMENTS d,LOCATIONS l WHERE e.DEPARTMENT_ID=d.DEPARTMENT_ID AND d.LOCATION_ID=l.LOCATION_ID
(2) Equivalent connection
Method 2: use JOIN ON to associate fields
Example 1: two table connection: query the ID of the company employee, last_ name,depatment_ id, department_ name
SELECT e.EMPLOYEE_ID,e.LAST_NAME,e.DEPARTMENT_ID,d.DEPARTMENT_NAME FROM EMPLOYEES e JOIN DEPARTMENTS d ON e.DEPARTMENT_ID=d.DEPARTMENT_ID
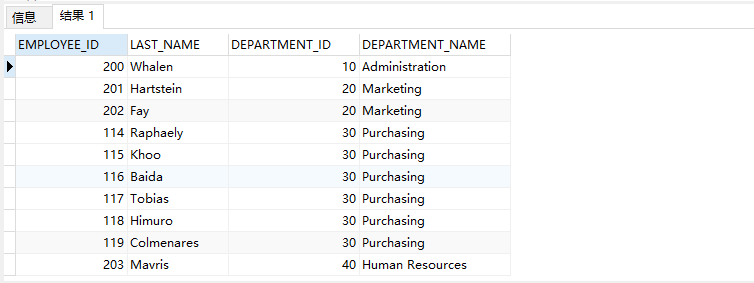
Example 2: three table connection: query the last of the company's employees_ name, department_ name, city
SELECT e.EMPLOYEE_ID,e.LAST_NAME,d.DEPARTMENT_ID,d.DEPARTMENT_NAME,l.CITY FROM EMPLOYEES e JOIN DEPARTMENTS d ON e.DEPARTMENT_ID=d.DEPARTMENT_ID JOIN LOCATIONS l ON d.LOCATION_ID=l.LOCATION_ID
(3) Non equivalent connection
Query the grade corresponding to employee salary
SELECT e.EMPLOYEE_ID,e.LAST_NAME,e.SALARY,j.GRADE_LEVEL from EMPLOYEES e,JOB_GRADES j WHERE e.SALARY BETWEEN j.LOWEST_SAL and j.HIGHEST_SAL
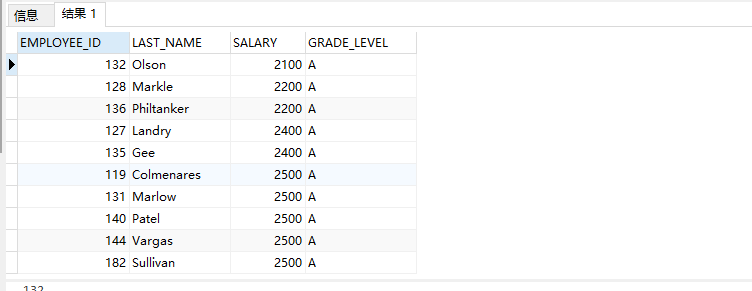
2. External connection
Left outer connection: left join
Meaning: matches all records in the left table and the records that meet the conditions on the right
Sketch Map:
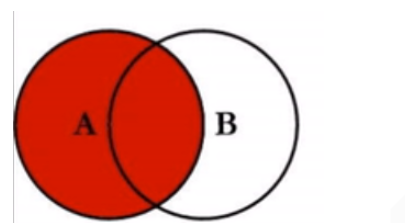
Example: query through left outer connection
SELECT e.EMPLOYEE_ID,e.LAST_NAME,e.DEPARTMENT_ID,d.DEPARTMENT_NAME FROM EMPLOYEES e LEFT JOIN DEPARTMENTS d ON e.DEPARTMENT_ID=d.DEPARTMENT_ID;
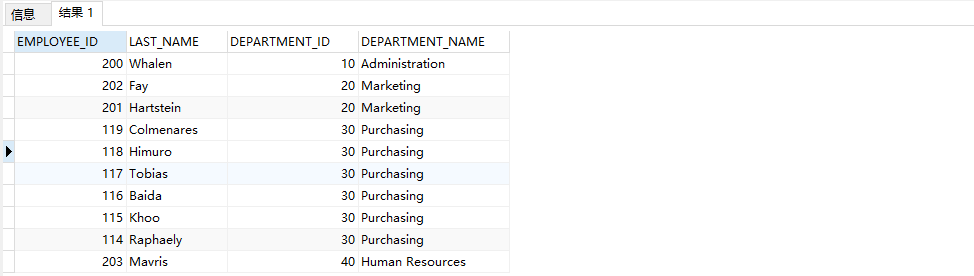
Right outer connection: right join
Meaning: matches all records in the right table and the records that meet the conditions on the left
Sketch Map:
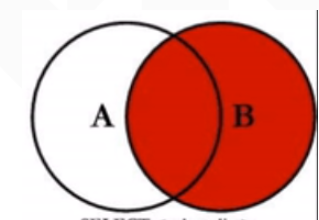
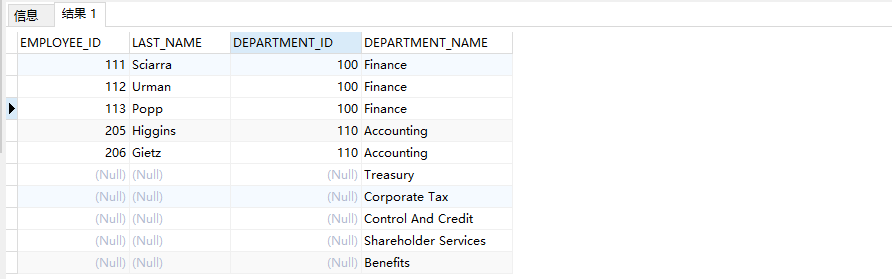
Example: query through right outer connection
SELECT e.EMPLOYEE_ID,e.LAST_NAME,e.DEPARTMENT_ID,d.DEPARTMENT_NAME FROM EMPLOYEES e RIGHT JOIN DEPARTMENTS d ON e.DEPARTMENT_ID=d.DEPARTMENT_ID;
full join
Meaning: matches all records in the left and right tables
Sketch Map:
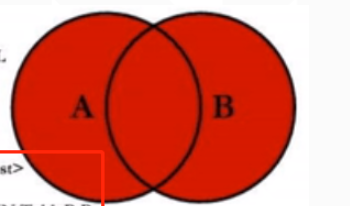
Example: query through full external connection
SELECT e.EMPLOYEE_ID,e.LAST_NAME,e.DEPARTMENT_ID,d.DEPARTMENT_NAME FROM EMPLOYEES e FULL JOIN DEPARTMENTS d ON e.DEPARTMENT_ID=d.DEPARTMENT_ID;
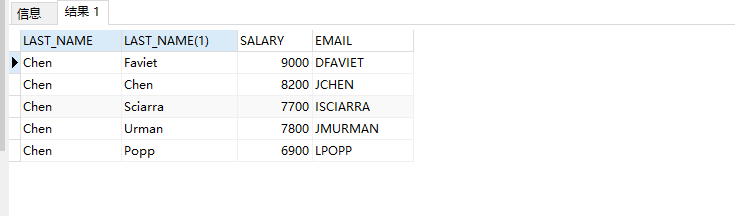
Self connection
Meaning: a way for tables to connect themselves
Example: query the Manager information of employee surname "chen"
SELECT emp.LAST_NAME,manager.LAST_NAME,manager.SALARY,manager.EMAIL FROM EMPLOYEES emp JOIN EMPLOYEES manager ON emp.MANAGER_ID=manager.MANAGER_ID WHERE LOWER(emp.LAST_NAME)='chen';
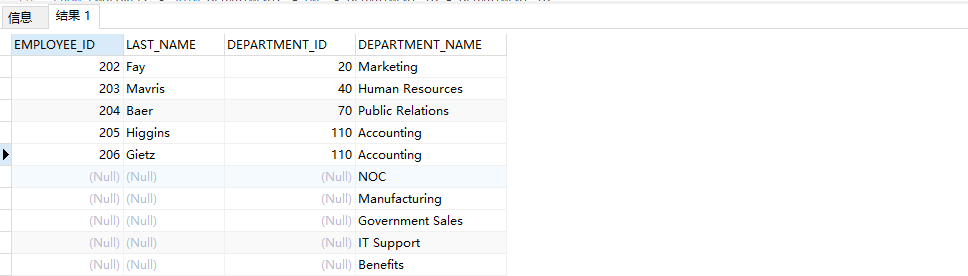
Cases of multi table query:
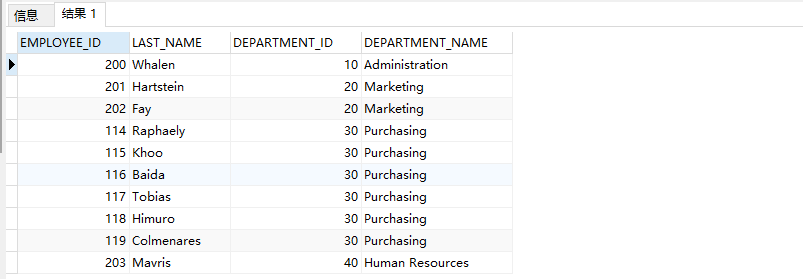
1. Displays the names, Department numbers and department names of all employees
Method 1: use "=" Association
select last_name,e.department_id,department_name from employees e,departments d where e.department_id = d.department_id(+)
Method 2: use Join on Association
select last_name,e.department_id,department_name from employees e left outer join departments d on e.department_id = d.department_id
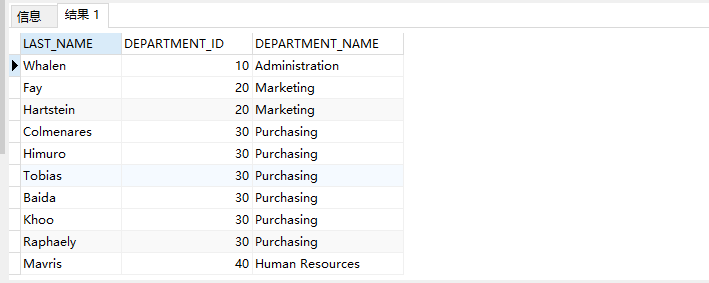
2. Query the job of department 90 employee_ ID and location of department 90_ id
select distinct job_id,location_id from employees e left join departments d on e.department_id = d.department_id where d.department_id = 90
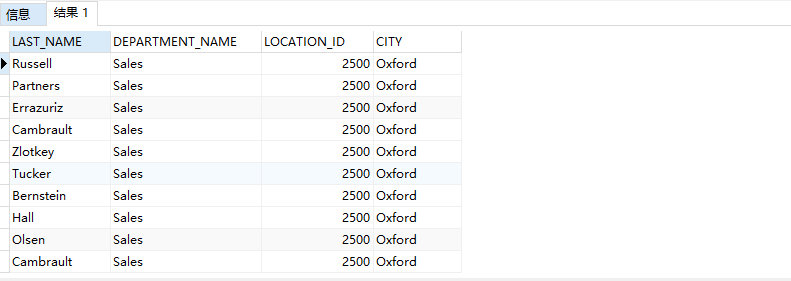
3. Select last for all employees with bonus_ name , department_ name , location_ id , city
select last_name,department_name,d.location_id,city from employees e join departments d on e.department_id = d.department_id join locations l on d.location_id = l.location_id where e.commission_pct is not null
4. Select the last name of the city's employees working in Toronto_ name , job_ id , department_ id , department_ name
select last_name , job_id , e.department_id , department_name from employees e ,departments d,locations l where e.department_id = d.department_id and l.city = 'Toronto' and d.location_id = l.location_id